A nanoplasma array laser and its manufacturing method
A plasma and nanowire array technology, which is applied in the field of plasma array lasers and its production, can solve the problems of no device formation, irregular growth of nanowire arrays, and limited laser power, and achieve the effect of increasing laser power
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
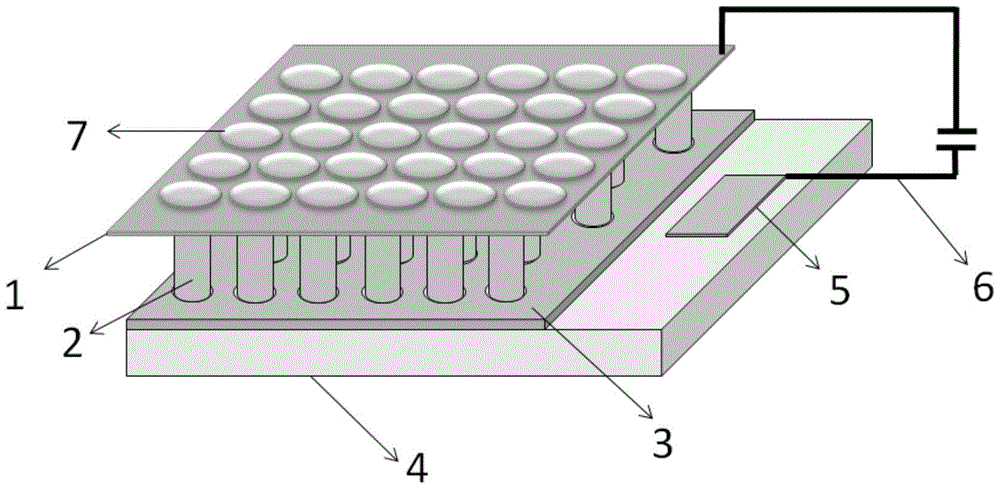
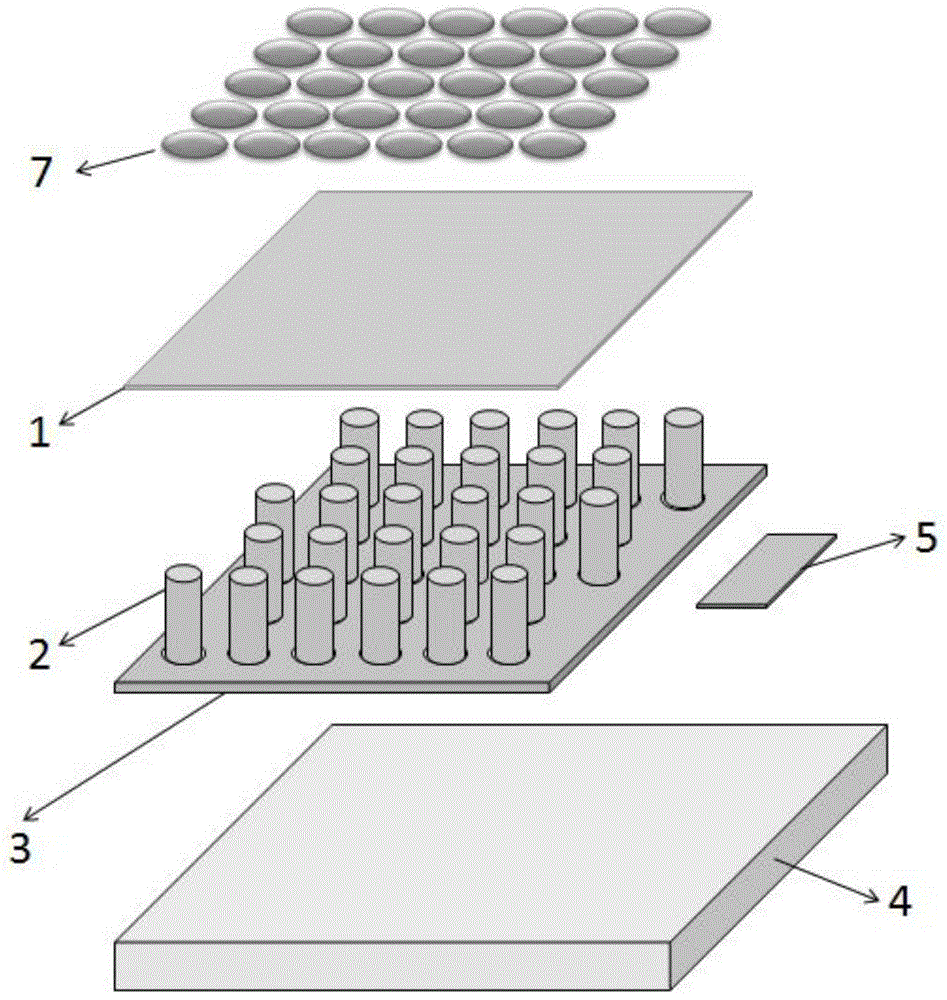
[0036] This embodiment provides a nanoplasma array laser, the structure of which is as follows figure 1 as shown, figure 2 is a schematic diagram of its structural disassembly, the nanowire array is composed of 19 coherent light sources, such as Figure 5 As shown, each coherent light source is identical, and the working mode is TEM 00 Die, some specific materials, parameters and dimensions are as follows:
