Patents
Literature
51results about How to "Reduce dangling keys" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Silicon-based solar cell, preparation method and photovoltaic module
PendingCN109494261AImprove performanceHigh voltageFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationDangling bondP type silicon
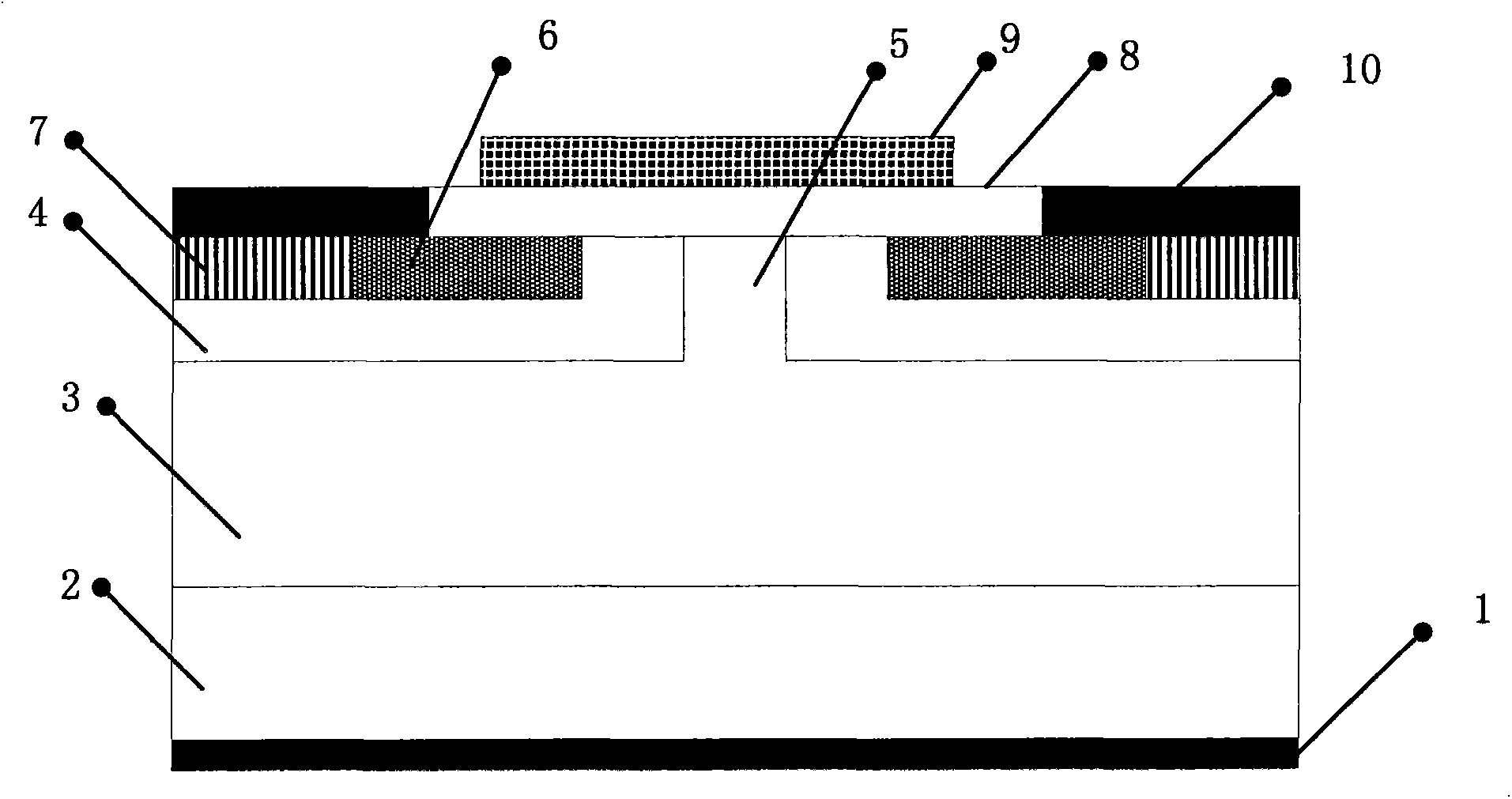
The invention discloses a silicon-based solar cell, a preparation method and a photovoltaic module, which belong to the technical field of solar cells. The silicon-based solar cell comprises a P-typecrystalline silicon substrate, a back tunneling passivation layer arranged on the back of the P-type crystalline silicon substrate, a group III element doped back doped silicon layer arranged on a partial region of the back tunneling passivation layer, a gallium oxide layer, a coating layer arranged on the gallium oxide layer, and a back electrode arranged on the coating layer. The gallium oxide layer is arranged on the back doped silicon layer and a region without the back doped silicon layer on the back tunneling passivation layer. In the solar cell, the P-type silicon surface is chemicallypassivated and field-passivated by negative charges carried by the gallium oxide layer. The number of dangling bonds and minority carriers of silicon atoms on the P-type silicon surface is reduced. The recombination rate of minority carriers is reduced. The voltage and current of the solar cell are improved. The photoelectric conversion efficiency of the solar cell is improved.
Owner:JA SOLAR TECH YANGZHOU
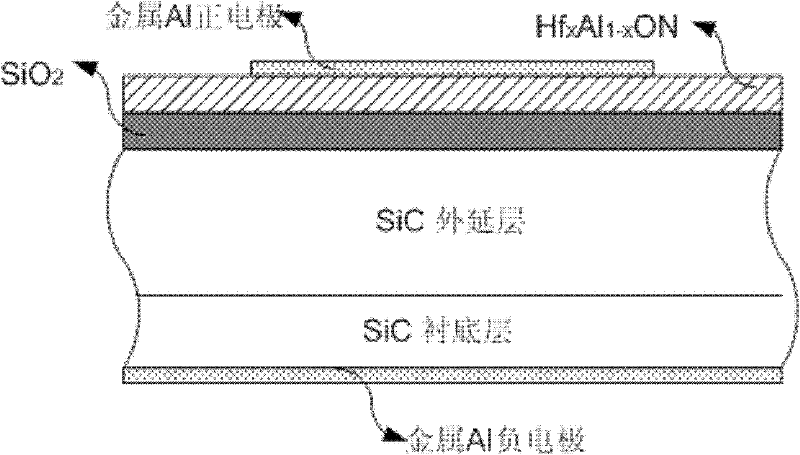
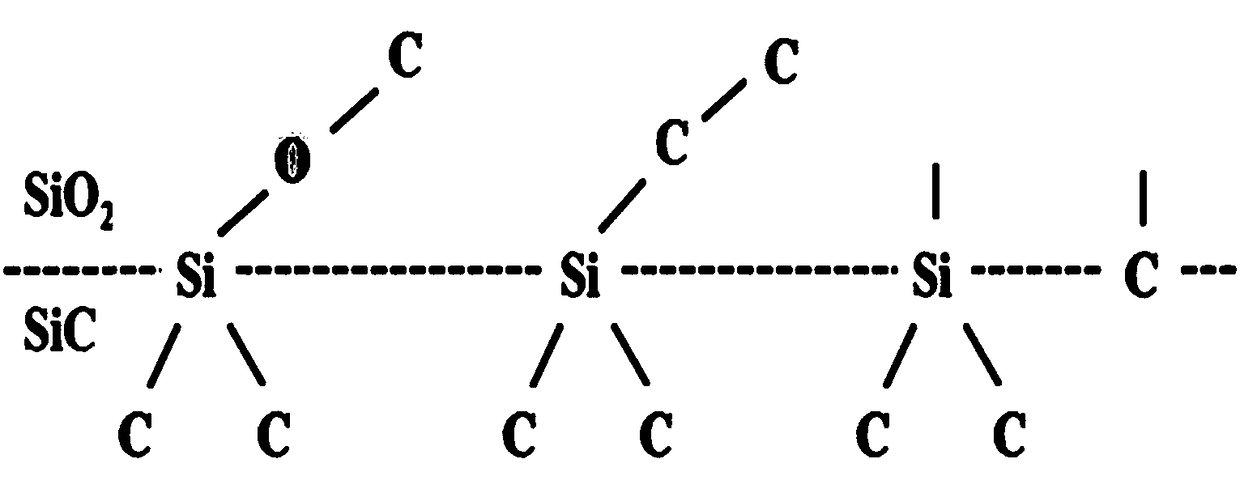
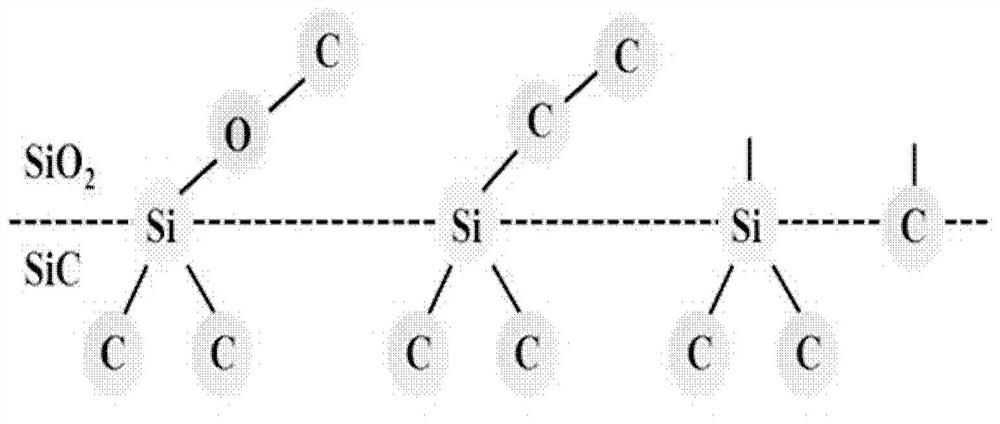
Silicon carbide (SiC) metal oxide semiconductor (MOS) capacitor with composite dielectric layer and manufacturing method for SiC MOS capacitor with composite dielectric layer
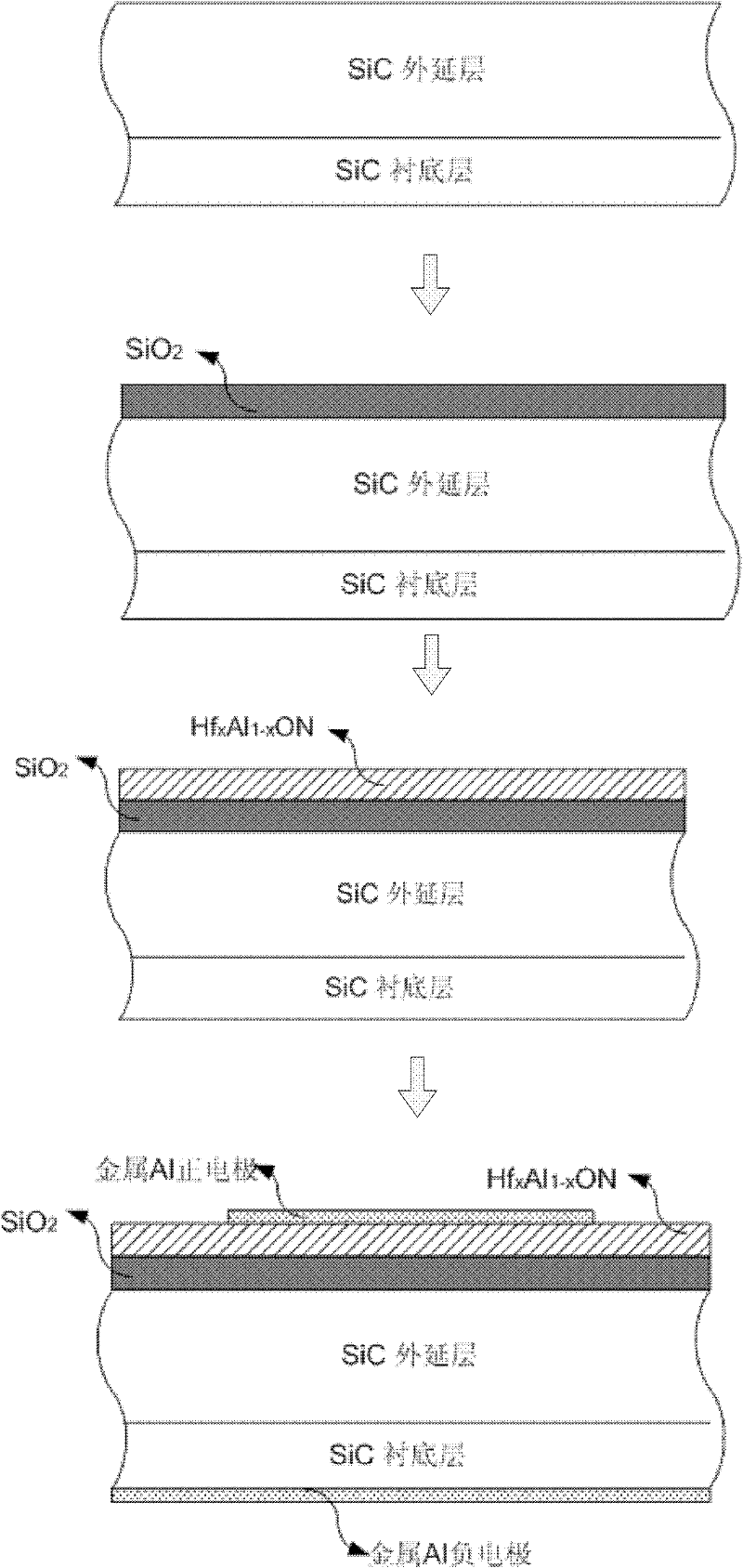
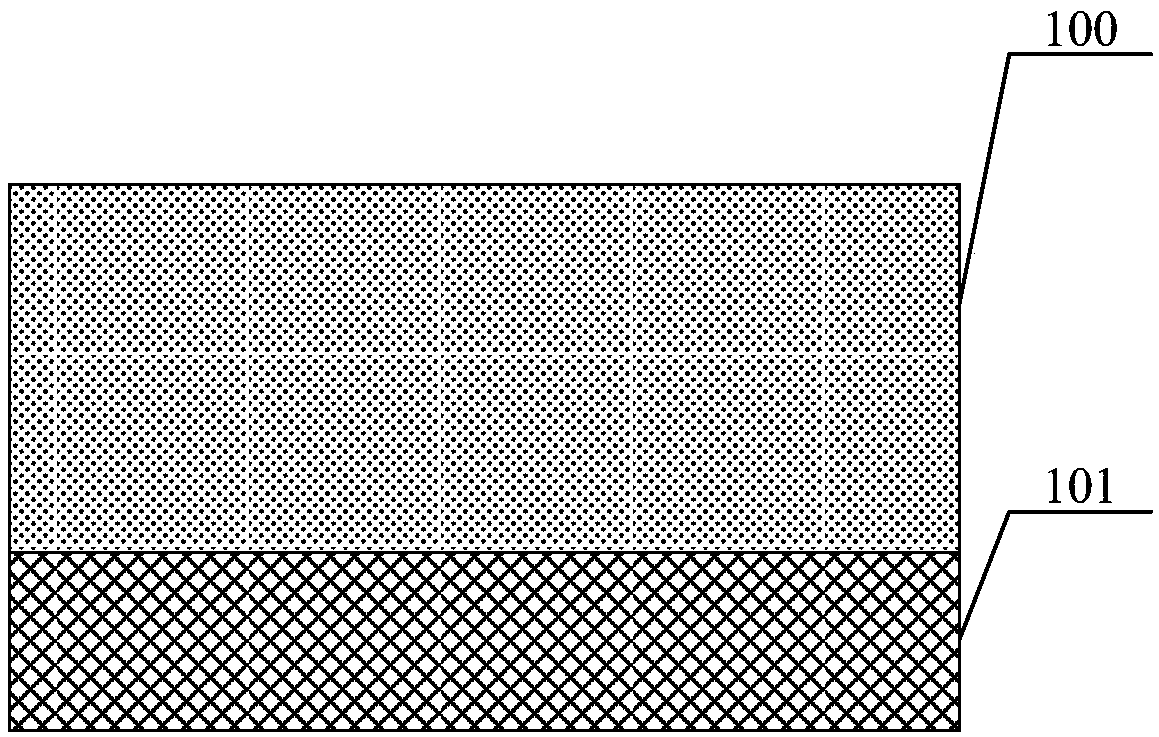
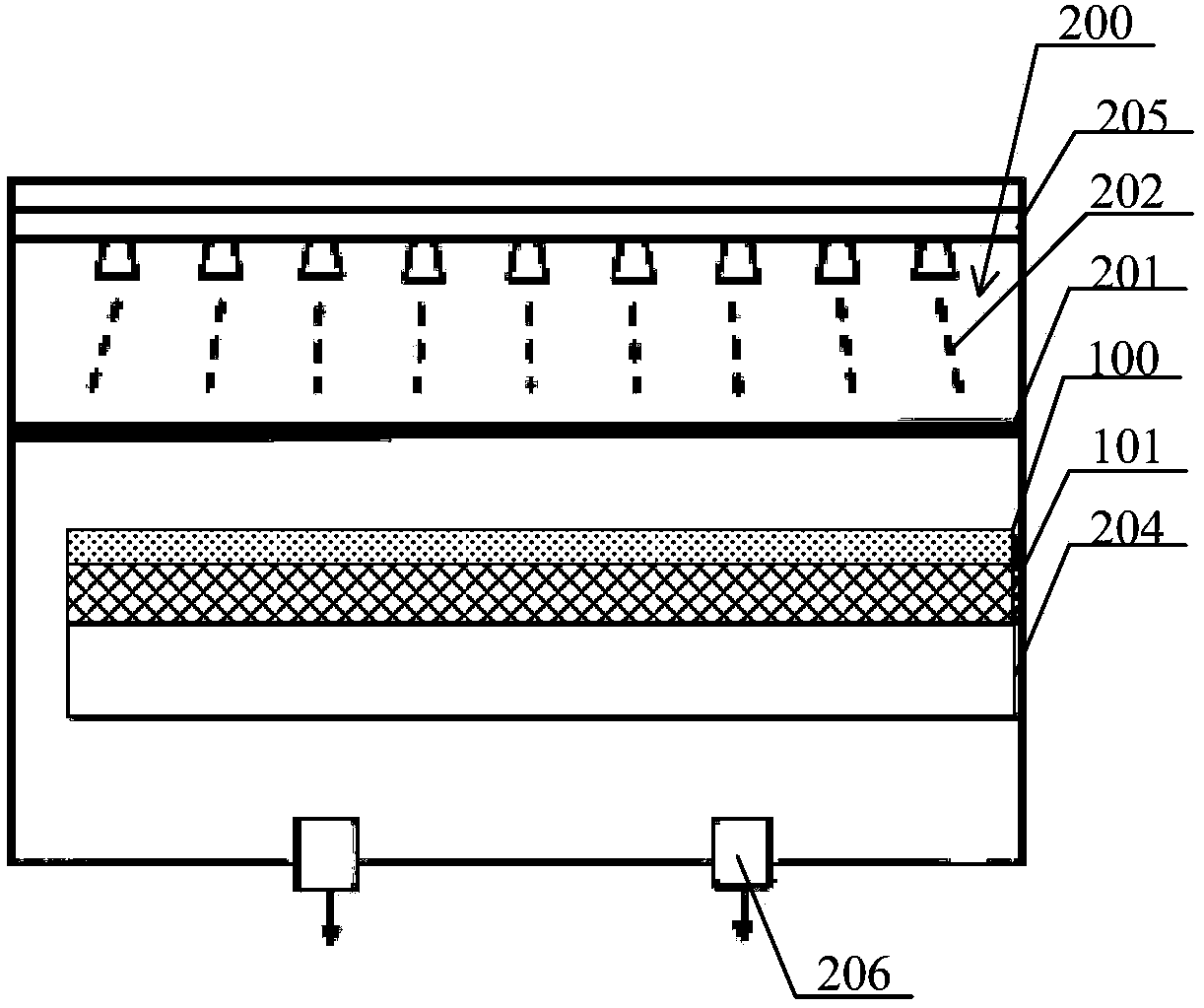
InactiveCN102244108ARelax interface stressReduce dangling keysSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesOxide semiconductorSic substrate
The invention discloses a silicon carbide (SiC) metal oxide semiconductor (MOS) capacitor with a composite dielectric layer, and mainly solves the problem that the conventional SiC MOS capacitor has high interface-state density and weak voltage endurance. The structure of the capacitor is that: an N-type heavy doping SiC substrate layer, an N-type light doping SiC epitaxy layer, an SiO2 transition layer and an HfxAl1-xON dielectric layer are sequentially arranged from bottom to top; the back of the SiC substrate and the surface of the HfxAl1-xON are sputtered with metal Al to form positive and negative electrodes respectively; the N-type SiC epitaxy layer is 10 to 100 mu m thick, the doping concentration is 1*10<15> to 5*10<15>cm<-3>; the SiO2 transition layer is 1 to 15 mu m thick, and the HfxAl1-xON dielectric layer is 10 to 30 mu m thick. The SiO2 transition layer and the HfxAl1-xON layer form a composite dielectric layer structure so as to reduce the interface-state intensity of the dielectric layer and the SiC interface, reduce the current leakage of the dielectric layer, improve the voltage-resisting capability of the dielectric layer, and improve the reliability of the SiC MOS devices. The invention also discloses a manufacturing method for a SiC power integrated circuit and a SiC power isolation device.