Patents
Literature
31 results about "Photon beams" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
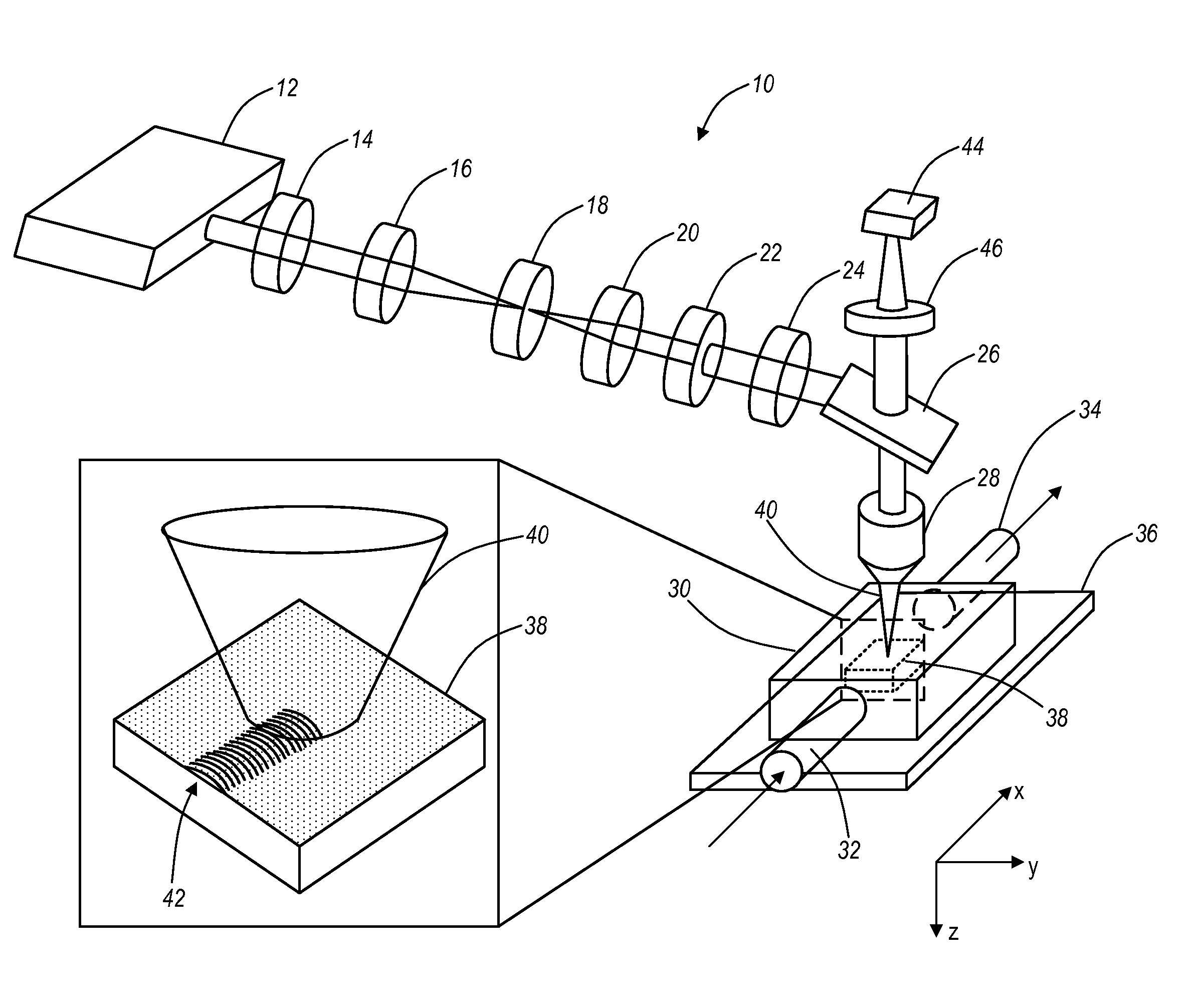
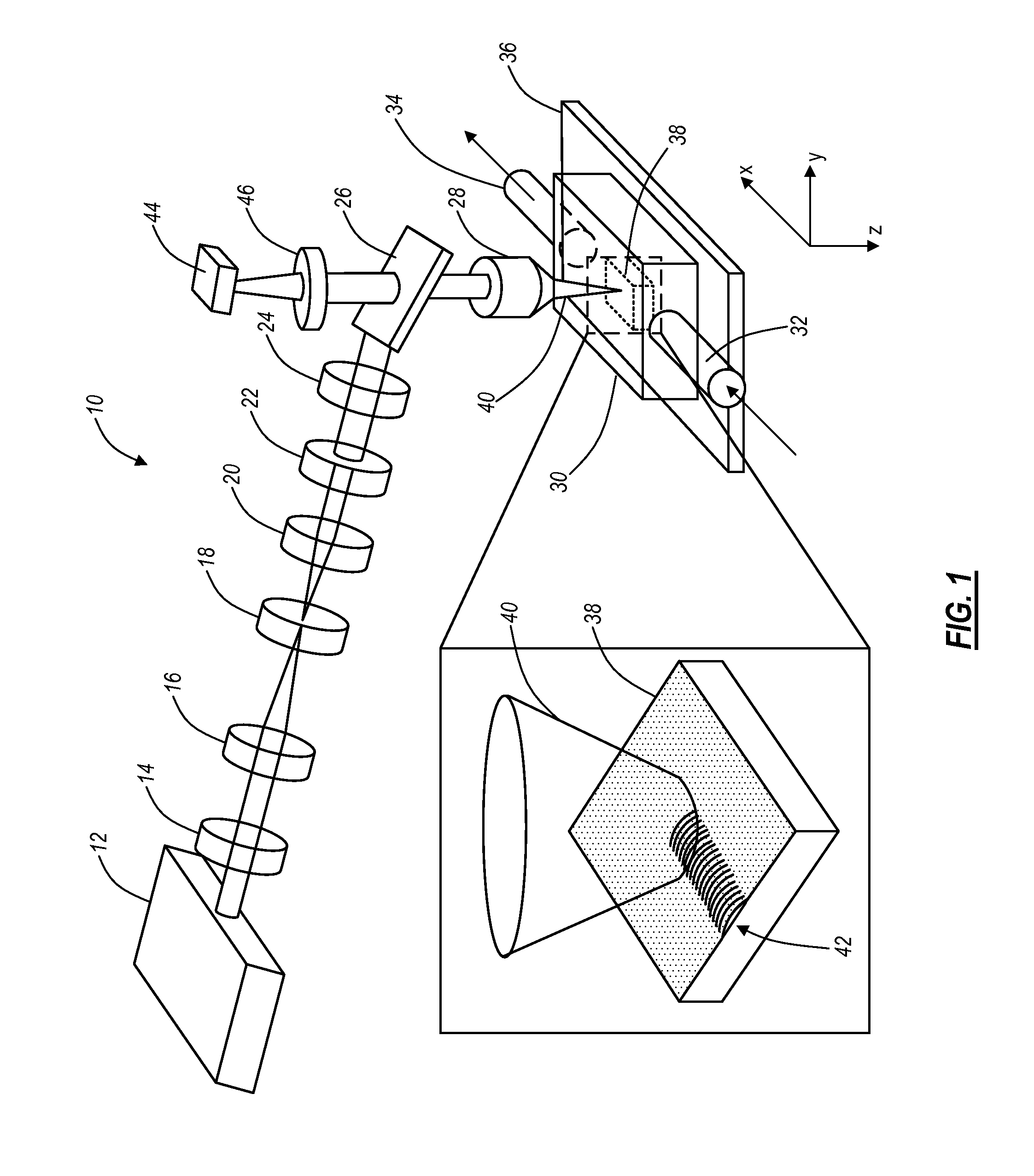
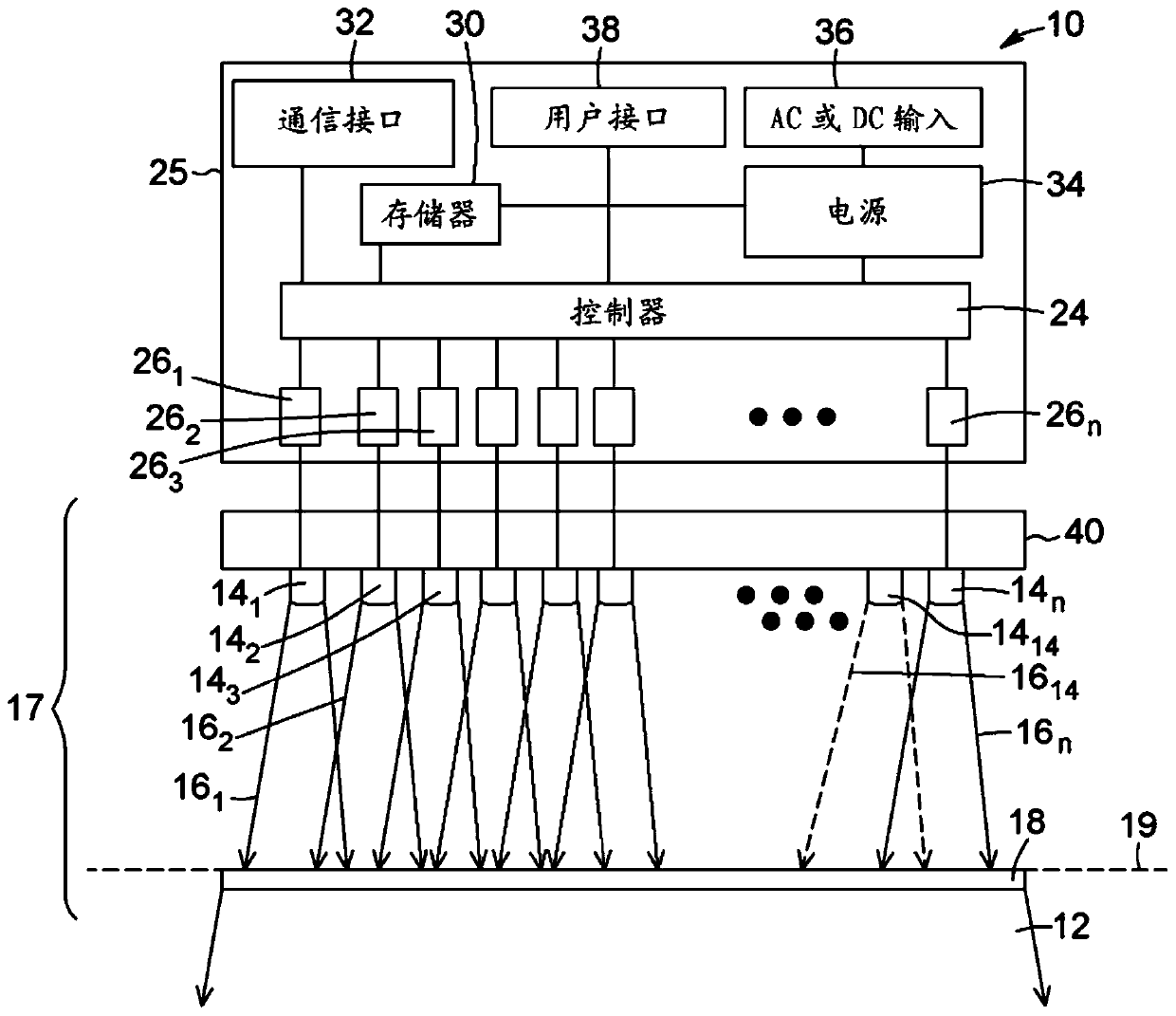
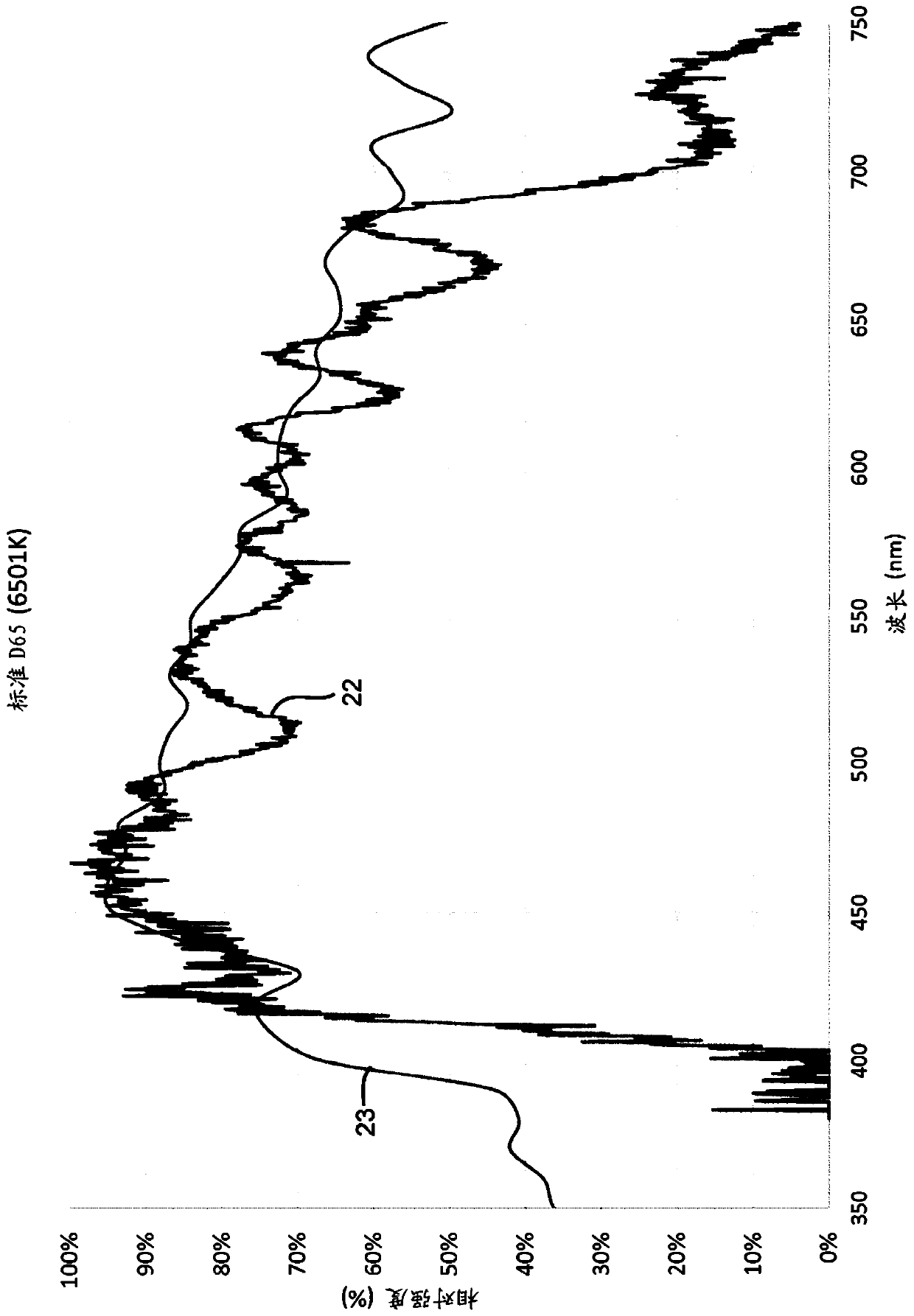
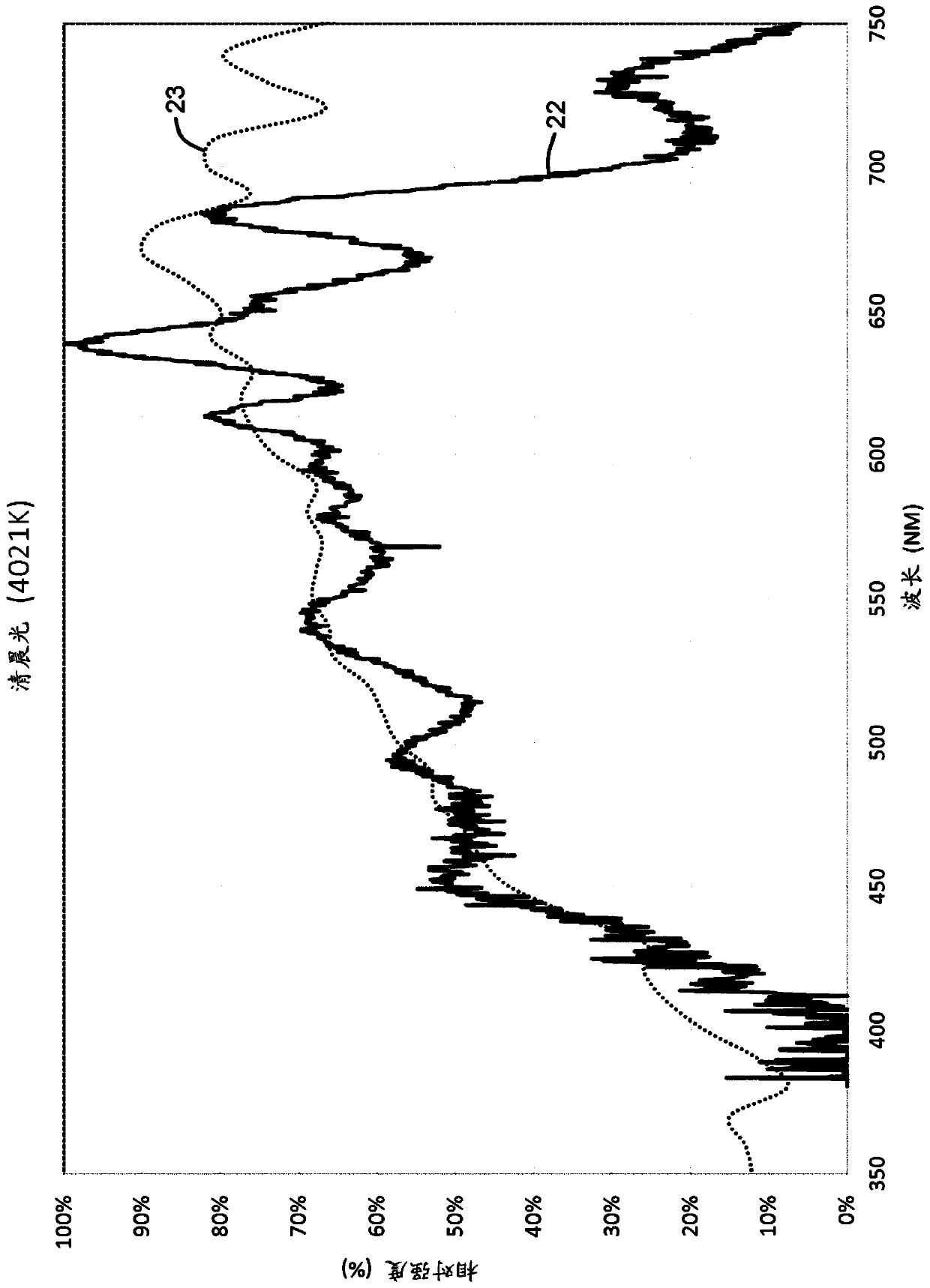
A photon beam consists of numerous photons which pass from the target, through beam modifying devices, and into the patient or phantom. Their usefulness depends on the energy and the volume to be treated.
All field simultaneous radiation therapy
InactiveUS8173983B1Increase dose rateOvercome disadvantagesRadiation pyrometryElectrotherapyProstate cancerEstrogen receptor
This invention describes a system for generating multiple simultaneous tunable electron and photon beams and monochromatic x-rays for all field simultaneous radiation therapy (AFSRT), tumor specific AFSRT and screening for concealed elements worn on to the body or contained in a container. Inverse Compton scattering renders variable energy spent electron and tunable monochromatic x-rays. It's spent electron beam is reused for radiation with electron beam or to generate photon beam. Tumor specific radiation with Auger transformation radiation is facilitated by exposing high affinity tumor bound heavy elements with external monochromatic x-rays. Heavy elements like directly iodinated steroid molecule that has high affinity binding to estrogen receptor in breast cancer and to iodinated testosterone in prostate cancer or with directly implanted nanoparticles into the tumor are exposed with tuned external monochromatic x-rays for tumor specific radiation therapy. Likewise, screening element's atom's k, l, m, n shell specific Auger transformation radiation generated by its exposure to external monochromatic x-rays is used to screen for concealed objects. Multiple beam segments from a beam storage ring or from octagonal beam lines are simultaneously switched on for simultaneous radiation with multiple beams. The beam on time to expose a tumor or an object is only a few seconds. It also facilitates breathing synchronized radiation therapy. The intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) and intensity modulated screening for concealed objects (IMSFCO) is rendered by varying beam intensities of multiple simultaneous beams. The isocentric additive high dose rate from simultaneously converging multiple beams, the concomitant hyperthermia and chemotherapy and tumor specific radiation therapy and the AFSRT's very low radiation to the normal tissue all are used to treat a tumor with lower radiation dose and to treat a radioresistant and multiple times recurrent tumors that heave no other alternative treatments.
Owner:SAHADEVAN VELAYUDHAN
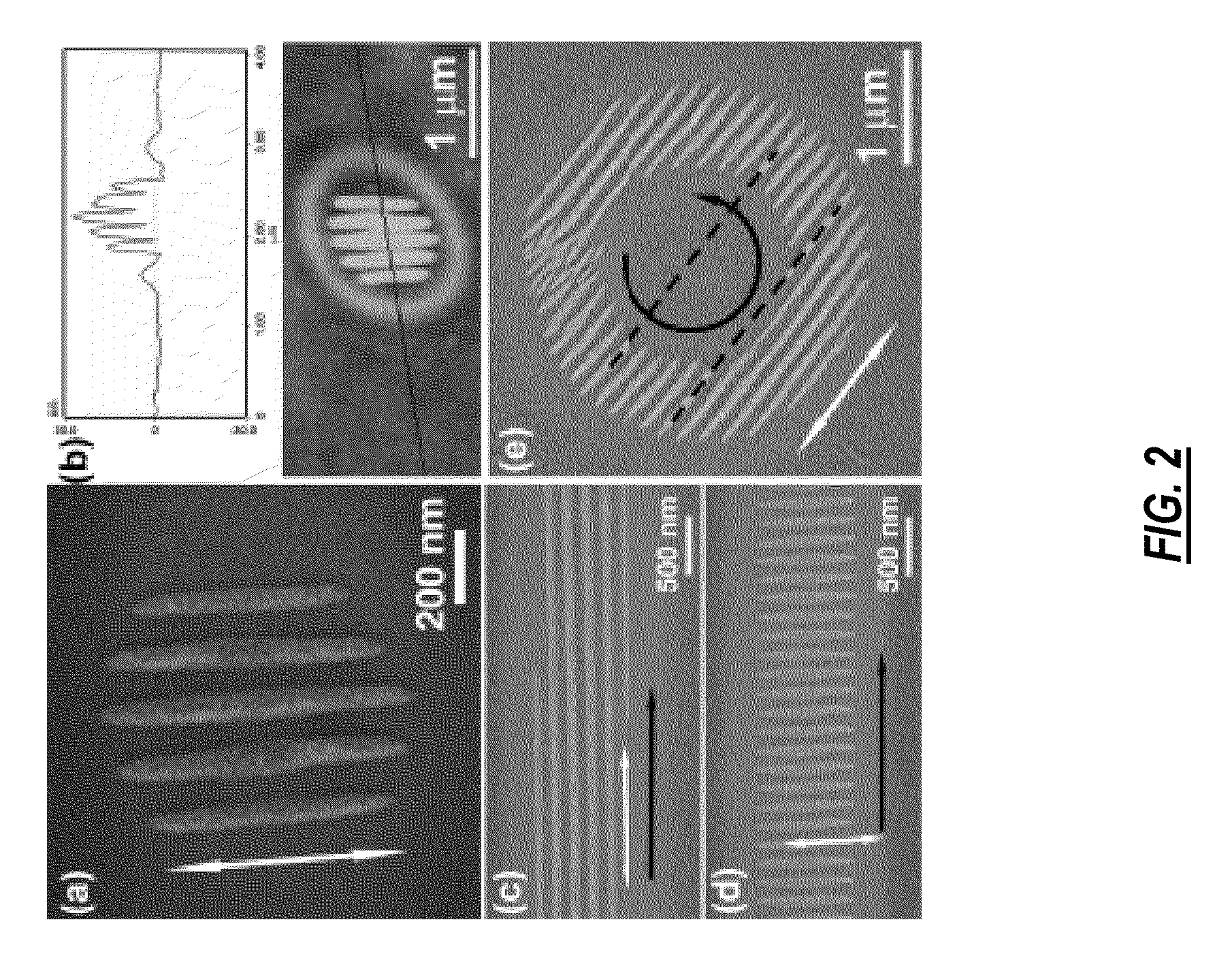
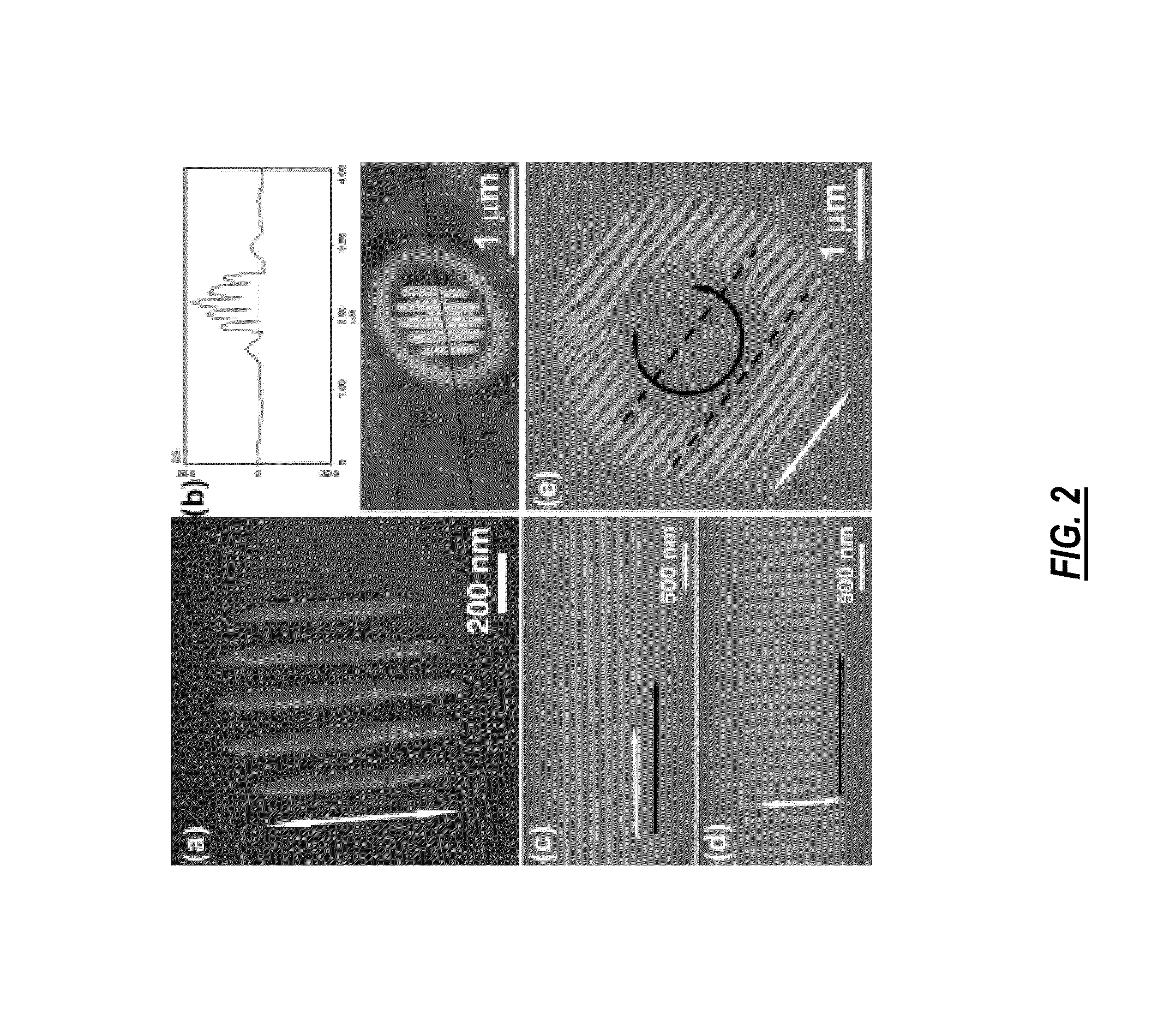
Light-induced directed self-assembly of periodic sub-wavelength nanostructures
ActiveUS20090214885A1Small feature sizeExcellent long-range orderCasting plantsNanoinformaticsWavelengthNanostructure
In various exemplary embodiments, the present invention provides a system for the light-induced directed self-assembly (LIDSA) of periodic sub-wavelength nanostructures, including: a light source for delivering a beam of photons; a reaction chamber disposed adjacent to the light source; a gas including one or more precursor materials disposed within the reaction chamber; and a substrate disposed within the reaction chamber, wherein the substrate is positioned and configured to receive the beam of photons; wherein the beam of photons causes a periodic sub-wavelength nanostructure of one or more constituents of the one or more precursor materials to form on a surface of the substrate. In various exemplary embodiments, the present invention also provides an associated method.
