Method for degrading pesticide residues on fruit and vegetables
A technology for pesticide residues and fruits and vegetables, which is applied in the field of degrading pesticide residues in fruits and vegetables, can solve the problems of little application value, unfavorable storage of fruits and vegetables, and little effect of removing pesticide residues, and achieves short time consumption, easy decomposition, and low degradation cost. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
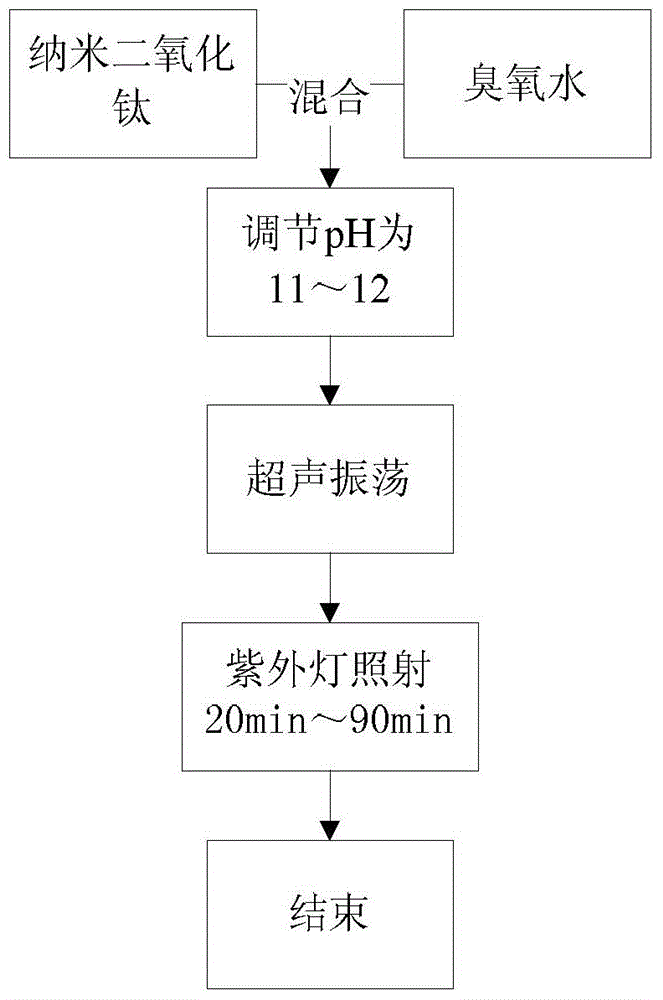
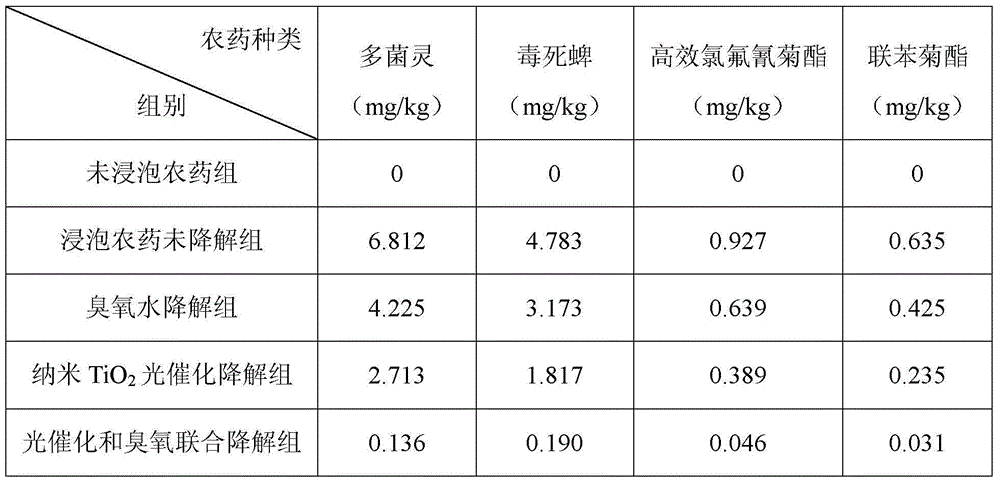
[0041] Preparation stage: Dissolve carbendazim, chlorpyrifos, cyhalothrin, and bifenthrin in 10L of water to obtain a mixed pesticide solution, including carbendazim, chlorpyrifos, cyhalothrin, and bifenthrin The concentration is 10ppm. Select 36 organic citrus with basically the same shape and size, and divide them into 6 parts on average. 1 part of unsoaked citrus is used as the control group, and the remaining 5 parts of citrus are placed in the mixed pesticide solution and soaked for 15 minutes, then taken out and dried in the shade, and then 4 parts are selected. As the experimental group, 1 as the control group.
[0042] Experimental stage:
[0043] 1. Mixing: Take 15L of ozone water with a concentration of 35mg / L from the high-concentration ozone generator and put it into the degradation device, add 7.5g nano-titanium dioxide (the particle size of nano-titanium dioxide is 30nm, and the kind is anatase), so that The concentration of nano titanium dioxide is 0.5mg / mL. ...
Embodiment 2
[0050] Preparation stage: Dissolve carbendazim, chlorpyrifos, cyhalothrin, and bifenthrin in 10L of water to obtain a mixed pesticide solution, including carbendazim, chlorpyrifos, cyhalothrin, and bifenthrin The concentration is 20ppm. Select 36 organic citrus with basically the same shape and size, and divide them into 6 parts on average. 1 part of unsoaked citrus is used as the control group, and the remaining 5 parts of citrus are completely soaked in the mixed pesticide solution for 25 minutes, then taken out and dried in the shade, and 4 parts are selected immediately. As the experimental group, 1 as the control group.
[0051] Experimental stage:
[0052] 1. Mixing: Take 15L of ozone water with a concentration of 65mg / L from the high-concentration ozone generating device and put it into the degradation device, add 12g of nano-titanium dioxide (the particle size of nano-titanium dioxide is 30nm, and the variety is anatase) to make the nano-titanium dioxide The concentr...
Embodiment 3
[0059] Preparation stage: Dissolve carbendazim, chlorpyrifos, cyhalothrin, and bifenthrin in 10L of water to obtain a mixed pesticide solution, including carbendazim, chlorpyrifos, cyhalothrin, and bifenthrin The concentration is 5ppm. Select 36 organic citrus with basically the same shape and size, and divide them into 6 parts on average. 1 part of unsoaked citrus is used as the control group, and the remaining 5 parts of citrus are completely soaked in the mixed pesticide solution for 25 minutes, then taken out and dried in the shade, and 4 parts are selected immediately. As the experimental group, 1 as the control group.
[0060] Experimental stage:
[0061] 1. Mixing: Take 15L of ozone water with a concentration of 30mg / L from the high-concentration ozone generator and put it into the degradation device, add 3.75g of nano-titanium dioxide (the particle size of nano-titanium dioxide is 50nm, and the kind is anatase), so that The concentration of nano titanium dioxide is 0...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com