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Method for manufacturing silicon oxynitride gate oxide layer
ActiveCN102122614ALow densityImprove reliabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSilicon oxideDangling bond
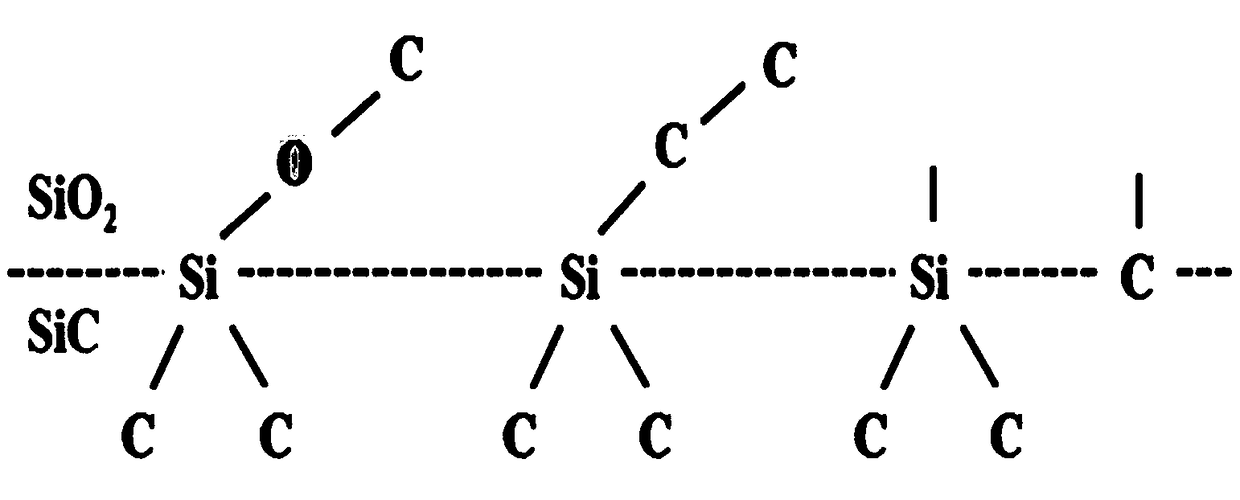
The invention provides a method for manufacturing a silicon oxynitride gate oxide layer of an MOS (metal oxide semiconductor) device, and the method comprises the following steps: firstly nitridizing on a provided silicon substrate for forming silicon oxynitride, then performing thermal oxidization for forming a first silicon oxide layer between the silicon oxynitride and the silicon substrate and a second silicon oxide layer on the silicon oxynitride, and then depositing polysilicon on the second silicon oxide layer after secondly annealing the silicon substrate; and etching for forming a gate and the silicon oxynitride gate oxide layer. The silicon oxide layer is introduced between the silicon substrate and the silicon oxynitride, thereby reducing dangling bonds between the silicon oxynitride gate oxide layer and the silicon substrate, further reducing the interface state charge density between the silicon oxynitride gate oxide layer and the substrate and improving certain properties of the MOS device, such as improving the stability of threshold voltage of the device, reducing the hot-carrier effect and the flicker noise of the device and the like.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP +1
Interface treatment technology for hetero junction solar cell
InactiveCN102386253ANo damagePromote productionFinal product manufactureChemical vapor deposition coatingGas phaseDangling bond
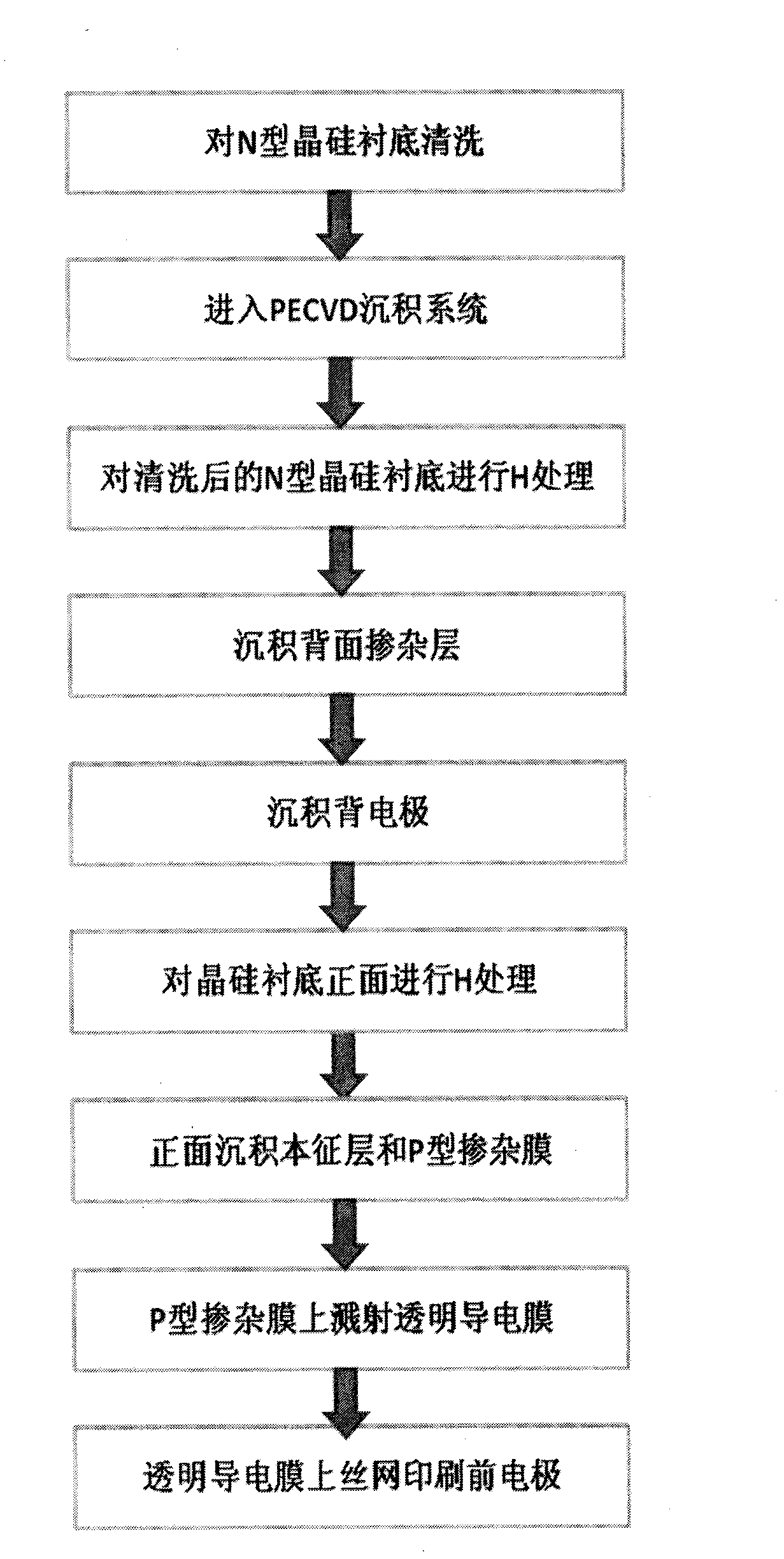
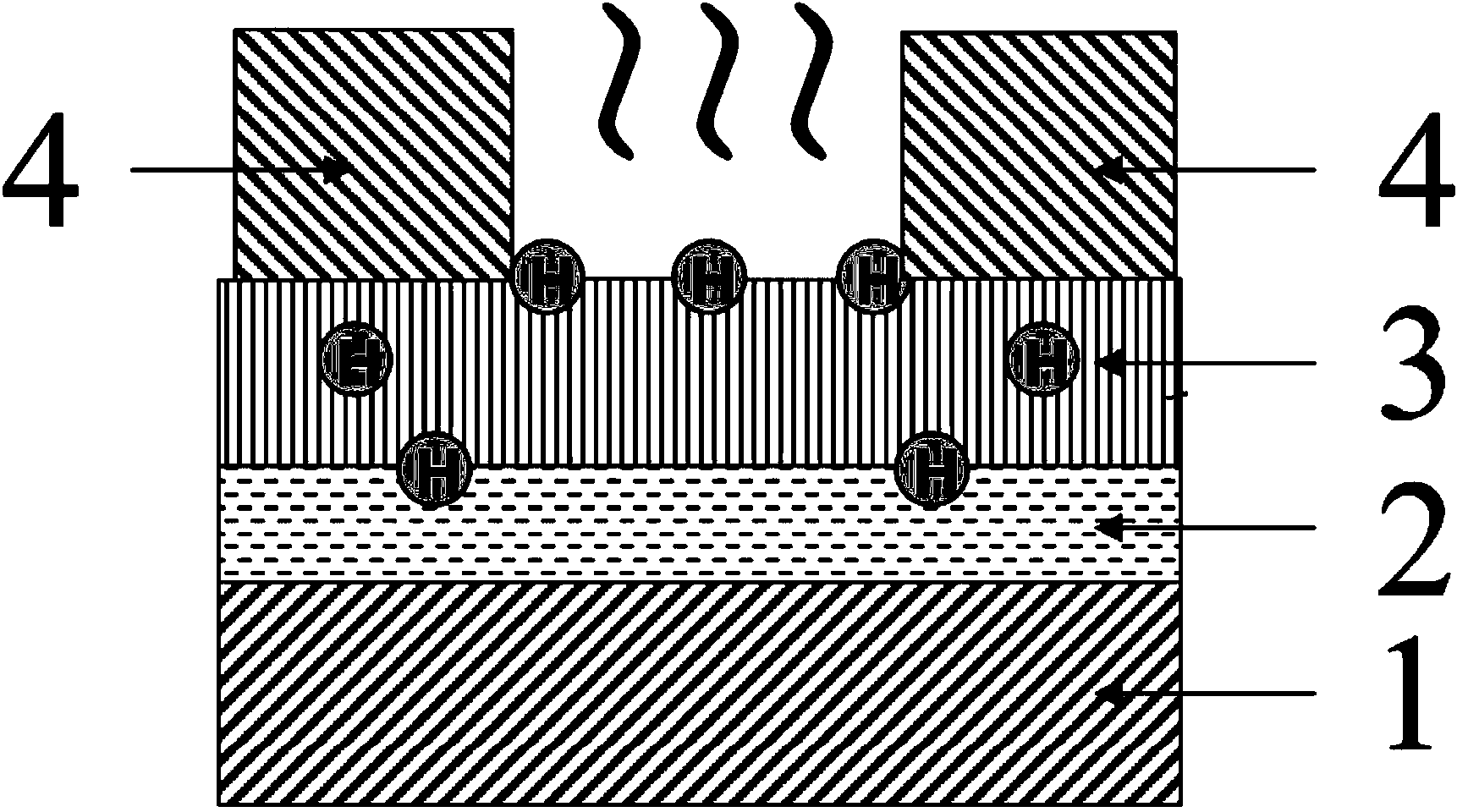
The invention discloses an interface treatment technology for a hetero junction solar cell. The method is characterized in that: the technology can be applied to the manufacturing of a thin film / crystalline silicon hetero junction solar cell, reaction gases can be ionized by utilizing a plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD) system or a hotwire chemical vapor deposition (HWCVD) system to generate H, and the H is transported to a crystalline silicon substrate by a gas phase and reacted with the surface of crystalline silicon to effectively passivate defect states such as unsaturated dangling bonds and the like on the surface of the crystalline silicon, reduce hetero junction interface recombination and facilitate improvement in the overall performance of the hetero junction solar cell.