Owner:JUNIVERSITI OF NORT KAROLINA EHT SHARLOTT
Visualizing Radiation Therapy Beam in Real-Time in the context of Patient's Anatomy
ActiveUS20150360056A1Material analysis by optical meansX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyReal time validationTreatment delivery
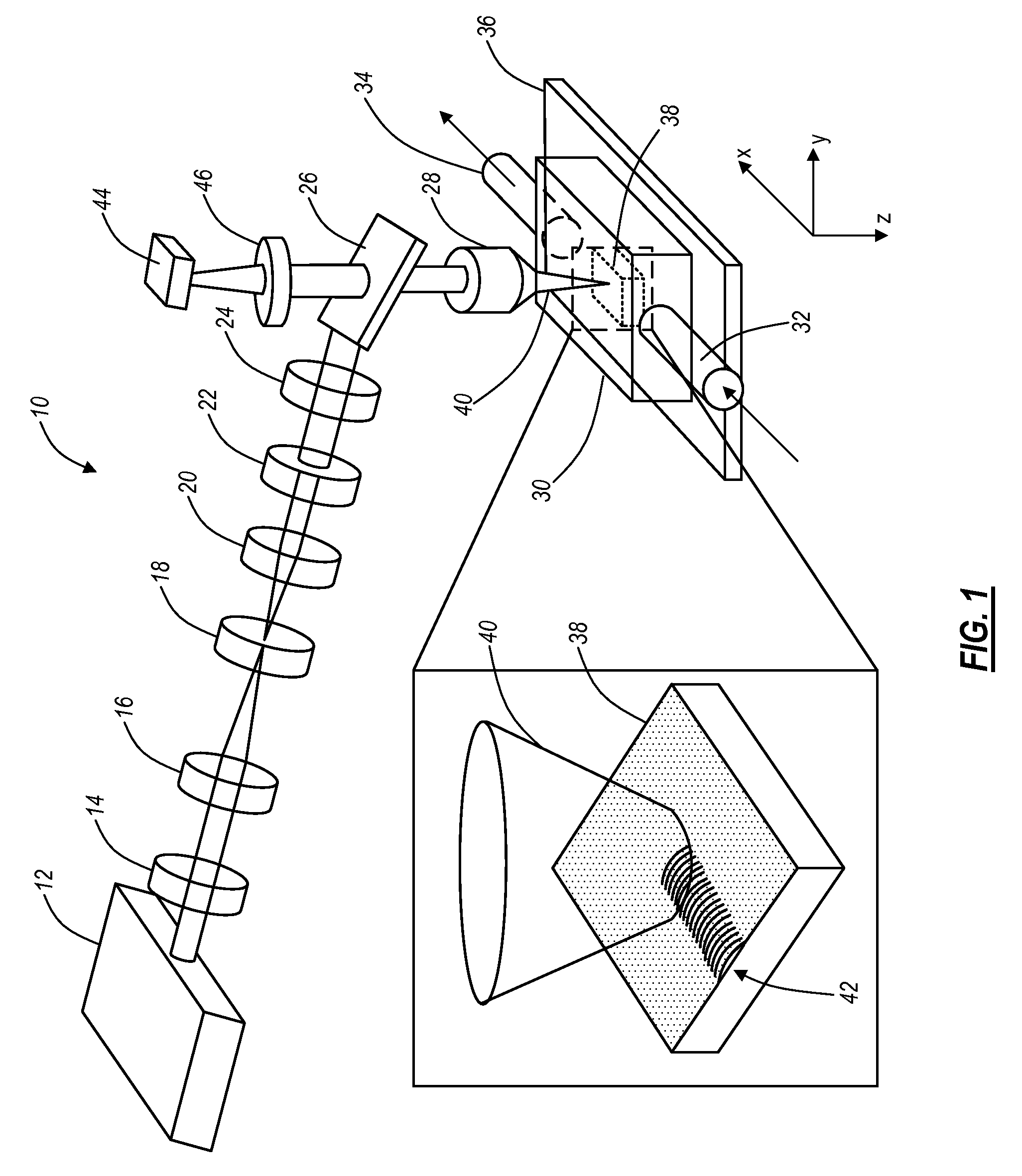
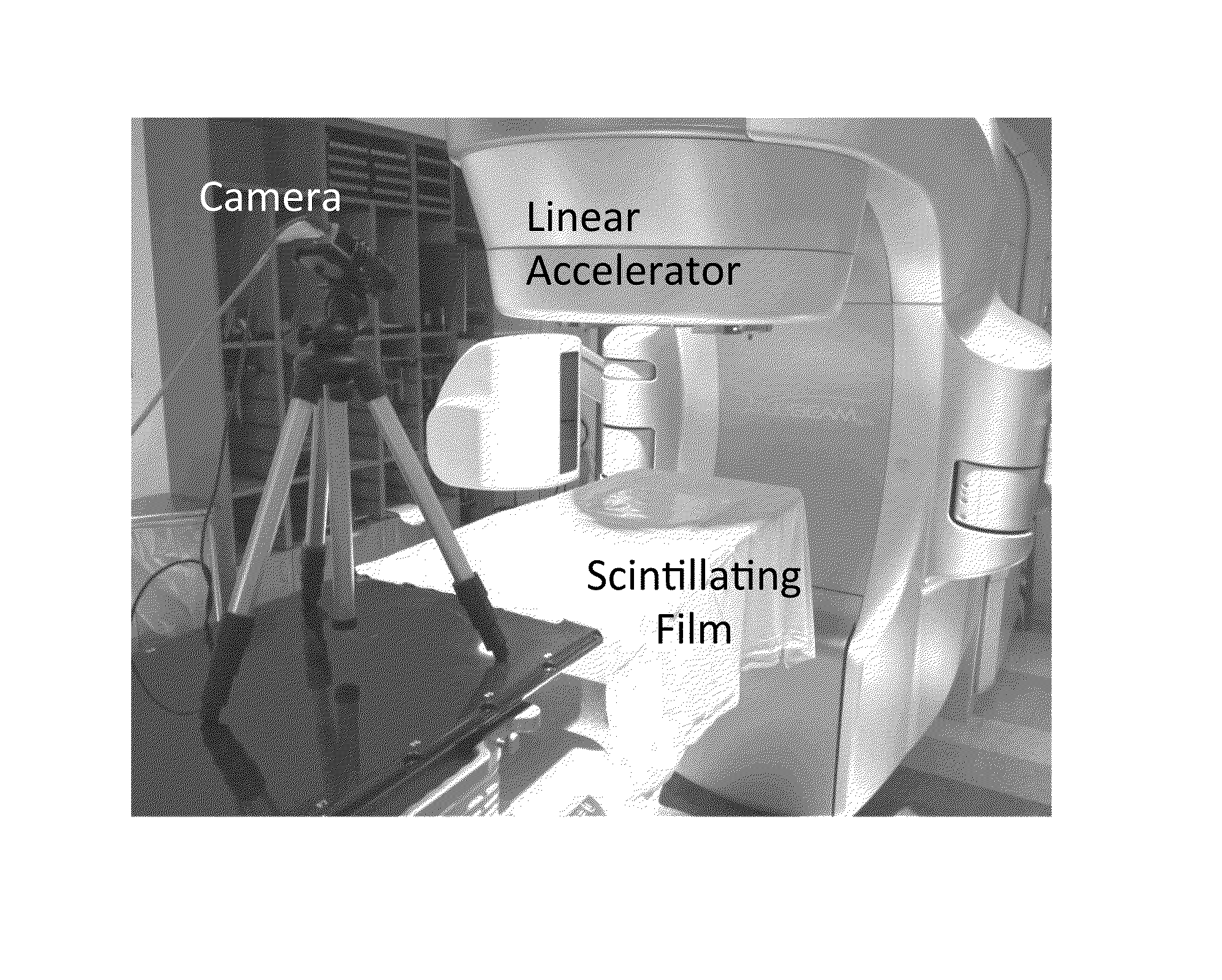
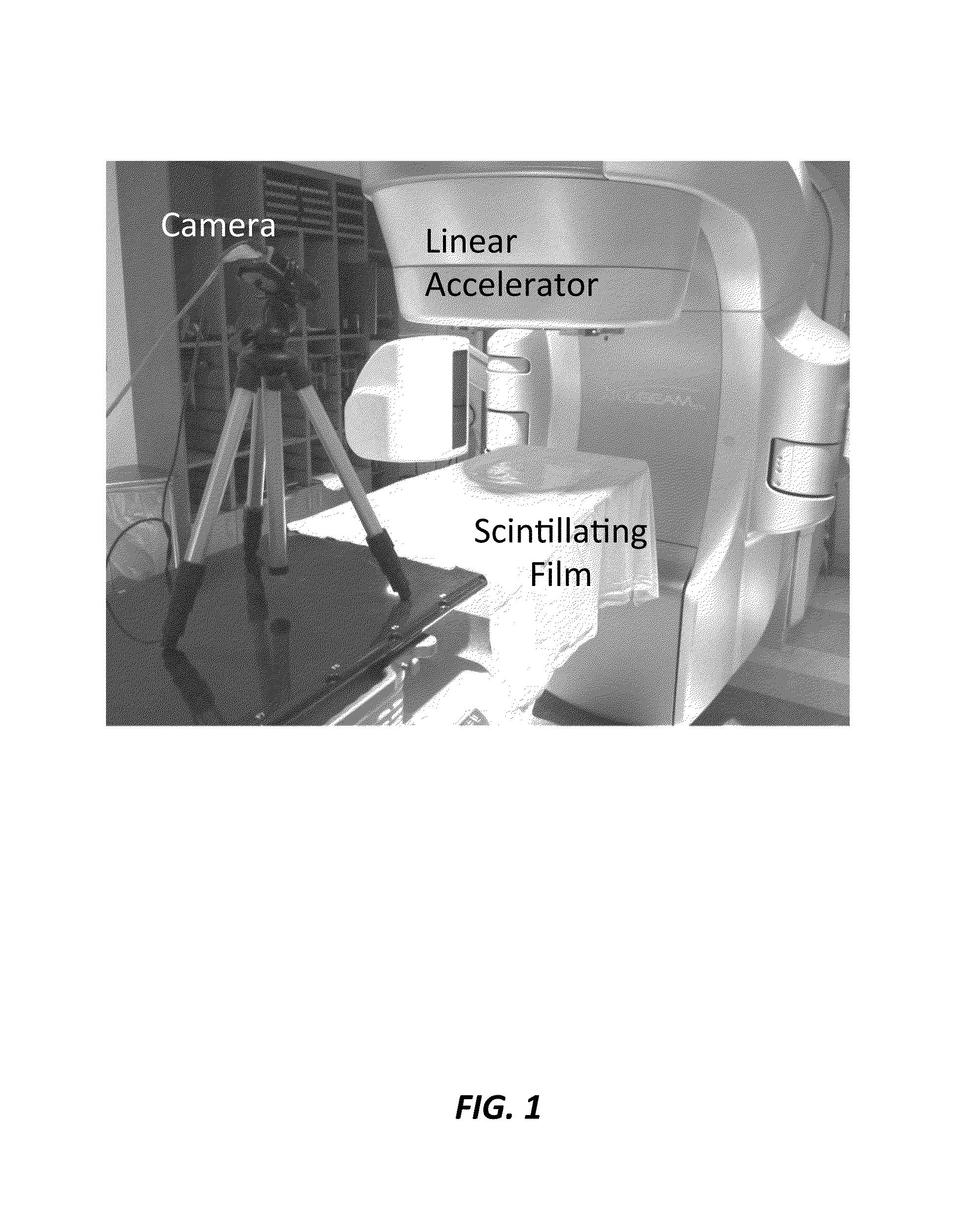
A method of real-time radiotherapy beam visualization is provided that includes disposing a free-form flexible scintillating sheet on a subject of interest, irradiating the subject of interest with a source of ionizing radiation, where the free-forming flexible scintillating sheet emits light when irradiated by the therapeutic photon beam, collecting the emitted light and collecting ambient light reflected from the subject of interest and surrounding objects using a camera, where the collected light is converted to image data by the camera, where the image data is communicated to an appropriately programmed computer, and processing the image data to determine beam characteristics and the characteristics of the subject of interest, using the appropriately programmed computer, where the beam characteristics and the characteristics of the subject of interest are displayed in real-time to a machine operator enabling real-time verification of treatment delivery.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
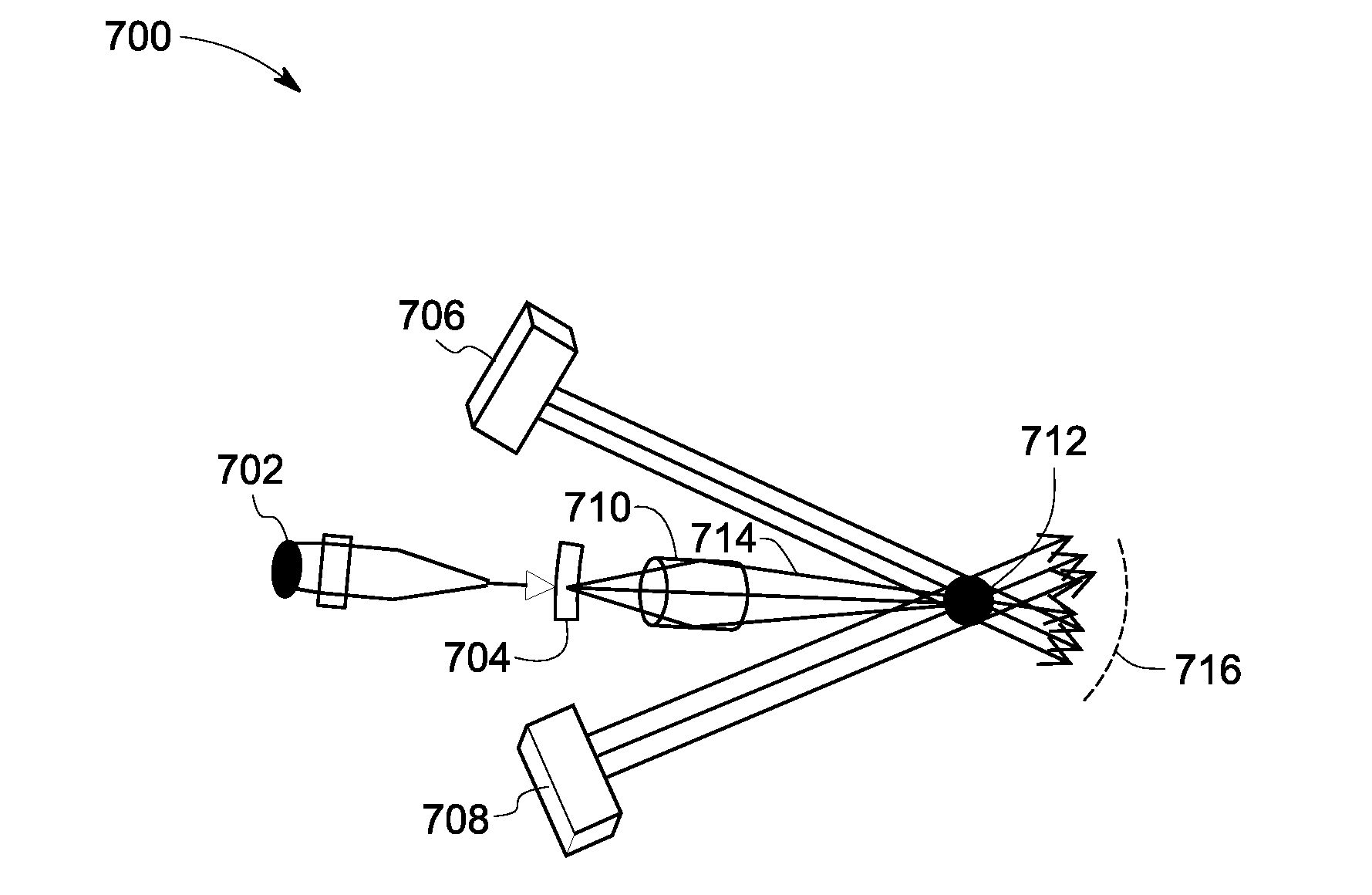
High flux photon beams using optic devices
A system for producing at least one high flux photon beam is provided. The system includes two or more photon sources configured to produce photon beams, and at least one first stage optic device coupled to at least one of the photon sources and providing at least one focused photon beam through total internal reflection, wherein at least one of the photon beams and the focused photon beams are combined at a virtual focal spot.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
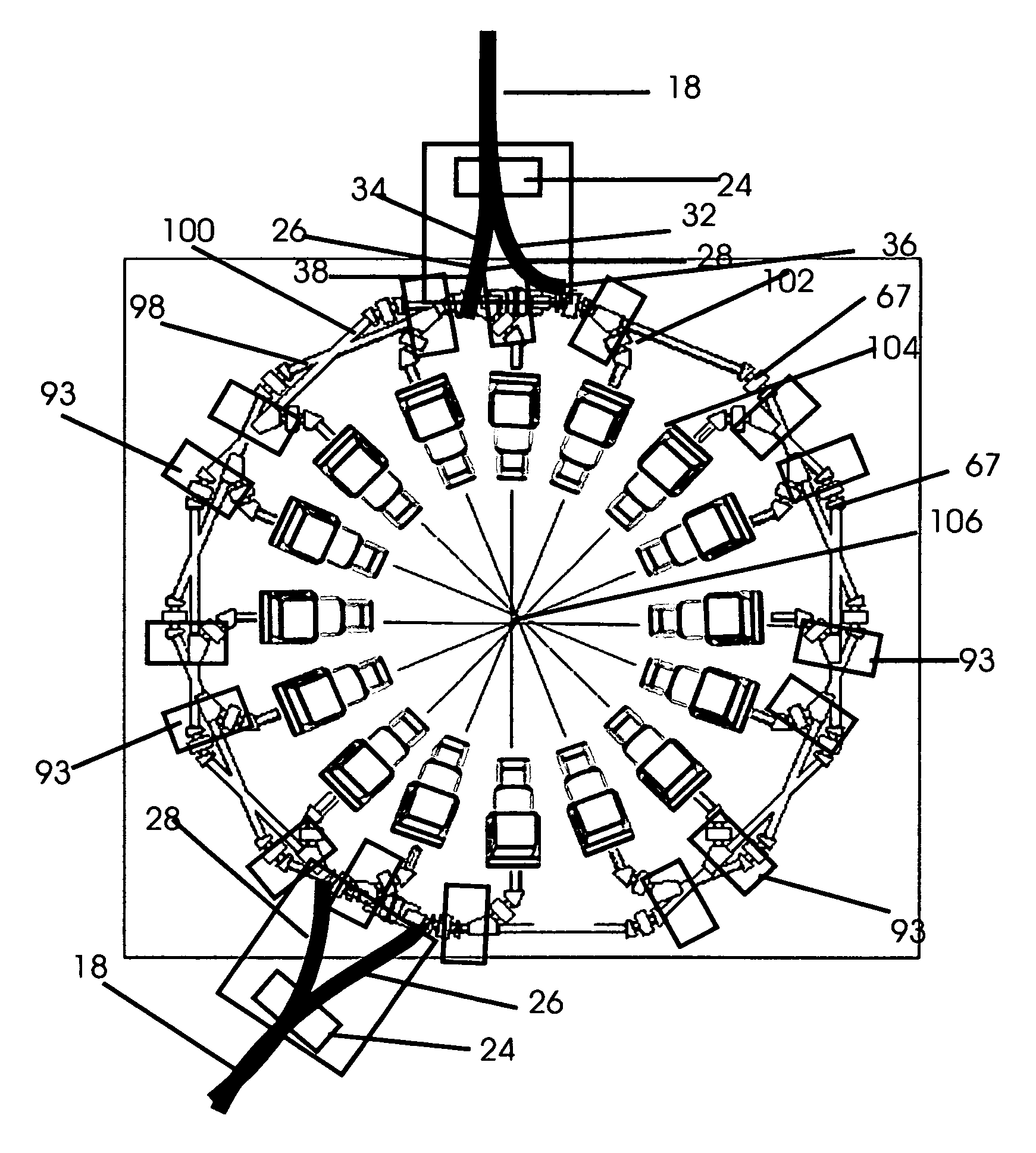
Extrahigh energy electron beam or photon beam radiotherapy robot system
ActiveCN104001270AObvious priceObvious installation site layout advantagesLight therapyPhoton Beam Radiation TherapyExternal irradiation
The invention provides an extrahigh energy electron beam or photon beam radiotherapy robot system which comprises a laser driving system, a laser plasma accelerator, an electron beam focusing system, a photon beam aiming system, a robot body and a laser beam stabilization system. The laser driving system generates and spreads intense laser pulses to the laser plasma accelerator installed at the tail end of the robot body, and therefore electron beams are generated; the electron beam focusing system guides the electron beams to diseased parts of a patient; the photon beam aiming system enables the electron beams to generate high energy photon beams so that extrahigh energy electron beam radiotherapy or photon beam radiotherapy can be performed; the robot body spreads the electron beams or the photon beams to the diseased parts of the patient in multiple directions; the laser beam stabilization system monitors the positions of laser beams and corrects errors. The extrahigh energy electron beam or photon beam radiotherapy robot system is more compact, more efficient, cheaper and easier to operate and has higher performance than an external irradiation radiation therapy system in the prior art.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
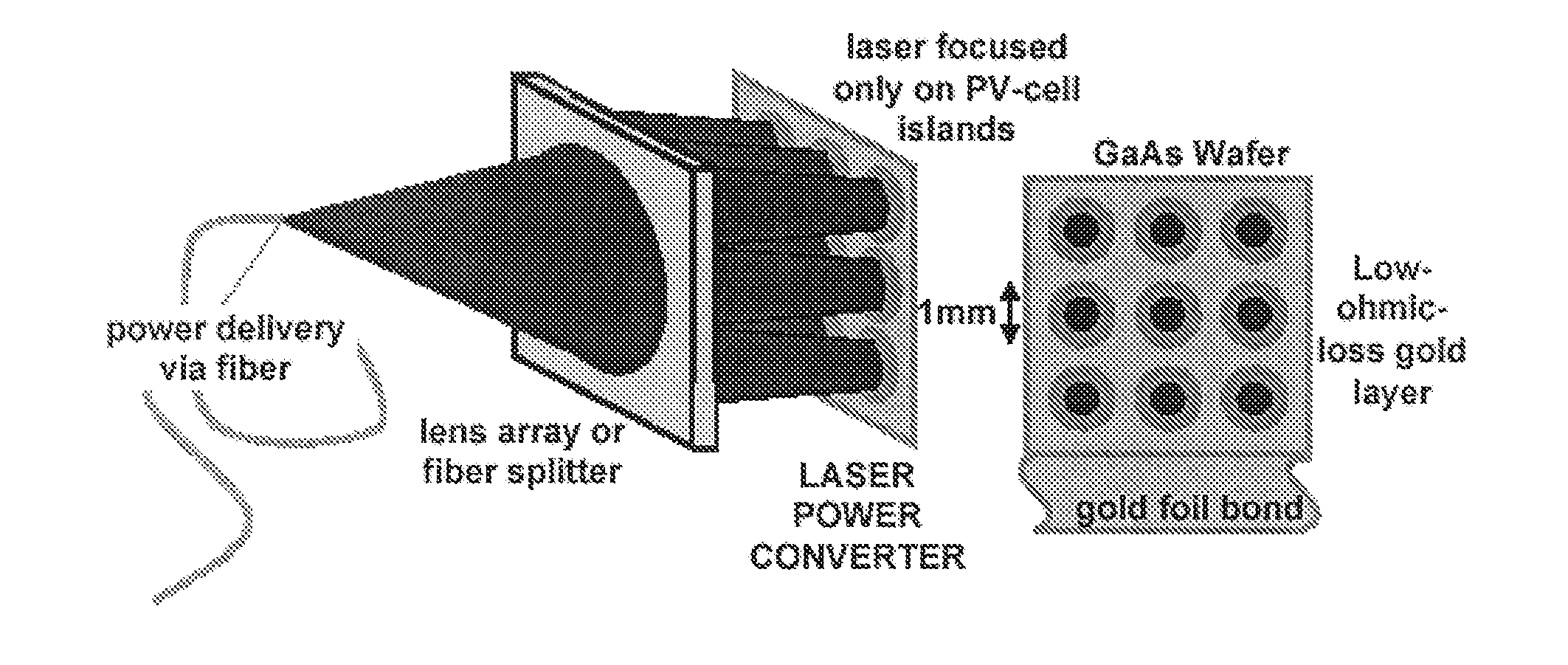
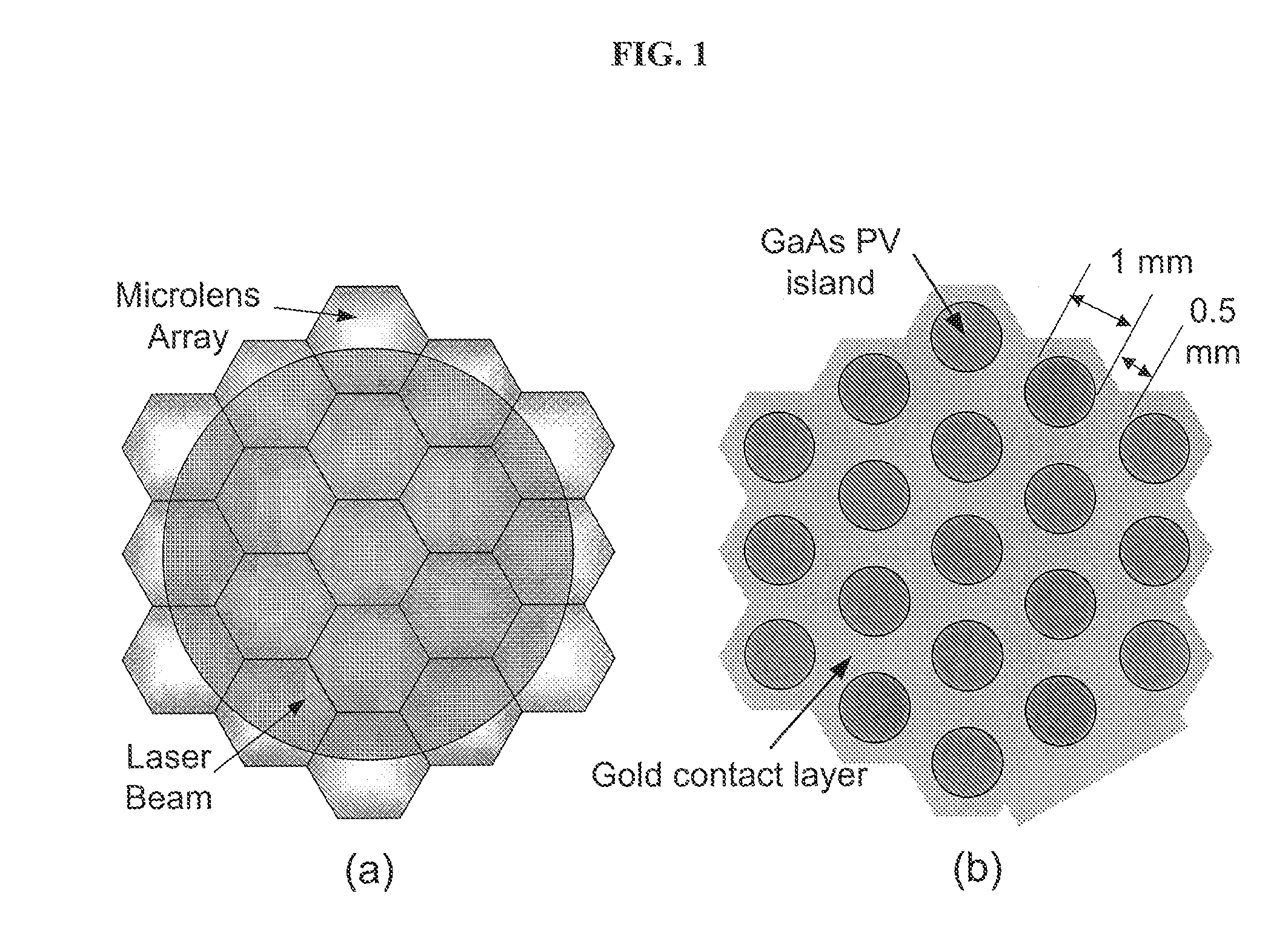
Pixelated photovoltaic array method and apparatus
InactiveUS20100116318A1Improve device efficiencyImprove photovoltaic conversion efficiencyPV power plantsPhotovoltaic energy generationOptical powerLight beam
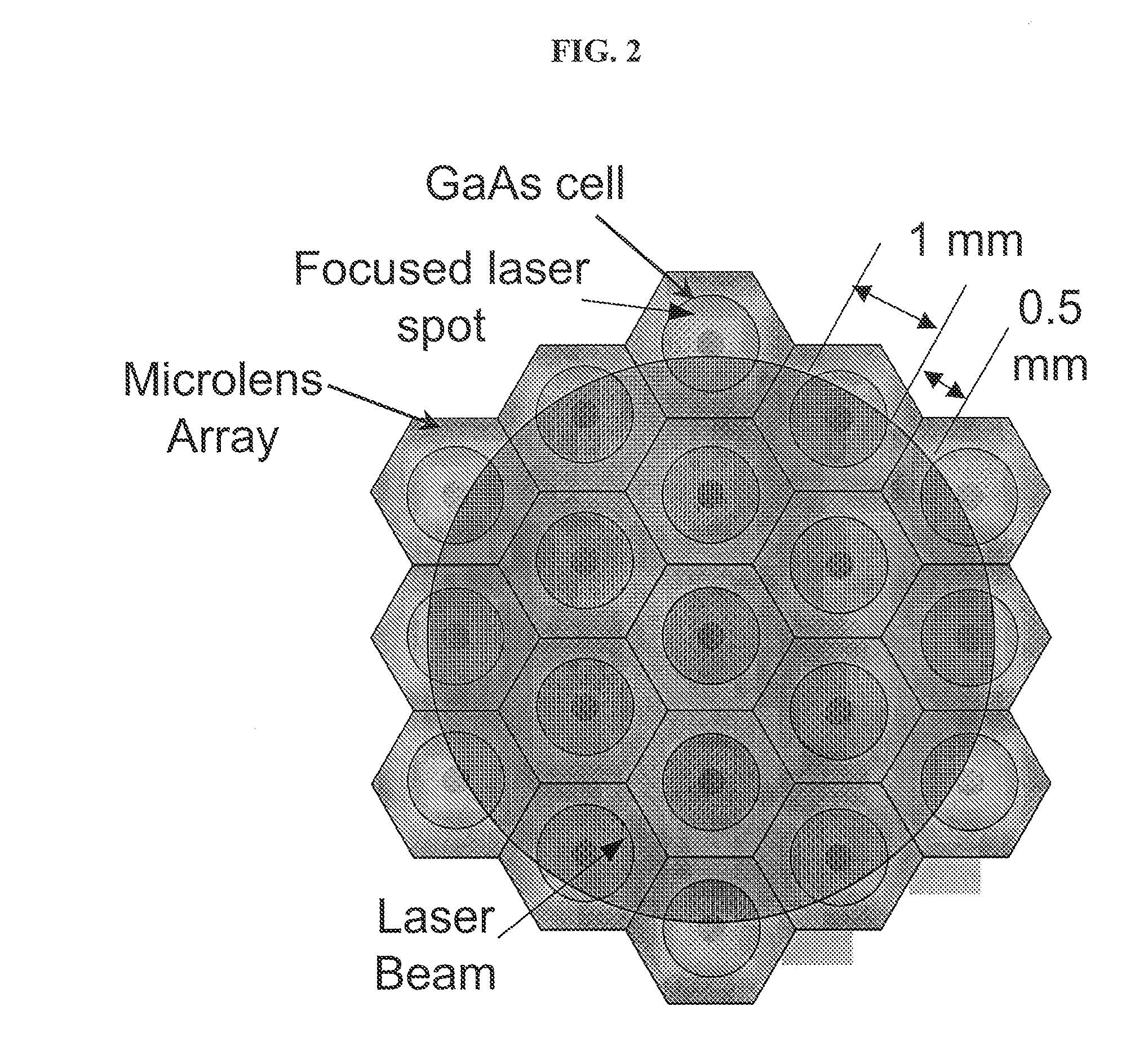
The present invention comprises a method and apparatus to increase the efficiency of photovoltaic conversion of light into electrical power and to achieve operation at higher optical power and therefore higher electrical power. Preferred embodiments increase the efficiency of photovoltaic power conversion of any source of a beam of photons by spatially dividing the beams into a plurality of individual beamlets, each beamlet focusing on an active photovoltaic region. The preferred architecture of the apparatus of the invention comprises spatially separated photovoltaic cells to substantially match the pattern of the spatially separated plurality of beamlets. Preferred embodiments result in a significant reduction in ohmic losses and current shunting, thereby increasing photovoltaic conversion efficiencies.
