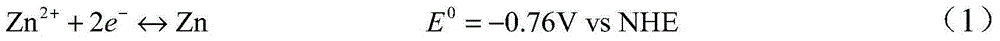Patents
Literature
124 results about "Zinc electrowinning" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
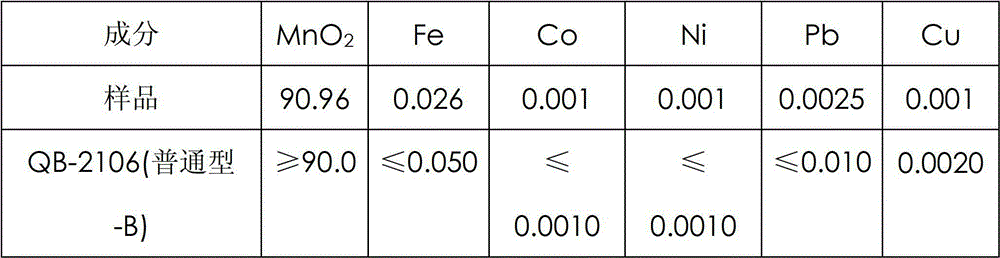
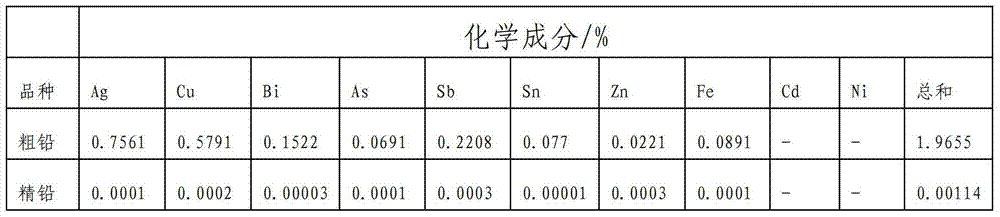
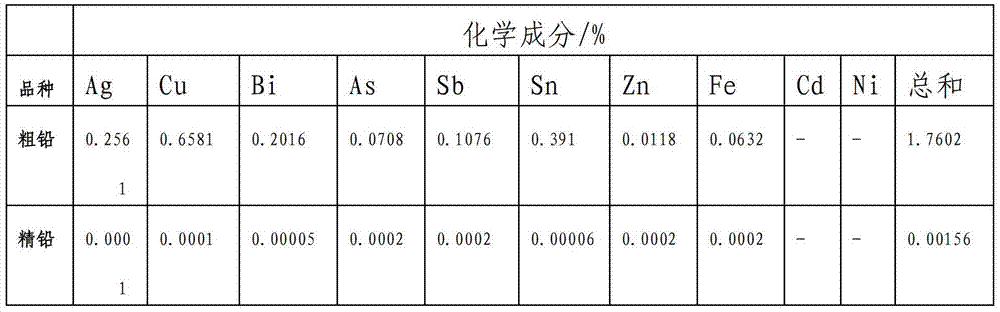
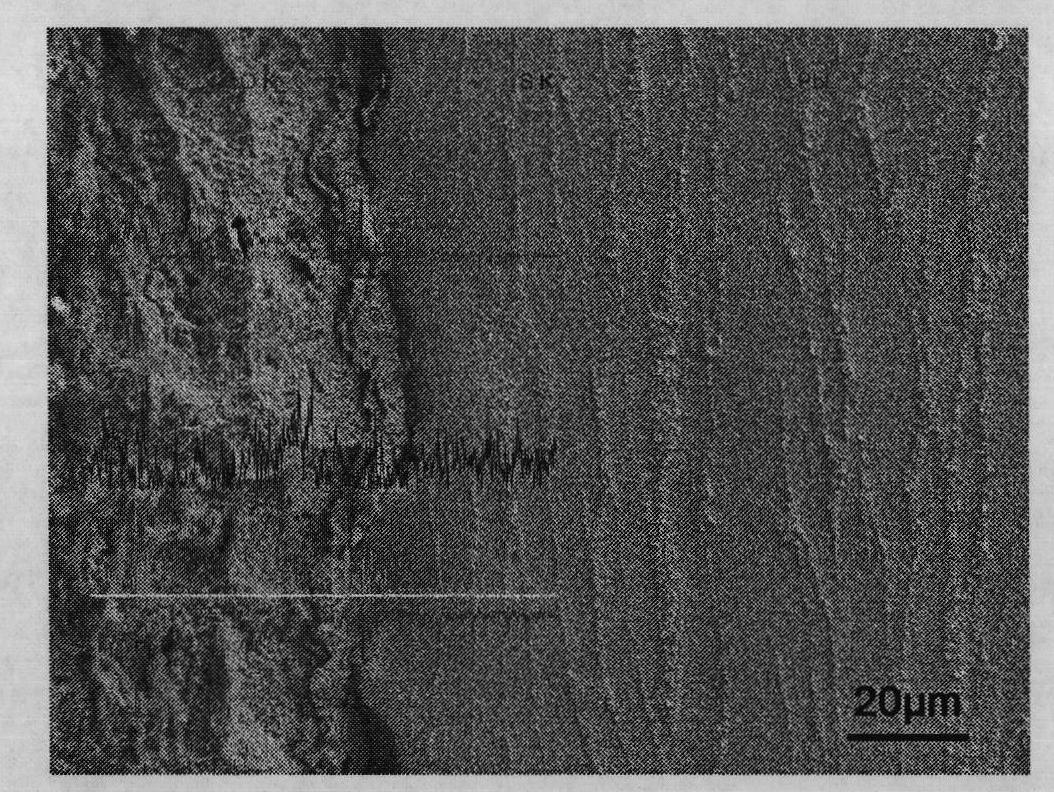
The electrolyte in cells for zinc electrowinning is essentially a solution of zinc sulfate containing approximately 200 to 700 grams per liter of zinc sulfate. These concentrations are illustrative, and the present invention can be practiced with greater or lesser concentrations.
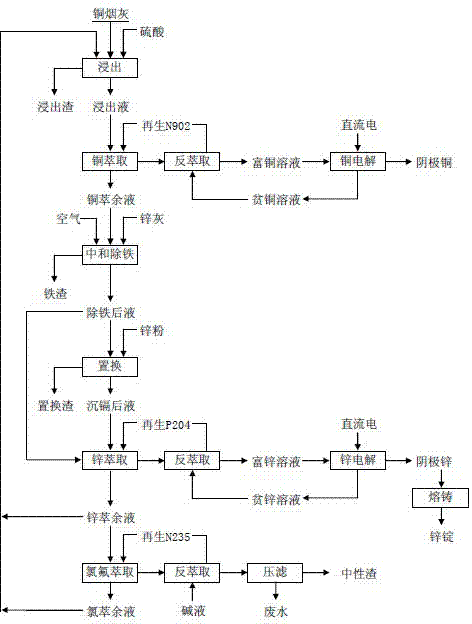
Technology for recovering production of electrolytic copper and zinc from smelting ash
ActiveCN102851693AWide adaptabilityFlexiblePhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementElectrolysisCopper oxide
The invention discloses a technology for recovering production of electrolytic copper and zinc from smelting ash. The technology comprises a step of smelting ash leaching, a step of copper extraction and purification through copper electrodeposition, a step of iron removal through neutralization, a step of cadmium removal, and a step of zinc extraction and purification through zinc electrodeposition. The method is characterized in that chemical components in the smelting ash are analyzed, and the smelting ash is leached by a sulfuric acid solution leaching agent; the leachate obtained after the above leaching reaction undergoes a separation operation of copper extraction and purification through the copper electrodeposition; the resultant copper extraction liquor is neutralized by high-zinc dust which is a neutralizer to remove iron; cadmium is displaced and deposited by zinc powder having a mass same with cadmium after the iron removal through the neutralization; and the zinc extraction is carried out through the zinc electrodeposition by casting zinc ingot products. The technology has a wide adaptability, adopts two steps to complete the exchange reaction of zinc oxide and copper oxide in the raw material with an acid, and adopts the high-zinc dust as the neutralizer, so the massive zinc loss caused by entrainment of routine neutralizers comprising calcium oxide and sodium hydroxide is avoided. A zinc extraction liquor obtained in the above step is purified by N235, so economy and effectiveness are realized.