Owner:CHANGZHOU HETE PHOTOELECTRIC
Method for improving N-typed DiMOSFET channel mobility based on N-typed nanometer thin layer
ActiveCN103928344AReduced interface roughnessImprove mobilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesN channelThin layer
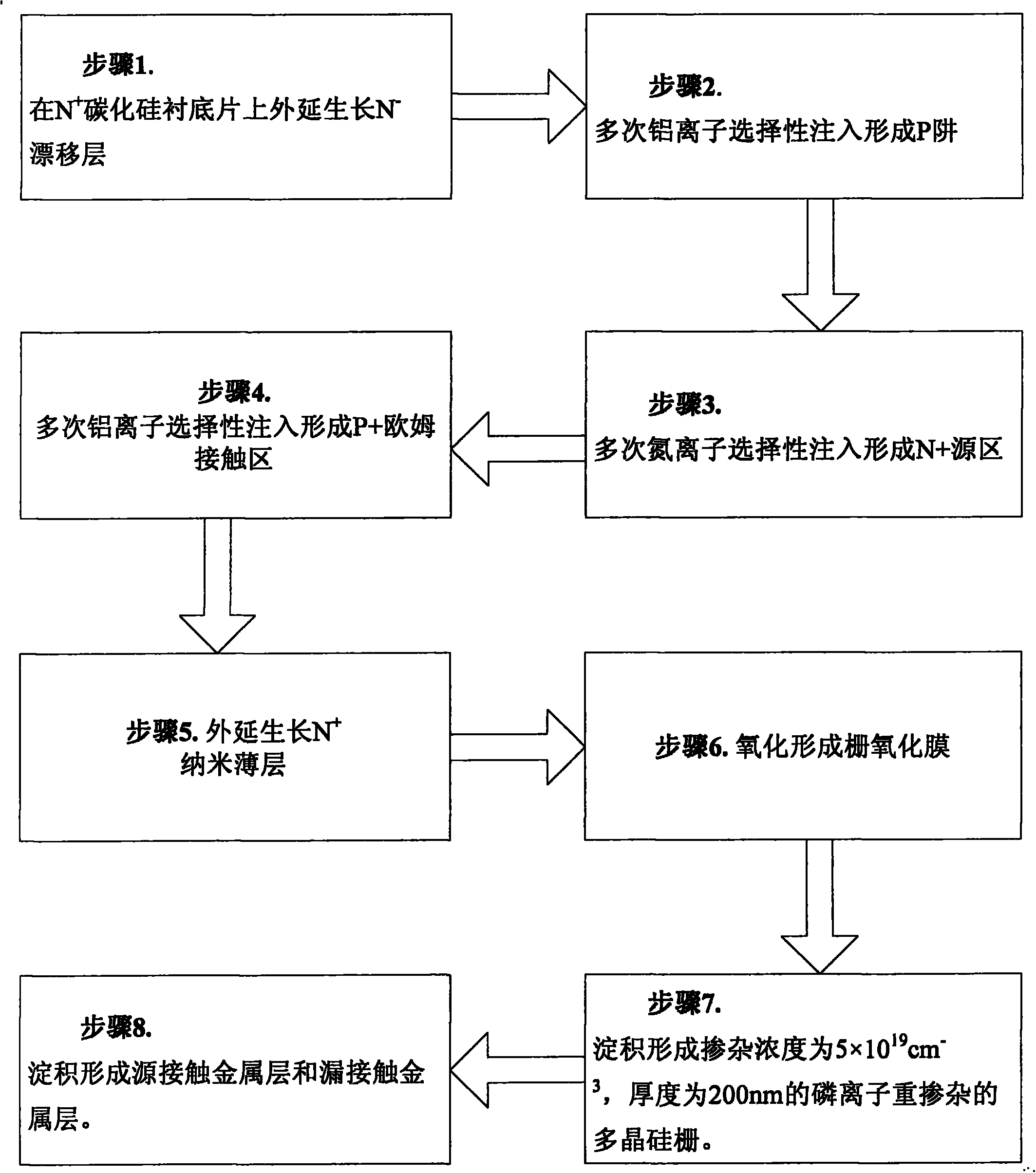
The invention discloses a method for improving N-typed DiMOSFET channel mobility based on an N-typed nanometer thin layer, the mode of nitrogen injecting of conducting channel layer through injection forming is changed to the mode of nitrogen injecting of conducting channel layer through an N+ epitaxial layer a formed by extension on the basis of an existing ion injection technology. For an N-channel DiMOSFET device, the extension thickness ranges from 10 nm to 20 nm, the doping concentration ranges from 1*10<18> cm<-3> to 1*10<19>cm<-3>, then oxidation is conducted in a gate oxide technology, nitrogen ions are only contained in a gate oxide layer and a Sic interface, and dangling bonds on the surface are reduced. Compared with existing ion injection nitrogen, the epitaxial layer a is introduced, the problems of rough contact interface of SiC and SiO2, high lattice loss, low activation rate and the like due to the nitrogen injection technology are avoided, and the SiC DiMOSFET device which is high in electronic mobility, low in on-resistance and low in power consumption is obtained.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
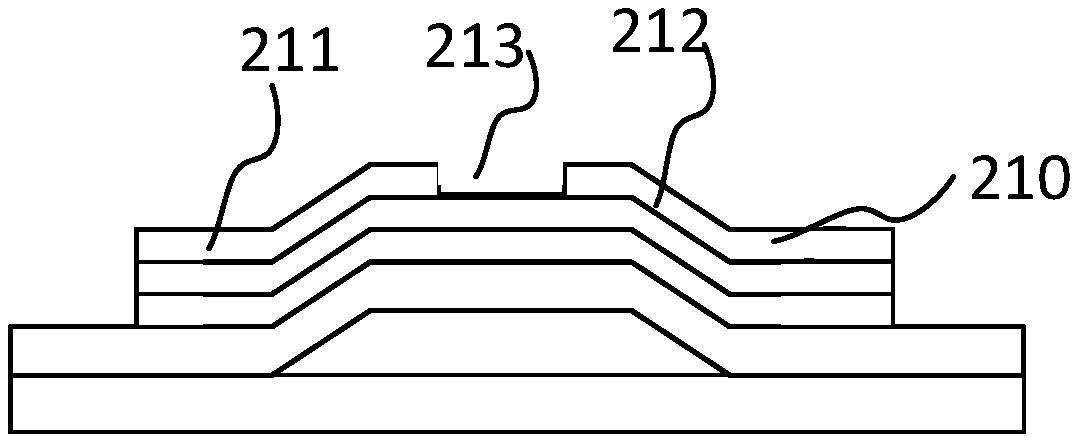
Method for manufacturing thin film transistor
ActiveCN108987279AGood light stabilityReduce driftTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrogenAmorphous silicon
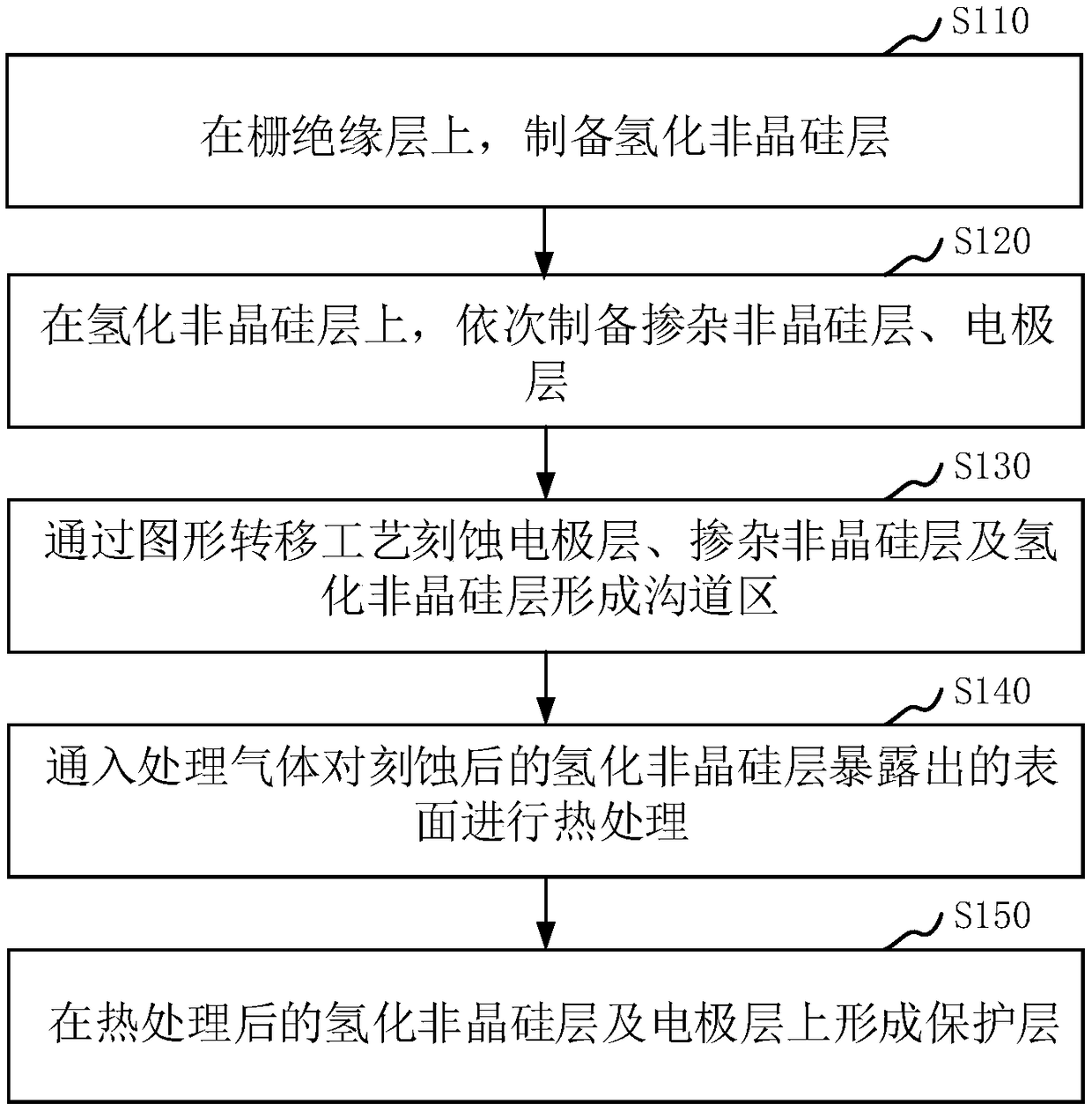
The inventionrelates to amethod for manufacturing a thin film transistor. The method includes etching a hydrogenated amorphous silicon layer to form a channel region by a pattern transfer process, andheat-treating the exposed surface of the etched hydrogenated amorphous silicon layer with a process gas including at least one of N2 and NH3 and containing no hydrogen gas. The probability of Si-H bond generated by Si-H combination is reduced, the ratio of Si-H bond in the hydrogenated amorphous silicon layer is reduced. The light stability of TFT is improved and the drift of threshold voltage Vth of TFT under light condition is reduced.
Owner:HKC CORP LTD +1
Silicon carbide oxidation method based on microwave plasma
InactiveCN108584963AImprove oxidation efficiencyImprove interface qualitySilicaMicrowaveOxygen plasma
Provided is a silicon carbide oxidation method based on a microwave plasma. The silicon carbide oxidation method comprises the steps that a silicon carbide substrate is provided; the silicon carbide substrate is placed in a microwave plasma generation device; oxygen-containing gas is introduced to generate an oxygen plasma; the oxygen plasma reacts with silicon carbide to generate silicon dioxidewith a preset thickness; the introducing of the oxygen-containing gas is stopped, and reaction is completed; the reaction temperature of the oxygen plasma and silicon carbide is 500-900 DEG C, and thereaction pressure of the oxygen plasma and silicon carbide is 400-1000 millitorrs. The silicon carbide oxidation method based on the microwave plasmas has the advantages that the oxidation efficiencyof the silicon carbide can be significantly improved, the thermodynamic non-equilibrium state can be achieved on interfaces of the silicon carbide and silicon dioxide, and the interface quality is greatly improved.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Quantum dot light-emitting device and preparation method thereof
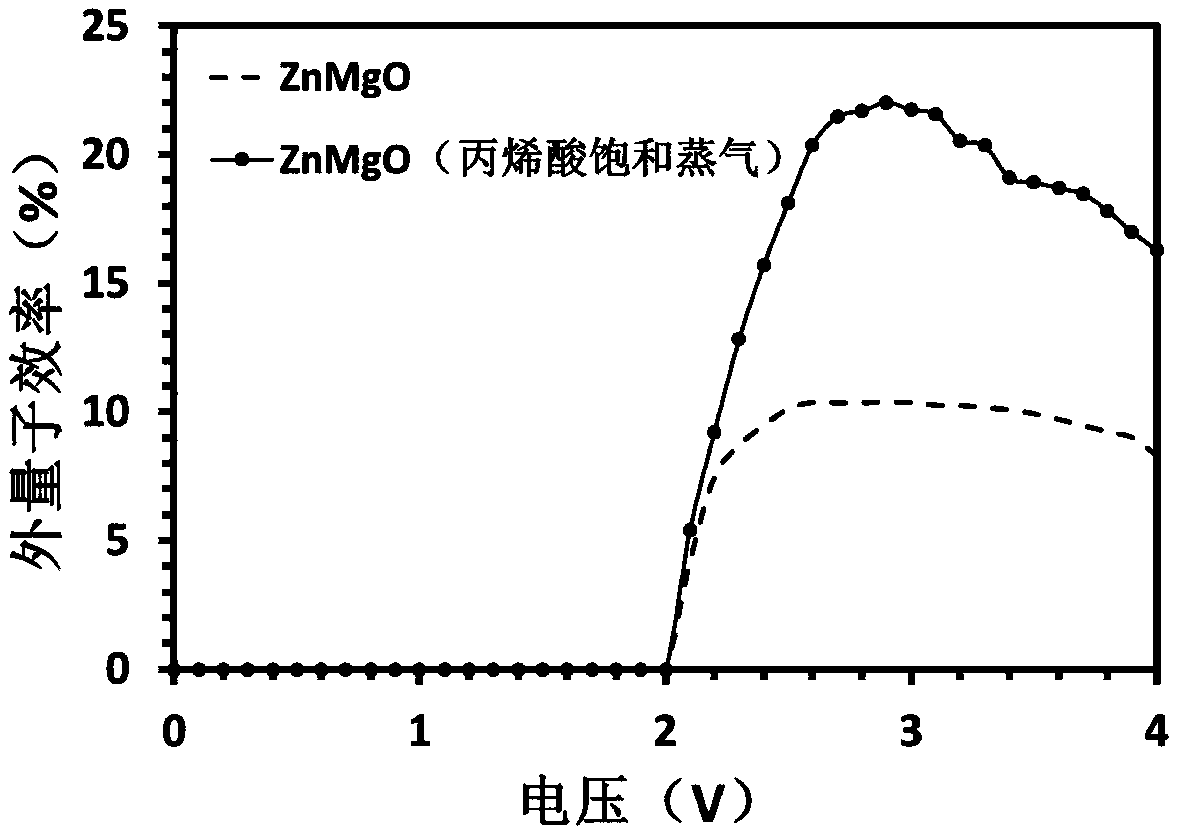
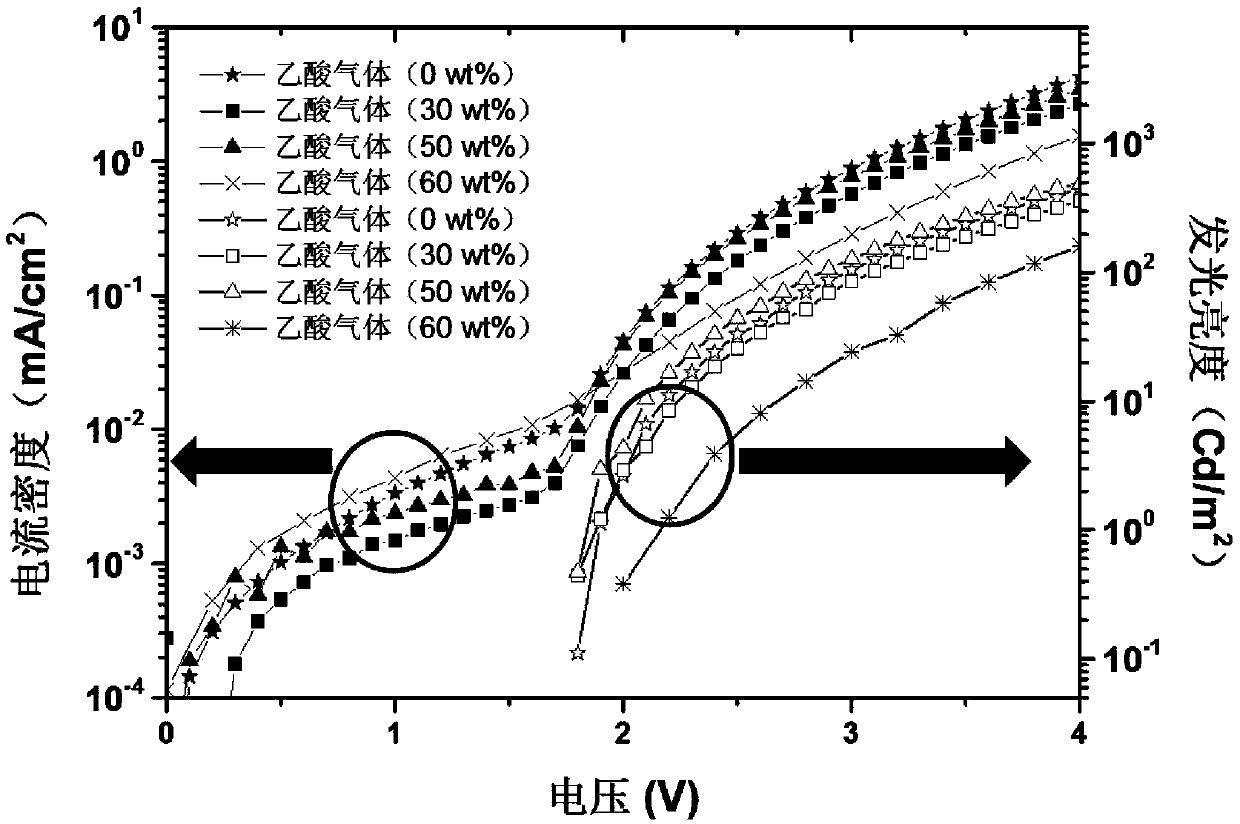
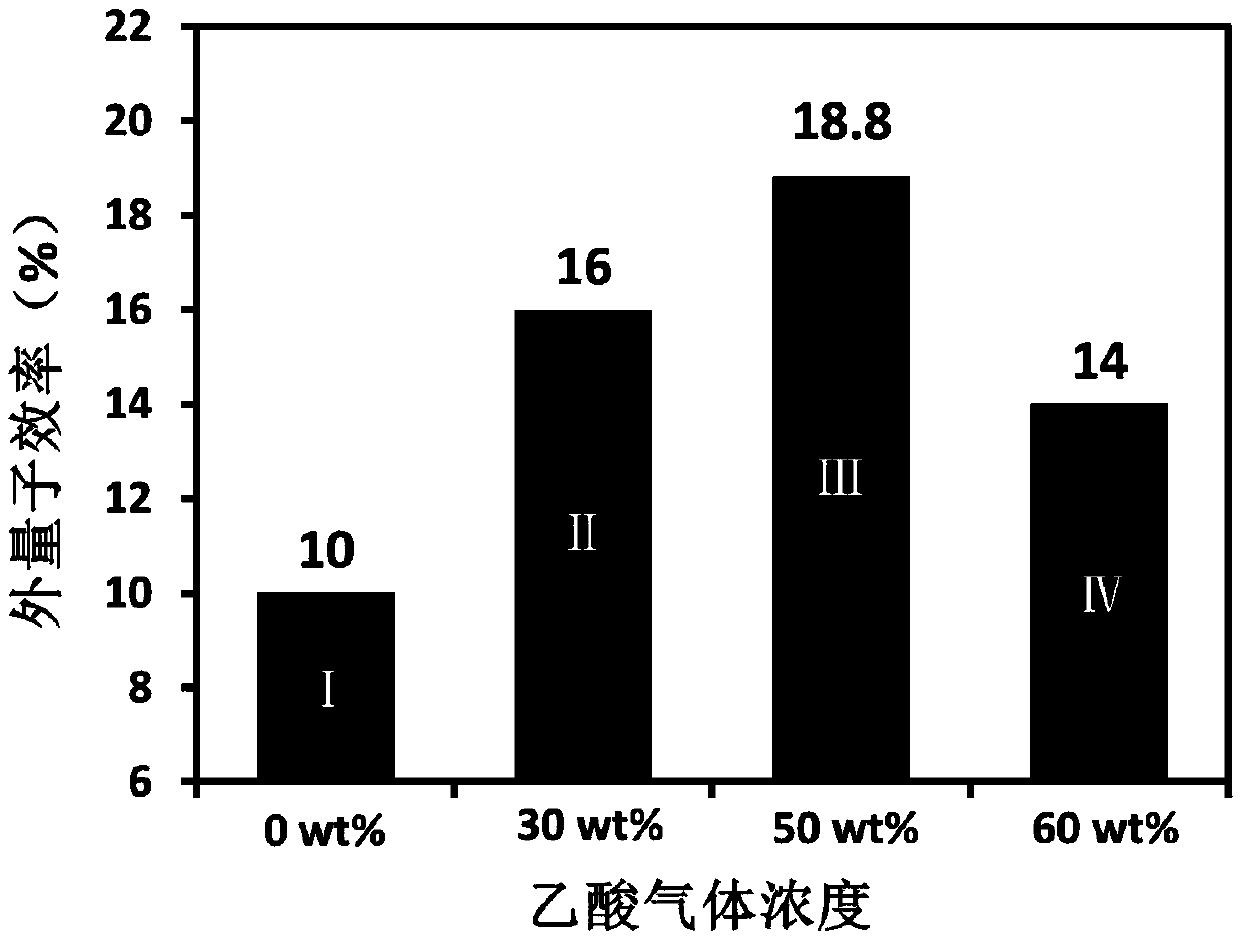
ActiveCN110911570AReduce dangling keysReduce or eliminate dangling keysSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOrganic acidQuantum dot
The invention provides a quantum dot light-emitting device and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: providing a to-be-processed part containing a nanocrystalline layer of the quantum dot light-emitting device; and carrying out acid treatment on the to-be-processed workpiece containing the nanocrystalline layer by adopting organic acid to obtain the quantum dot light-emitting device. By carrying out the acid treatment on a to-be-processed workpiece containing a nanocrystalline layer, on one hand, acid reacts with hydroxyl ion ligands on the surfaceof the nanocrystal (the surface of the nanocrystal usually carries the hydroxyl ion ligands due to a synthesis process at present) to form acid radical ion ligands and generate water, so that the hydroxyl ion ligands on the surface of the nanocrystal are greatly reduced or eliminated; on the other hand, the acid can be directly used as a surface ligand of the oxide nanocrystal, a large number ofdangling bonds on the surface of the nanocrystal are reduced or even eliminated, and therefore the defect mode of the surface of the nanocrystal is reduced. Therefore, quantum dot fluorescence quenching caused by quenching interaction between the oxide nanocrystalline and the quantum dot can be effectively inhibited, and the luminous efficiency of the device is further improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Amorphous thin film post-hydrogenation treatment method and silicon heterojunction solar cell preparation method
ActiveCN109449257AImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyImprove passivation effectFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationHeterojunctionHydrogen atom
The invention provides an amorphous thin film post-hydrogenation treatment method and a silicon heterojunction solar cell preparation method. The post-hydrogenation treatment method comprises the following steps: providing an amorphous thin film to be processed and placing the amorphous thin film in a reaction chamber provided with a hot wire; and introducing a reaction gas into the reaction chamber, performing hot wire catalytic decomposition on the reaction gas to at least generate hydrogen atoms, and performing thermal radiation on the amorphous thin film to be processed, so that the hydrogen atoms are diffused into the amorphous thin film to be processed, so as to realize the post-hydrogenation treatment of the amorphous thin film to be processed. According to the amorphous thin film post-hydrogenation treatment method provided by the invention, the hydrogen atoms are diffused into the thin film in the process of treating the amorphous thin film under the hot wire thermal radiationcondition, so that the defect state density such as dangling bonds in the thin film can be reduced; and the post-hydrogenation treatment method provided by the invention can be applied to an amorphous silicon / crystalline silicon heterojunction solar cell, such as a window material thereof, thus the passivation performance and the light transmittance performance of a window layer can be significantly improved, and the photoelectric conversion efficiency of the solar cell can be improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for manufacturing low-offset flat band voltage SiC MOS capacitor
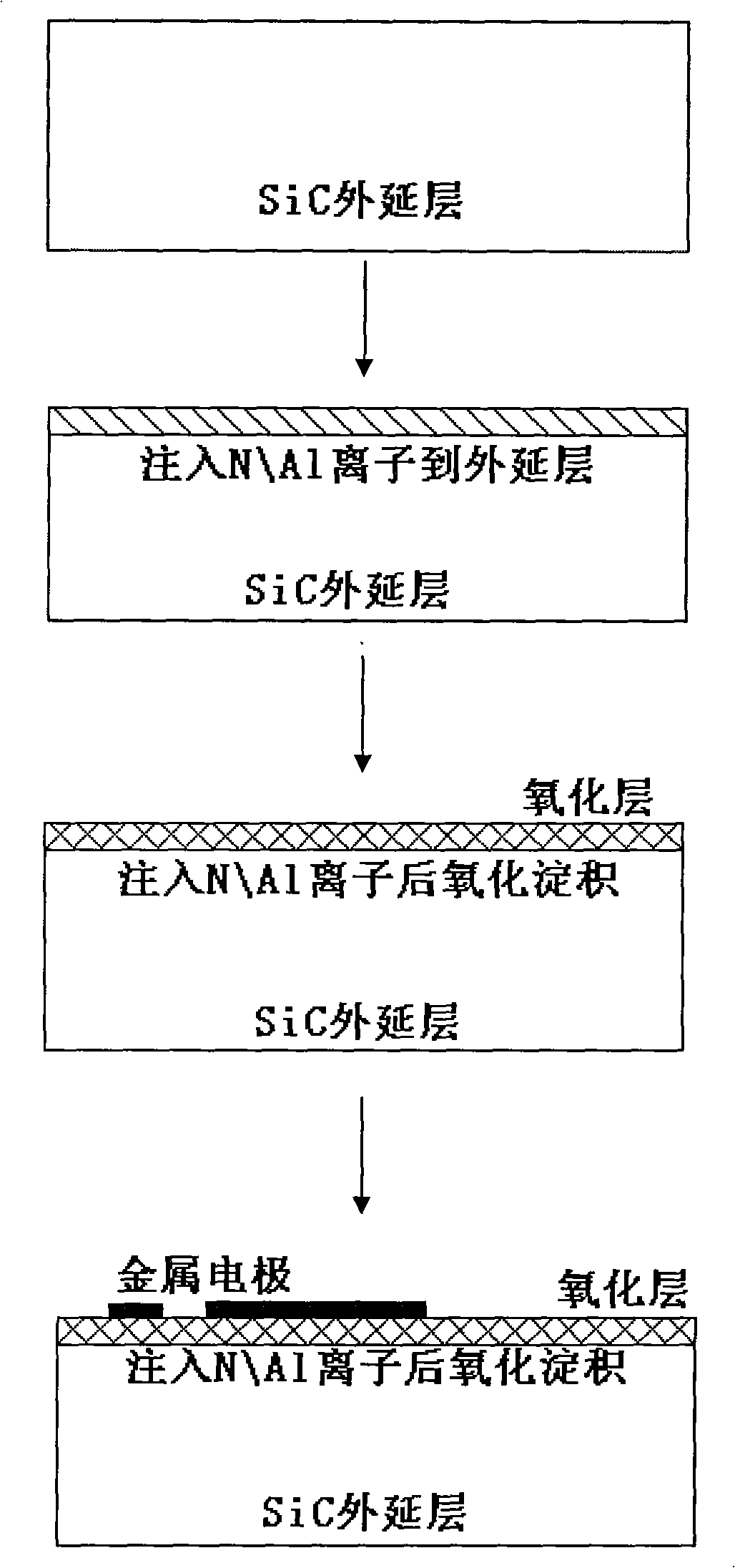
InactiveCN101540280AReduce dangling keysRelax interface stressSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhysicsLow offset
The invention discloses a method for manufacturing a low-offset flat band voltage SiC MOS capacitor, which mainly solves the problem that the trap intensity of a SiC / SiO2 interface is too high. The method comprises the following manufacturing processes: cleaning an N-SiC epitaxy material; after injecting N<+> into a SiC epitaxy layer by ion injection, injecting Al<-> into the epitaxy layer; oxidizing a layer of SiO2 on the epitaxy layer after the ion injection in the mode of dry-oxygen; sequentially finishing the annealing in Ar gas environment, the wet-oxygen oxidation annealing in wet-oxygen environment and the cold treatment in the Ar gas environment of an oxidized sample wafer; depositing a layer of SiO2 on the sample wafer after the cold treatment by chemical vapor deposition and first annealing the sample wafer in the Ar gas environment; and manufacturing an electrode by vacuum sputtering of Al and carrying out second annealing in the Ar gas environment so as to finish manufacturing the whole capacitor. The invention has the advantages of accurate control of N<+>\Al<-> doses, low trap intensity of the SiC / SiO2 interface, small flat band voltage offset of the SiC MOS capacitor and simple achieving process and can be used for improving the characteristics of the SiC / SiO2 interface of an N type SiC MOS device.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Forming method for fin-type field-effect tube
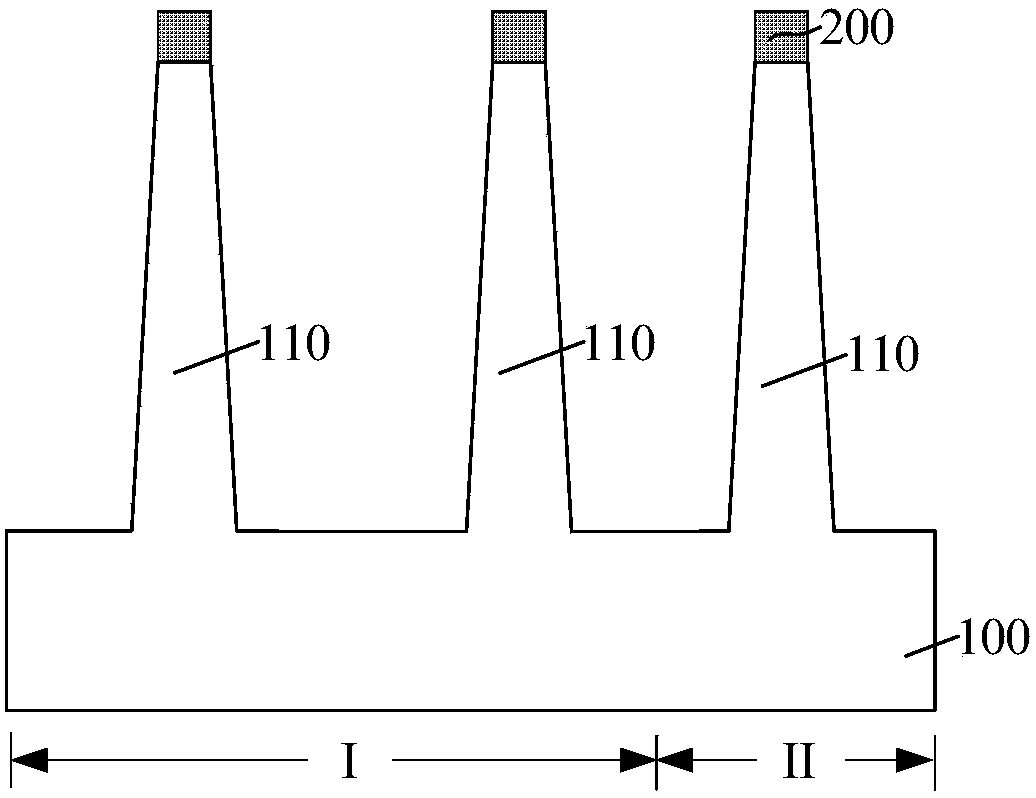
InactiveCN107919283AReduce dangling keysImprove interface stateSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDangling bondEngineering
The invention discloses a forming method for a fin-type field-effect tube, and the method comprises the steps: providing a substrate which is provided with a plurality of split fin parts, wherein thefin parts are provided with first atoms; forming a pseudo-gate structure which stretches across the fin parts and covers the top surfaces and side wall surfaces of a part of fin parts, and comprises agate oxidation layer and a pseudo-gate electrode layer located on the gate oxidation layer; removing a part of the pseudo-gate electrode layer by certain thickness; carrying out the annealing processing of the tops of the fin parts through the gas comprising second atoms after the part of the pseudo-gate electrode layer is removed, wherein the second atoms can form chemical bonds with the first atoms in the annealing processing. According to the invention, after the part of the pseudo-gate electrode layer is removed, the gas comprising second atoms is employed for the annealing processing ofthe tops of the fin parts. Because the second atoms can form chemical bonds with the first atoms in the annealing processing, the annealing processing is suitable for the reduction of the semiconductor atom dangling bonds in corner regions of the tops of the fin parts (such as a silicon atom dangling bond), improves the interface state between the gate oxidation layer and the fin parts, and solvesa problem of pea discharge caused by the sharp corners of the corner regions.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP +1
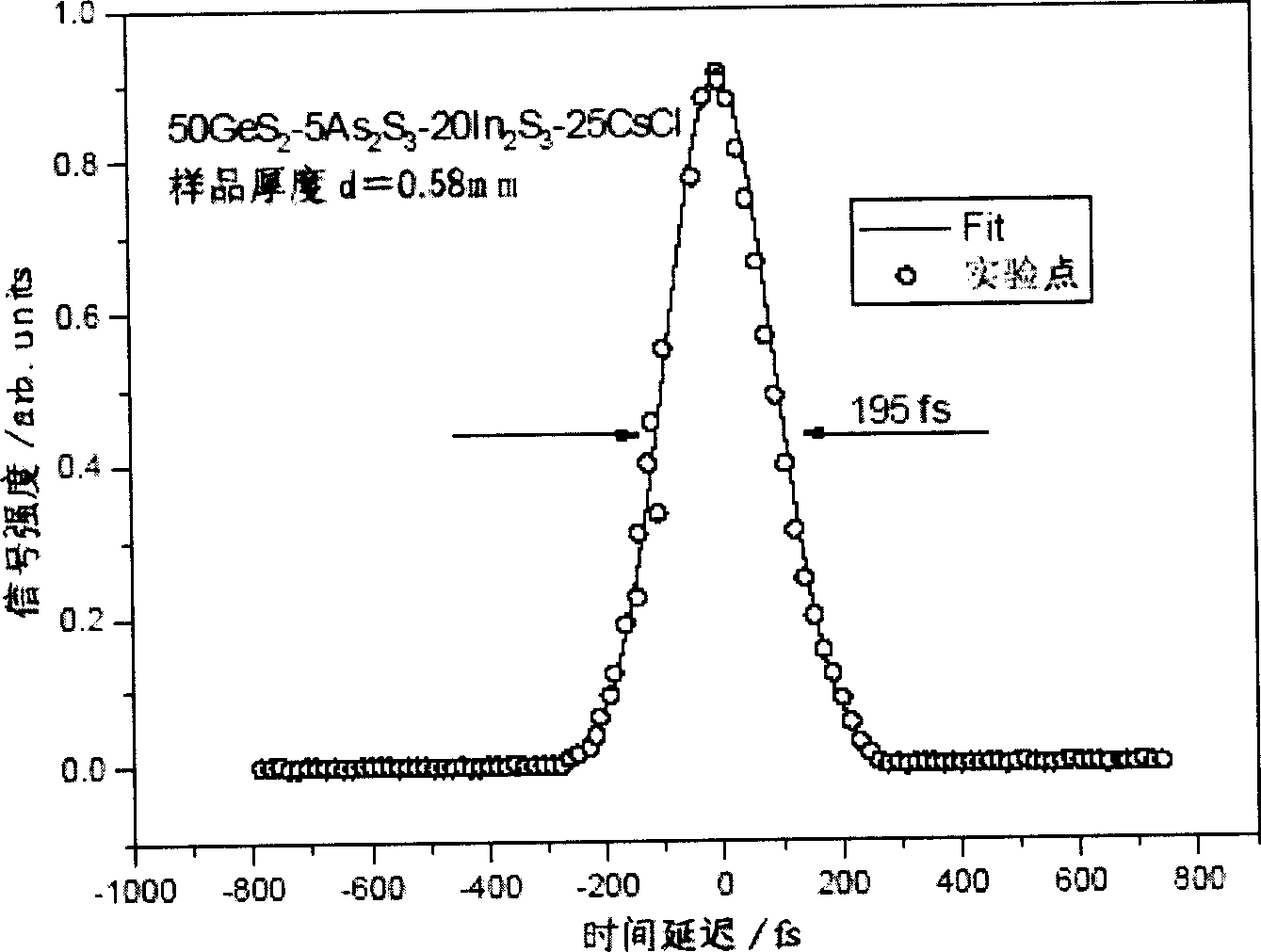
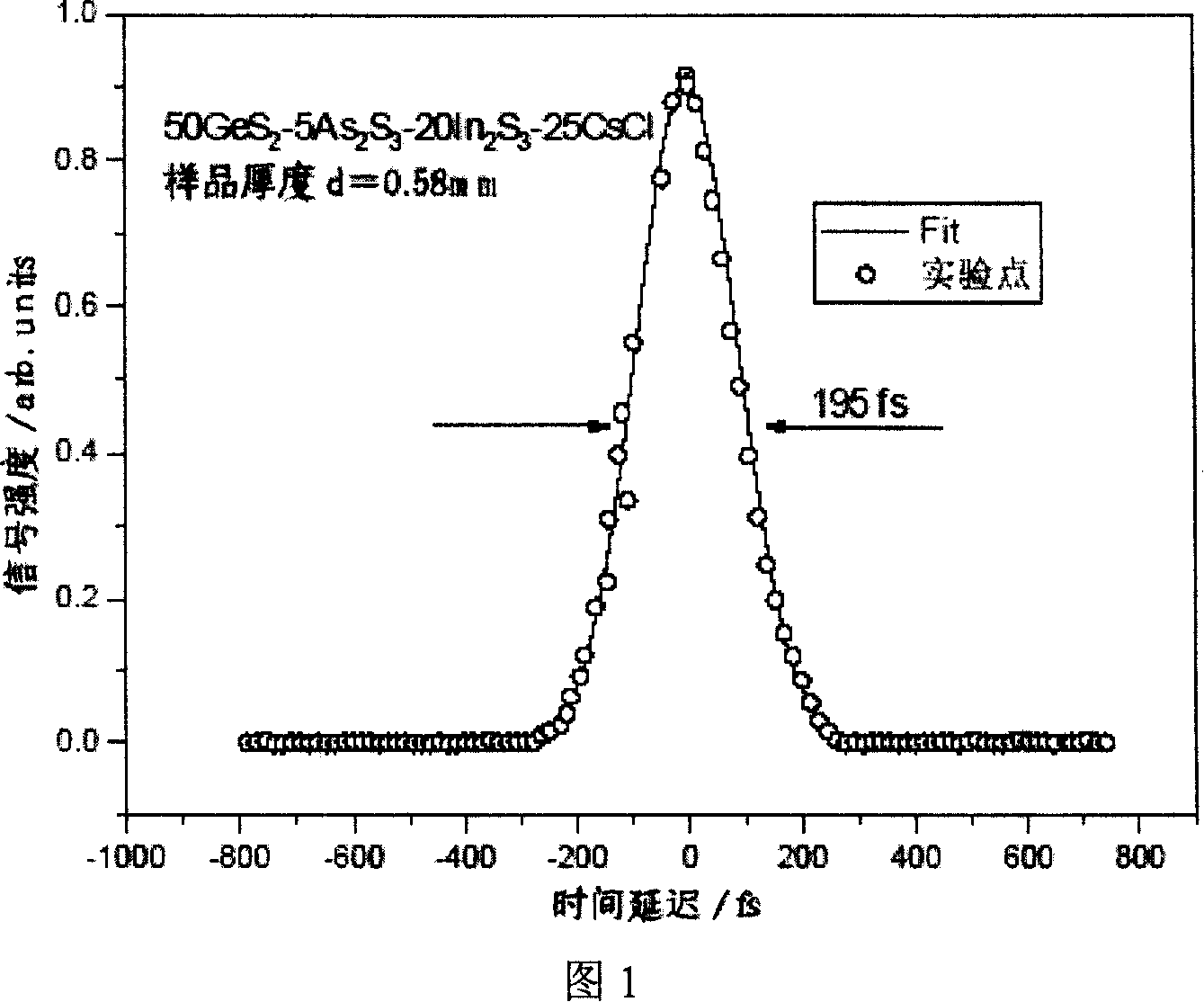
Sulfur halogen glass and its production for superfast light switch
A sulfur halogen glass for ultra-fast photo-switch and its production are disclosed. The sulfur halogen glass consists of In2S3 20í½35mol, MX 25í½40mol, As2S3 4í½10mol and GeS2 20-50mol. MX is mixture of any one kind or two kinds and above. It has better quality and glass forming ability, less consumption and larger linear optical refractive index.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
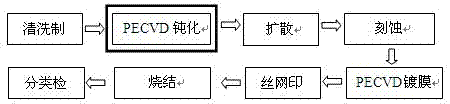
Method for improving surface passivation of solar cell
ActiveCN102856438AImprove life expectancyImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesSilanesCrystallographic defect
The invention discloses a method for improving surface passivation of a solar cell. The method includes steps of A, placing a silicon wafer in acidic or alkaline solution with certain concentration to perform cleaning and surface texture making treatment; B, placing the silicon wafer after surface texture making treatment into a graphite boat, and placing the graphite boat with the silicon wafer into tubular PECVD (plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition) equipment to perform hydrogen ion passivation; C, only filling a certain flow of ammonia into the tubular PECVD equipment under the action of plasmas to carry out a passivation process. The passivation process can be carried out without filling silane into the tubular PECVD equipment. The method has the advantages that the minority carrier lifetime of the silicon wafer is prolonged by the passivation action of hydrogen ions, dangling bonds and crystal defects on surfaces of the silicon wafer are reduced, passivation process time is short, the method is simple and is easy to implement, and the purpose of improving photovoltaic conversion efficiency of the solar cell is achieved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG FORTUNE ENERGY
Hydrogenated amorphous silicon film preparation method
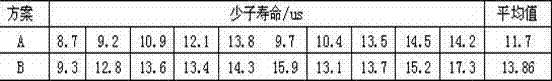
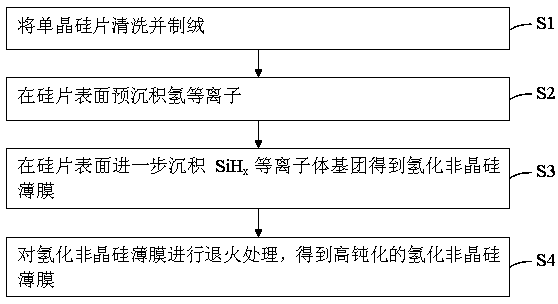
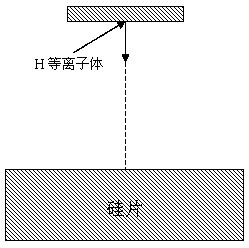