Owner:HRL LAB
Nanometer plasma array laser device and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN104538837AAchieve laser emissionIncrease laser powerOptical wave guidanceExcitation process/apparatusDielectricResonant cavity
The invention provides a nanometer plasma array laser device and a manufacturing method of the laser device and belongs to the technical field of optics. According to the method, photons excited by an electrical pump semiconductor nanowire p-n junction array are utilized for interacting with surface metal-dielectric films to generate surface plasmon polaritons (SPP), and then photon beams generated in a nanowire resonant cavity are restrained and regulated. According to the method, the double advantages of semiconductor nanometer structure geometric limitation and limitation and constraint of a surface plasma mode field to beams are combined, a semiconductor nanowire is utilized for integrating a working substance and the resonant cavity and achieving mode field constraint on surface plasmas, and finally the nanometer plasma laser device is formed.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method of testing electronic components
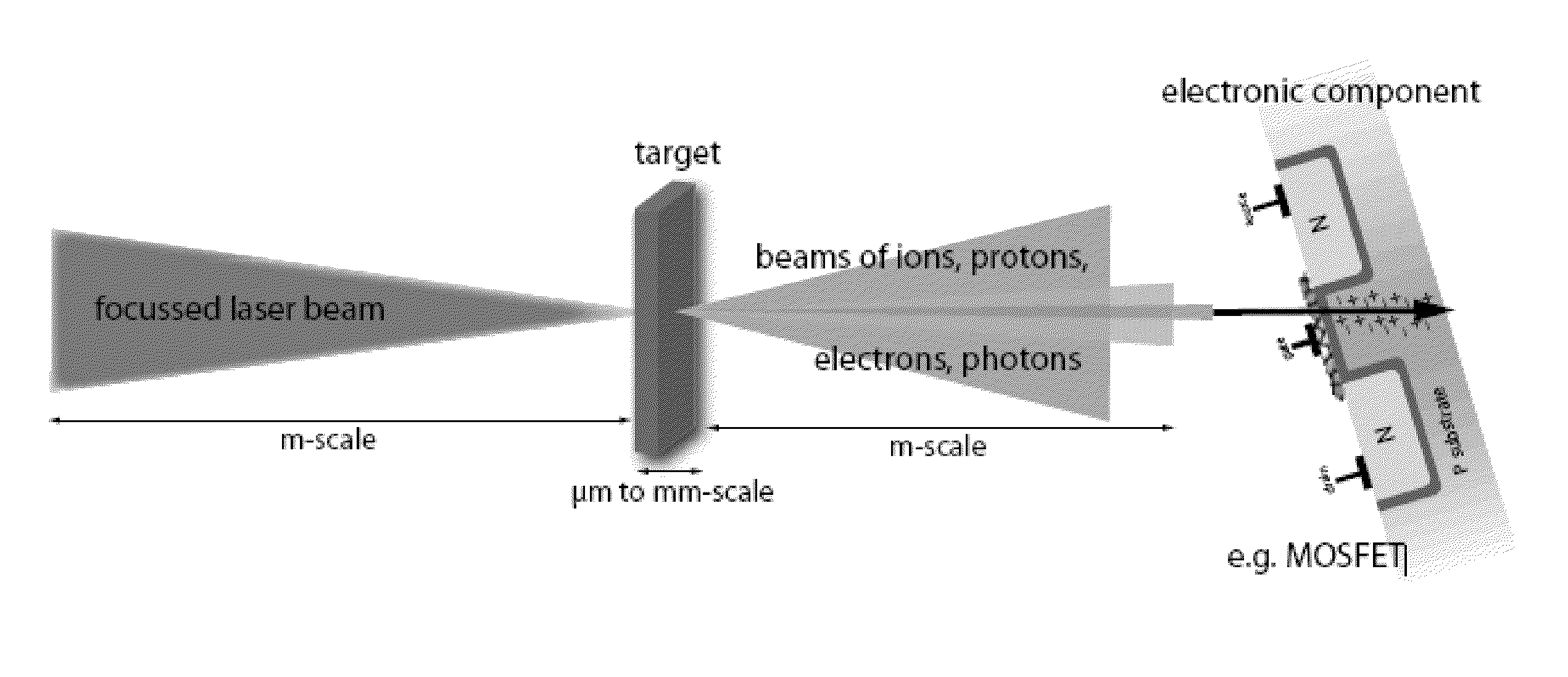
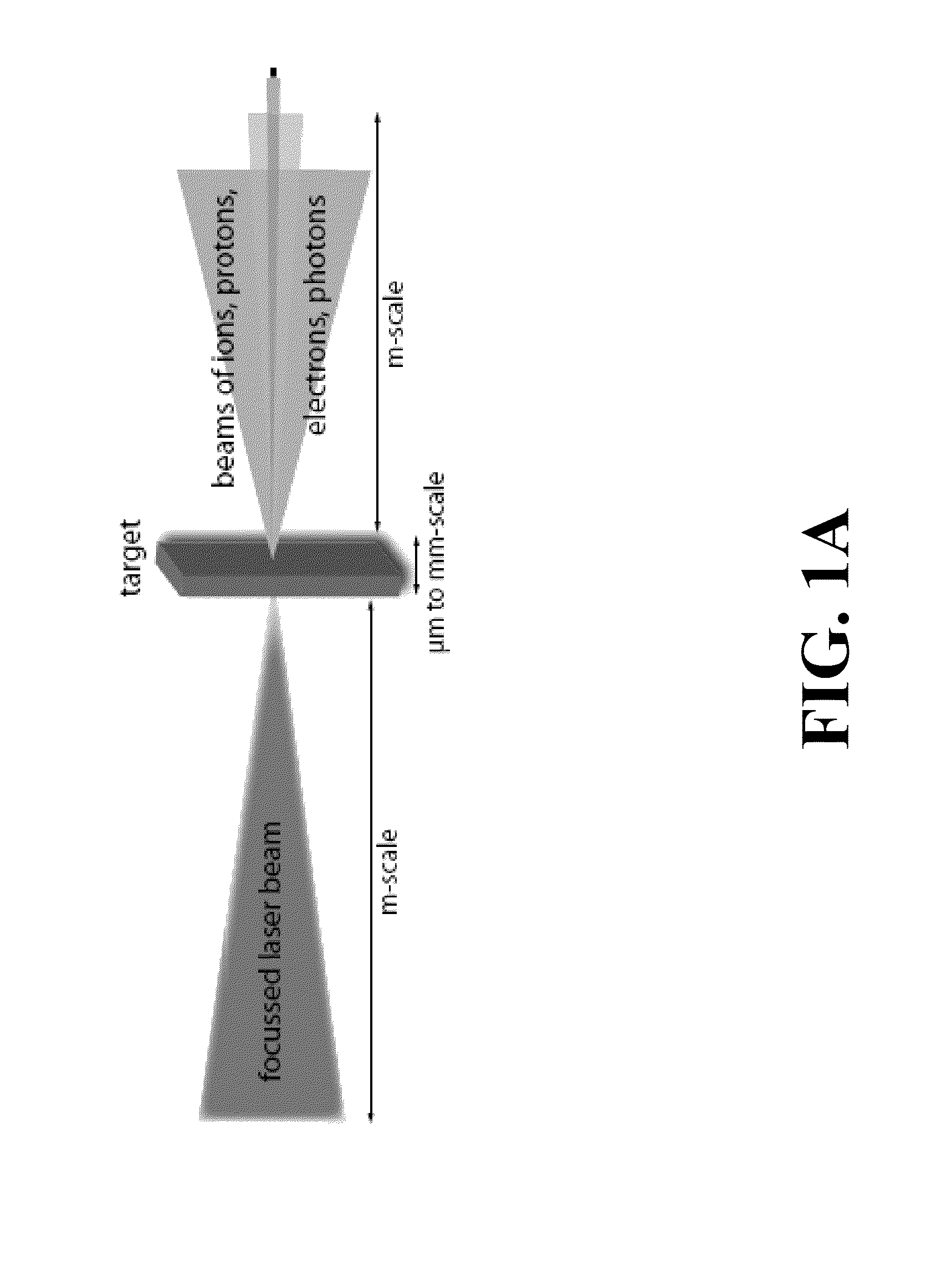
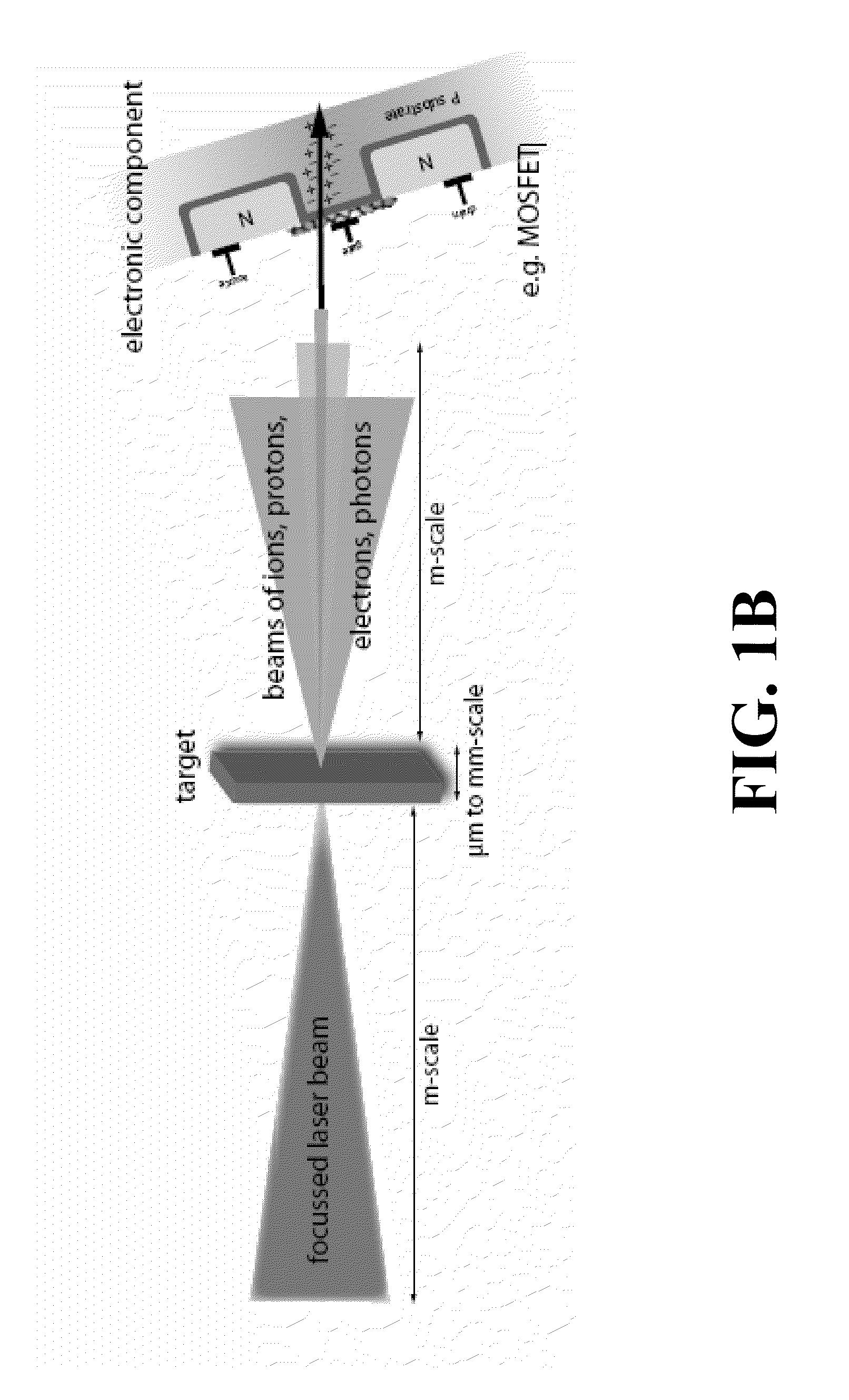
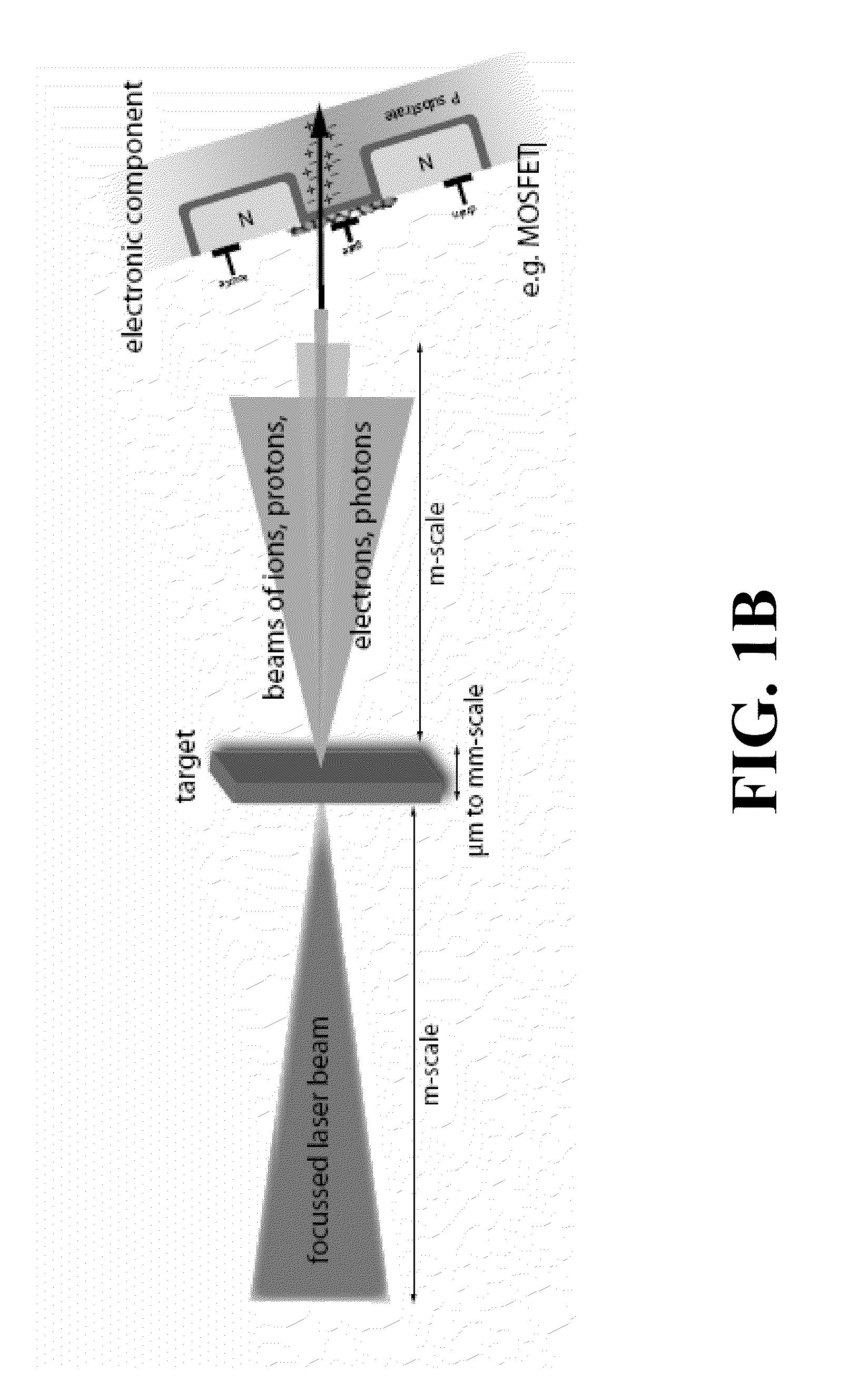
ActiveUS20110240888A1Apparent advantageEnergy based chemical/physical/physico-chemical processesRadiation therapyRadioactive agentNuclear power
A method for testing the sensitivity of electronic components and circuits against particle and photon beams using plasma acceleration, in which the flexibility of the multifaceted interaction can produce several types of radiation such as electron, proton, ion, neutron and photon radiation, and combinations of these types of radiation, in a wide range of parameters that are relevant to the use of electronic components in space, such as satellites, at high altitudes or in facilities that work with radioactive substances such as nuclear power plants. Relevant radiation parameter ranges are accessible by this method, which are hardly accessible with conventional accelerator technology. Because of the compactness of the procedure and its versatility, radiation testing can be performed in smaller laboratories at relatively low cost.
Owner:RADIABEAM TECH
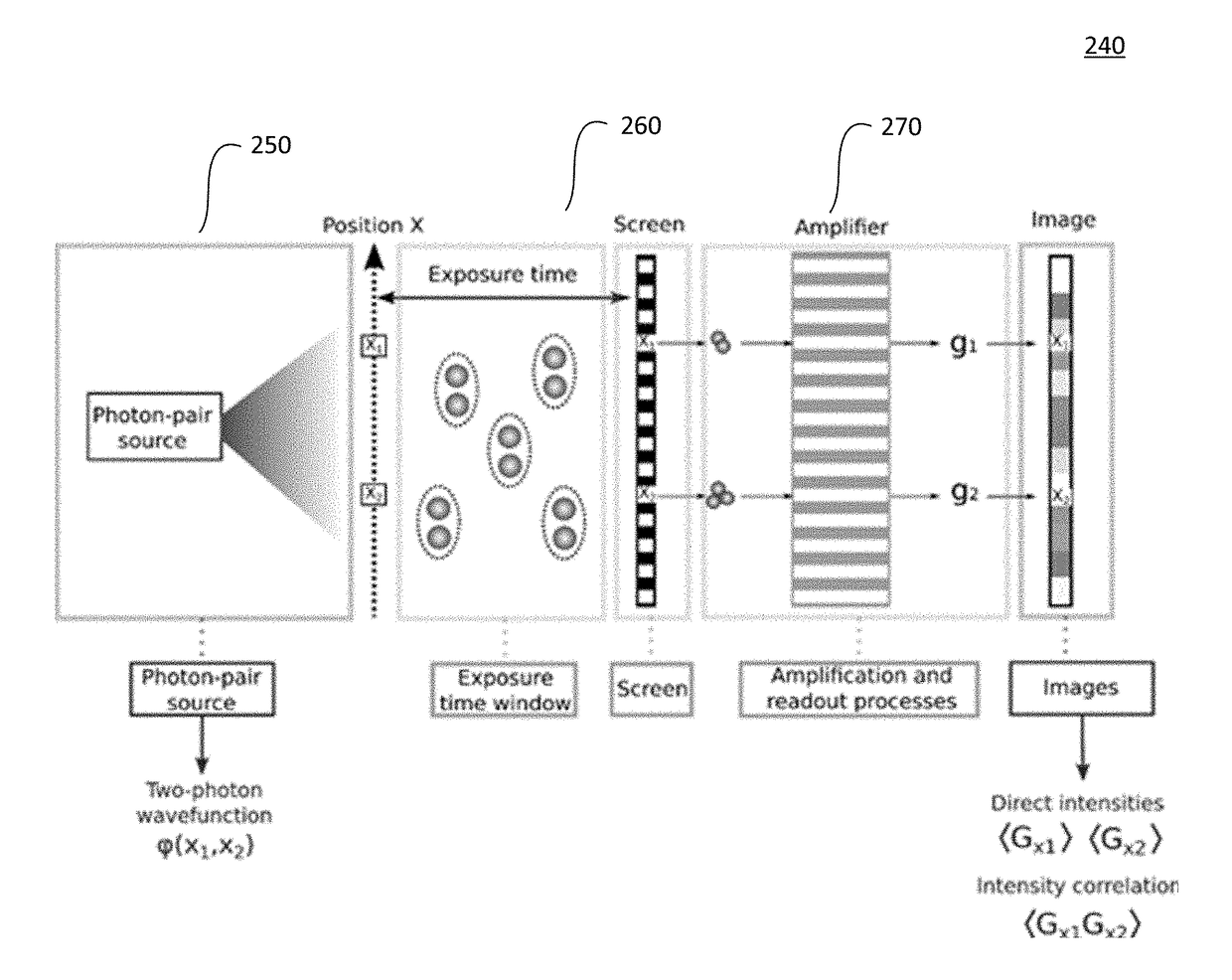
Method and system for quantum information processing and computation
PendingUS20180032896A1Well formedQuantum computersImage enhancementInformation processingSpatial light modulator
A quantum information processing system comprises a light source, a detector, at least one spatial light modulator and at least one optical lens. The light source is configured to provide a beam of entangled photons. The at least one optical lens is configured to project the resultant beam onto the spatial light modulator, either by direct imaging or by performing a full or partial optical Fourier transform. Said spatial light modulator includes a plurality of discrete pixels and is configured to select one or more of the plurality of discrete pixels to generate a resultant beam from said beam of entangled photons. The resultant beam from said spatial light modulator is projected onto the detector. For optical computation, such as search algorithms, the configuration and projections are repeated to find the optimal solution.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
Method of testing electronic components
ActiveUS8947115B2Electric discharge tubesEnergy based chemical/physical/physico-chemical processesRadioactive agentNuclear power
A method for testing the sensitivity of electronic components and circuits against particle and photon beams using plasma acceleration, in which the flexibility of the multifaceted interaction can produce several types of radiation such as electron, proton, ion, neutron and photon radiation, and combinations of these types of radiation, in a wide range of parameters that are relevant to the use of electronic components in space, such as satellites, at high altitudes or in facilities that work with radioactive substances such as nuclear power plants. Relevant radiation parameter ranges are accessible by this method, which are hardly accessible with conventional accelerator technology. Because of the compactness of the procedure and its versatility, radiation testing can be performed in smaller laboratories at relatively low cost.
