Protein for controlling rice leaf morphology and root hair development, and coding gene and application thereof
A gene and rice technology, which is applied to the protein that controls rice leaf shape and root hair development and its coding gene and application field, can solve the problem of not discovering the function and regulation mechanism of Aux/IAA protein, and achieve the effect of enriching genetic diversity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] Example 1: Phenotypic and genetic analysis of mutant dnl1
[0044] 1. Phenotypic analysis of mutant dnl1
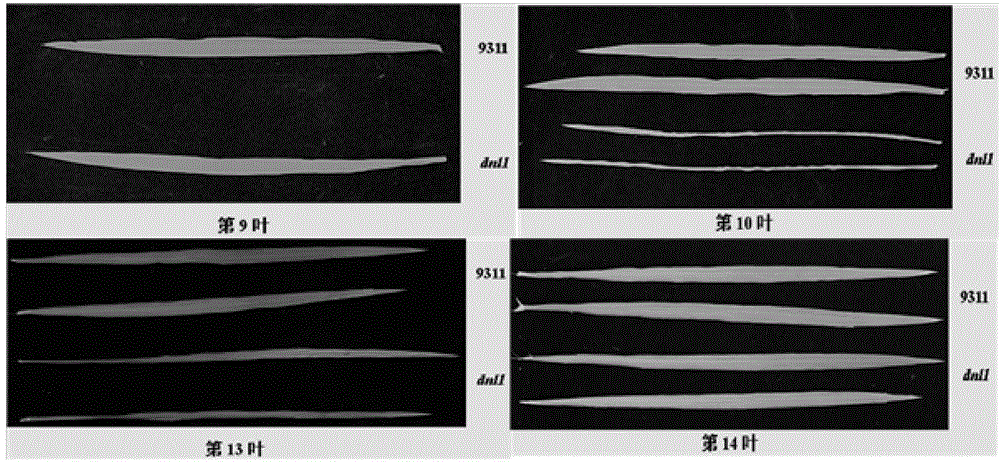
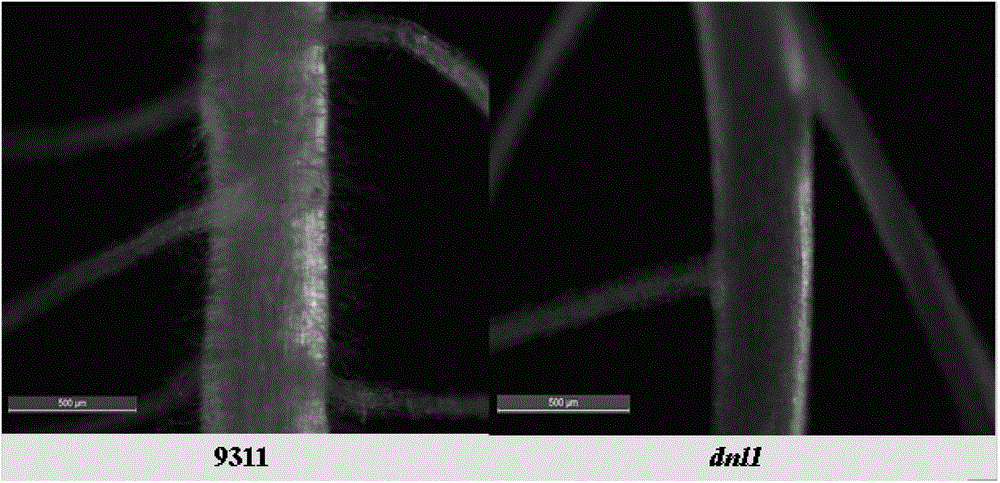
[0045] Indica rice 93-11 was irradiated to obtain a mutant with stunted leaves and plants in the seedling stage but tended to be normal in the later stage, tentatively named as the dynamic narrowleaf mutant dnl1 (dynamic narrowleaf 1). changed, but narrowed significantly in mid-growth, and the leaves returned to normal in later stages ( figure 1 ). In addition, the mutant has shorter plant height, shorter internodes, shorter panicle length, fewer secondary branches, fewer seeds, and significantly lower seed setting rate. The growth period is delayed by about 7-10 days. Characterized by various aspects of dysplasia. In addition, the root growth and development of dnl1 were significantly inhibited, which showed that under hydroponic conditions, the number of lateral roots and root hairs of plants after 14 days were significantly and extremely significantly differe...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Example 2: Acquisition of DNL1 protein and its encoding gene DNL1
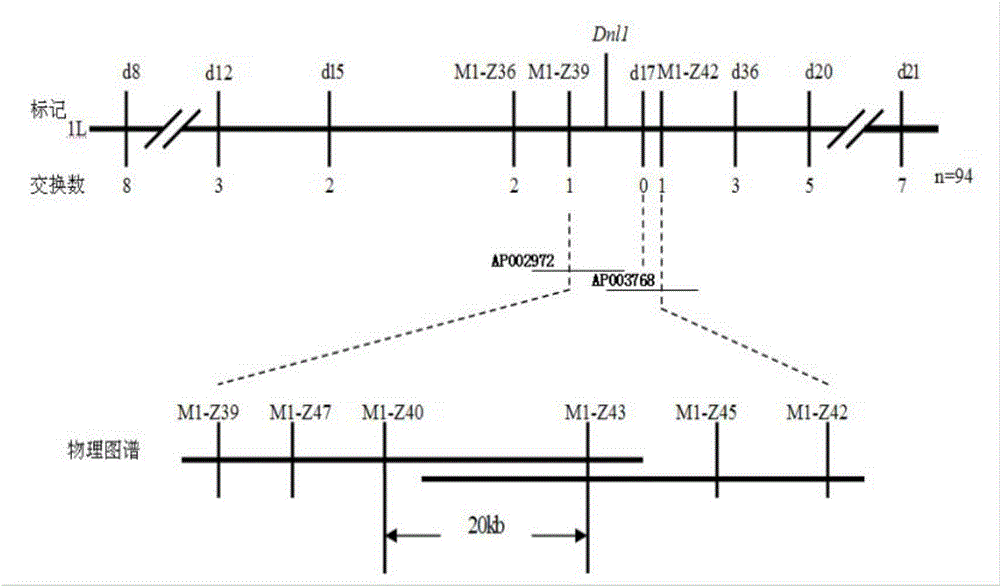