Owner:江西自立环保科技有限公司
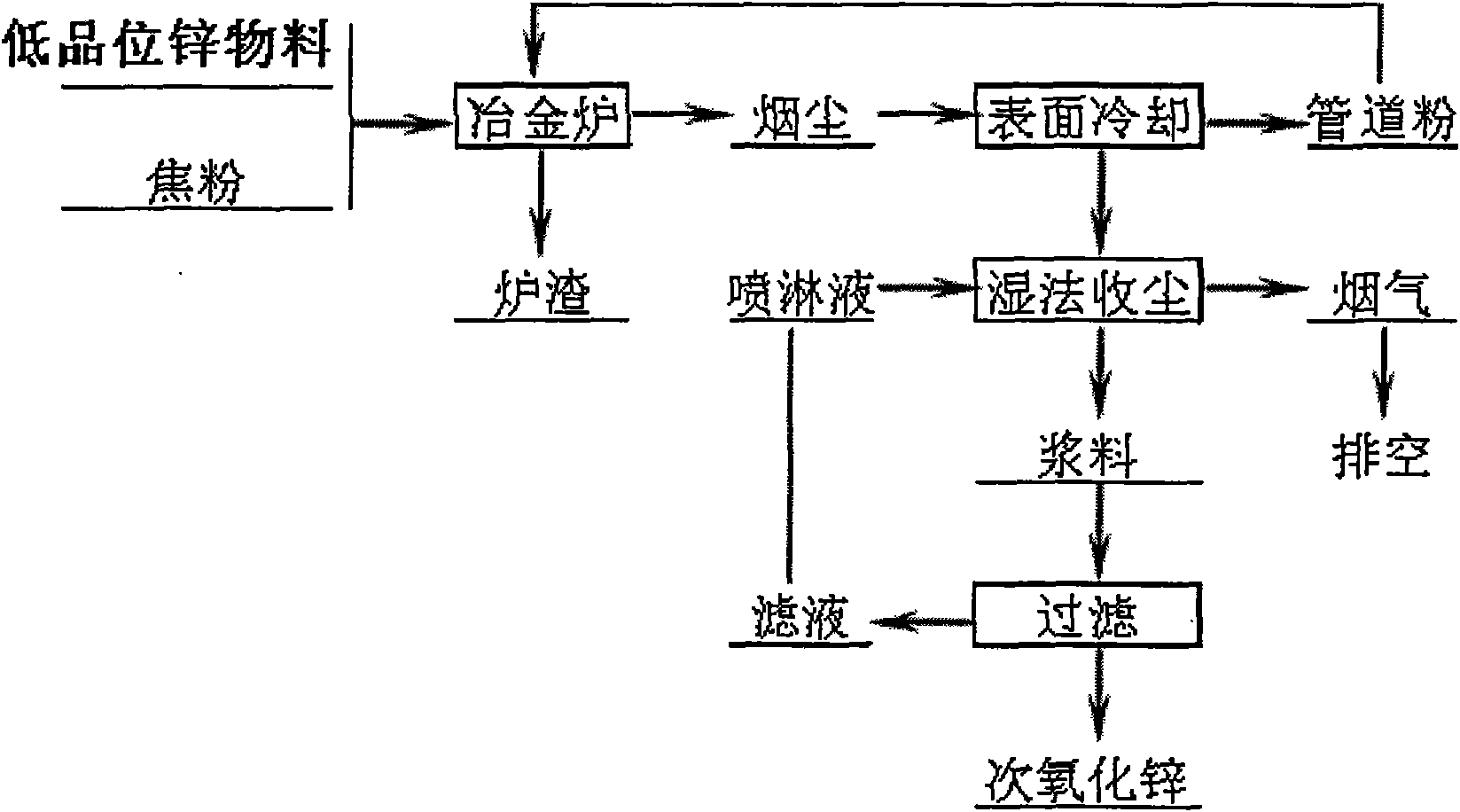
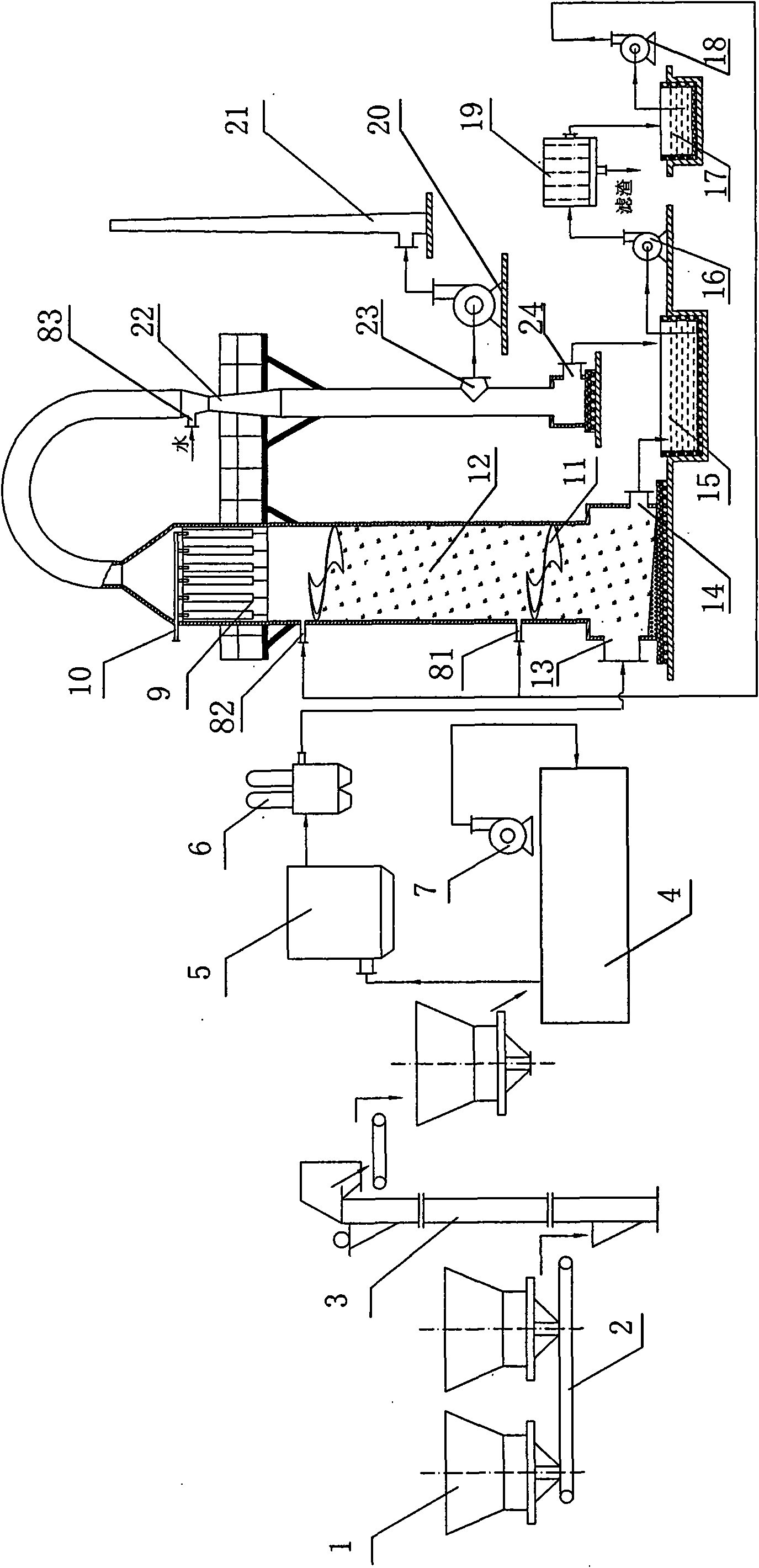
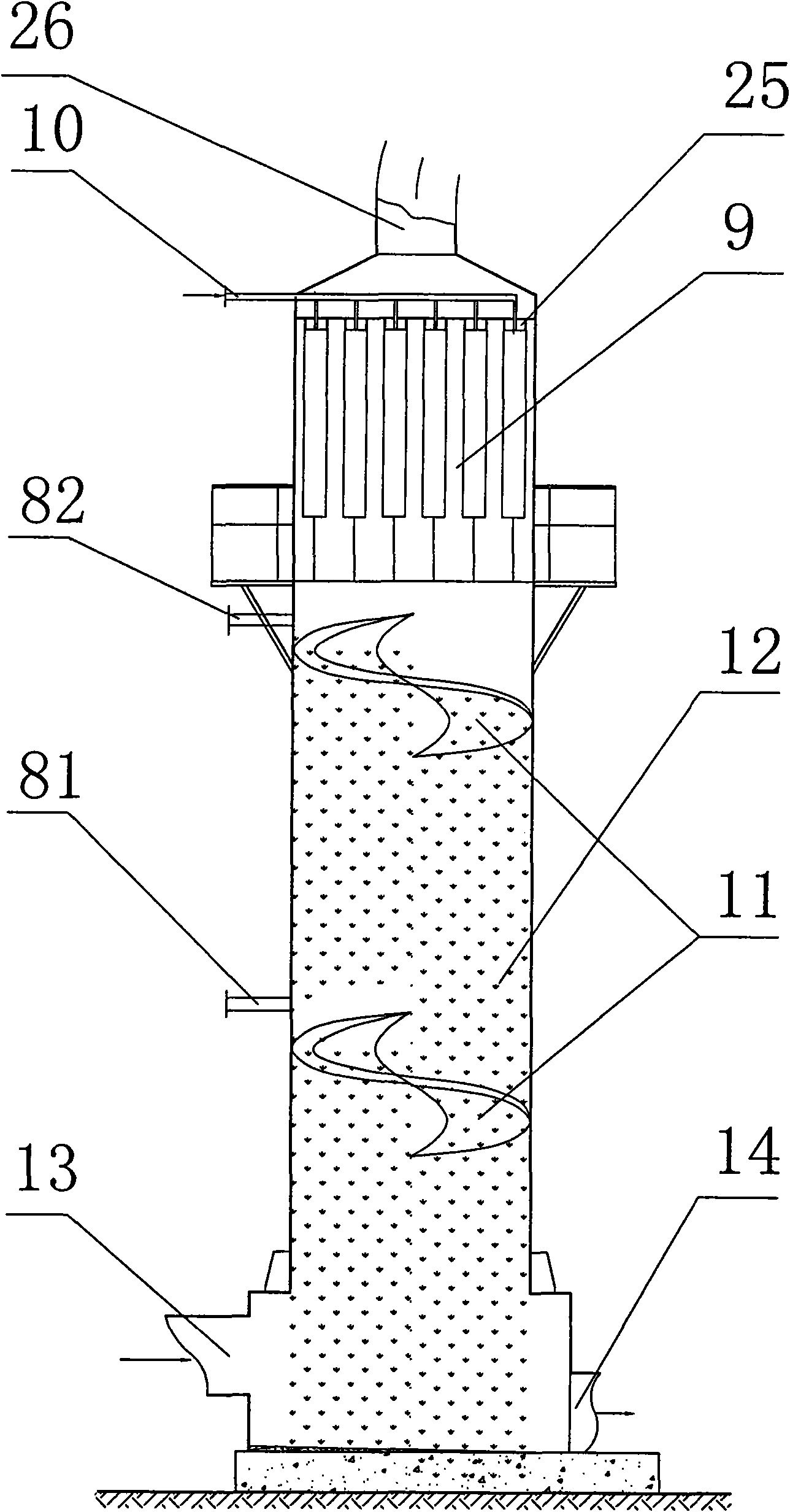
Cleaning and dust collecting method of volatilized zinc oxide and device thereof
InactiveCN101608266AAvoid the situation that the temperature is too high to burn the bagReduce cooling areaCombination devicesProcess efficiency improvementElectrolysisZinc Oxide Paste
The invention relates to a cleaning and dust collecting method of volatilized zinc oxide and a device thereof. Low grade zinc material is reduced and volatilized in a metallurgical furnace with reducing atmosphere; volatilized flue gas enters a spraying-cloth bag tower via an oxidizing chamber and a surface cooler; the zinc oxide in the flue gas is collected; fluorine and chlorine enter spraying solution; sulfur dioxide forms ZnSO3 to enter secondary zinc oxide paste; after the secondary zinc oxide paste is separated through filter pressing, the filter liquor returns to be circularly used; and filter residue is secondary zinc oxide product. The invention has the advantages that fluorine, chlorine and sulfur dioxide in the flue gas can be removed during the dust