Owner:RADIABEAM TECH
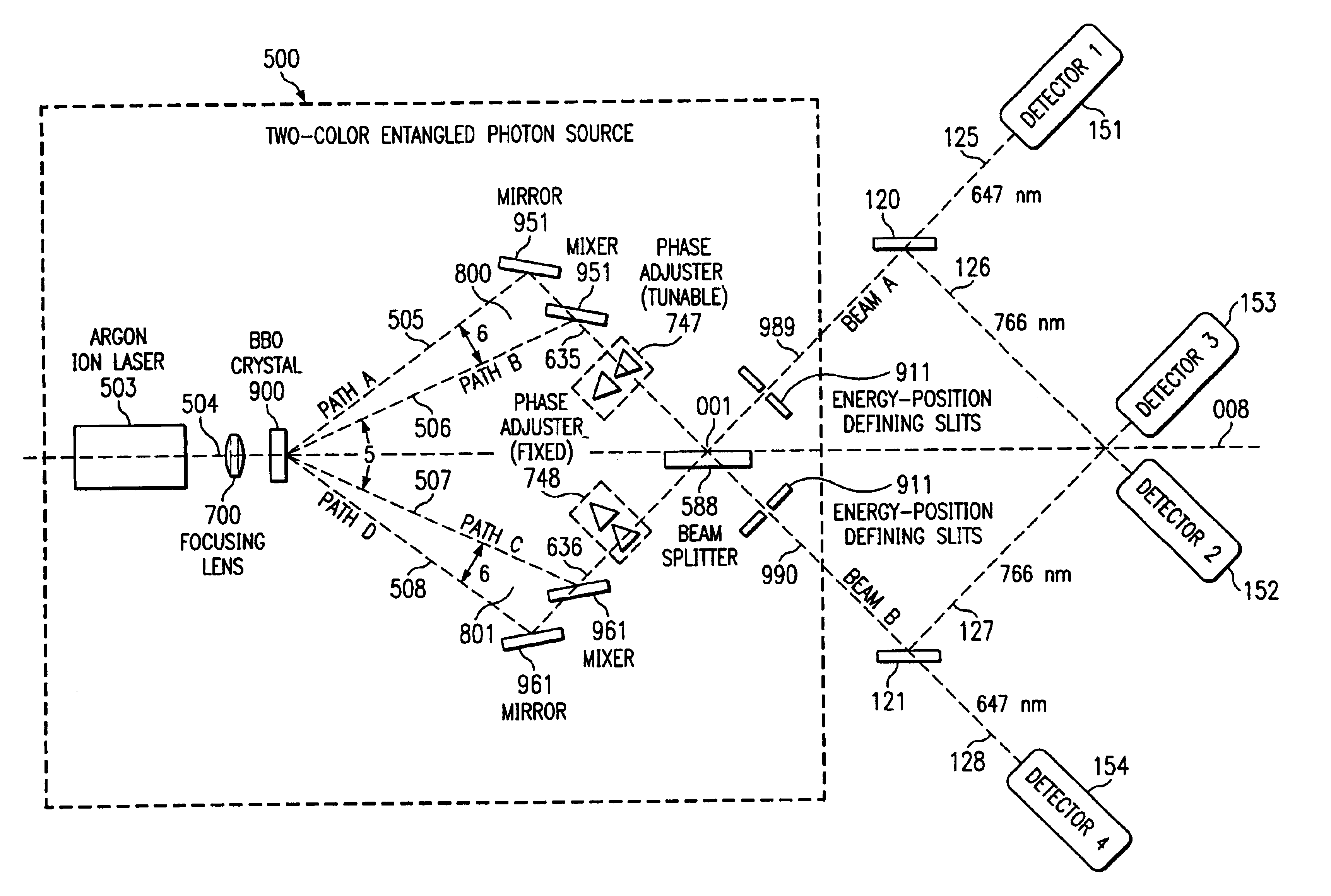
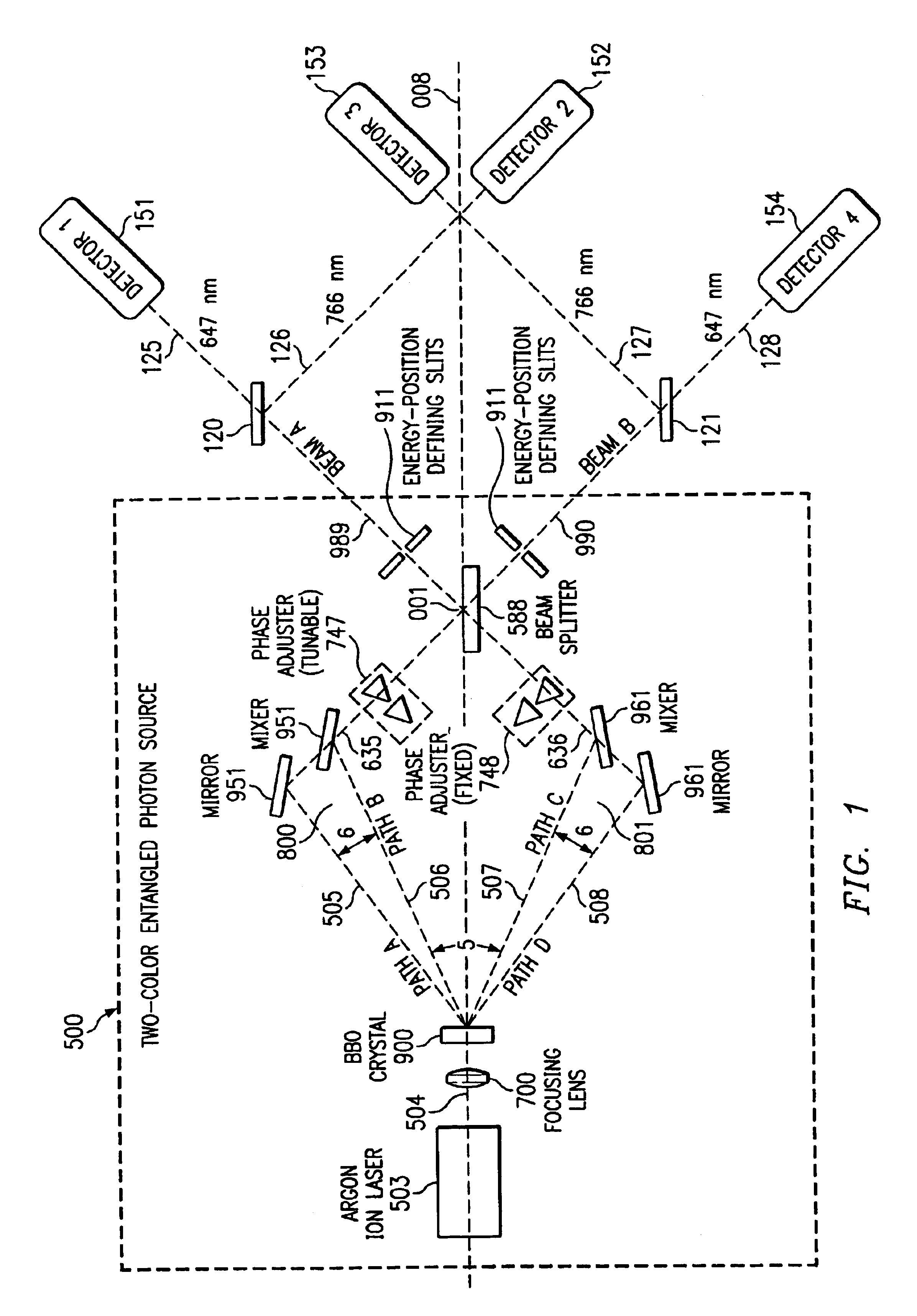
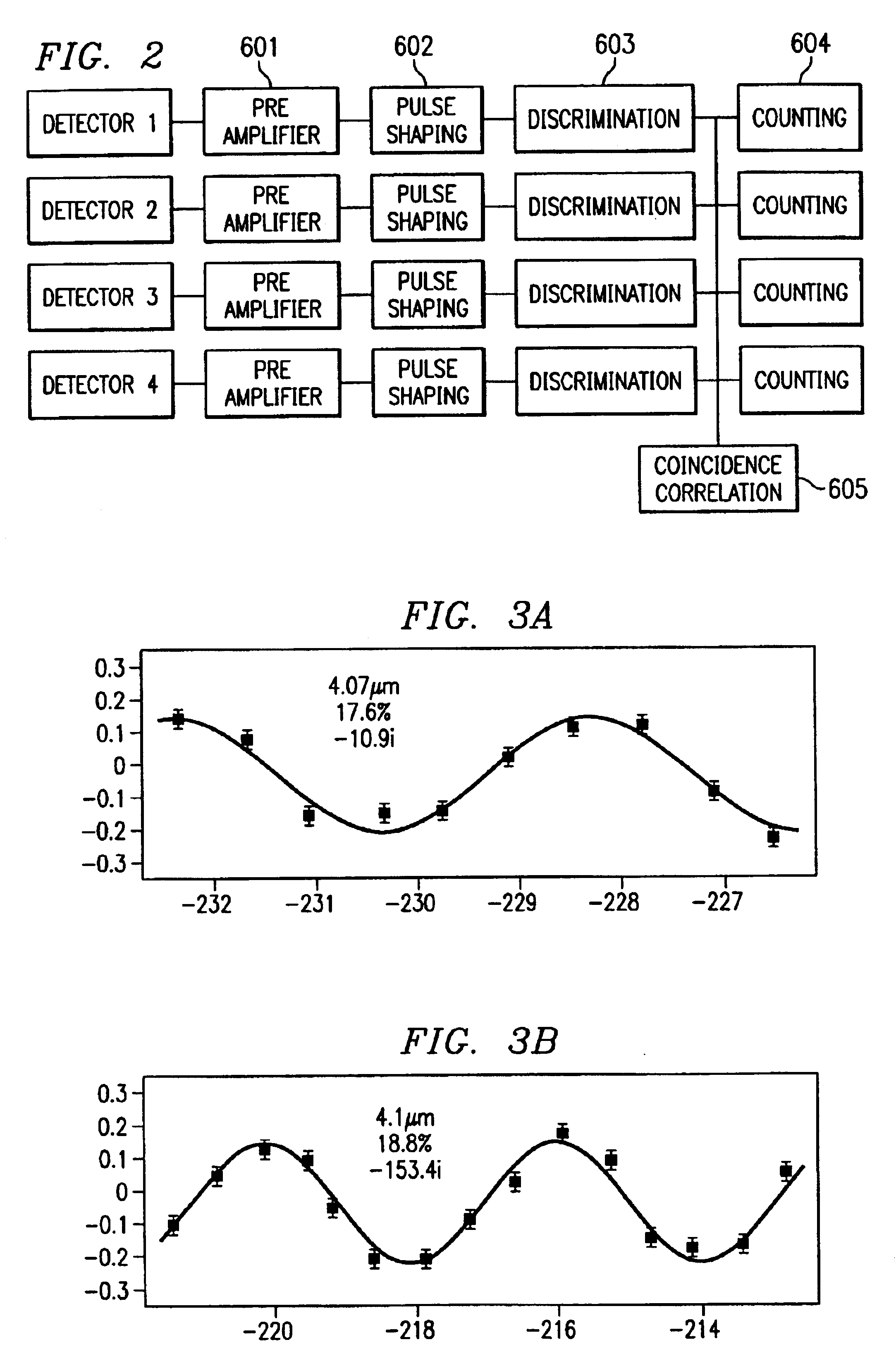
Interferometric source of multi-color, multi-beam entangled photons with mirror and mixer
53 Systems and methods are described for an interferometric source of multi-color, multi-beam entangled photons. An apparatus includes: a multi-refringent device optically coupled to a source of coherent energy, the multi-refringent device providing a beam of multi-color entangled photons; a condenser device optically coupled to the multi-refringent device, the condenser device i) including a mirror and a mixer and ii) converging two spatially resolved portions of the beam of multi-color entangled photons into a converged multi-color entangled photon beam; a tunable phase adjuster optically coupled to the condenser device, the tunable phase adjuster changing a phase of at least a portion of the converged multi-color entangled photon beam to generate a first interferometeric multi-color entangled photon beam; and a beam splitter optically coupled to the condenser device, the beam splitter combining the first interferometeric multi-color entangled photon beam with a second interferometric multi-color entangled photon beam.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
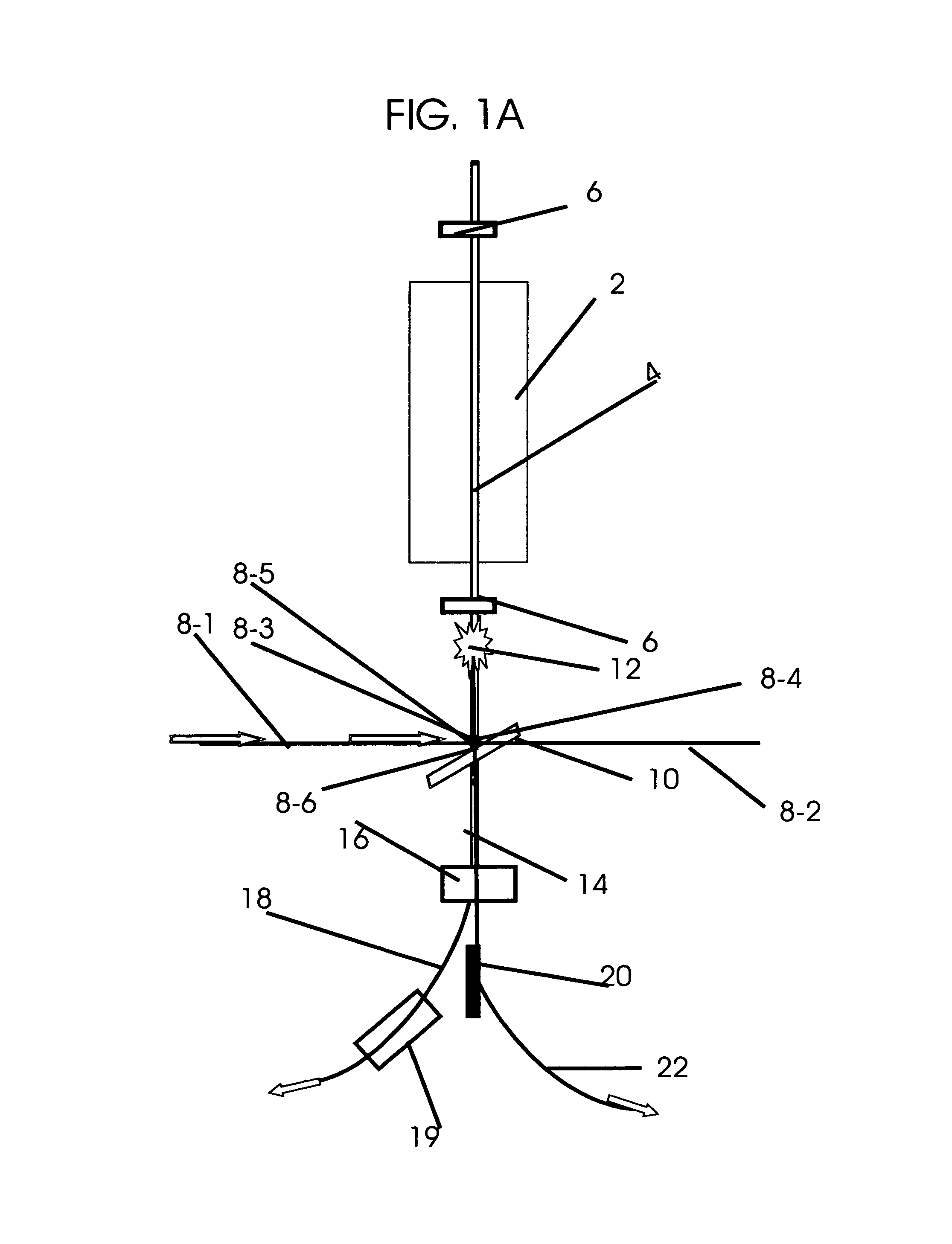
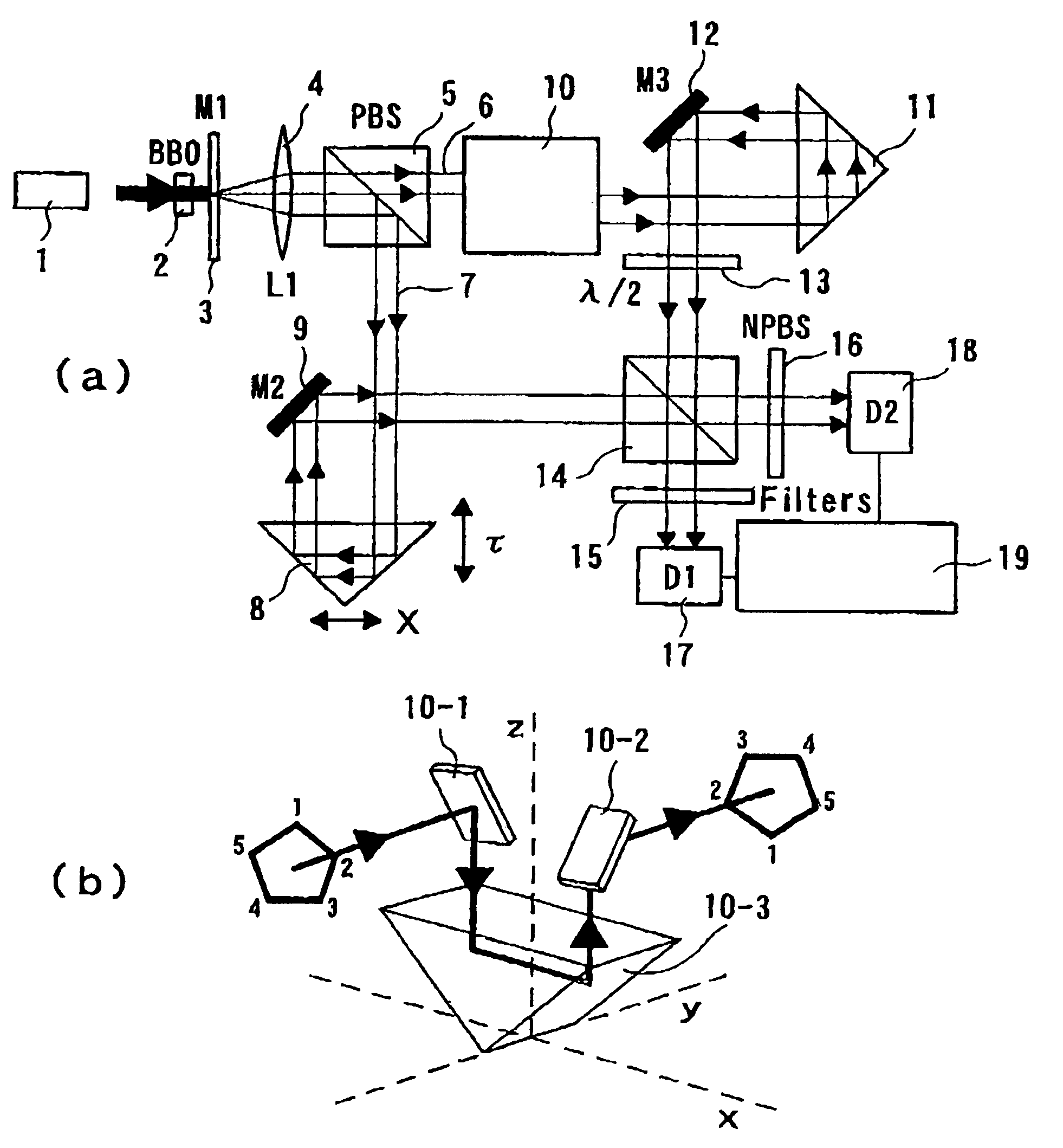
High-luminance quantum correlation photon beam generator
InactiveUS7486433B2Improve efficiencySolve the real problemQuantum computersLaser detailsBeam splitterTime delays
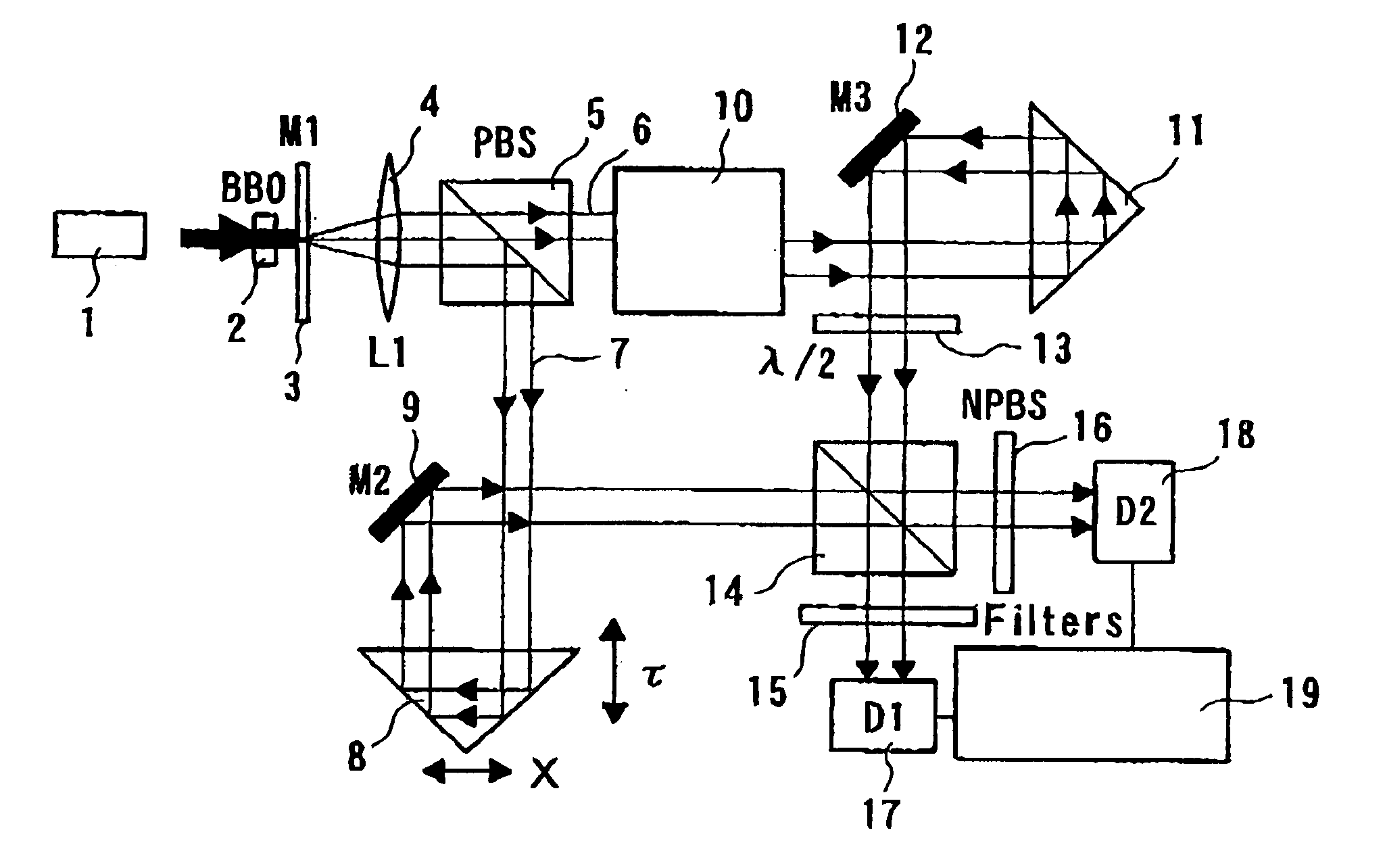
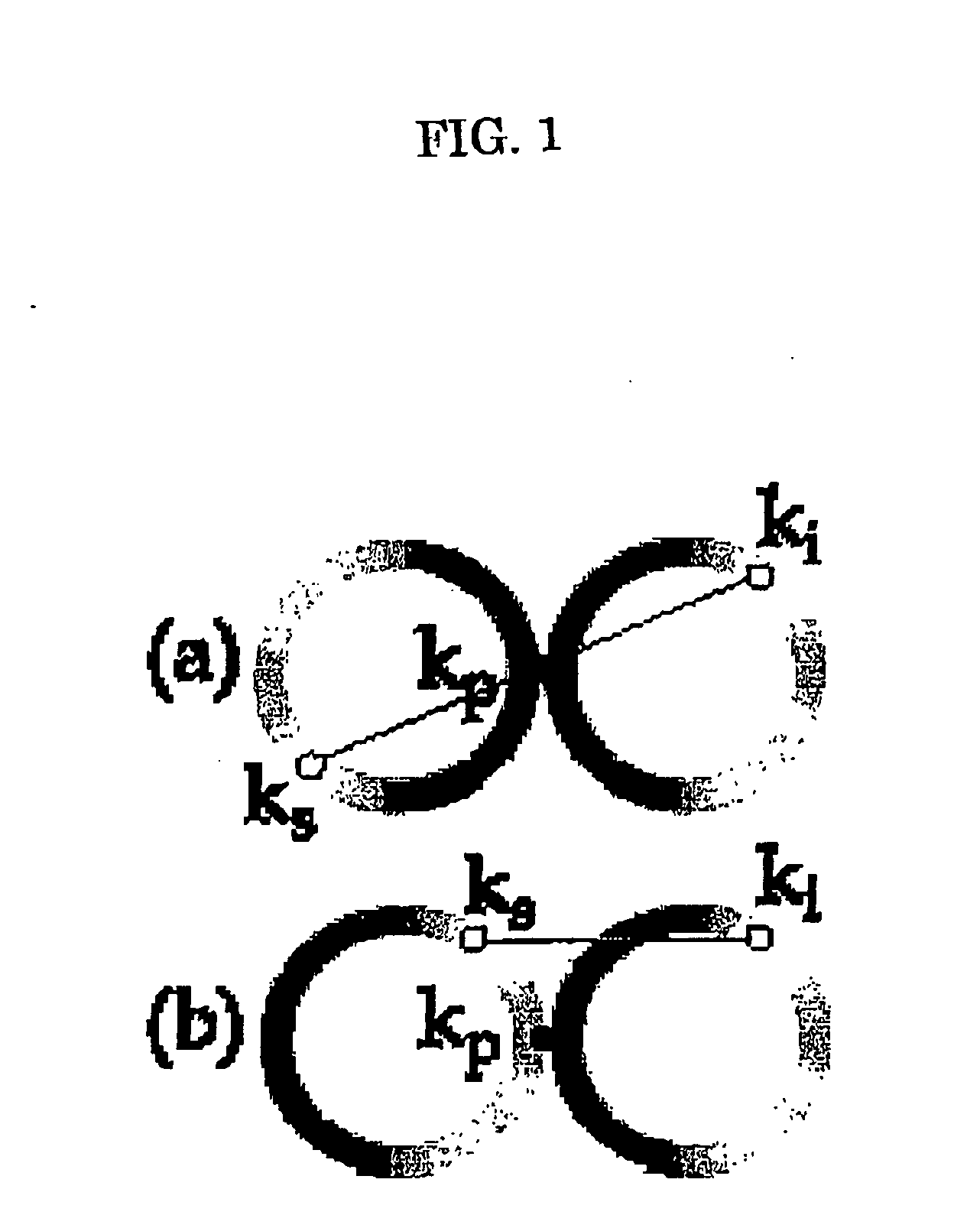
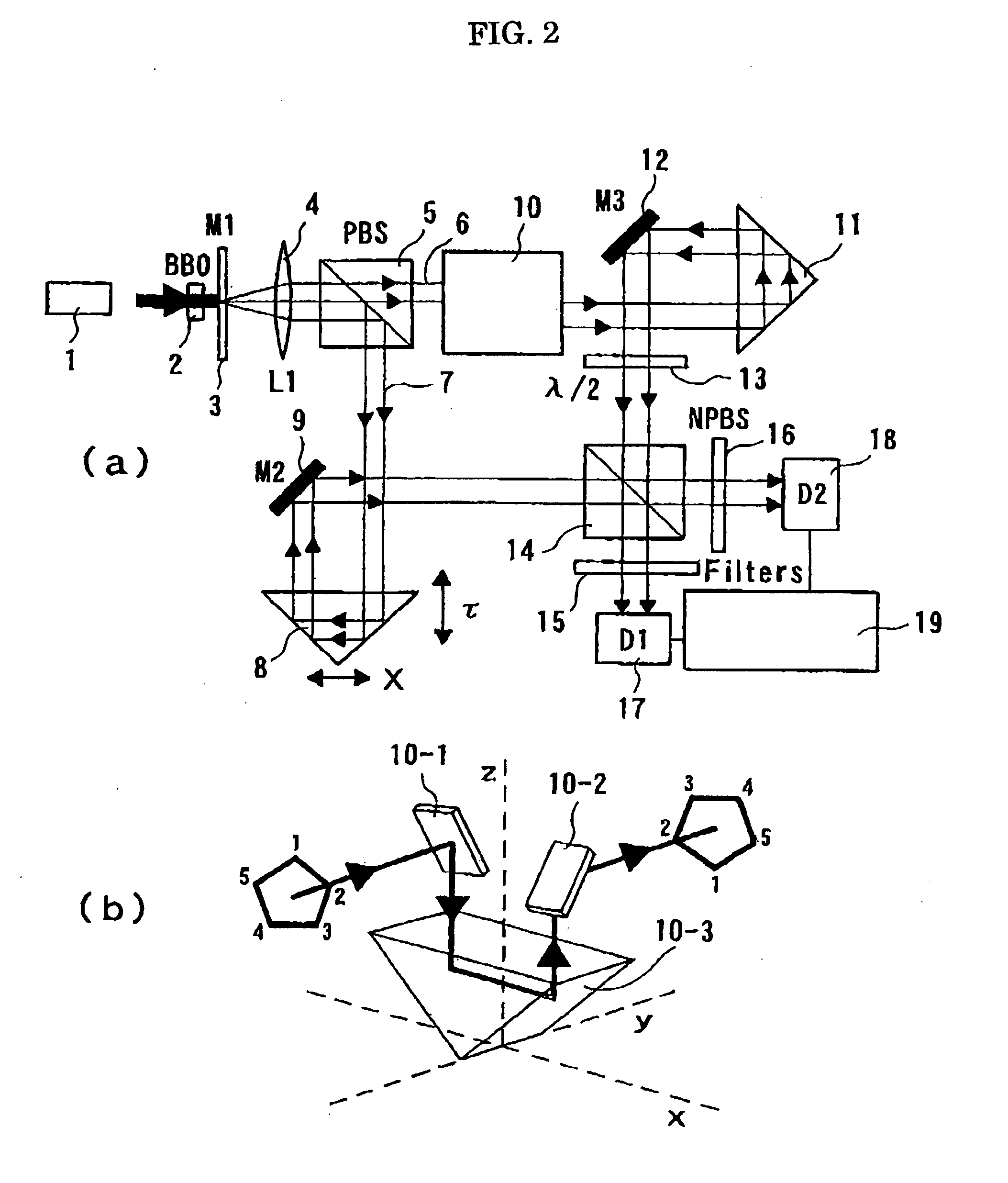