[0037] The semiconductor substrate 4 is a gallium nitride (GaN) substrate;
[0038] The insulating dielectric layer 3 is SiO 2 Thin film layer, its thickness is 300nm;
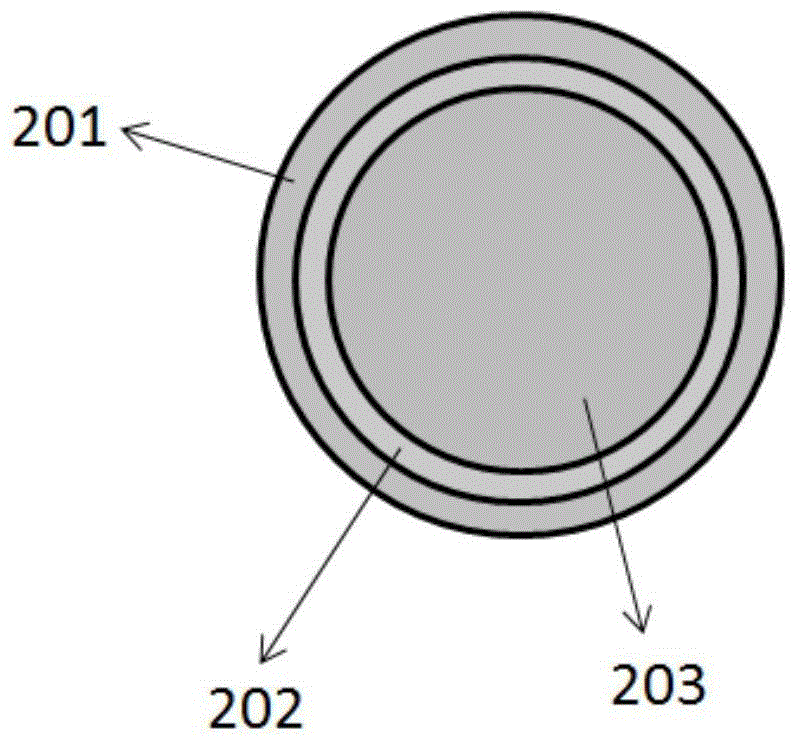
[0039] The SiO 2 The film layer 3 is provided with a circular through-hole array arranged in a hexagonal close-packed array, such as Figure 4 As shown, the diameter of the through hole is 200nm, and the distance between the centers of adjacent through holes is 1 μm; ZnO nanowires 203 are grown at each position of the through hole, and the length thereof is 3 μm;
[0040] The sides of the ZnO nanow...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com