collection process, so as to enable the secondary zinc oxide to be directly used as the raw material for producing electrolytic zinc, the technological process can be reduced, the investment can be saved, and the invention is energy-saving and environment protective.
Owner:广西冶金研究院有限公司
Synergistic leaching-copper arsenate removing method for leaching residues in high-iron zinc calcine and high-iron zinc sulfide concentrate
InactiveCN103789544AHigh recovery rateEfficient reductionProcess efficiency improvementHydrometallurgyCopper sulfate
The invention belongs to the field of wet metallurgy of zinc, and particularly relates to a synergistic leaching-copper arsenate removing method for leaching residues in high-iron zinc calcine and high-iron zinc sulfide concentrate. The method comprises the following steps: mixing the leaching residues in the high-iron zinc calcine with the high-iron zinc sulfide concentrate; mixing zinc electrowinning waste liquor and a part of sulfuric acid-containing solution prepared from concentrated sulfuric acid and synergistically leaching; adding a reaction dosage of industrial iron powder into a synergistically-leached copper arsenate-removing primary solution; replenishing a proper amount of copper sulfate as required; reacting; performing liquid-solid separation on reaction ore pulp to obtain cuprous arsenide precipitate serving as a copper-leaching raw material and a copper arsenate-removing secondary solution; returning the copper arsenate-removing secondary solution to a zinc hydrometallurgy process to further recover valuable metals therein. The method is clean and efficient, efficient leaching of copper and efficient reduction of Fe<3+> can be realized, the solution treatment amount is small, the comprehensive recovery rate of valuable metals in a zinc hydrometallurgy process is increased comprehensively, and the smelting flow is simplified.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH TECH IND SALES MANAGEMENT +1
Method of recycling zinc, manganese, lead and silver from zinc electrowinning anode mud
ActiveCN102912138AWide variety of sourcesLess investmentProcess efficiency improvementPregnant leach solutionElectrolysis
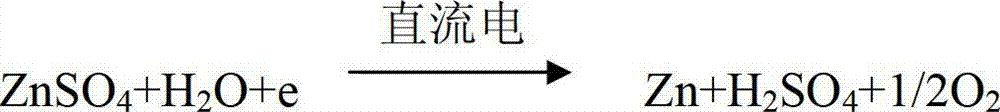
The invention discloses a method of recycling zinc, manganese, lead and silver from zinc electrowinning anode mud. The method comprises the following steps of: after carrying out wet ball grinding on the zinc electrowinning anode mud, filtering, wherein filtrate is taken as a raw material for a zinc smelting system; mixing filter residues and acidic solution, adding a reducing agent to carry out reduction reaction, leaching manganese, filtering to obtain leaching liquid and leaching slag, purifying the leaching liquid, and preparing manganese dioxide through an electrolysis method; and recycling lead and silver with the leaching slag as high-lead slag and a raw material of a lead smelting system. The method, provided by the invention, has the characteristics of less investment, simple process, low cost, easiness in operation and the like; the whole process is a green metallurgical process flow, and is environmental-friendly, the comprehensive recovery and utilization efficiency of resources can be effectively improved, the battery-level manganese dioxide obtained by electrolysis is taken as a new energy material so as to be beneficial for environmental protection and high value-added utilization of resources. The method is easy to realize large-scale industrial application.