A high-luminance quantum correlation photon beam generator in which a laser light source (1) emits a laser pumped light and a parametric crystal (2) generates a pair of two photons of a signal photon and an idler photon on receiving the pumped light to emit two photon beams. Further, a beam splitter (5) splits a signal photon beam (6) from an idler photon beam (7), a mode inverter (10) rotates one of the signal photon beam, (6) and the idler photon beam (7) 180° around its geometric center, a phase adjusting means (8) adjusts phases of the signal photon beam (6) and the idler photon beam (7) based on an optical time delay, and a beam coupling means (14) overlays the signal photon beam (6) with the idler photon beam (7) in a common-line polarized annular shape by the mode inverter (10) to bring them into a quantum correlated state.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
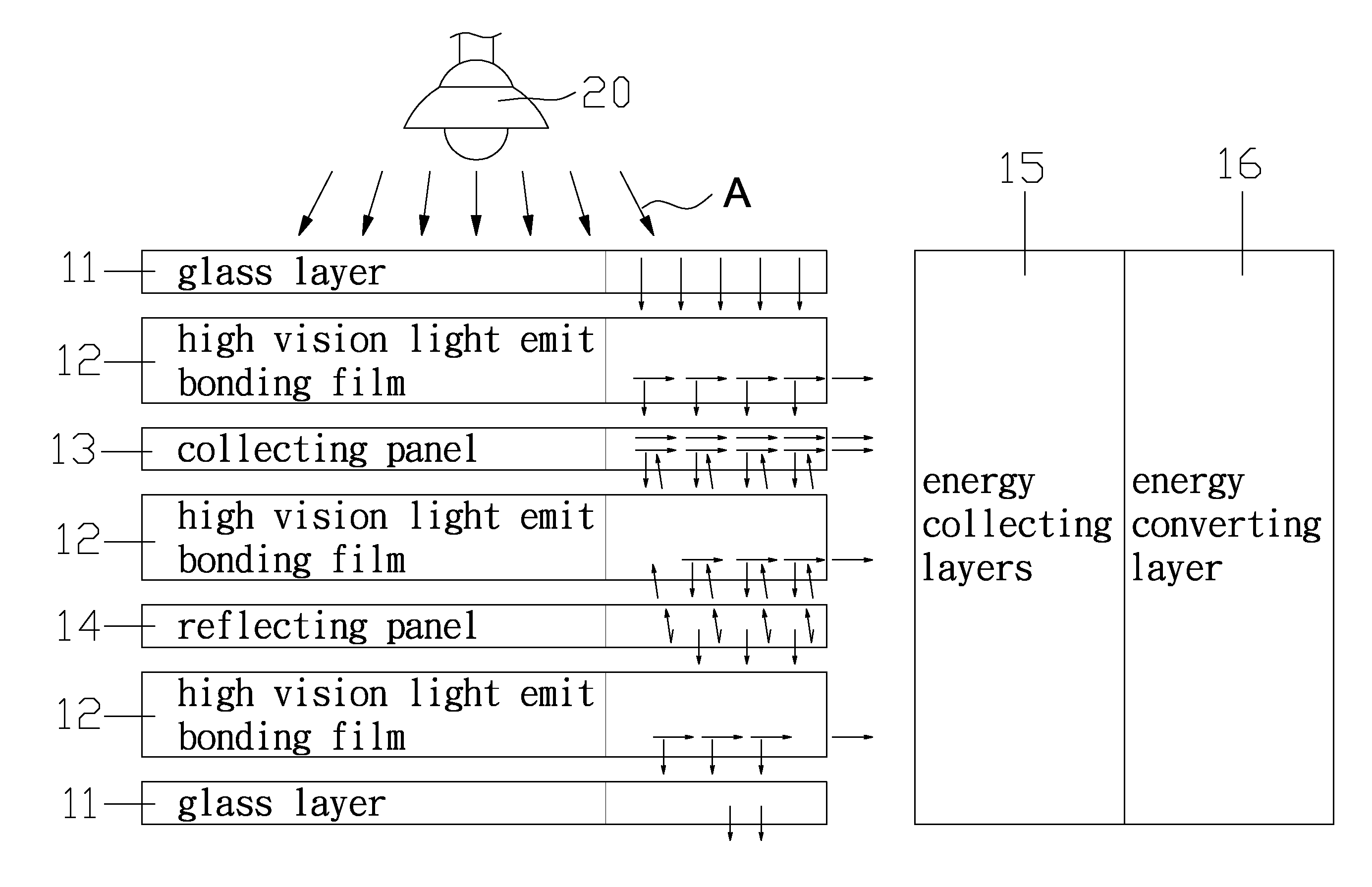
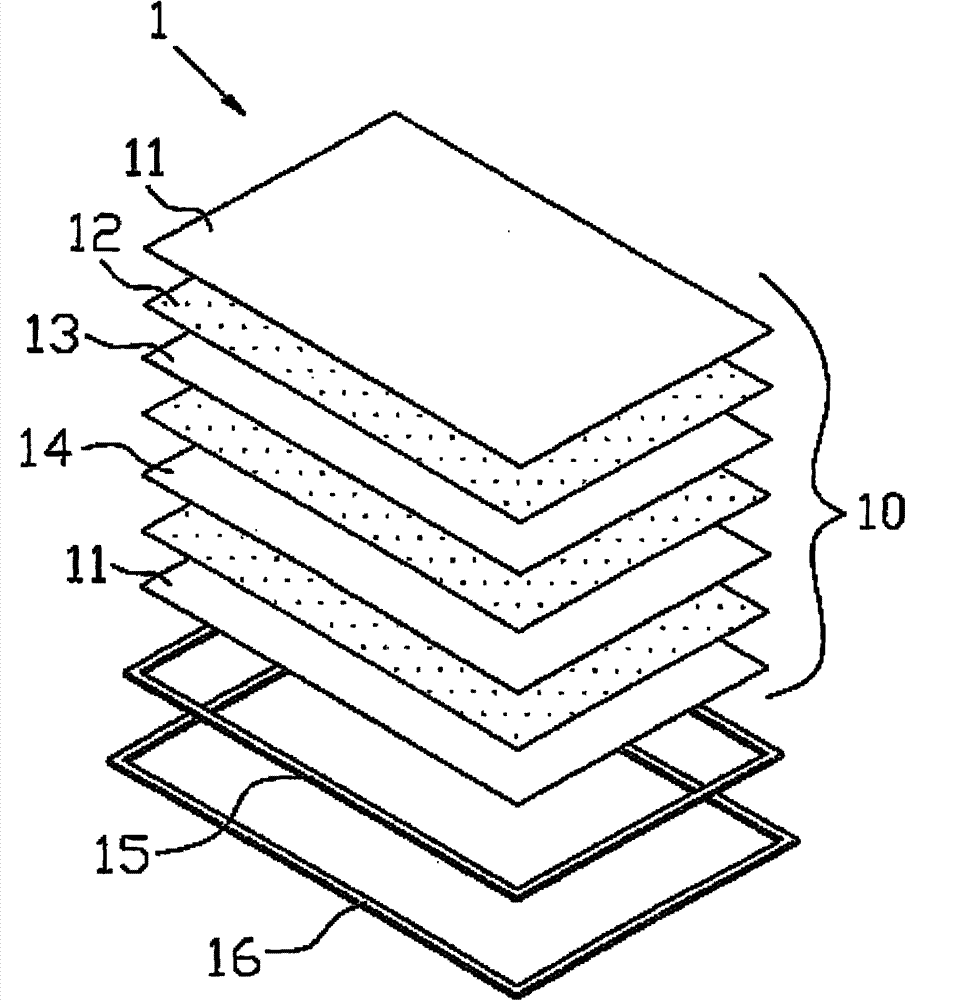
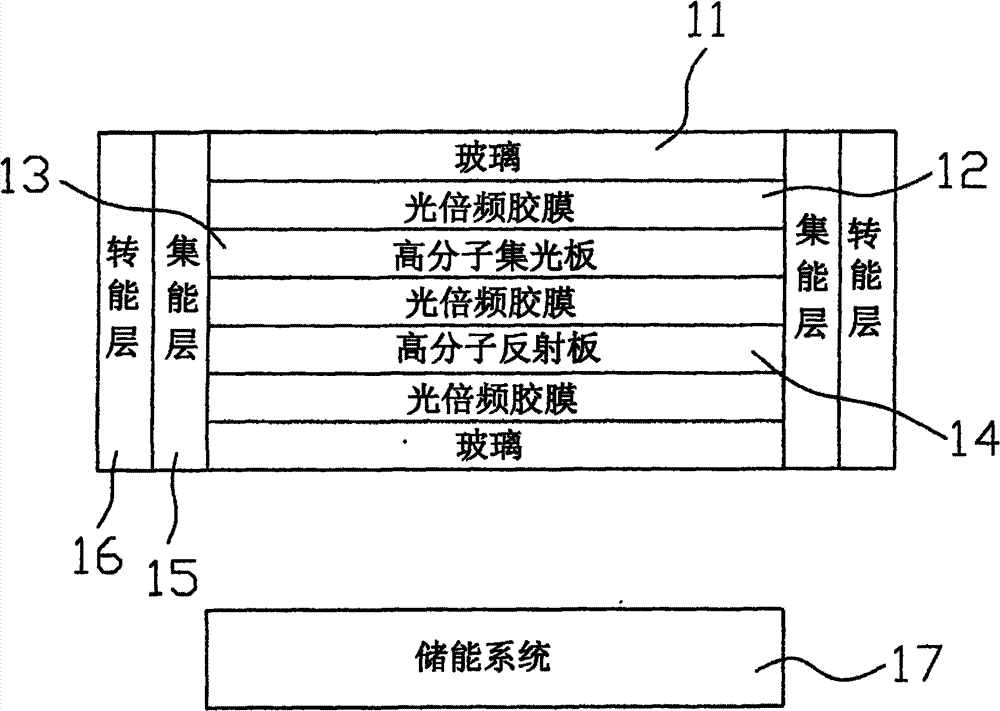
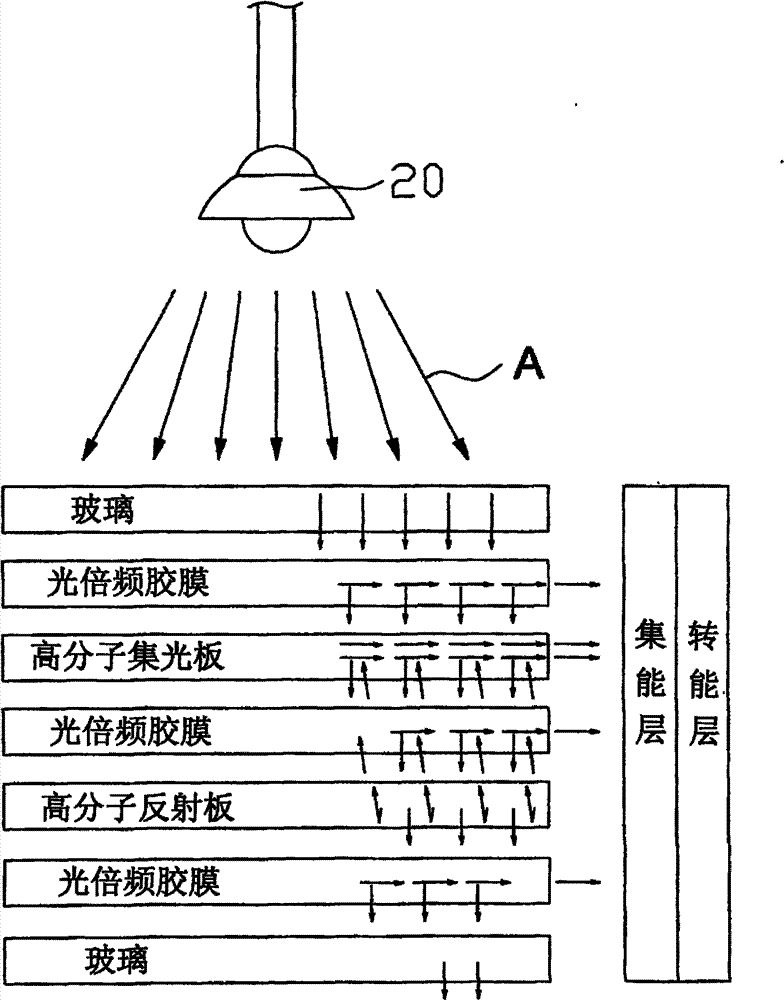
Glass system of a solar photovoltaic panel
InactiveUS20120247537A1Efficient collectionMaterial nanotechnologyPV power plantsLight energyEngineering
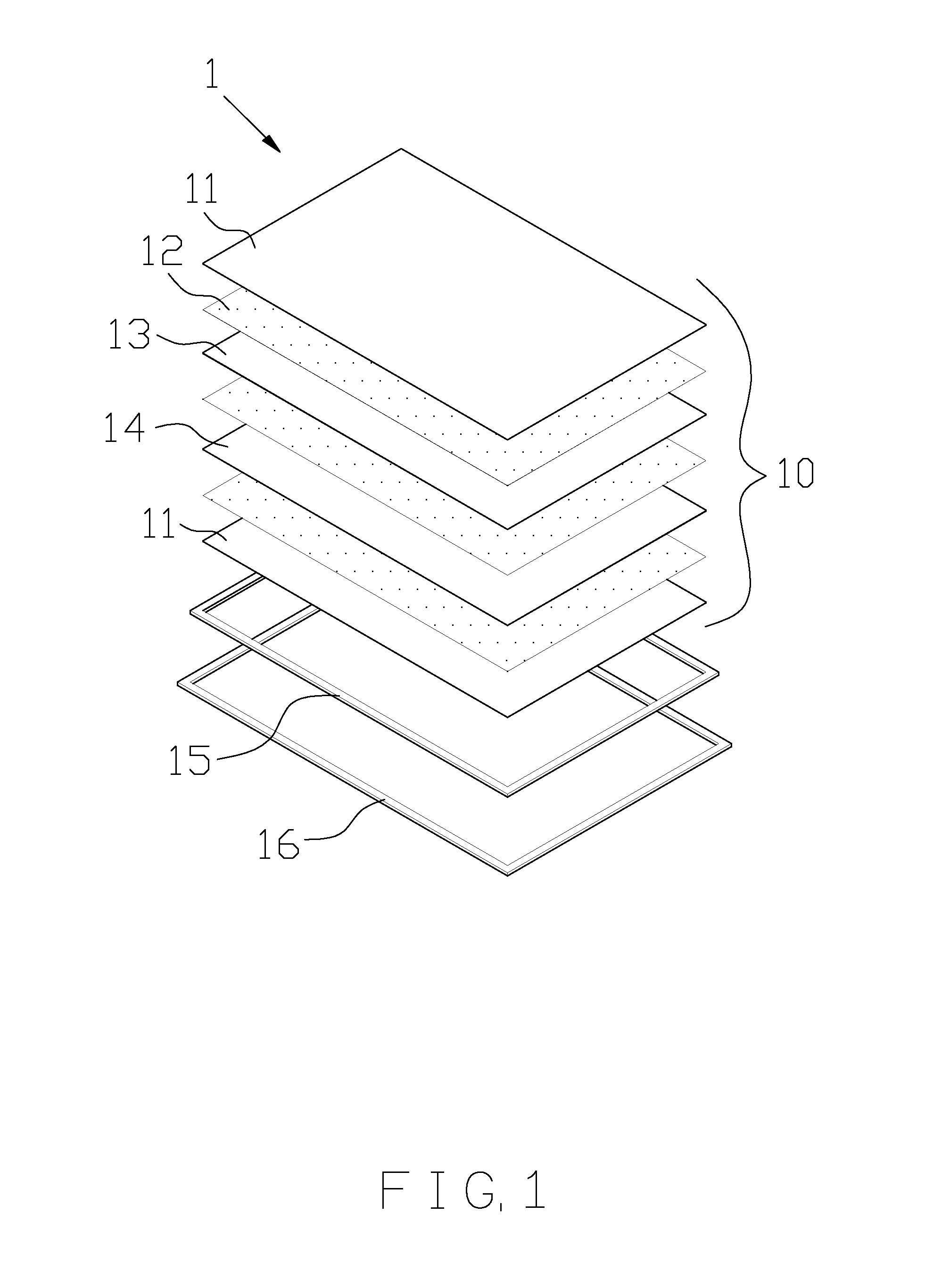
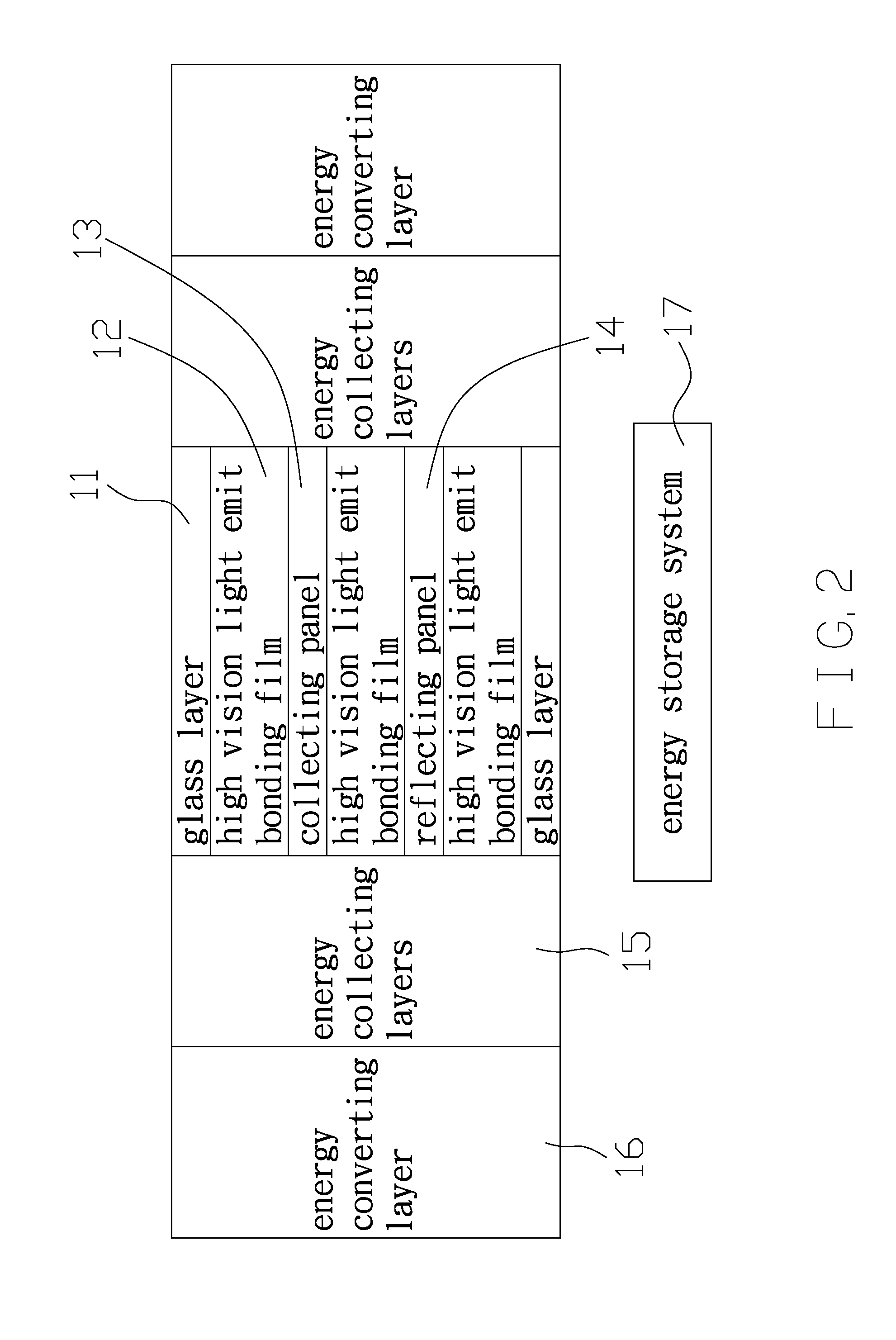
A glass system of a solar photovoltaic panel contains: an energy guiding assembly in which two energy collecting layers, two energy converting layers, and an energy storage system are fixed, the energy guiding assembly conducting a light energy in a single direction by ways of nano particles, the two energy collecting layers being provided to collect photon beams of the energy guiding assembly, each energy converting layer transmitting an electrical energy in each energy collecting layer toward the energy storage system. The energy guiding assembly also includes two glass layers on a top surface and a bottom surface of the energy guiding assembly respectively to retain a collecting panel, a reflecting panel, and a plurality of high vision light emit bonding films. The two energy collecting layers and the two energy converting layers cover two outer sides of the energy guiding assembly respectively.