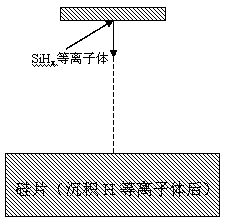
ActiveCN109545656AReduce defect densityReduce dangling keysFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrogenPlasma deposition
The invention discloses a hydrogenated amorphous silicon film preparation method. The method comprises steps that S1, a single crystal silicon chip is cleaned and texturied; S2, hydrogen plasmas are pre-deposited on the surface of the silicon chip; S3, a SiHx plasma group is further deposited on the surface of the silicon chip to obtain a hydrogenated amorphous silicon film, and x=1 or 2 Or 3; andS4, the hydrogenated amorphous silicon film is annealed to obtain a highly-passivated hydrogenated amorphous silicon film. The method is advantaged in that through combination of early stage treatment of H plasma deposition for the silicon chip and annealing treatment of the a-Si:H film, interface area defect density is effectively reduced, the a-Si / c:Si interface quality is optimized, and efficiency of an HIT battery is further improved.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Preparation method of mesa type extending wavelength indium gallium arsenic detector with low stress passivation
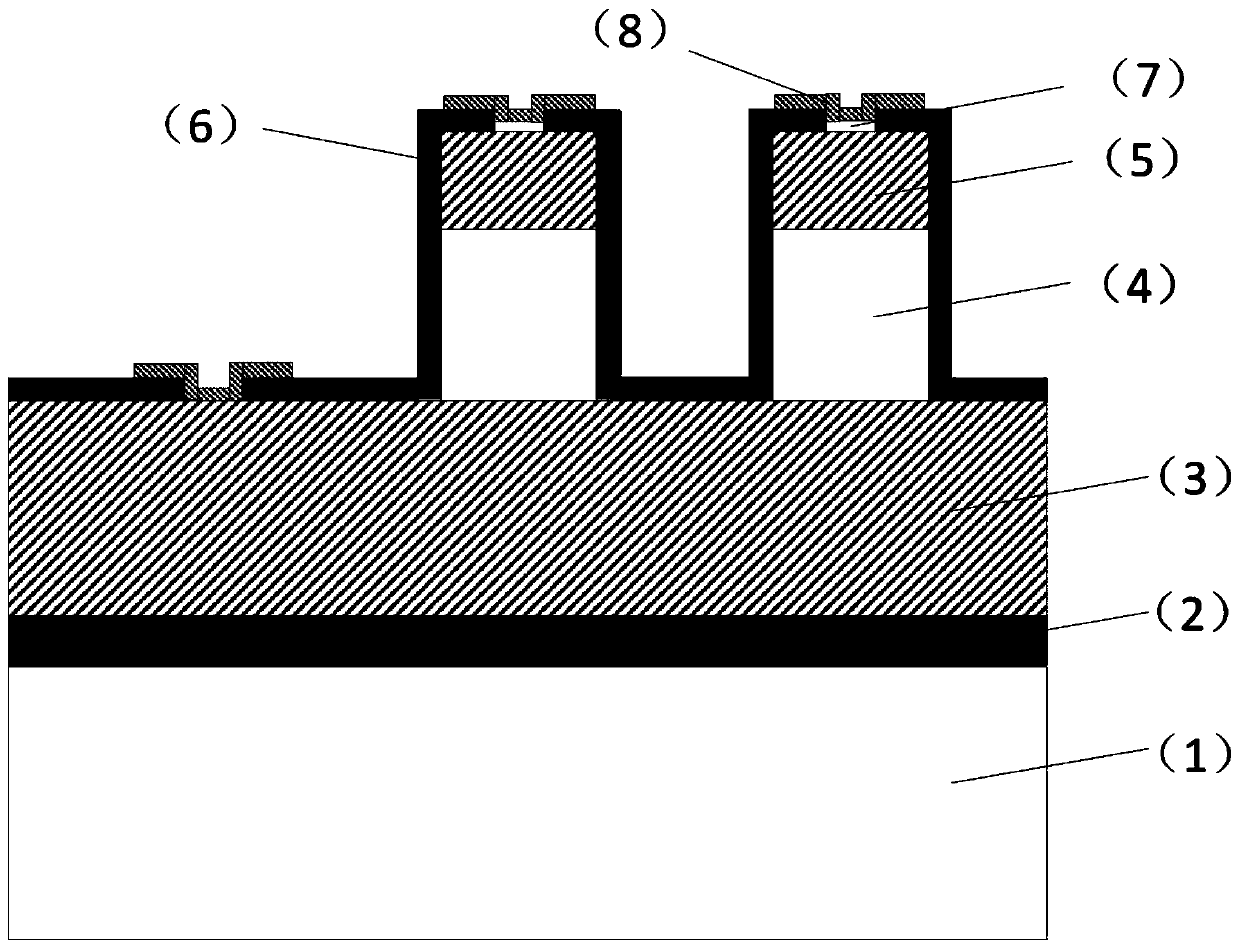
ActiveCN109755349AImprove passivation effectReduce dangling keysFinal product manufactureChemical vapor deposition coatingIndiumInductively coupled plasma
The invention discloses a preparation method of a mesa type extending wavelength indium gallium arsenic detector with low stress passivation. The mesa type extending wavelength indium gallium arsenicdetector structurally includes an N<+> type InP layer, a compositional graded N<+> type In<x>Al<1-x>As buffer layer, an In<x>Ga<1-x>As absorbed layer, a P<+> type In<x>Al<1-x>As cap layer, a silicon nitride SiN<x> passivation film, a P electrode and a thickened electrode which are successively grown on a semi-insulated InP substrate. The passivation film is a low stress silicon nitride passivationfilm grown by an inductively coupled plasma chemical vapor deposition technique. The preparation method of the mesa type extending wavelength indium gallium arsenic detector with low stress passivation has the advantages that the low stress silicon nitride film is used for passivation, the warping degree of a large area array detector chip is controlled to be less than 10[mu]m, a focal plane device with the low blind pixel rate is realized advantageously, the low stress silicon nitride passivation film has high reliability, and the passivation effects of the surface and the side face of the low stress silicon nitride passivation film are good.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
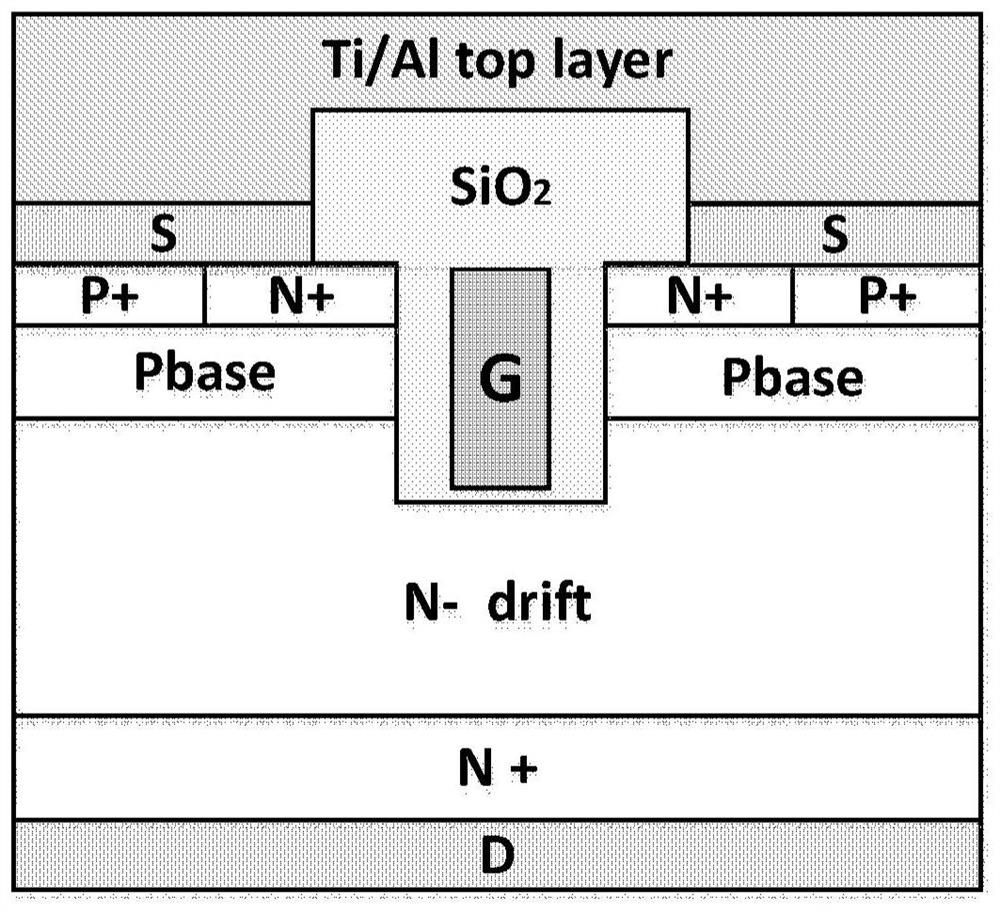
Silicon carbide MOSFET and manufacture method thereof
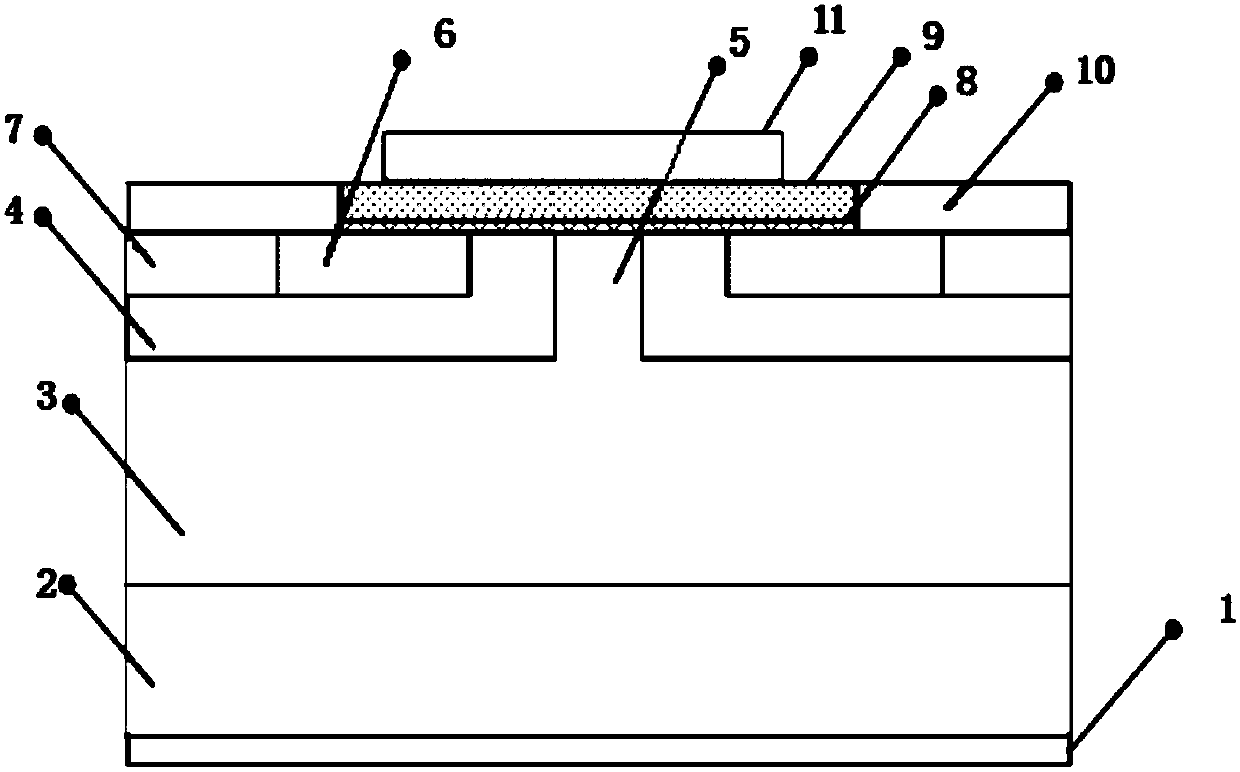
InactiveCN107871781ARelax interface stressReduce dangling keysSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMOSFETLattice mismatch
The invention provides a silicon carbide MOSFET and manufacture method thereof and is used for solving a problem of high interface density of a silicon carbide MOSFET in the prior art. The silicon carbide MOSFET includes an interface layer formed by alkaline earth metal oxide. The interface layer is longitudinally arranged between a silicon dioxide gate medium layer and a JFET area of the MOSFET and is transversely arranged between two N+ source region contacts of the MOSFET. The silicon carbide MOSFET relieves lattice mismatch between silicon carbide and silicon dioxide in a traditional silicon carbide MOSFET, so that the interface stress is relieved, dangling bonds are reduced, interface property is improved and device performance is improved.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV +1
Hydrogen-passivated zinc oxide-base thin film transistor and preparation method thereof
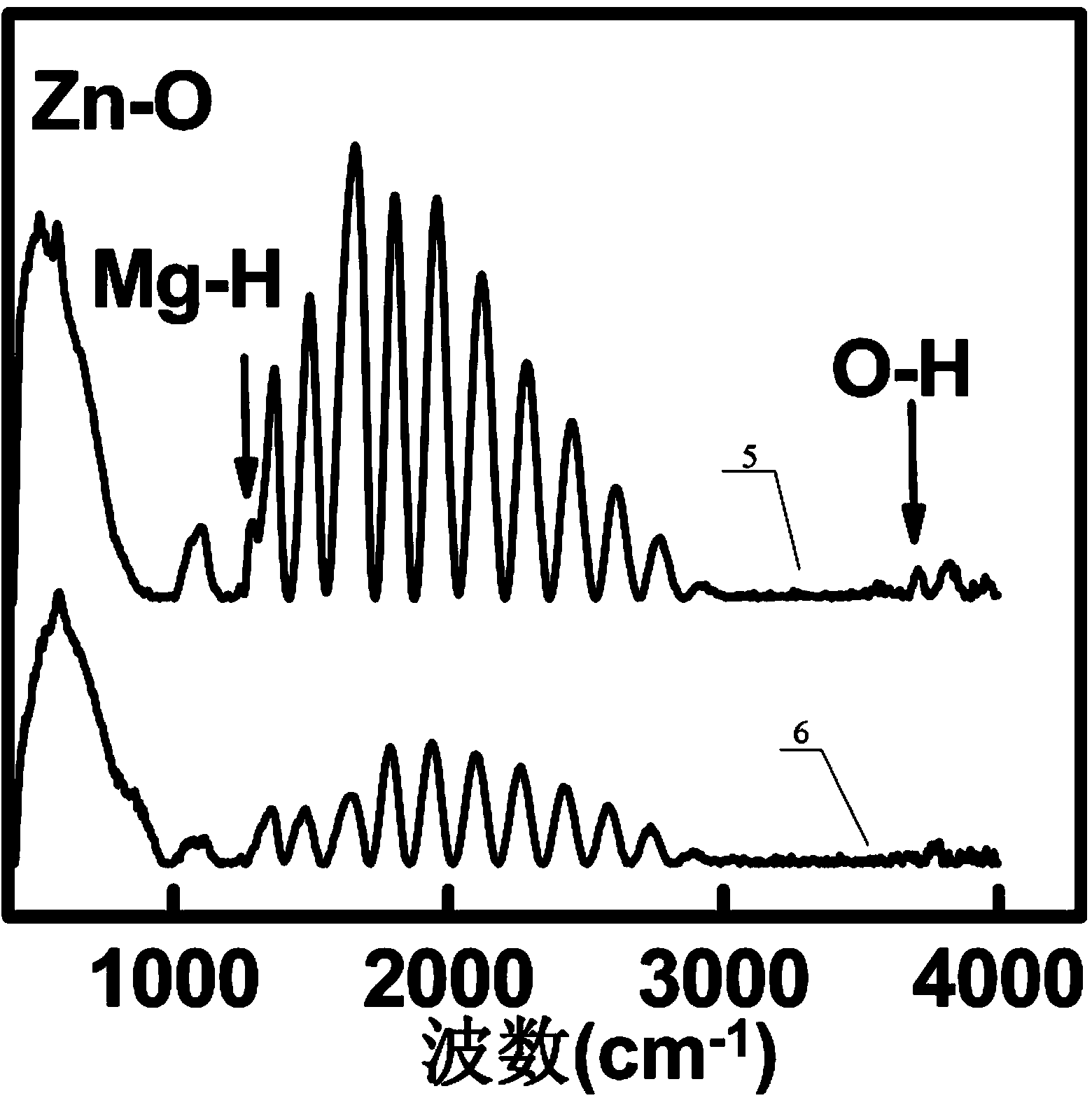
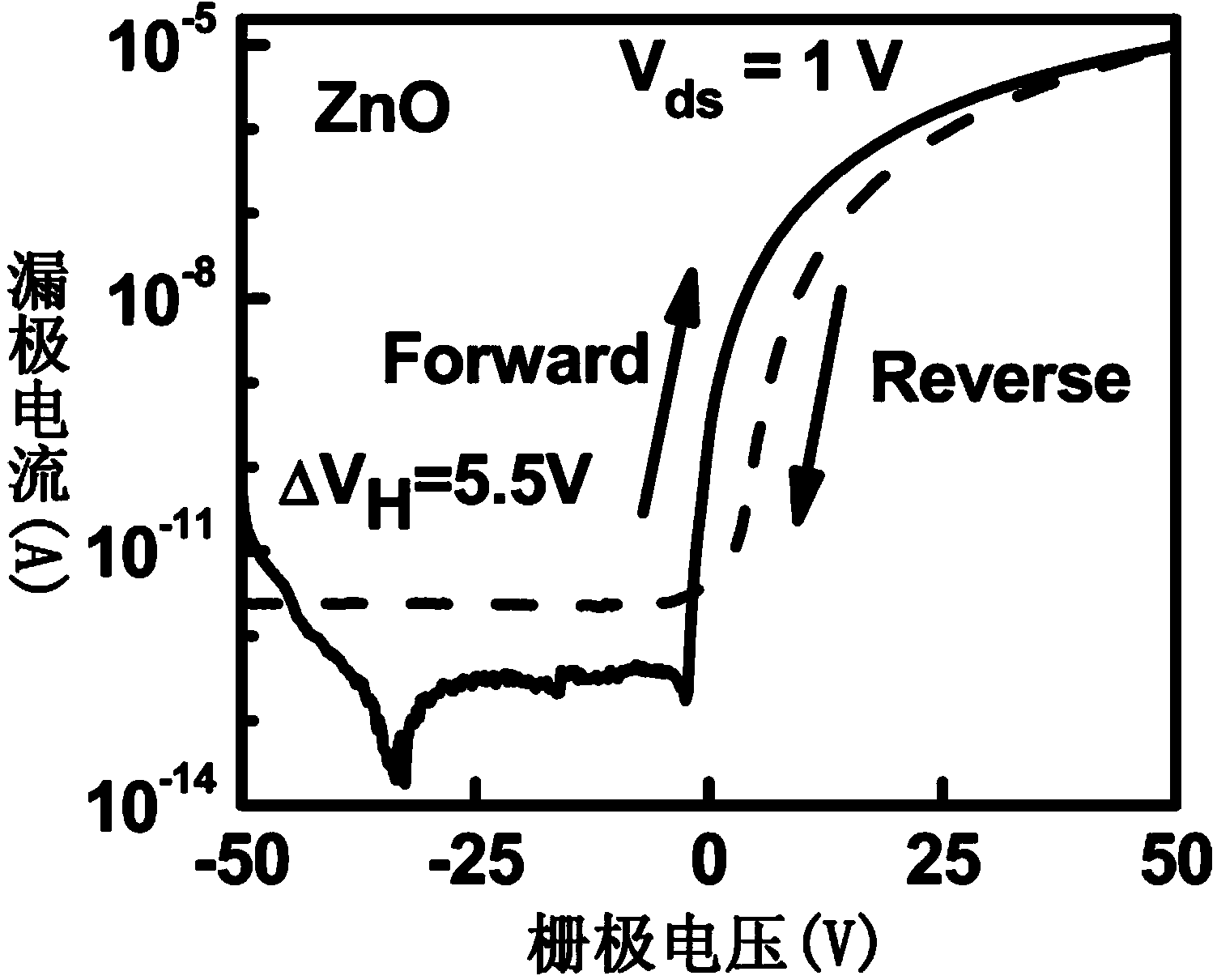
InactiveCN104037234AReduced oxygen vacanciesReduce dangling keysTransistorVacuum evaporation coatingSemiconductor materialsRadio frequency magnetron sputtering
The invention discloses a hydrogen-passivated zinc oxide-base thin film transistor. According to the hydrogen-passivated zinc oxide-base thin film transistor, a zinc oxide-base semiconductor material doped with titanium or magnesium and passivated through hydrogen plasma is used as a channel layer. A preparation method of the hydrogen-passivated zinc oxide-base thin film transistor includes the steps that a highly-doped P-type silicon wafer on which silicon dioxide grows is used as a substrate, radio frequency magnetron sputtering is conducted on a composite target of Ti and zinc oxide or Mg and zinc oxide, and meanwhile a small zinc oxide thin film layer doped with Ti or Mg is formed on the substrate through first masking deposition; in-situ hydrogen plasma processing is conducted; direct current sputtering is conducted on the zinc oxide-base thin film layer on which in-situ hydrogen plasma processing is conducted, an Al electrode is prepared through secondary masking deposition, and then the hydrogen-passivated zinc oxide-base thin film transistor is obtained. The hydrogen-passivated zinc oxide-base thin film transistor has the advantages of being high in electron mobility, good in electrical stability, high in switch ratio and the like. The preparation method is simple in process and low in cost, and threshold voltage of a device can be adjusted through hydrogen passivation time and the content of dopants.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Manufacturing method of groove MOSFET device based on microwave plasma oxidation
PendingCN112133634AImprove oxidation efficiencyReduce electronic defectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesCarbide siliconMOSFET
A manufacturing method of a groove MOSFET device based on microwave plasma oxidation comprises the step that after a groove gate is etched, silicon carbide on the surface of the groove gate is oxidized into silicon dioxide through microwave plasma to form a groove gate oxide layer. The step of forming the groove gate oxide layer comprises the steps as follows: placing a silicon carbide substrate subjected to groove gate etching in a microwave plasma generating device; introducing oxygen-containing gas to generate oxygen plasma; reacting the oxygen plasma with silicon carbide to generate silicon dioxide with a preset thickness; and stopping introducing the oxygen-containing gas, and ending the reaction; wherein the reaction temperature of the oxygen plasma and the silicon carbide is 500-900DEG C, and the reaction pressure is 400-1000 mTorr. The oxidation efficiency of silicon carbide can be remarkably improved, the interface quality is improved, and a uniform gate dielectric layer is formed.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