Owner:HUNAN HERMES SAFE ENVIRONMENT PROTECTION SCI
Cathode plate anticorrosive coating for zinc electrowinning and preparation method of cathode plate anticorrosive coating
ActiveCN102953093AImprove corrosion resistanceExtended service lifePhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementEpoxyInter layer
The invention provides a cathode plate anticorrosive coating for zinc electrowinning and a preparation method of the cathode plate anticorrosive coating. The method comprises the step of coating anticorrosive paints on a part between a liquid level line which is easy to corrode of the cathode plate and a conductive beam by means of spraying or blade coating, wherein the anticorrosive paints consist of a base layer, an intermediate layer and a surface layer, the base layer is epoxy modified paint with excellent binding force with base material of the cathode plate, the intermediate layer is anticorrosive paint which is used for connecting the base coat with the finishing coat and has excellent corrosion resistance performance, and the surface layer is anticorrosive and wearable finishing coat. By using the anticorrosive coating, the service life of the cathode plate can be obviously prolonged by 1 / 3-1 / 2, and the replacing frequency of aluminum plates is reduced, so that the production cost of electrowinning zinc is reduced, and the production benefit is improved.
Owner:KUNMING HENDERA SCI & TECH
Manufacturing method of highly-conductive and heat-resisting electrode cross beam component
The invention provides a casting method of a highly-conductive and heat-resisting electrode cross beam component. The method comprises the following steps of: 1. selecting alloy materials; 2. manufacturing a metal mold according with sizes of the component; 3. founding and forming casting alloy materials; 4. and performing thermal process to cast formed pieces; wherein the composition ingredientsof the adopted alloy materials include elements of Al, Mg, Si, Zr, Ce and B; the mass percent content of each composition ingredient contains 0.5-1.0% of Mg, 0.4-0.8% of Si, 0.6-0.8% of Zr, 0.05-0.1%of Ce, and 0.03-0.06% of B; the allowance is Al and inevitable impurities; the mass percent ratio of the impurity elements contained in the alloy materials is that: Fe is less than or equal to 0.2%, Cu is less than or equal to 0.05%, Mn is less than or equal to 0.02%, Cr is less than or equal to 0.02%, Zn is less than or equal to 0.05% and Ti is less than or equal to 0.05%. With the casting method, the aluminum alloy electrode cross beam component with good thermal resistance, mechanical property and high electrical conductivity performance can be cast, the electric conductivity can be up to 45% IACS (International Annealed Copper Standard), the temperature can be up to 250 DEG C in long-term application, and the casting method can be used for manufacturing the electrode cross beam components needed by the industrial field of electrolytic zinc.
Owner:沈阳铸研科技有限公司
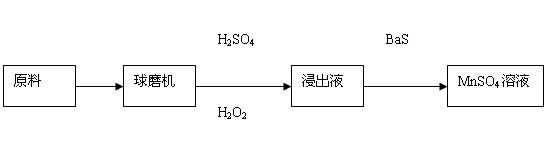
Method for directly leaching electrolytic zinc anode mud manganese dioxide
InactiveCN102168177AReasonable workmanshipTo achieve the purpose of energy saving and emission reduction green smeltingProcess efficiency improvementManganese sulphatePregnant leach solution
The invention relates to a method for directly leaching electrolytic zinc anode mud manganese dioxide, in particular to a method for directly leaching an electrolytic zinc anode mud manganese dioxide by adopting a process for recovering metal manganese with a wet method and using electrolytic zinc anode mud manganese dioxide as a raw material. The technical scheme of the invention is realized by the following steps of: conveying a blocky and flaky manganese dioxide raw materials into a ball mill for ball-milling; after ball-milling the manganese dioxide raw material by the ball mill, directly entering a pulpifying pool for pulpifying and carrying out heavy metal impurity removal on pulpified leaching liquid to obtain a qualified manganese sulfate solution; and directly providing the qualified manganese sulfate solution for an electrolytic zinc manufacturer to meet the requirement of electrolytic zinc on manganese. Because the process is reasonable, the method can ensure that the qualified manganese sulfate solution is produced. Additionally, the method for recovering metal manganese by wet method smelting is adopted, and the aims of energy saving, emission reduction and green smelting are achieved. The invention has the advantages of simple process, less investment and low energy consumption. Because the operation is simple and convenient, the method is easy for application and popularization.