Owner:MEI AARON
Optical hyperpolarisation with light endowed with orbital angular momentum
InactiveUS20130200895A1Limited reliefThe implementation process is simpleEnergy based chemical/physical/physico-chemical processesElectric/magnetic detectionMomentumPhotonics
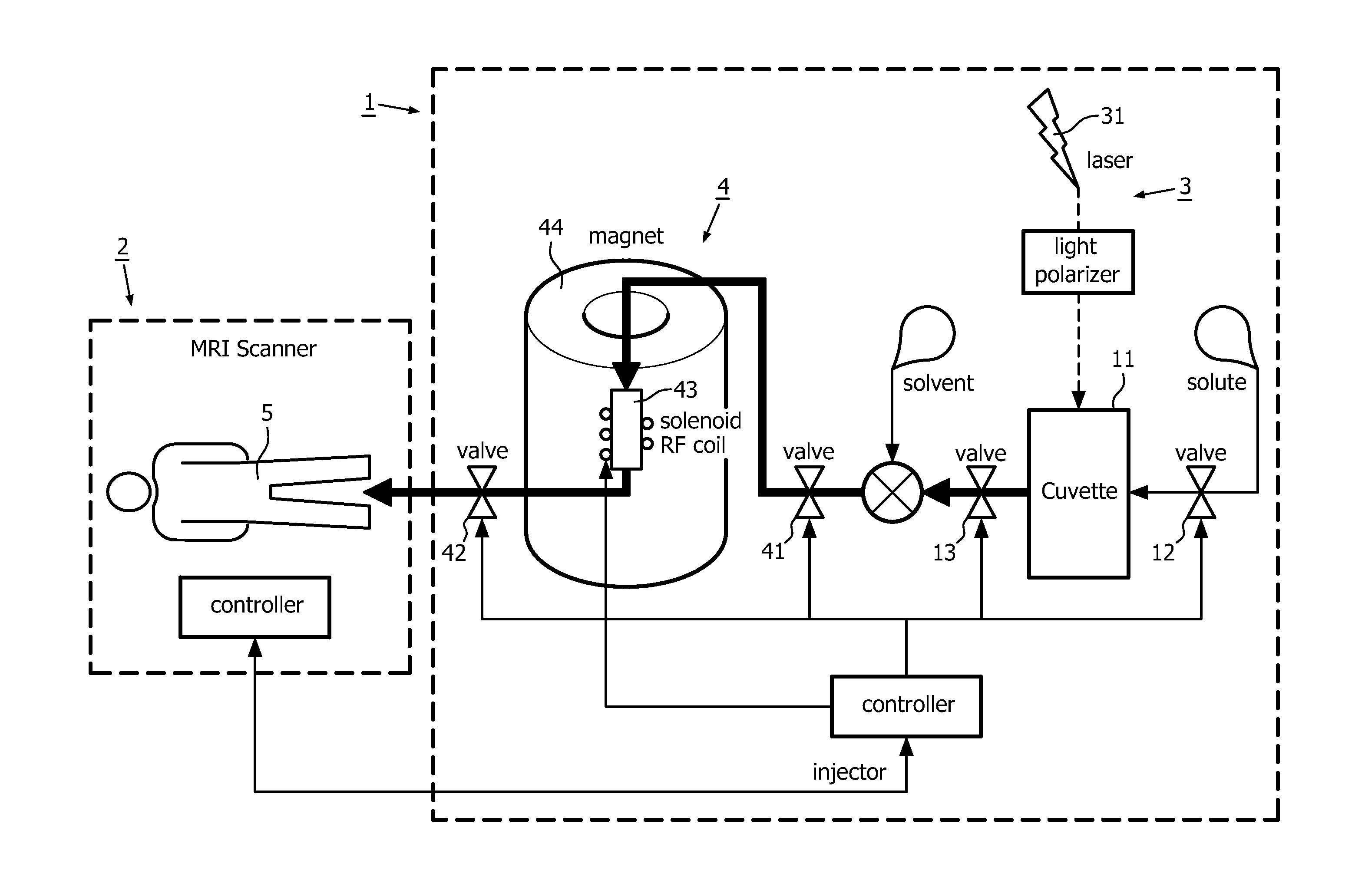
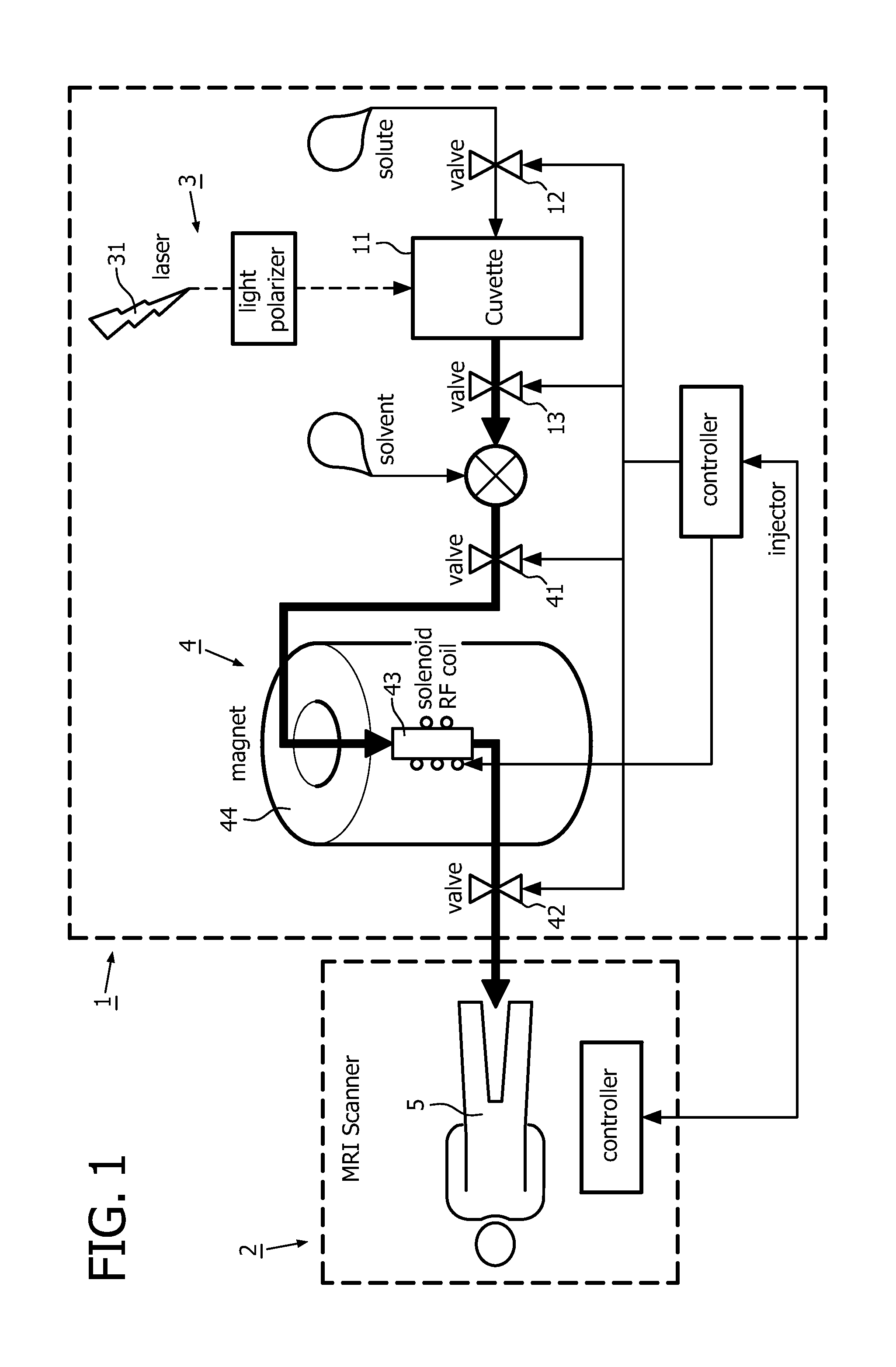
A dispenser is provided for producing a nuclear hyperpolarised contrast agent. The dispenser comprises a chamber to receive a compound. A photonic hyperpolarisation system generates an OAM-photonic beam endowed with orbital angular momentum and is arranged to direct the OAM-photonic beam into the chamber so as to generate nuclear hyperpolarisation in the compound. The chamber has an output over which the hyperpolarised compound can be issued. Since the hyperpolarisation is generated ex-vivo, the penetration depth of the OAM-photonic beam in biological tissue is irrelevant for the present invention.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Method for introducing dislocation on silicon chip
InactiveCN101882573AControl dislocation densityControl dislocation regionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingX-rayControllability
The invention discloses a method for introducing dislocation on a silicon chip. The surface of the silicon chip is radiated by energy beams enough to damage silicon lattices; density-controlled dislocation is introduced into the radiated area; the density of the dislocation is controlled by the intensity of the energy beams, and the density of the introduced dislocation is higher when the energy is stronger; the dislocation can be positioned on the surface of the silicon chip or in the silicon chip; and the energy beams can be electron beams, ion beams, electromagnetic wave beams, alpha X-ray beams, neutron beams or photon beams. The method introduces the controllable dislocation on the silicon chip, is simple and convenient to operate, is well compatible with the conventional integrated circuit process, has the advantages of no damage or contamination to the silicon chip, strong controllability and high repeatability, and is favorable for large-scale industrial production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
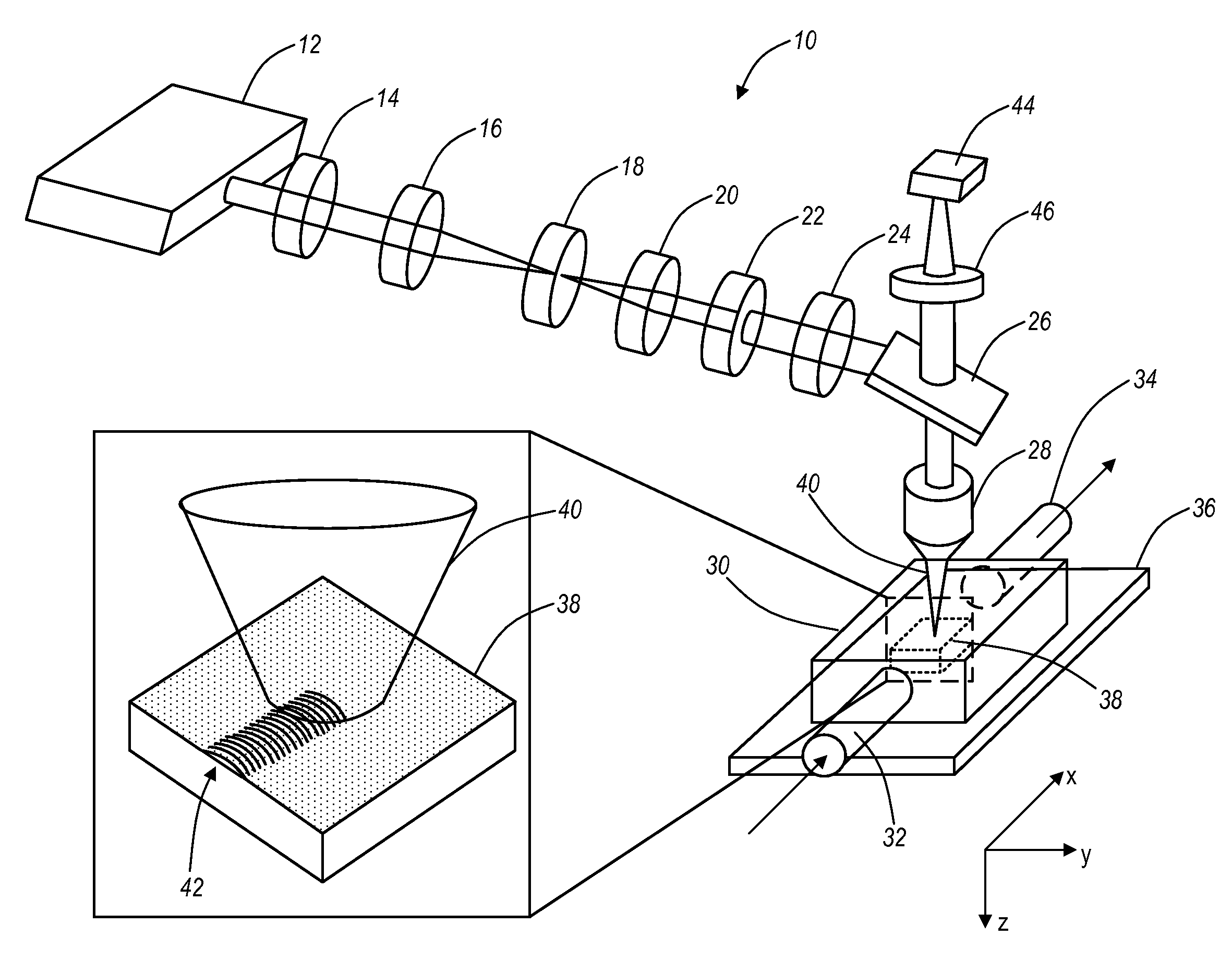
Device for generating a beam of photons with wavelengths defining a substantially continuous supercontinuum
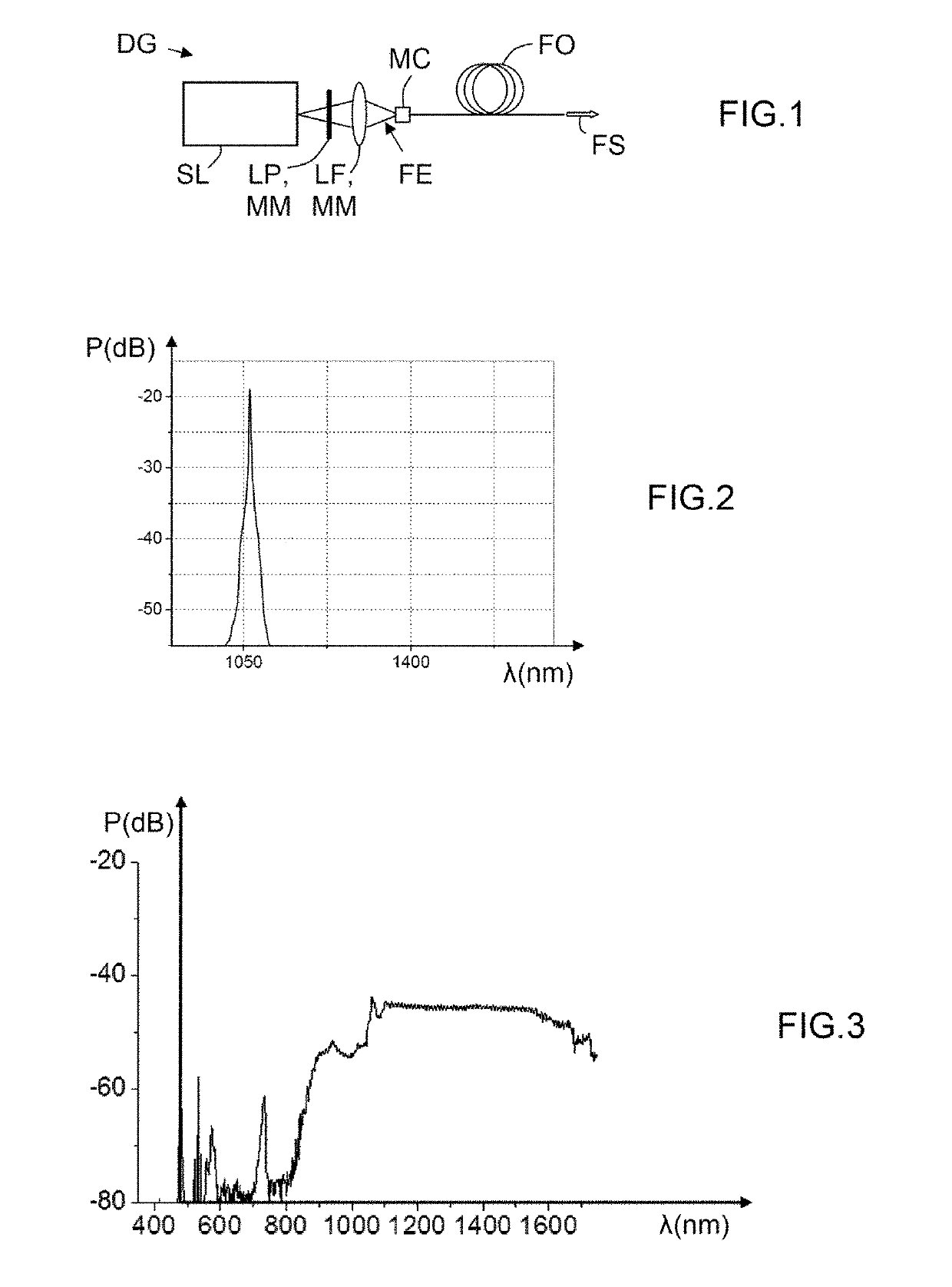
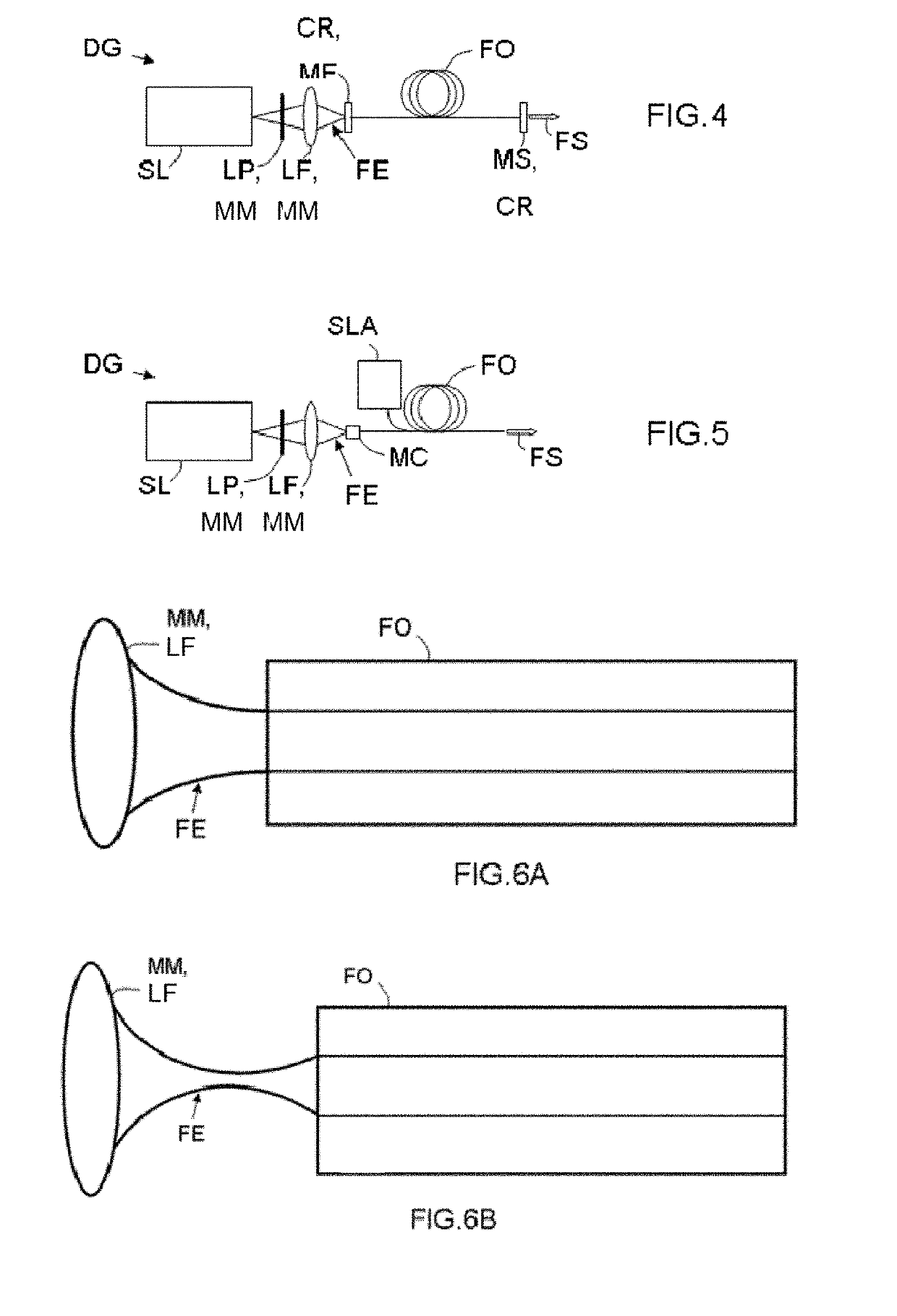
ActiveUS20190123506A1Good conditionHighly spatially coherentLaser using scattering effectsActive medium shape and constructionLight beamPrimary photon
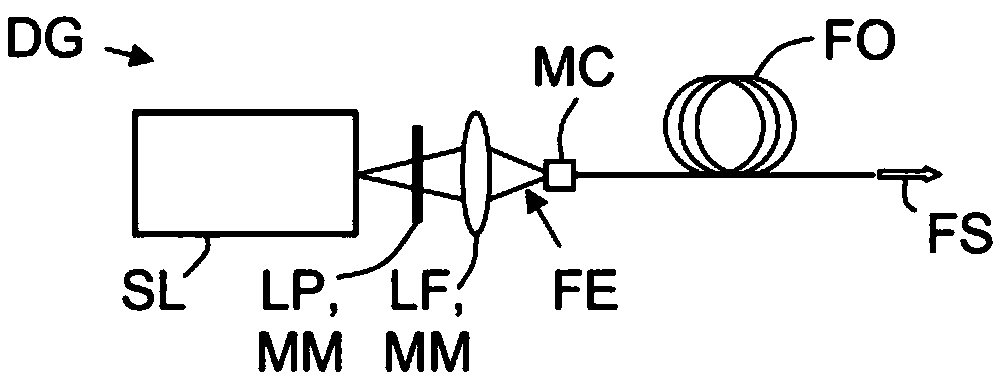
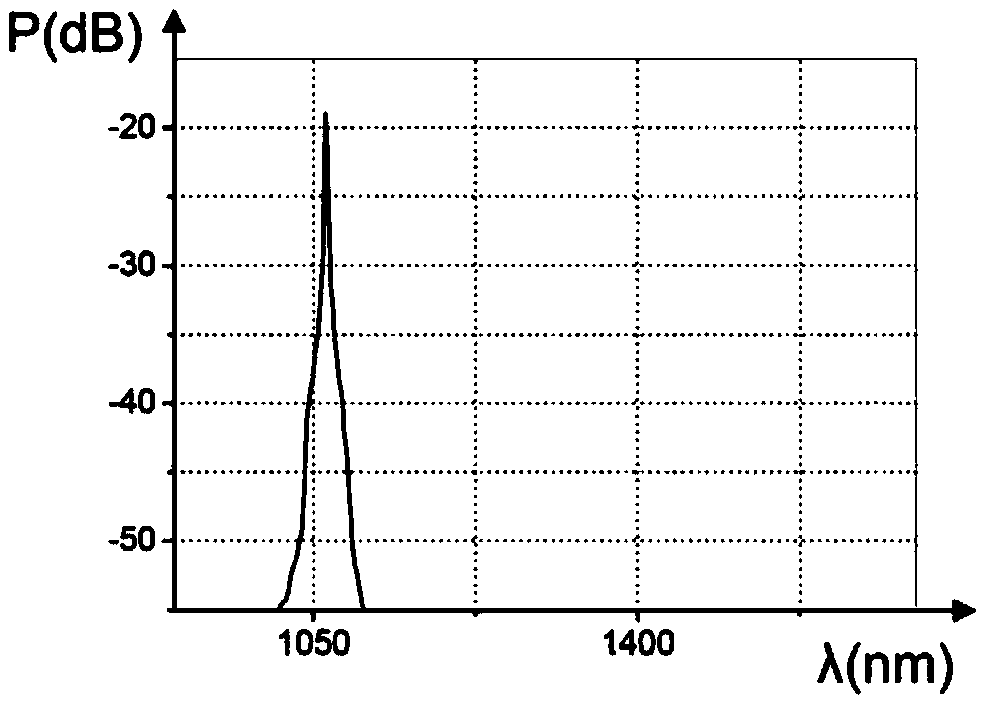
A generating device includes at least one pulsed laser source that delivers primary photons having at least one wavelength in a single spatial mode and in pulses having a high pump energy, forming means that act on the primary photons to deliver an input beam, and at least one optical fiber having at least ten modes between which the pump energy is initially distributed, and able to relocate the latter via a non-linear effect into a fundamental mode, before generating secondary photons of various wavelengths by wavelength conversions from the wavelength of the primary photons in the fundamental spatial mode.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI +1
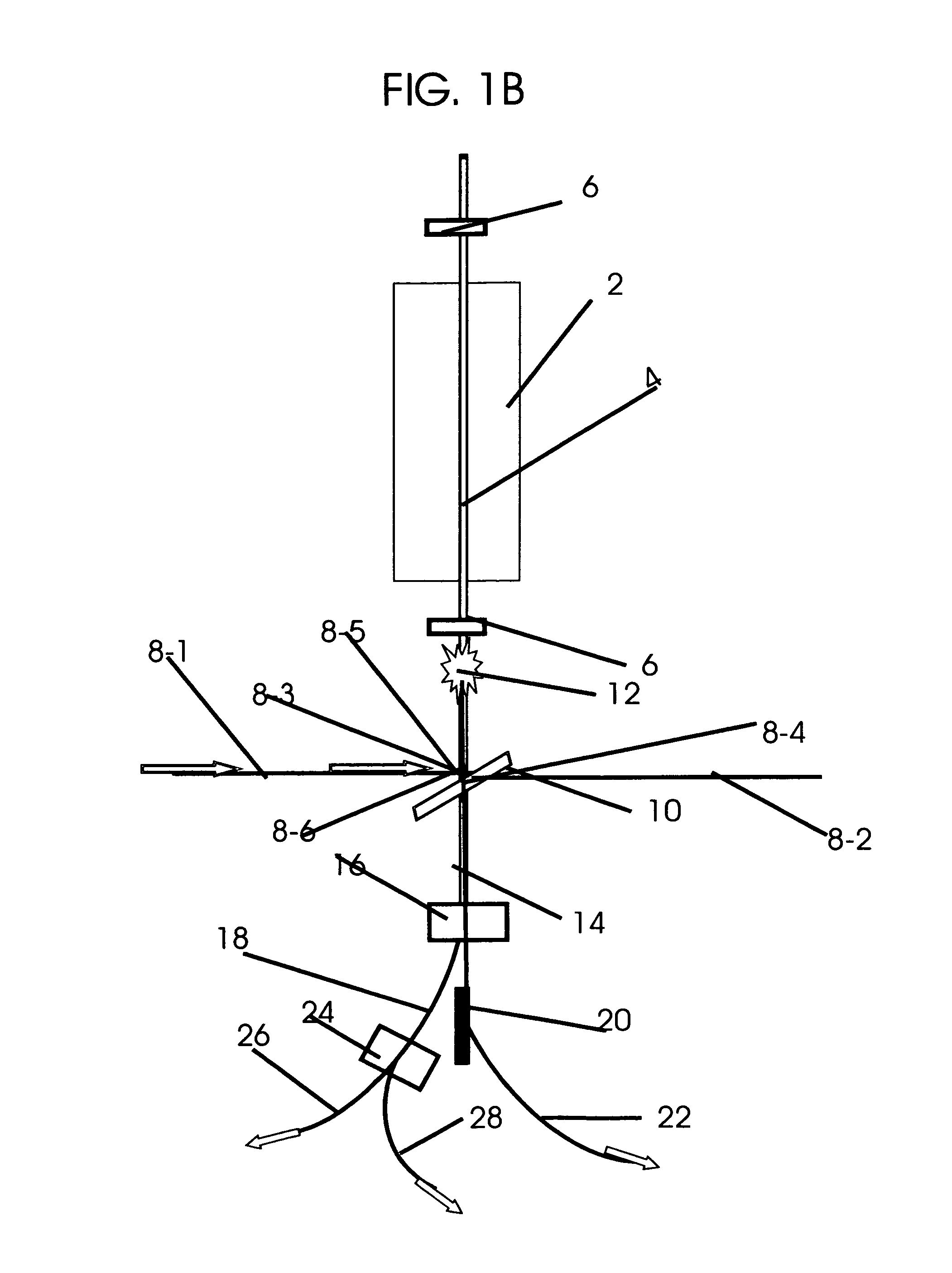
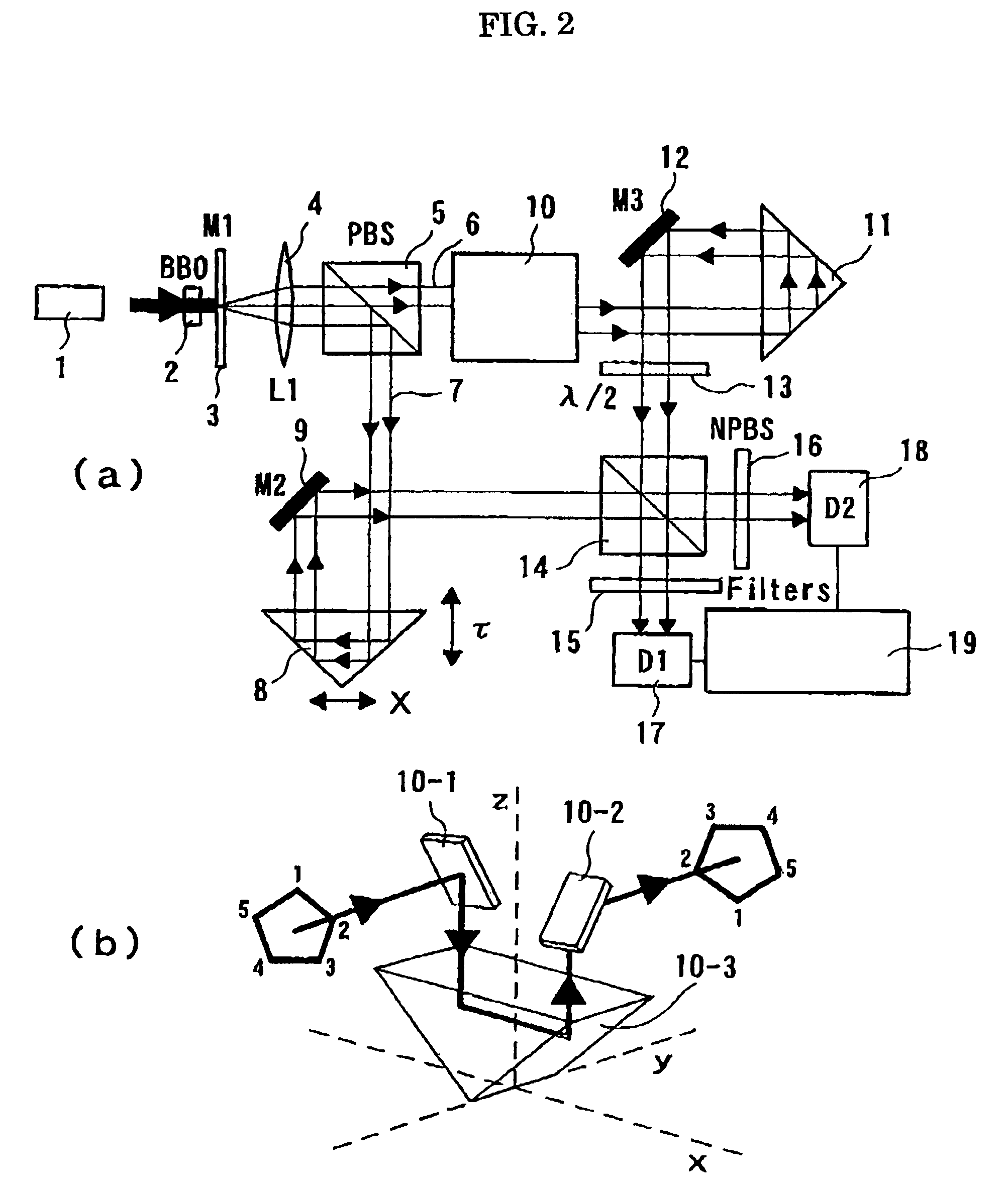
High-Luminance Quantum Correlation Photon Beam Generator
InactiveUS20080049302A1Improve efficiencySolve the real problemQuantum computersLaser detailsTime delaysBeam splitting
A high-luminance quantum correlation photon beam generator a photon beam of a quantum correlated pair characterized by includes: a laser light source (1) operable to emit a laser pumped light; a parametric crystal (2) operable to generate a pair of two photons of a signal photon and an idler photon on receiving the pumped light from the laser light source (1) to emit two photon beams along two non-concentric cones; a beam splitting means (5) operable to split a signal photon beam (6) from an idler photon beam (7); a mode inverter (10) operable to rotate one of the annular signal photon beam (6) and the idler photon beam (7) 180° around its geometric center; a phase adjusting means (8) operable to adjust phases of the signal photon beam (6) and the idler photon beam (7) based on an optical time delay; and a beam coupling means (14) operable to overlay the signal photon beam (6) with the idler photon beam (7) in a common-line polarized annular shape by the mode inverter (10) to bring them into a quantum correlated state.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Device for generating a beam of photons with wavelengths defining a substantially continuous supercontinuum
The invention relates to a generation device (DG) which comprises: at least one pulsed laser source (SL) outputting primary photons having at least one wavelength in a single spatial mode and in pulses having high pump energy; shaping means (MM) acting on the primary photons in order to output an input beam (FE); and at least one optical fibre (FO) having at least ten modes between which the pumpenergy is initially distributed and suitable for relocating the latter by non-linear effect in a fundamental mode, before generating secondary photons with different wavelengths by converting wavelengths from the wavelength of the primary photons in the fundamental spatial mode.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECH SCI (C N R S) +1
Nondestructive inspection system using nuclear resonance fluorescence
ActiveUS8804911B2Improve accuracyImprove reliabilityX-ray tube with very high currentX-ray apparatusNuclear reactor coreIsotope
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH +1
Light-induced directed self-assembly of periodic sub-wavelength nanostructures
ActiveUS8541066B2Small feature sizeExcellent long-range orderCasting plantsNanoinformaticsWavelengthSub wavelength
In various exemplary embodiments, the present invention provides a system for the light-induced directed self-assembly (LIDSA) of periodic sub-wavelength nanostructures, including: a light source for delivering a beam of photons; a reaction chamber disposed adjacent to the light source; a gas including one or more precursor materials disposed within the reaction chamber; and a substrate disposed within the reaction chamber, wherein the substrate is positioned and configured to receive the beam of photons; wherein the beam of photons causes a periodic sub-wavelength nanostructure of one or more constituents of the one or more precursor materials to form on a surface of the substrate. In various exemplary embodiments, the present invention also provides an associated method.