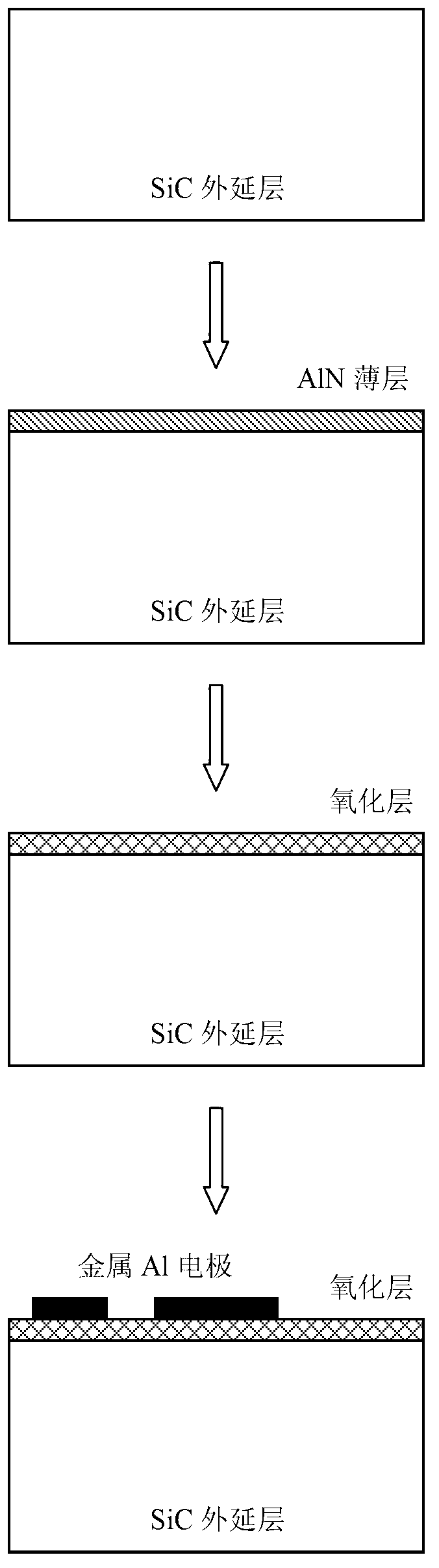
Preparation method for low excursion flat belt voltage silicon carbide (SiC) metal oxide semiconductor (MOS) capacitance
InactiveCN102842489AReduce dangling keysRelax interface stressSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOxide semiconductorCapacitance
The invention discloses a manufacturing method for a low excursion flat belt voltage silicon carbide (SiC) metal oxide semiconductor (MOS) capacitance, mainly solving the problem of higher trap density of an silicon dioxide (SiO2) / SiC interface. The manufacturing process of the low excursion flat belt voltage SiC MOS capacitance is as follows: standardly cleaning nitrogen silicon-carbide (N-SiC) epitaxial material; depositing a layer of aluminum nitride (AlN) with the thickness in a range of 1-10nm on the cleaned N-SiC epitaxial material with a molecular beam epitaxy method; dry-oxygen oxidizing a layer of SiO2 with the thickness in a range of 10-100nm on the N-SiC epitaxial material processed by the epitaxy AlN; finishing annealing and cooling in turn to the oxidized N-SiC epitaxial material in argon environment; manufacturing an electrode on the cooled N-SiC epitaxial material through vacuum sputtering aluminum, and secondarily annealing in the argon environment to finish manufacturing the whole SiC MOS capacitance. The low excursion flat belt voltage SiC MOS capacitance has the advantages of low in trap density of the SiO2 / SiC interface, small in MOS capacitance flat belt voltage excursion and simple in technology, thereby being used for improving SiO2 / SiC interfacial characterization of SiC MOS capacitance.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Nanometer silicon film cathode and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN104357800AGood repeatabilityIncrease the electric field strengthVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingDensity distributionNanometre
The invention discloses a nanometer silicon film cathode and a manufacturing method thereof. The nanometer silicon film cathode consists of a bottom electrode, a nanocrystalline silicon-containing silicon dioxide layer (nanocrystalline silicon particles are embedded into silicon dioxide) and a top electrode, which are sequentially manufactured on a substrate, wherein the nanocrystalline silicon-containing silicon dioxide layer is prepared by combining a sputtering method with a high-temperature annealing process. In a preparation process of the nanocrystalline silicon-containing silicon dioxide layer, the partial pressure ratio of argon and oxygen, which are introduced into a coating cavity, or the sputtering power of a silicon target and a silicon dioxide target is regulated to control the sizes and density distribution of the nanocrystalline silicon particles in the nanocrystalline silicon-containing silicon dioxide layer to realize the periodically changing layered distribution of the density of the nanocrystalline silicon particles with proper particle sizes in the nanocrystalline silicon-containing silicon dioxide layer. A manufacturing process for the nanometer silicon film cathode is compatible with a silicon microelectronic processing process, and stable electron emission performance is achieved.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
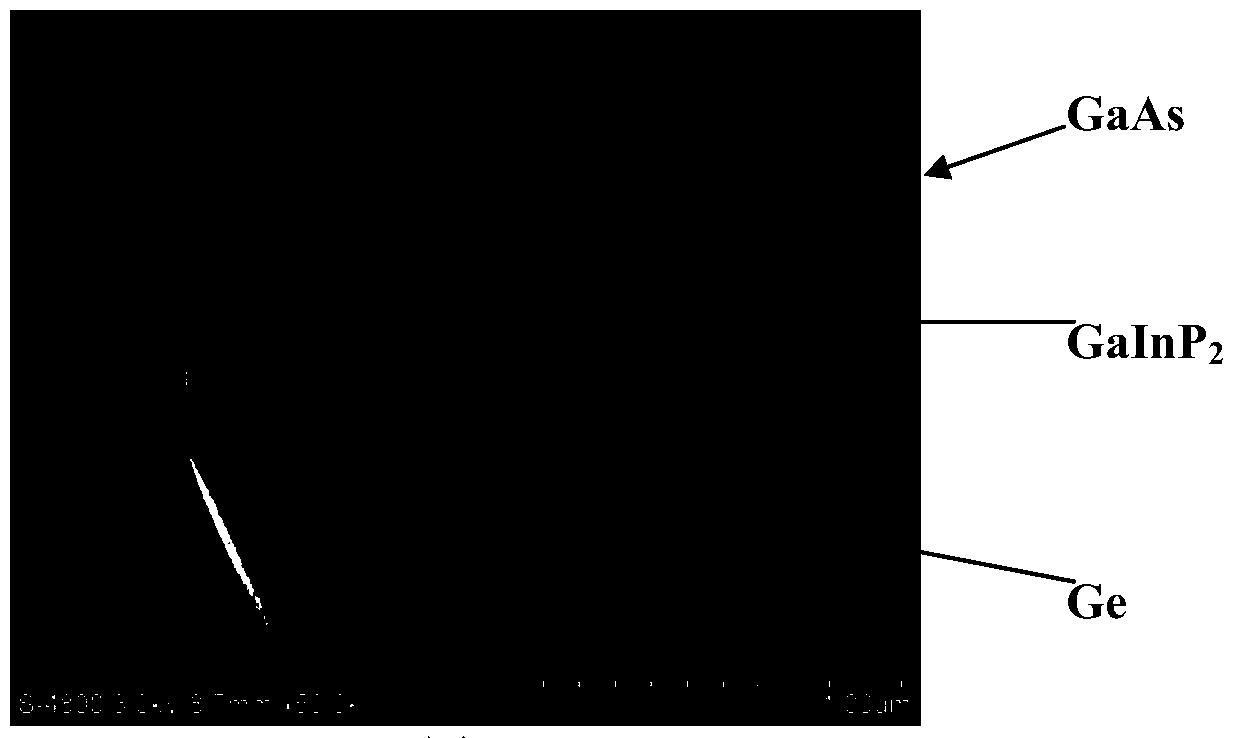
Preparation method of heterojunction thermal photovoltaic cell
ActiveCN104638060BAvoid recombinationImprove collection efficiencyFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesHeterojunctionElectrode Contact
The invention relates to a method for manufacturing hetero-junction thermal photovoltaic batteries. The method includes manufacturing procedures of sequentially growing emitting regions, electrode contact layers and upper electrodes on the upper surfaces of base regions; photoetching the upper electrodes; eroding the upper electrodes and the electrode contact layers; manufacturing optical anti-reflection layers; arranging lower electrodes on the lower surfaces of the base regions by means of vapor deposition. The base regions comprise p-Ge layers with narrow forbidden bands. N-Ga<x>In<y>P layers with wide forbidden bands are used as the emitter regions, and the thicknesses of the n-Ga<x>In<y>P layers are smaller than 500nm. The method has the advantages that the n-Ga<x>In<y>P layers with the wide forbidden bands and precisely adjustable Ga to In proportions are used as the emitter regions, p-Ge substrates with narrow forbidden bands are used as the base regions, accordingly, hetero-junction structures with the emitter regions and the base regions which are provided with precisely matched crystal lattices can be formed, Ga<x>In<y>P / Ge interface recombination can be reduced, light absorbed by the emitter regions with wide band gaps can be reduced, light absorbed by the base regions can be increased, recombination of photon-generated carriers at the type-n emitter regions and the surfaces of the type-n emitter regions can be reduced, the photon-generated carrier collection efficiency can be improved, and the photoelectric conversion efficiency of the batteries can be effectively improved.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONIC TECH GRP CORP NO 18 RES INST
Method for manufacturing silicon oxynitride gate oxide layer
ActiveCN102122614BLow densityImprove reliabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSilicon oxideDangling bond
