Preparation method of heterojunction thermal photovoltaic cell
A thermal photovoltaic cell and heterojunction technology, which is applied in the manufacture of circuits, electrical components, and final products, can solve the problems of reducing the collection efficiency of photogenerated carriers, the number of semiconductor functional layers, and the impact on battery conversion efficiency. Conducive to battery efficiency, improved photoelectric conversion efficiency, and high photoelectric conversion efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
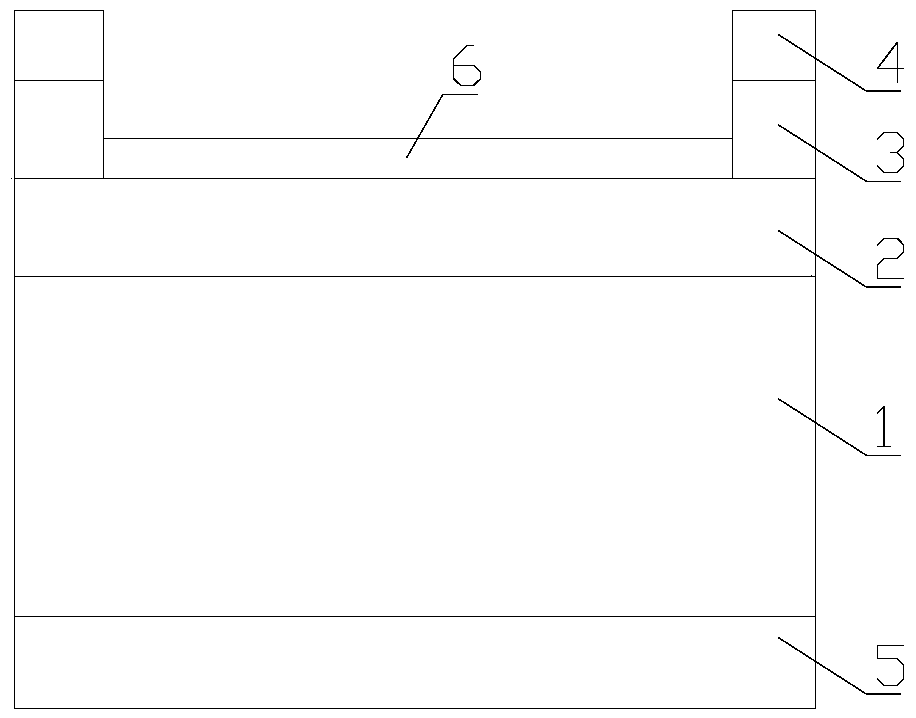
[0033] The method for preparing a heterojunction thermal photovoltaic cell is characterized in that it includes the following preparation steps:
[0034] Step 1: sequentially grow the emitter region, the electrode contact layer and the upper electrode on the base region
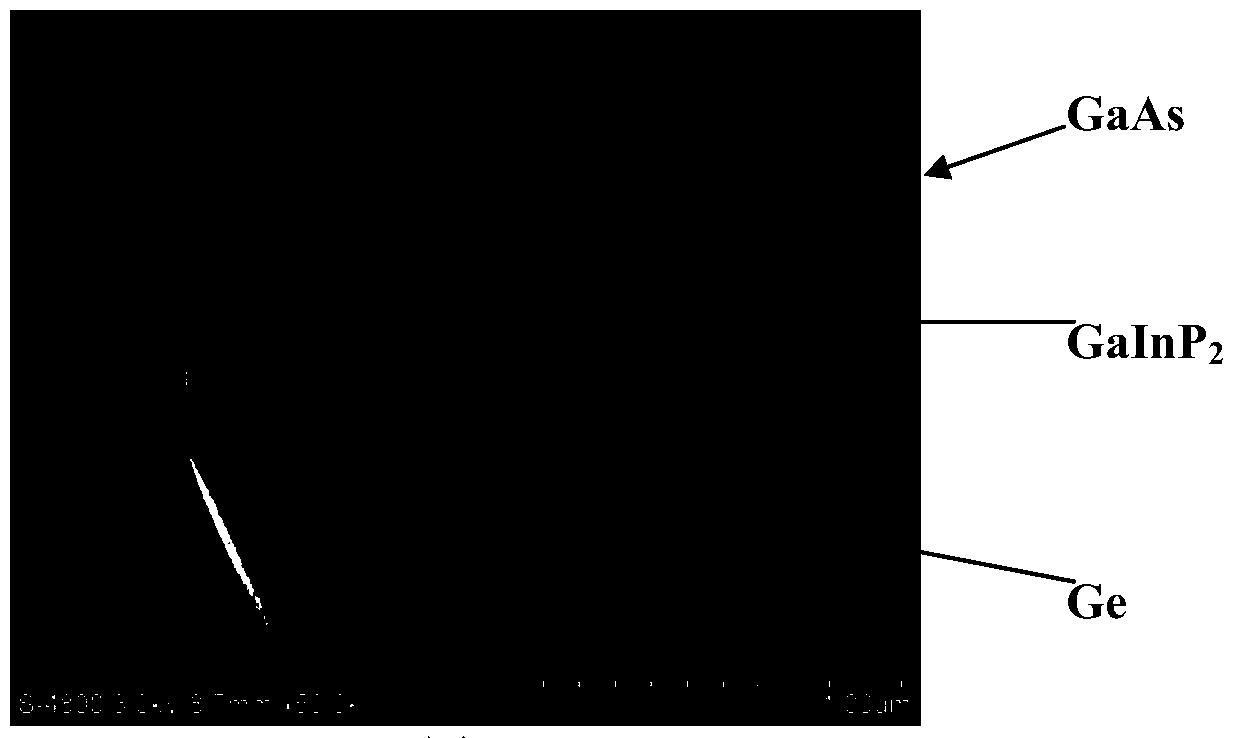
[0035] (1) Place the p-Ge layer substrate with a narrow bandgap width of 50-500 μm as the base area in the MOCVD equipment, and grow n-Ga with a thickness of less than 500 nm and a wider bandgap width on the p-Ge layer substrate x In y The p layer is used as an emission region, wherein x=0.4~0.8, y=1-x; the forbidden band width of the p-Ge layer is 0.66eV; the n-Ga x In y The band gap of the P layer is 1.9eV;
[0036] ⑵In n-Ga x In y The epitaxial growth of 30nm to 1000nm thick on the P layer is used as a heavily doped n-GaAs layer or a heavily doped n-GaInP layer for making an electrode contact layer;
[0037] (3) Evaporate a layer of Ag, Au, Cu, Ti, Pd, Ni or Al film on the electrode contact layer as th...
Embodiment
[0050] Step 1 Select the p-type Ge substrate as the base region
[0051] Doped with Be, Mg, B or Zn, the doping concentration is 10 15 ~10 17 cm -3 A p-type Ge single crystal with a relatively narrow band gap (about 0.66eV), cut along the Ge(001) crystal plane with an inclination of 6° in the [111] direction, and cut into a wafer substrate with a thickness of 50-500 μm as the base region 1;
[0052] Step 2 On the base region, grow the emitter region and the electrode contact layer with a wider band gap in sequence
[0053] Put the p-type Ge substrate in the MOCVD equipment, in GaInP 2 Before starting to grow, the p-Ge substrate was heated in H 2 Heating to 600-800°C in an atmosphere, maintaining the temperature and passing phosphine (PH 3 ) for 50 to 500 seconds, and then pass the carrier gas (H 2 ) carries the saturated vapor of the metal-organic source into the reaction chamber, the metal-organic source includes the precursors trimethylgallium (TMGa), trimethylindium (...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com