Owner:JUNIVERSITI OF NORT KAROLINA EHT SHARLOTT
Method and system for in-situ testing grade of big ore block by electron-air shielding radiation effect
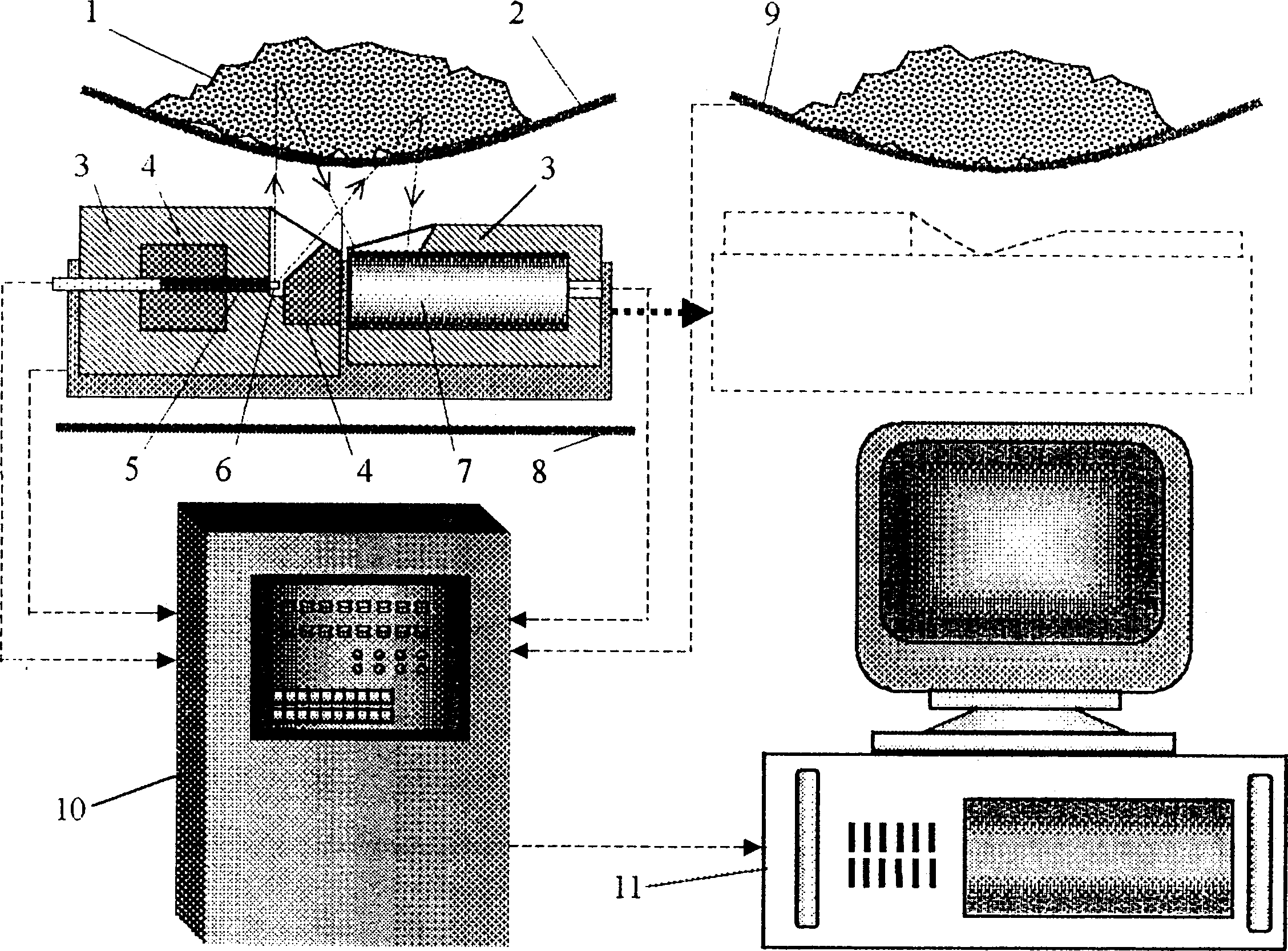
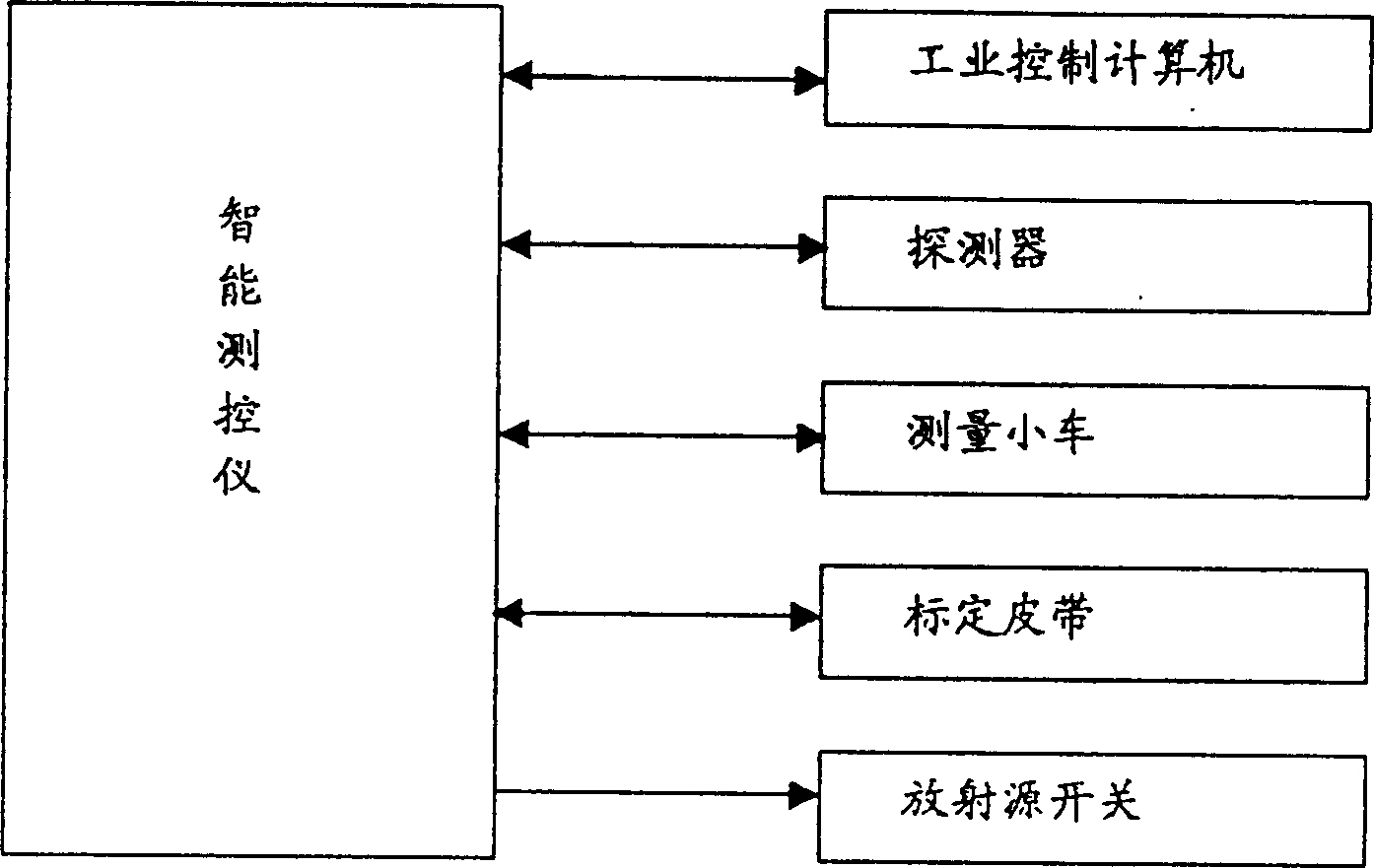
InactiveCN1179207CImprove detection efficiencyLow costMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationNuclear radiation detectionRadioactive sourcePhoton beams
An in-line test method and system for fast analyzing the grade of big ore block in metal mine or ore dressing plant is composed of intelligent controller, radioactive source, detector, scaled belt and industrial control computer. The said radioactive source and detector, which are isolated by lean uranium, are arranged on a frame. the included angle between photon beams emitted by radioactive source and received by detector must be less than 60 deg.C. The said detector has heater and temp controller for constant temp (40-60 deg.C). Its advantages include high analysis speed and efficiency and low error less than 0.4%.
Owner:DANDONG DONGFANG MEASUREMENT&CONTROL TECHCO +1
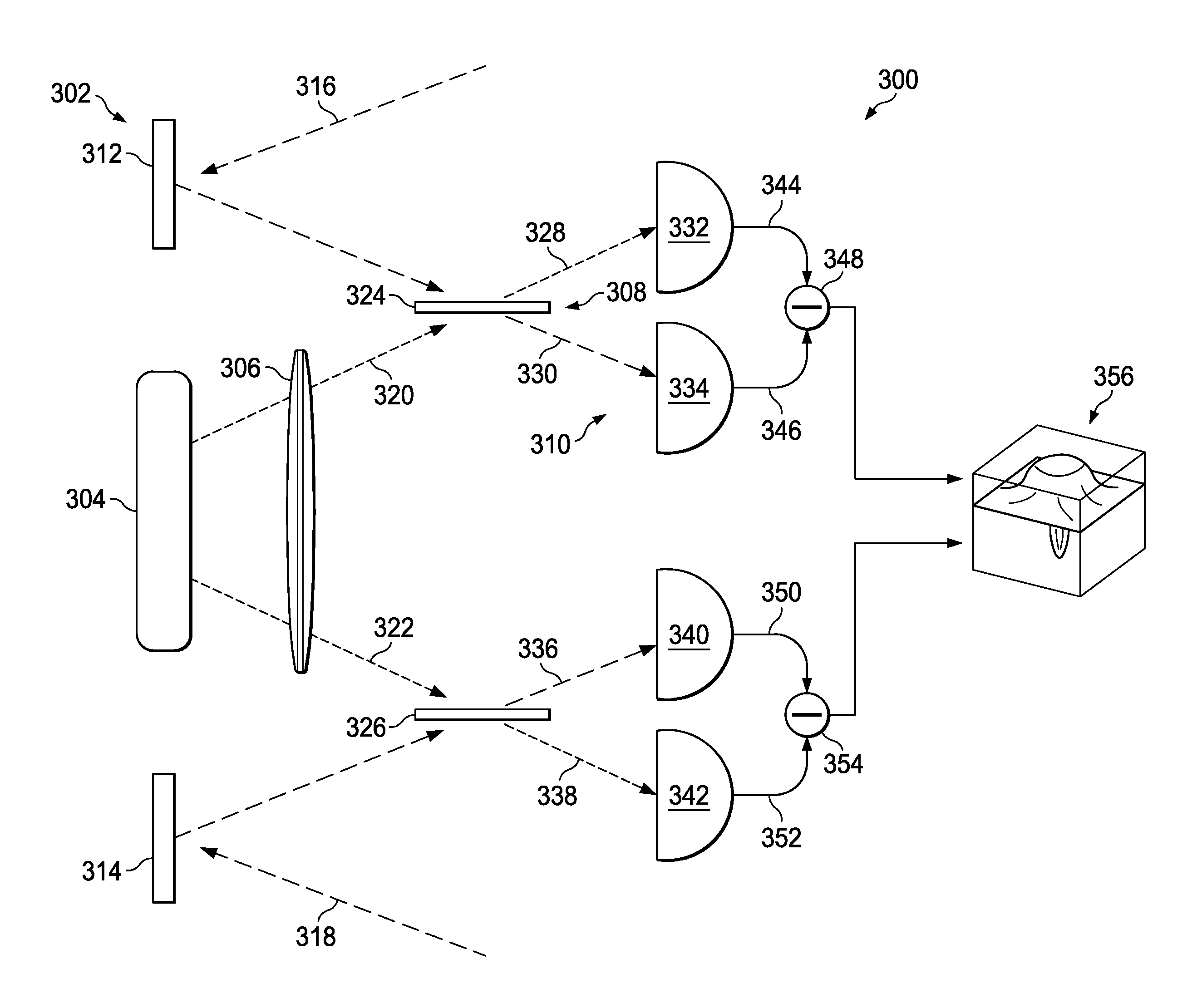
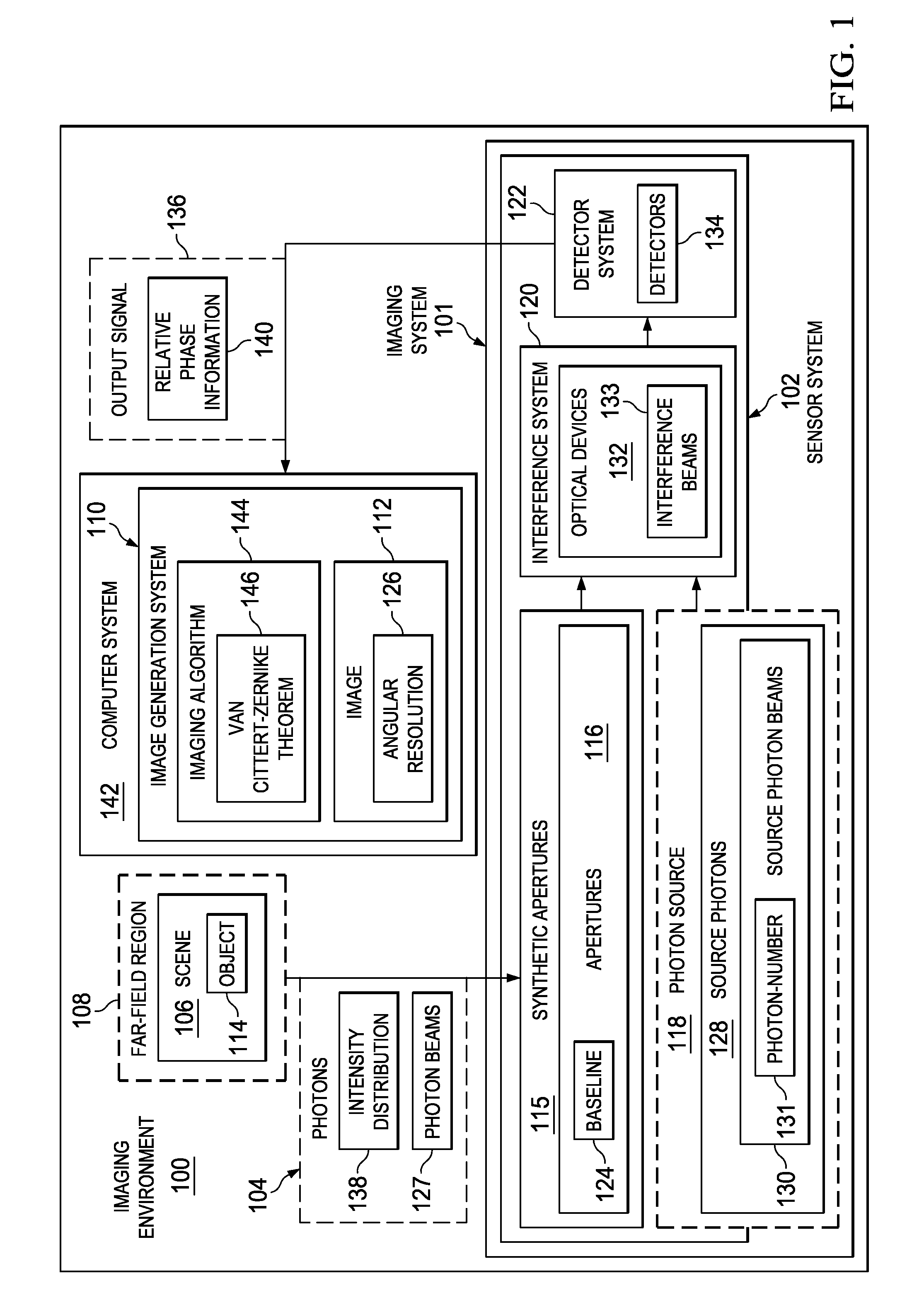
Angular resolution of images using photons having non-classical states
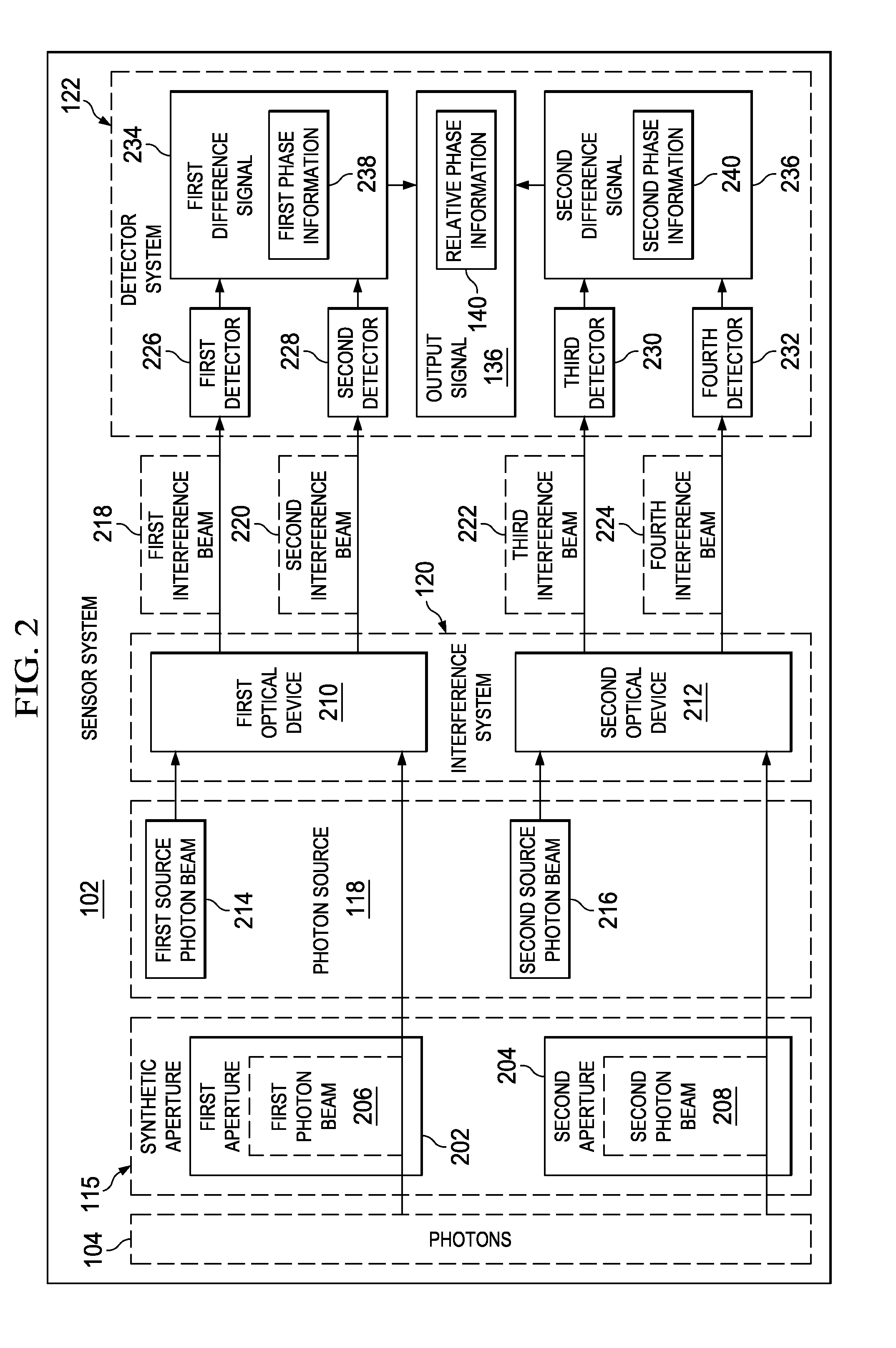
A method, apparatus, and system for improving the angular resolution of an image. A plurality of photon beams originating from a scene are received at a sensor system. Each of the plurality of photon beams is interfered with a corresponding source photon beam in a plurality of source photon beams to form a plurality of interference beams. Each of the plurality of source photon beams has a non-classical state. Fluctuations in a photon-number of the each of the plurality of source photon beams are reduced to within selected tolerances. An output signal is formed based on the plurality of interference beams. The output signal is configured for use in generating an image of the scene.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
A nanoplasma array laser and its manufacturing method
InactiveCN104538837BAchieve laser emissionIncrease laser powerOptical wave guidanceExcitation process/apparatusDielectricElectricity
The invention provides a nano-plasma array laser and a manufacturing method thereof, belonging to the field of optical technology. The invention utilizes the interaction between the photons excited by the p-n junction array of electrically pumped semiconductor nanowires and the surface metal-dielectric film to generate surface plasmon polaritons (SPPs), and then constrains and regulates the photon beams generated in the nanowire resonant cavity . The present invention combines the dual advantages of geometric limitation of semiconductor nanostructures and surface plasmon mode field constraints on light beams, uses semiconductor nanowires to realize the integration of working materials and resonant cavities and surface plasmons to achieve mode field constraints, and finally forms a semiconductor nanoplasma laser .
