Method for detecting deletion mutation of nucleic acid molecule
A technology for nucleic acid molecules and deletion mutations, which is applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbiological determination/inspection, etc., and can solve the problems of PCR product contamination, multiple operation steps, false positives, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
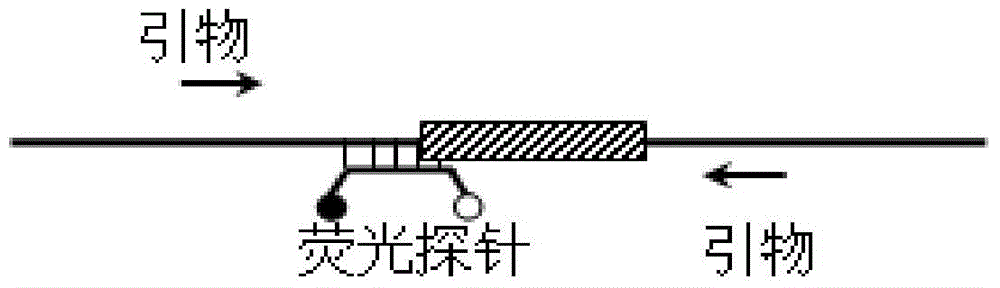
[0124] Example 1: The self-quenching fluorescent probe melting curve analysis method is used for the detection of short-segment (tens of bases) gene deletions.
[0125] In this example, taking the detection of the 16 bp deletion c.176-191del16 in the gap junction protein-encoding gene (GJB2 gene) (NCBI sequence number NC_000013.11) as an example, a fluorescent probe P1 and a pair of primers F1 and R1, the double-stranded hybrid formed by the hybridization of the fluorescent probe with the gene fragment before and after the deletion can form different melting points (there are 4 bases at the 3′ end of the probe that are complementary to the wild-type nucleic acid molecule, but not complementary to the nucleic acid molecule with the deletion mutation) , based on which the genotype of the sample can be determined. The probe and primer sequences used are:
[0126] P1:5′-HEX-CAGCAACACCCTGCAGCCAG GCTG -BHQ1-3' (SEQ ID NO: 1), where the underlined part indicates the 4 bases with d...
Embodiment 2
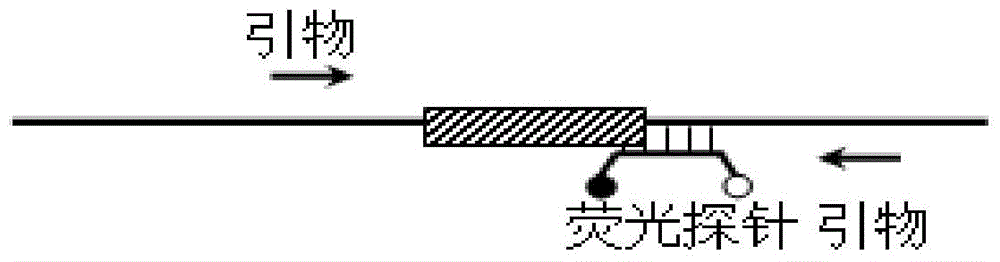
[0132] Example 2: The self-quenching fluorescent probe melting curve analysis method is used for the detection of gene deletions with medium fragment length (hundreds of bases).
[0133] This example takes the β-globin gene (HBB gene, NCBI reference sequence number is NG_000007.3) 619bp gene deletion Del619 (deletion position is g.71609-72227) as an example, and designs a fluorescent probe for this type of gene deletion P2 and primer sets F2, R2 and R3, the double-stranded hybrids formed by the hybridization of the fluorescent probes with the gene fragments before and after the deletion can form different melting points (6 bases at the 3′ end of the probe are complementary to the wild-type nucleic acid molecule, and the presence of The nucleic acid molecule of the deletion mutation is not complementary), based on which the genotype of the sample can be judged. The probe and primer sequences used are:
[0134] P2: 5′-ROX-CCGCATATAAATATTTCTGCATATAAATTGTAAC TGATGT GG-BHQ2-3' (...
Embodiment 3
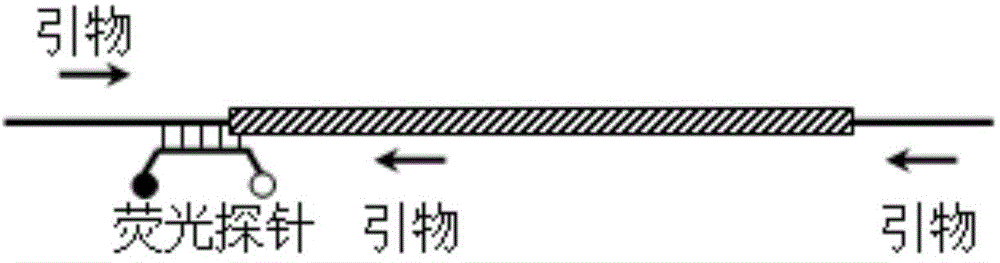
[0141] Example 3: The melting curve analysis method of self-quenching fluorescent probe is used for large gene deletion.
[0142] In this example, the Southeast Asian deletion type (-- SEA ) (deletion position is g.26264-45564) as an example, design a fluorescent probe P3 and primer set F3, R4 and R5 for this type of gene deletion, and the double-stranded hybrid formed by hybridization between the fluorescent probe and the gene fragment before and after the deletion can be Different melting points are formed (4 bases at the 3' end of the probe are complementary to the wild-type nucleic acid molecule, and not complementary to the nucleic acid molecule with deletion mutation), based on which the genotype of the sample can be judged.
[0143] The probe and primer sequences used are:
[0144] P3:5′-FAM-CGCCTTGGGGAGGTTC TAGC -BHQ1-3' (SEQ ID NO: 8), where the underlined part indicates the 4 bases with differences in matching;
[0145] F3: 5'-CCGTCCGACTCAAGGAC-3' (SEQ ID NO: 9);...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com