The invention provides a method for manufacturing a silicon oxynitride gate oxide layer of an MOS (metal oxide semiconductor) device, and the method comprises the following steps: firstly nitridizing on a provided silicon substrate for forming silicon oxynitride, then performing thermal oxidization for forming a first silicon oxide layer between the silicon oxynitride and the silicon substrate and a second silicon oxide layer on the silicon oxynitride, and then depositing polysilicon on the second silicon oxide layer after secondly annealing the silicon substrate; and etching for forming a gate and the silicon oxynitride gate oxide layer. The silicon oxide layer is introduced between the silicon substrate and the silicon oxynitride, thereby reducing dangling bonds between the silicon oxynitride gate oxide layer and the silicon substrate, further reducing the interface state charge density between the silicon oxynitride gate oxide layer and the substrate and improving certain properties of the MOS device, such as improving the stability of threshold voltage of the device, reducing the hot-carrier effect and the flicker noise of the device and the like.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP +1
Method for manufacturing grooved MOSFET device on basis of two-step microwave plasma oxidation
ActiveCN108766887AImprove oxidation efficiencyReduce electronic defectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesMOSFETGate dielectric
The invention provides a method for manufacturing a grooved MOSFET device on the basis of two-step microwave plasma oxidation. The method comprises the step that after a grooved gate is etched, silicon carbide on the surface of the grooved gate is oxidized into silicon dioxide by means of microwave plasmas to form a grooved gate oxide layer. The grooved gate oxide layer is formed through the stepsthat the silicon carbide substrate after the grooved gate is etched is placed in a microwave plasma generation device; first oxygen-containing gas is introduced, the temperature of generated oxygen plasmas rises to the first temperature at a first temperature rising speed, and low-temperature plasma oxidation is conducted at the first temperature under the first pressure; the temperature of the oxygen plasmas rises to the second temperature at a second temperature rising speed, second oxygen-containing gas is introduced, and high-temperature plasma oxidation is conducted at the second temperature under the second pressure until silicon dioxide with the predetermined thickness is generated; and the oxygen-containing gas stops being introduced, and the reaction is finished. According to themethod, the oxidation efficiency of silicon carbide can be significantly improved, the interface quality is improved, and the uniform gate dielectric layer is formed.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method of storage bit and preparation method of MRAM
PendingCN111864059AReduce dangling keysImprove performanceMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsDigital storageDangling bondCritical magnetic field
The invention provides a preparation method of a storage bit and a preparation method of an MRAM. The preparation method comprises step of forming the magnetic tunnel junction, and after the step of forming the magnetic tunnel junction, the preparation method further comprises the following step of performing gas passivation treatment on the side wall of the magnetic tunnel junction to reduce dangling bonds on the surface of the side wall. According to the preparation method, passivation treatment is carried out through the gas, dangling keys on a surface of a side wall can be reduced, surfaceimpurities can be removed, and vacancies in the surface layer and on the surface can be filled, so defect density is reduced, device stability is improved, influence of etching damage on performanceparameters such as TMR is relieved, the TMR loss reduction rate, the TMR discrete value and the critical voltage discrete value of the device array can be reduced, and the critical magnetic field is improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HIKSTOR TECHOGY CO LTD
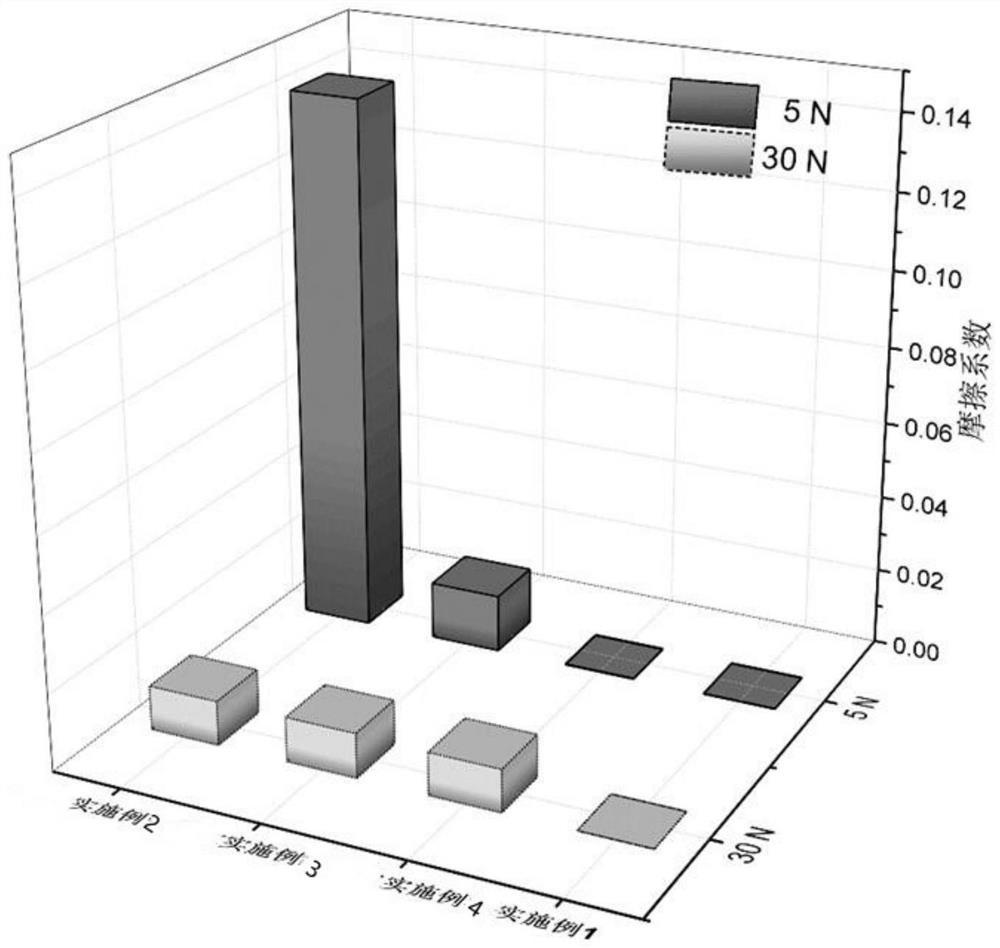
Solid self-lubricating coating and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN114351088AHigh hardnessImprove wear resistanceVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingGraphiteDiamond
The invention discloses a solid self-lubricating coating and a preparation method thereof.The coating is formed by compounding a hard diamond-like phase serving as an intrinsic supporting layer and a soft graphitization phase serving as a surface lubricating layer, the hard diamond-like phase is formed by mixing sp2 and sp3 hybrid carbon structures, and the atomic percentage content of sp3 is 25-70%; the soft graphitized phase is mainly composed of an sp2 hybrid carbon structure, the atomic percentage content of sp2 is 90% or above, and the content of a six-membered ring structure is 60% or above; the composite lubricating coating has the advantages of high hardness, high bearing capacity, low abrasion, super-lubricity and friction coefficient lt; 0.01, the solid self-lubricating coating material can provide wear-resistant lubricating protection for a matrix or a workpiece in various environments such as high load and high speed, the preparation method is simple, the operability is high, industrial production is easy, and the solid self-lubricating coating material is excellent in comprehensive performance, long in service life and high in reliability.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
Method for improving radiation resistance capability of VDMOS device
InactiveCN106783573AImprove radiation resistanceLow densityMaterial nanotechnologySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNitrogenNitrogen oxide
The invention discloses a method for improving radiation resistance capability of a VDMOS device, belongs to the technical field of manufacturing of a semiconductor. According to the method, a gate oxide layer in the VDMOS device is replaced by a three-layer-structured gate, so that the radiation resistance capability of the VDMOS device is improved; and the three-layer-structured gate consists of a nitrogen oxide layer, an oxyhydrogen synthesized oxide layer and a nitrogen oxide layer which are laminated in a recombination manner in sequence. The three-layer-structured gate oxide layer is manufactured by combination of two technologies of H<2>-O<2> synthesis and nitrogen gate oxide and by making the best of the two parties. Compared with conventional oxidization and H<2>-O<2> synthesis and oxidization, the radiation resistance capability of the VDMOS device can be improved by adoption of the method.