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
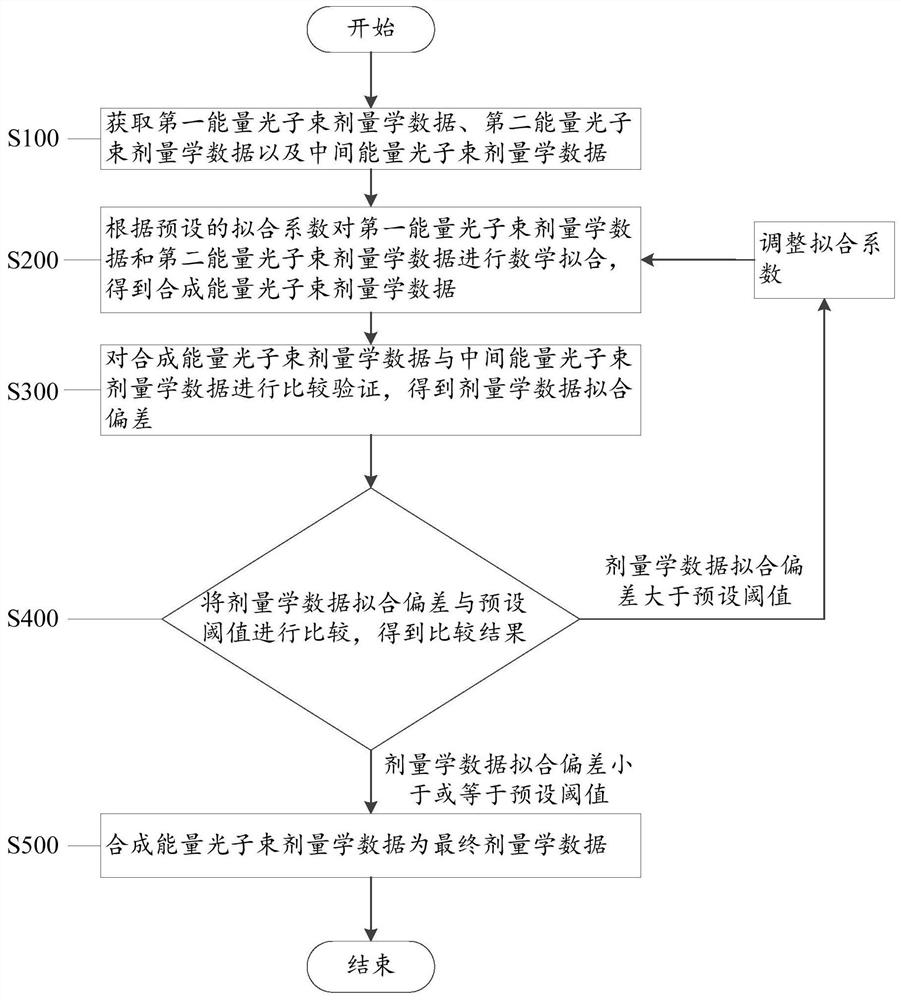
Photon energy synthesis method and system of a medical linear accelerator
ActiveCN109513118BX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyParticle physicsQuantum electrodynamics
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Apparatus and method for dispensing a hyperpolarized fluid
InactiveUS9222995B2Limited reliefThe implementation process is simpleMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsEnergy based chemical/physical/physico-chemical processesMomentumAngular momentum
A dispenser is provided for producing a nuclear hyperpolarized contrast agent. The dispenser comprises a chamber to receive a compound. A photonic hyperpolarization system generates an OAM-photonic beam endowed with orbital angular momentum and is arranged to direct the OAM-photonic beam into the chamber so as to generate nuclear hyperpolarization in the compound. The chamber has an output over which the hyperpolarized compound can be issued. Since the hyperpolarization is generated ex-vivo, the penetration depth of the OAM-photonic beam in biological tissue is irrelevant for the present invention.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Solar photovoltaic panel glass system
ActiveCN102013842BEasy to limitHas industrial applicabilityBatteries circuit arrangementsPV power plantsLight guidePhotoelectric conversion
The invention discloses a transparent light-transmitting energy-converting solar photovoltaic panel glass system mainly comprising an energy guiding layer, an energy collecting layer, an energy converting layer and an energy storing system, wherein the energy guiding layer guides optical energy to move in a single direction through nanometer light-guiding particles in a structure and collects photon beams on the energy collecting layer; and the energy converting layer can effectively transmit and apply or store the electric energy in the energy collecting layer in the energy storing system. The transparent light-transmitting solar photovoltaic panel glass system can effectively collect indoor and outdoor light sources for photoelectric conversion and prevent the damage of high-temperaturewaste heat on parts and has both attractiveness and industrial application and economy.
Owner:厦门钧钛新材料科技有限公司
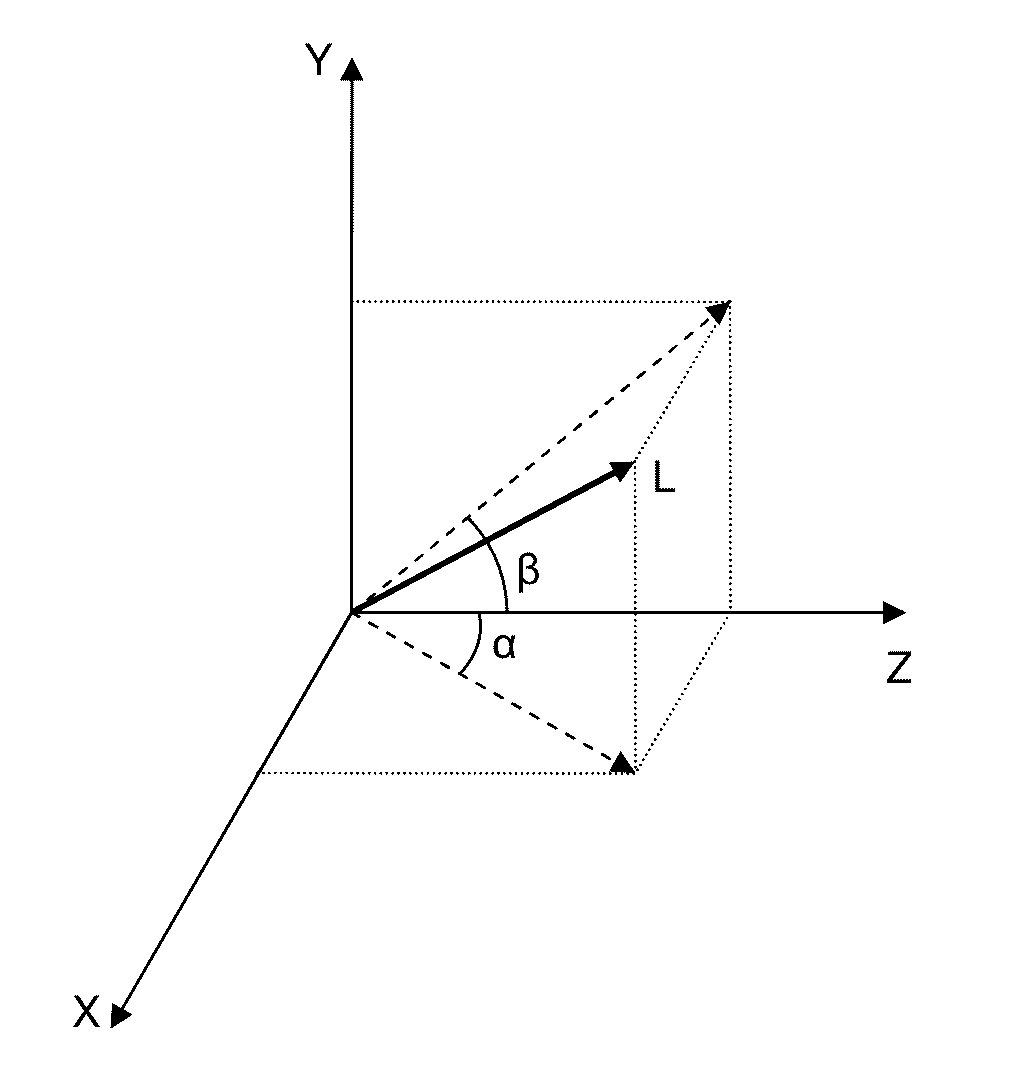
Method and system for adjusting the alignment of a photonic beam
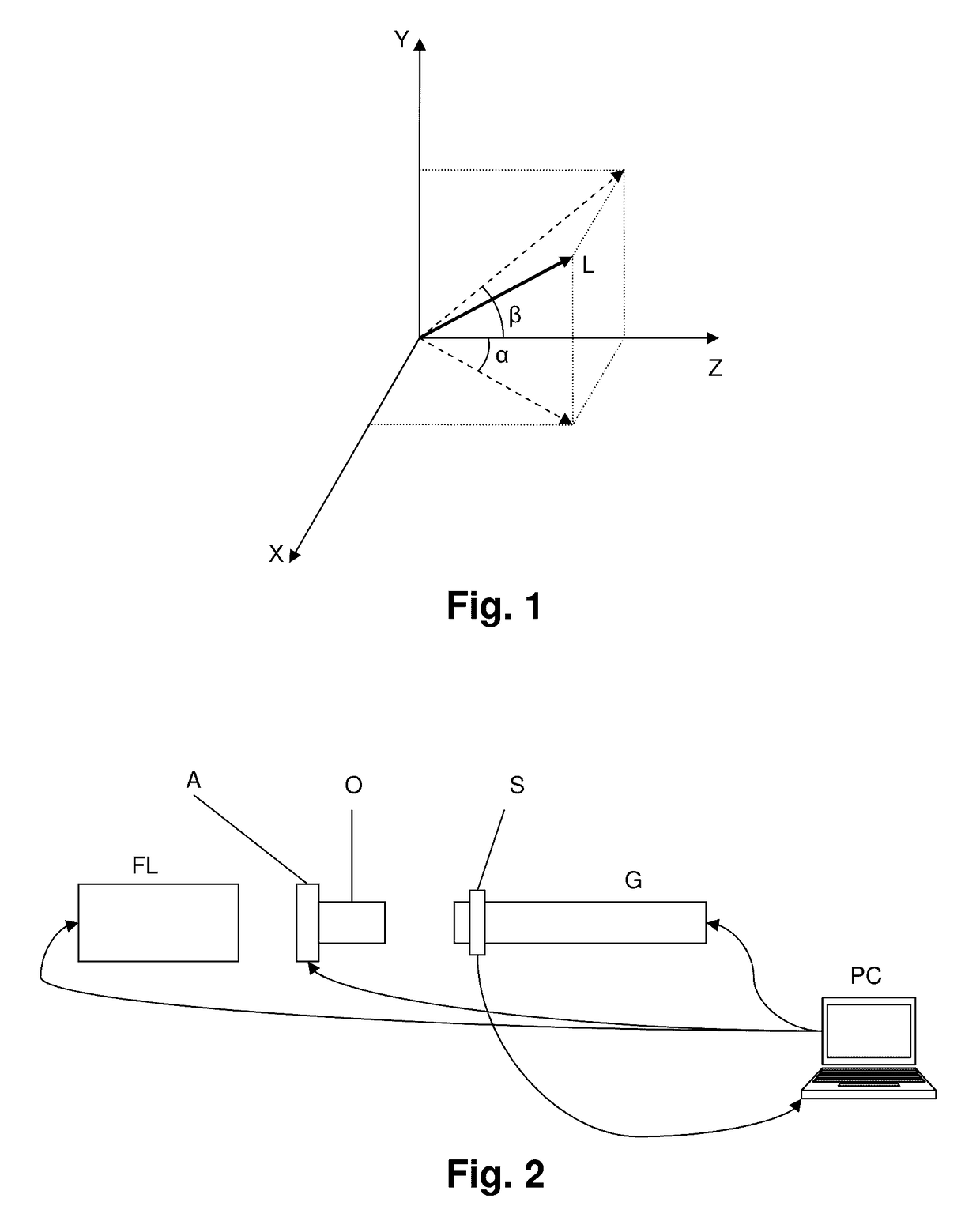
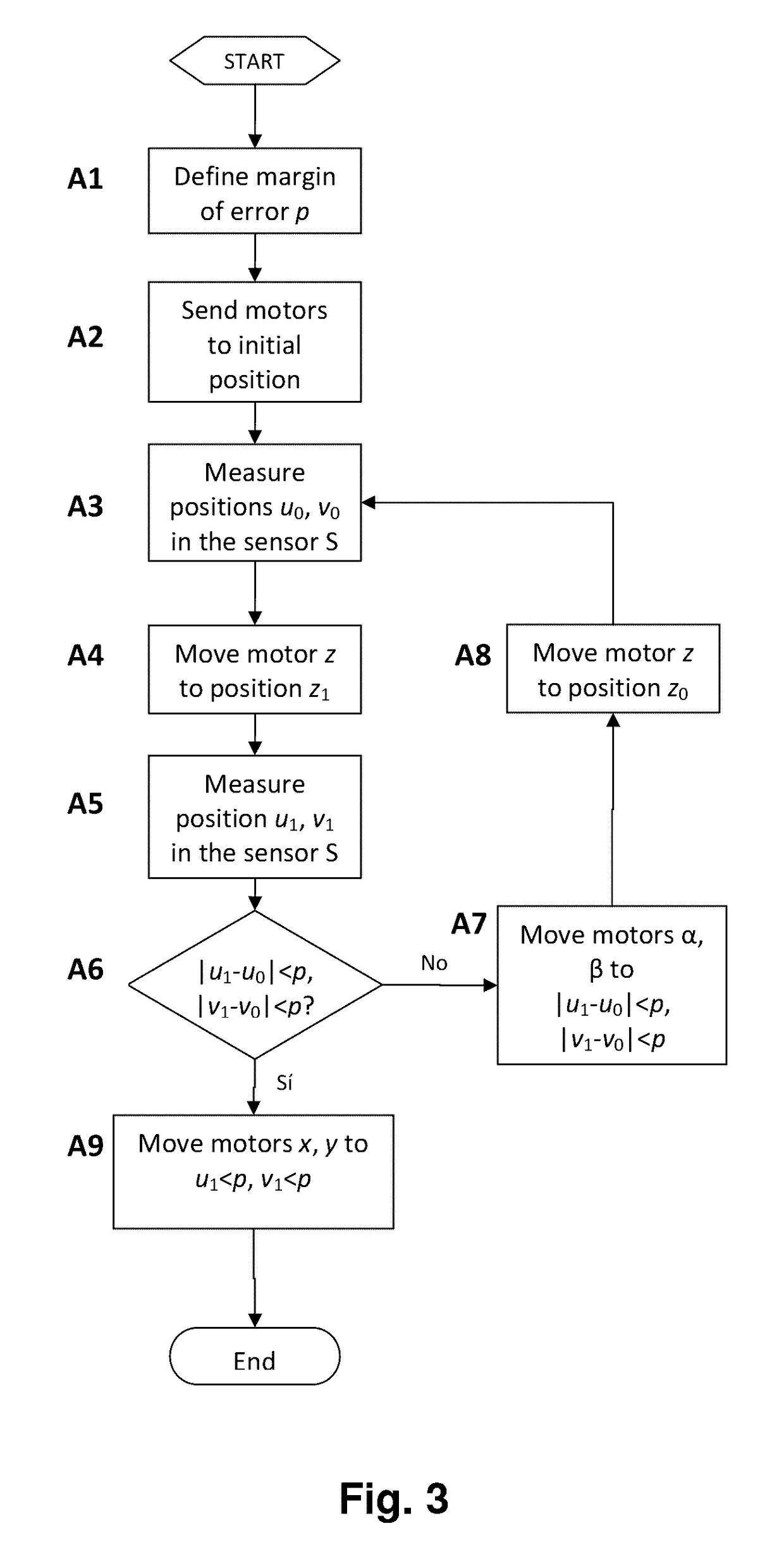
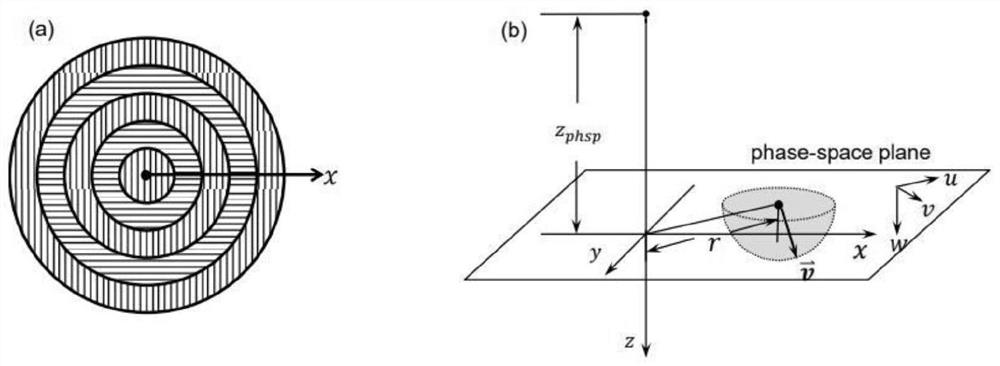
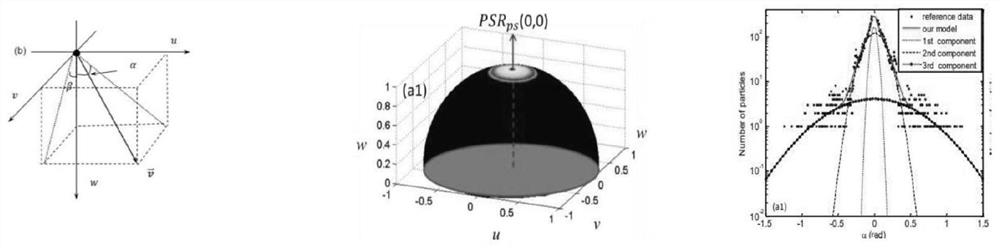
The method comprises:detecting the positions (uo, vo) and (u1, v1) of said photonic beam (L) according to the coordinate axes X, Y on a first and second plane XY, which cut an optical axis X at a first and second point, respectively;comparing the results of said positional detections (uo, vo) and (u1, v1), and:if there are discrepancies which lie outside the margin of error (p), adjusting the angle of the photonic beam (L) according to the angle α and / or the angle β in order to overcome said discrepancies; orif there are no discrepancies which lie outside said margin of error (p), considering the angle of said photonic beam (L) as being properly adjusted.The system is adapted to implement the method set out by the invention.
Owner:JEANOLOGIA
Construction method of medical linear accelerator photon source model function
ActiveCN113230549AFew modeling parametersModeling parameters are clearMedical simulationMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesParticle physicsRadiation field
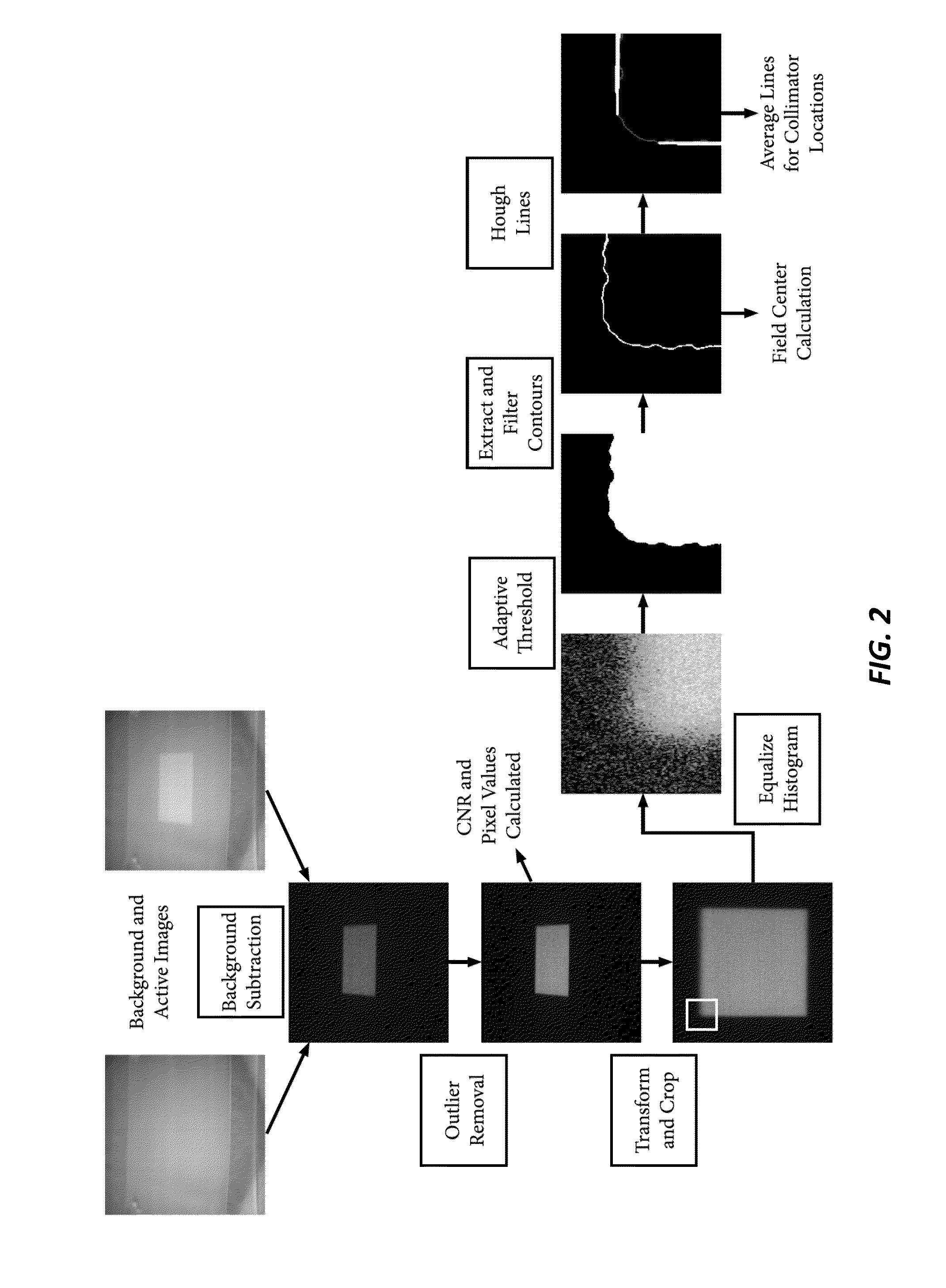
The invention relates to the technical field of radiation dose measurement, provides a construction method of a medical linear accelerator photon source model function, and is used for calculating the dose of rays in a radiation treatment scheme. A source model of a treatment photon beam of the accelerator comprises two parts, namely a source model of original ray photons and a source model of scattered ray photons. Physical parameters in source model functions of the two parts are emission point position coordinates of particles, projection values of unit momentum vectors in the three-dimensional orthogonal direction and energy of the particles. The photon fluence information, the energy spectrum information and the photon unit momentum direction information on any phase space plane can be accurately calculated by utilizing the model function, the source model construction method and thought are suitable for construction of photon beam source models of various nominal energies of accelerators used in radiotherapy, and the method has the advantages of being few in modeling parameters, the physical significance of each parameter in the function is clear, the use is convenient, and the radiation field photon distribution information can be reproduced truthfully by using a mathematical analysis method.
Owner:HARBIN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
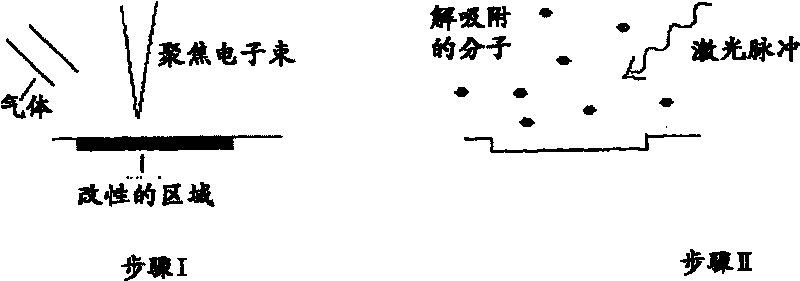
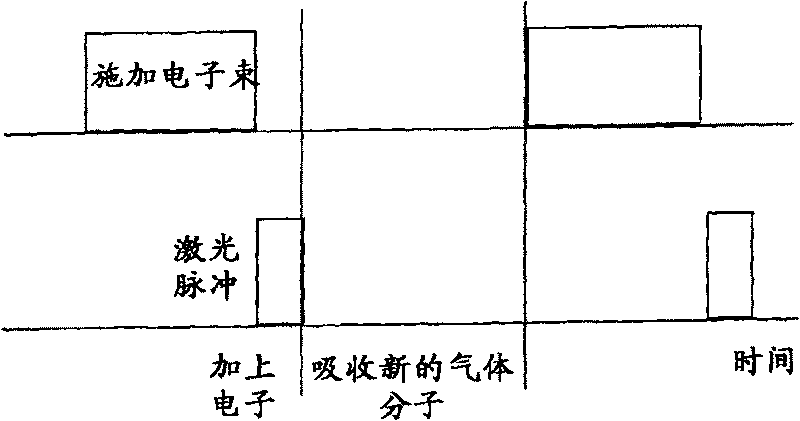
Method for etching surface material with induced chemical reaction by focused electron beam on surface
InactiveCN1479175BElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical reactionCompound (substance)
The invention refers to a procedure for etching of materials at the surface by focussed electron beam induced chemical reactions at said surface. The invention is characterized in that in a vacuum atmosphere the material which is to be etched is irradiated with at least one beam of molecules, at least one beam of photons and at least one beam of electrons, whereby the irradiated material and the molecules of the beam of molecules are excited in a way that a chemical reaction predetermined by said material and said molecules composition takes place and forms a reaction product and said reactionproduct is removed from the material surface - irradiation and removal step.
Owner:NAWOTEC +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com