[0049] About 400 pairs of SSR markers were used to analyze the polymorphism of dnl1 and Wuyunjing 8. Among them, 103 pairs of markers revealed the polymorphism of the two parents. These 103 pairs of markers were used to analyze the F gene produced by the cross between dnl1 and Wuyunjing 8. 2 The linkage analysis was carried out in a small population consisting of 10 typical dynamic narrow-leaf individual plants. The results showed that the microsatellite markers RM9 and RM302 on chromosome 1 were linked to the dynamic narrow-leaf trait. Furthermore, using the SSR and STS (previously designed) markers that show polymorphism between the two parents on chromosome 1, the F 2 A population of 94 dynamic narrow-leaf plants was analyzed. The linkage group of the region where the DNL1 gene is located was constructed by MAPMAKEER3.0 software, and the DNL1 gene was preliminarily located between the STS markers d1...
Embodiment 3
[0055] Example 3: Complementation assay of the dnl1 phenotype of the narrow-leaf mutant
[0056] 1. Construction of complementary vector pDNL1
[0057] Analysis of the restriction site of the BAC clone covering the DNL1 gene shows that the BAC clone (from Nipponbare) can be cut with Kpn I and Xba I double restriction enzymes to obtain a fragment containing the full-length DNL1 gene, so a pair of primers are designed. Kpn I and Xba I linkers were added to the 5' end to amplify DNL1 gene upstream (before the start codon) 2.2kb, downstream (after the stop codon) 1.5kb, the total length of the fragment of 5.9kb, ligated to the corresponding enzyme of the vector pCAMBIA1301 in the cut point. Select positive clones to extract plasmid DNA to form complementary vector pDNL1.
[0058] Complementary fragment primer:
[0059] DNLKpnF 5'-GGACTGGTACCTTCCAATCTGAAAGGAGGGAGGGGG-3' (SEQ ID NO. 33)
[0060] DNLXbaR 5'-CCTCATCTAGAGACCTTTCCTTTGTCCCCAGTT-3' (SEQ ID NO. 34)
[0061] The Kpn I ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com