Owner:NO 47 INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP
Method for manufacturing semiconductor integrated circuit
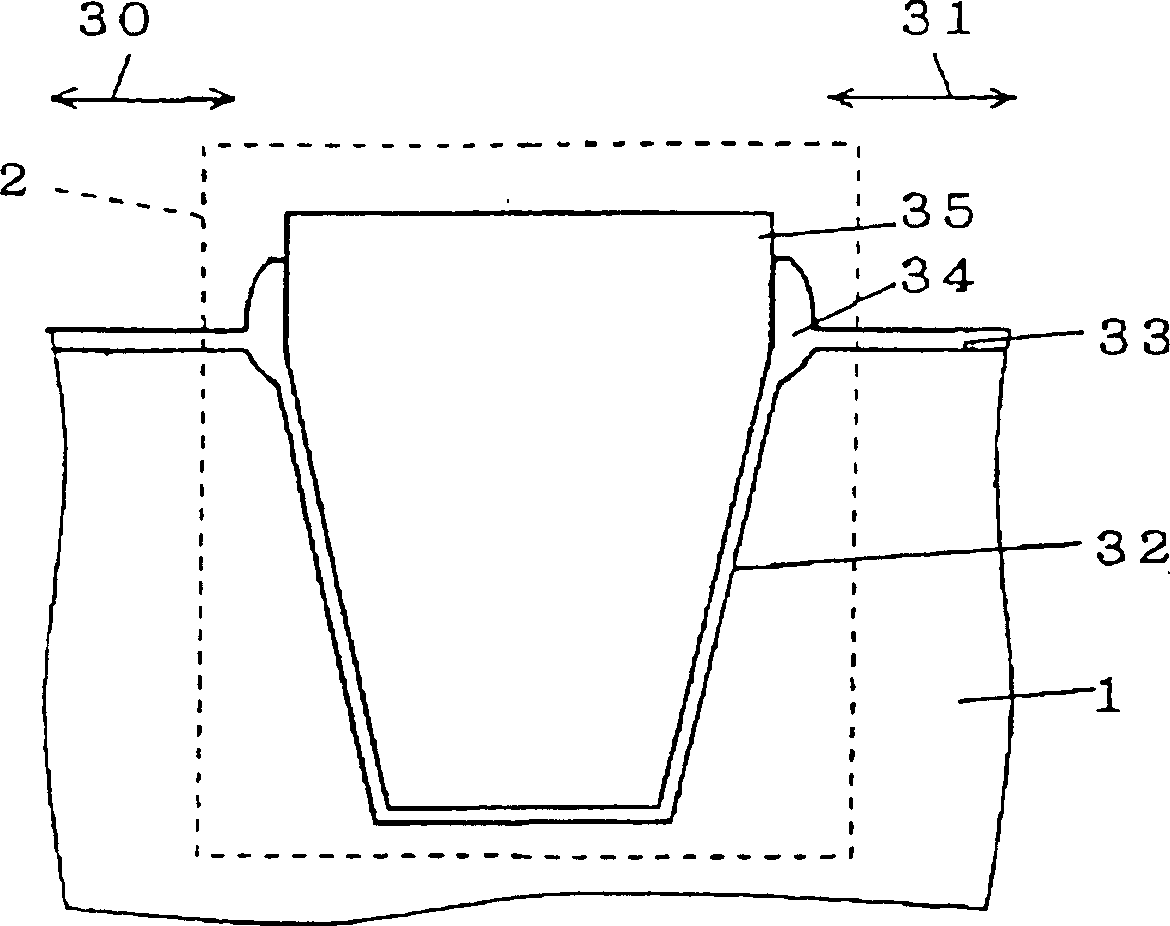
InactiveCN1134059CReduce leakage currentImprove separation characteristicsTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSemiconductorIntegrated circuit
Isolation characteristics of an isolation trench can be enhanced. Elements to be isolated by an isolation trench (STI 2) are formed in active semiconductor regions shown by arrows 30 and 31 on a semiconductor substrate 1. The STI 2 is filled with SiOF.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Semiconductor device and method of forming the same
ActiveCN109148577BImprove reliabilityGood shape consistencySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDevice materialEngineering
A semiconductor device and a method for forming the same, wherein the method includes: providing a substrate with several fins on the substrate; forming an initial doping region and a dielectric layer, the initial doping regions are respectively located in the several fins, and initially The doped region includes a bottom region and a top region located on the bottom region, the dielectric layer covers the fin, the initial doped region and the substrate; a trench penetrating through the dielectric layer is formed in the dielectric layer, and the initially doped region is located in the trench bottom, and the trench exposes the top region; etching removes the top region at the bottom of the trench, so that the bottom region forms a doped region. The method improves the shape consistency of the top surface of the doped region in different fins at the bottom of the groove, and improves the reliability of the semiconductor device.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP +1
CMOS transistor and manufacturing method thereof
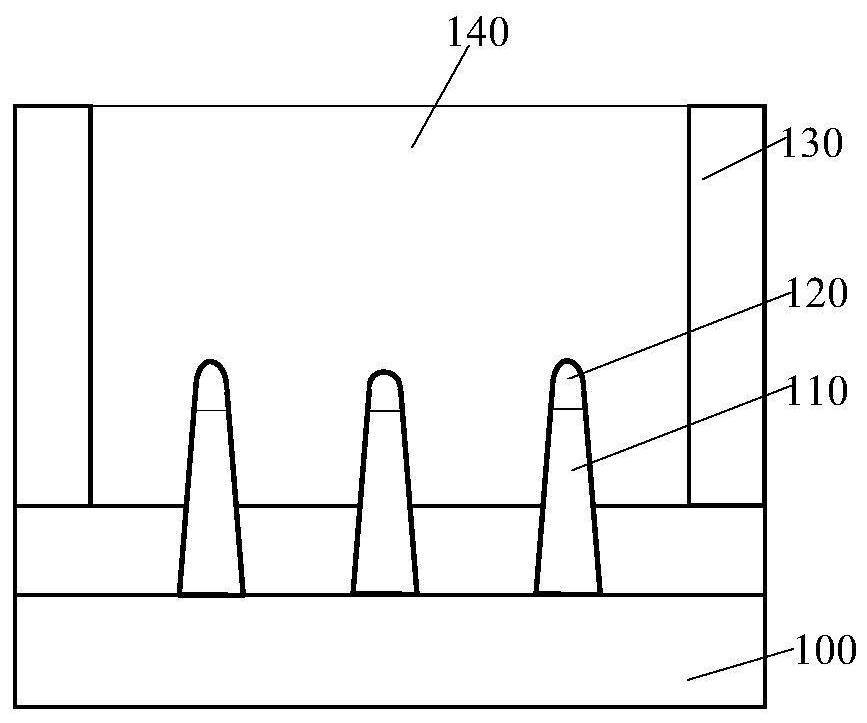
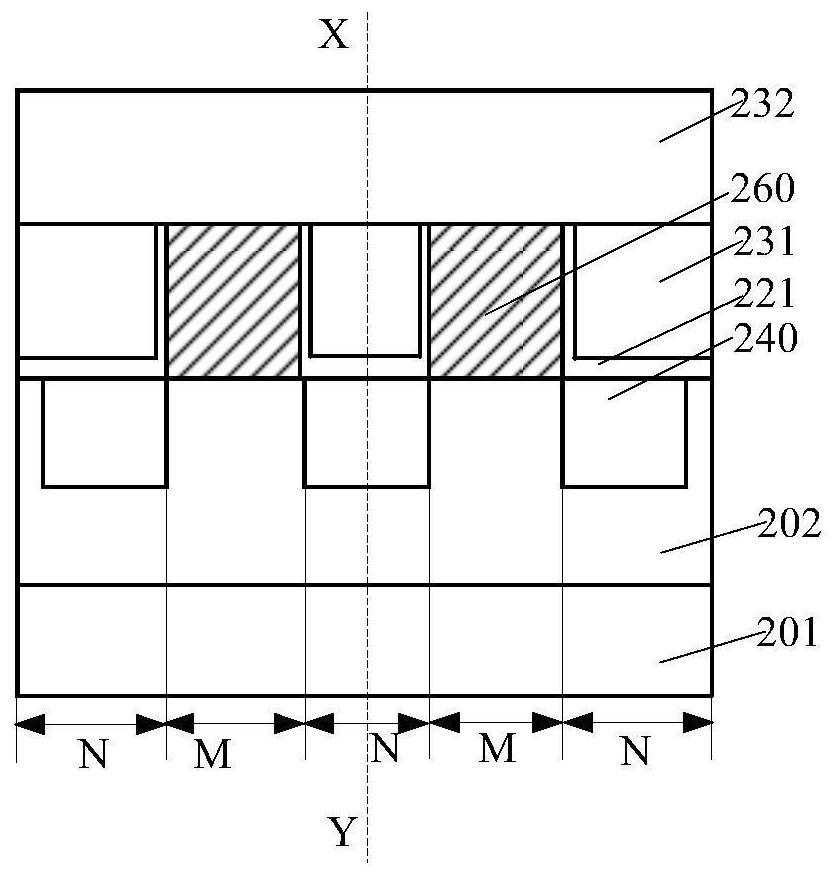
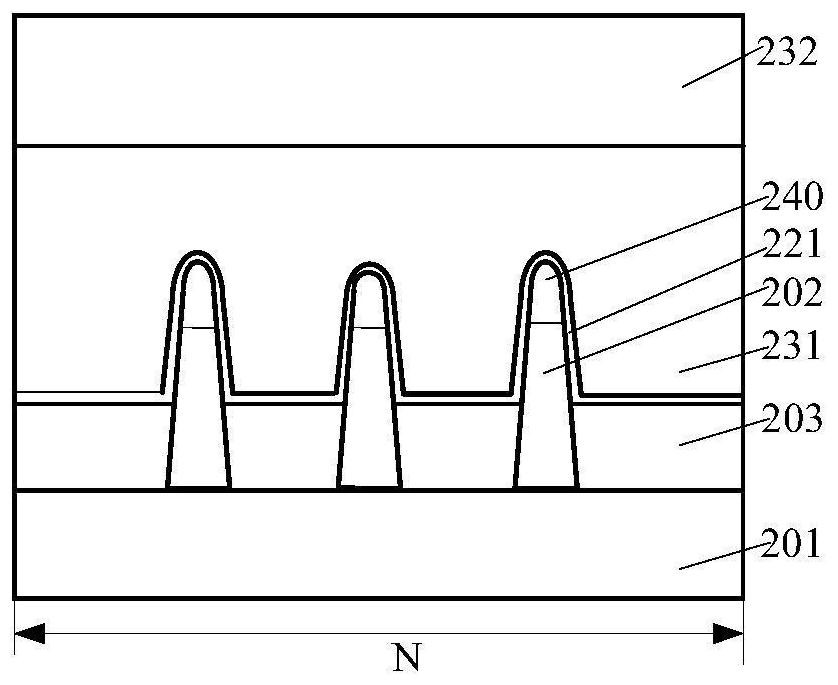
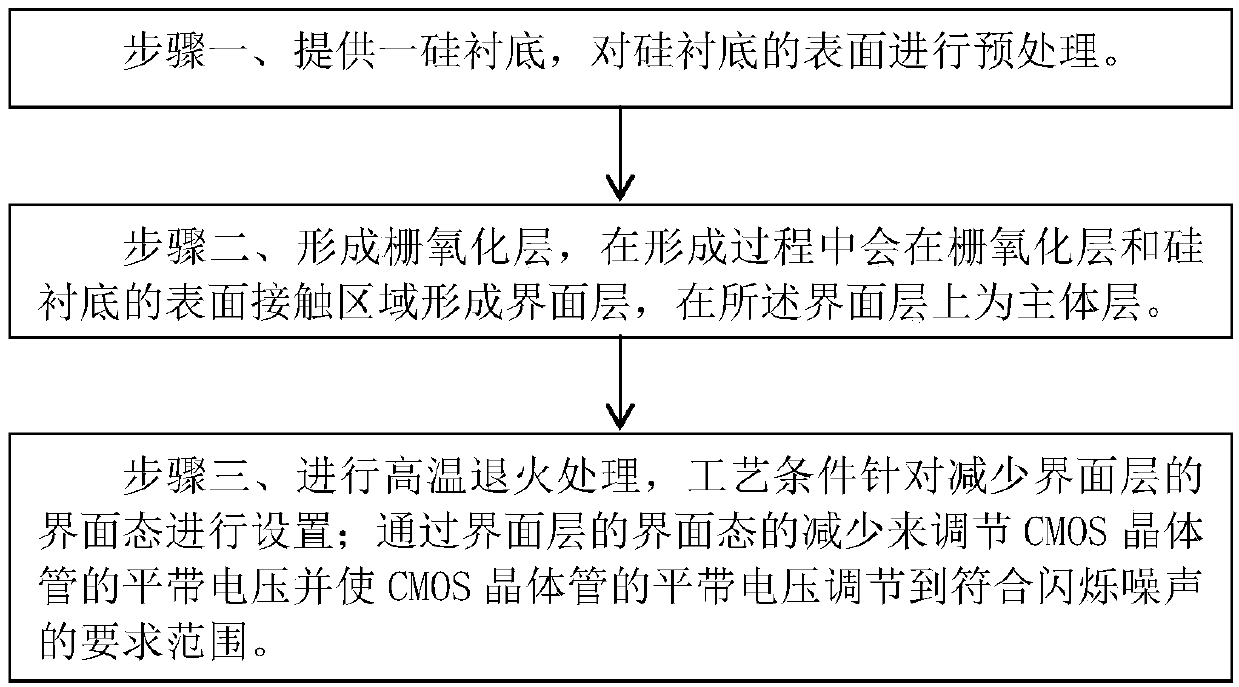
InactiveCN109545848AIncrease the value of xReduce dangling keysSemiconductor devicesCMOSInterface layer
The invention discloses a CMOS transistor, which comprises a gate oxide layer formed on the surface of a silicon substrate. The gate oxide layer comprises an interface layer formed on the surface of the silicon substrate and a main layer located on the interface layer. The interface layer has a SiOx structure, wherein x is between 1 and 2. The main layer includes a SiO2 layer. Before the formationof the interface layer, the surface of the silicon substrate has a pretreated structure for reducing the interface state of the interface layer. After the formation of the gate oxide layer, the interface layer is annealed at high temperature to reduce the interface state of the interface layer. The flat-band voltage of the CMOS transistor is adjusted by reducing the interface state of the interface layer, and the flat-band voltage of the CMOS transistor is adjusted to a range required for scintillation noise. The invention further discloses a manufacturing method of the CMOS transistor. The interface state of the gate oxide layer can be reduced and controlled, and therefore, the scintillation noise of the device can be reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUALI INTEGRATED CIRCUTE MFG CO LTD
Sulfur halogen glass and its production for superfast light switch
A sulfur halogen glass for ultra-fast photo-switch and its production are disclosed. The sulfur halogen glass consists of In2S3 20í½35mol, MX 25í½40mol, As2S3 4í½10mol and GeS2 20-50mol. MX is mixture of any one kind or two kinds and above. It has better quality and glass forming ability, less consumption and larger linear optical refractive index.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com