A method for removing chloride ions from hydrometallurgy zinc leaching solution
A technology of hydrometallurgy and leaching solution, which is applied in the direction of improving process efficiency, can solve problems such as rising production costs, and achieve the effects of low cost, extensive promotion value, and short process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
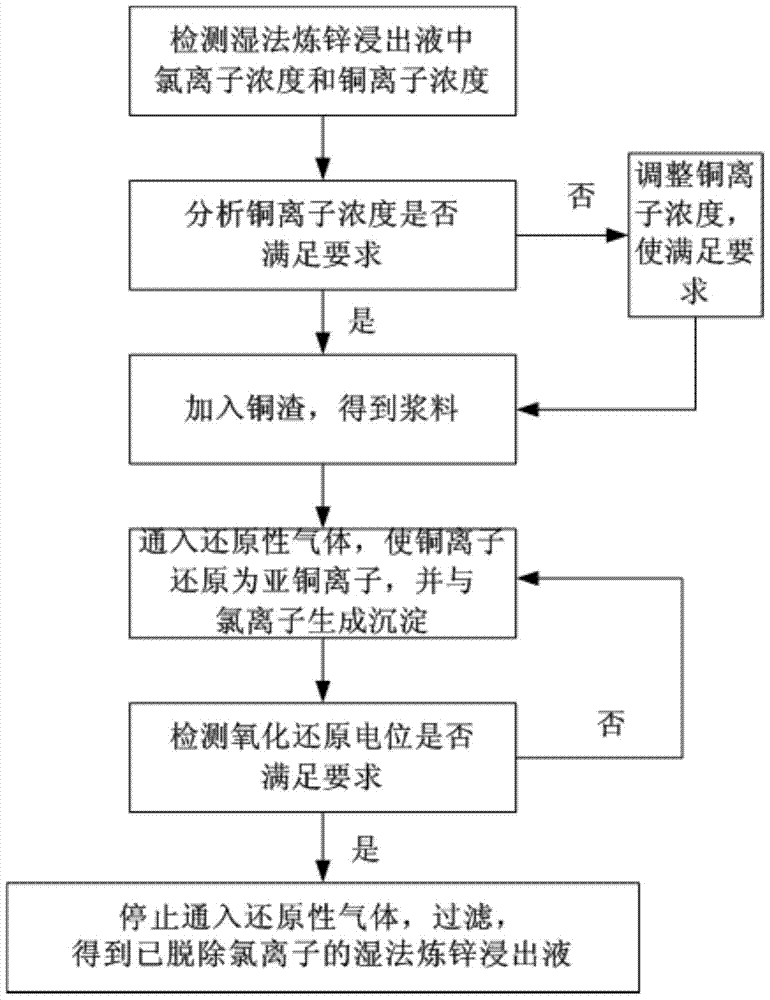
[0026] combine figure 1 , the present embodiment removes the method for chloride ion from hydrometallurgy zinc leaching liquid and comprises the following steps:
[0027] Step 1, respectively detecting the concentration of chloride ions and the concentration of copper ions in the zinc hydrometallurgy leaching solution, the concentration of recorded chloride ions is C1, the concentration of copper ions is C2, and the units of C1 and C2 are mg / L;
[0028] In this embodiment, take 1L of zinc hydrometallurgy leaching liquid, measure C1=1346mg / L, C2=820mg / L;
[0029] Step 2. Analyze the concentration C2 of copper ions measured in step 1. If C2 satisfies C2 ≥ 1.7C1, then enter step 3; Adjust to C3 so that C3 satisfies C3:C1=(1.7~5.0):1, and then enter step three; the unit of C3 is mg / L;
[0030] After analysis, C2 in this example does not satisfy C2≥1.7C1, therefore, the concentration of copper ions in the hydrometallurgy leachate is adjusted to C3=2334mg / L by adding copper sulfat...
Embodiment 2
[0036] combine figure 1 , the present embodiment removes the method for chloride ion from hydrometallurgy zinc leaching liquid and comprises the following steps:
[0037] Step 1, respectively detecting the concentration of chloride ions and the concentration of copper ions in the zinc hydrometallurgy leaching solution, the concentration of recorded chloride ions is C1, the concentration of copper ions is C2, and the units of C1 and C2 are mg / L;
[0038] In this embodiment, take 1L of wet-process zinc leaching solution, and measure C1=1152mg / L, C2=774mg / L;
[0039] Step 2. Analyze the concentration C2 of copper ions measured in step 1. If C2 satisfies C2 ≥ 1.7C1, then enter step 3; Adjust to C3 so that C3 satisfies C3:C1=(1.7~5.0):1, and then enter step three; the unit of C3 is mg / L;
[0040] After analysis, C2 in this example does not satisfy C2≥1.7C1, therefore, the concentration of copper ions in the zinc hydrometallurgy leaching solution is adjusted to C3=1913mg / L by addi...
Embodiment 3
[0046] combine figure 1 , the present embodiment removes the method for chloride ion from hydrometallurgy zinc leaching liquid and comprises the following steps:
[0047] Step 1, respectively detecting the concentration of chloride ions and the concentration of copper ions in the zinc hydrometallurgy leaching solution, the concentration of recorded chloride ions is C1, the concentration of copper ions is C2, and the units of C1 and C2 are mg / L;
[0048] In this embodiment, take 1L of zinc hydrometallurgy leaching solution, and measure C1=906mg / L, C2=861mg / L;
[0049] Step 2. Analyze the concentration C2 of copper ions measured in step 1. If C2 satisfies C2 ≥ 1.7C1, then enter step 3; Adjust to C3 so that C3 satisfies C3:C1=(1.7~5.0):1, and then enter step three; the unit of C3 is mg / L;
[0050] After analysis, C2 in this example does not satisfy C2 ≥ 1.7C1, therefore, the concentration of copper ions in the zinc hydrometallurgy leaching solution is adjusted to C3=1812mg / L by...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com