Owner:济源市东方化工有限责任公司
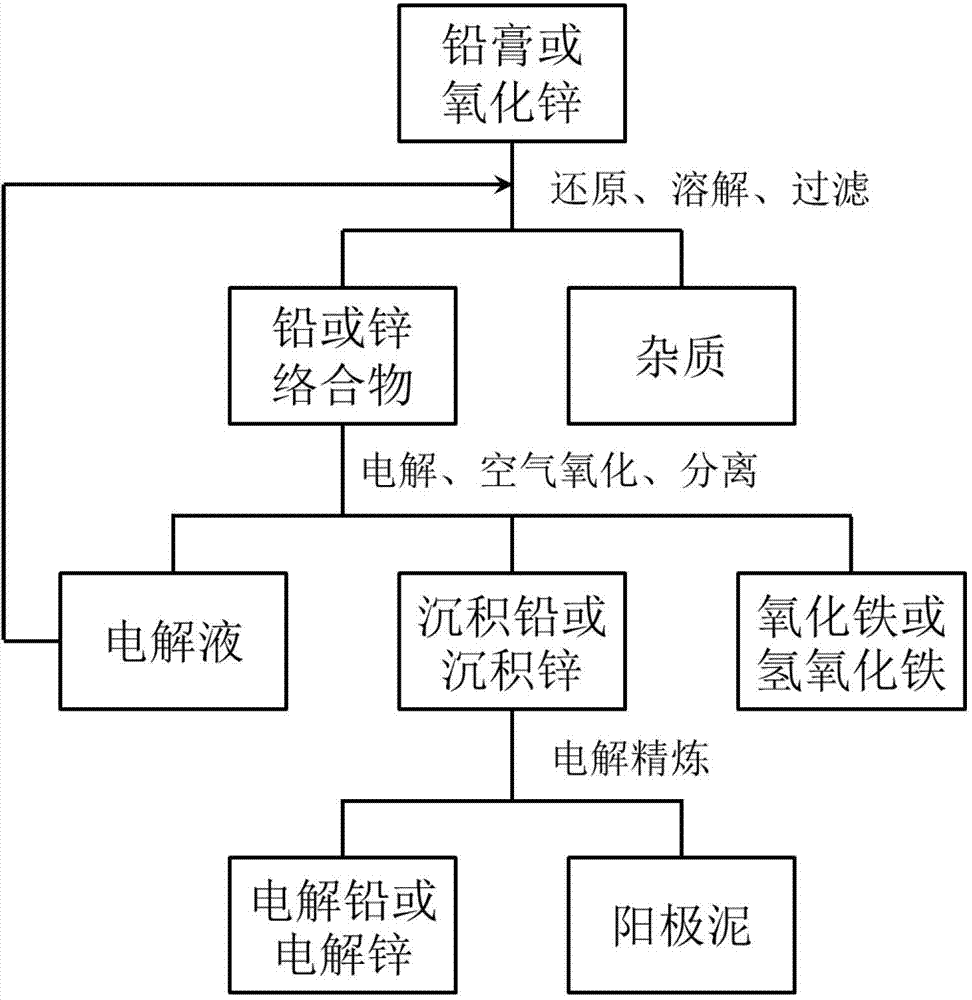
Metal electrolytic method in alkaline solutions
ActiveCN103540954AReduce oxidationHigh purityPhotography auxillary processesFerric hydroxideZinc compounds
The invention discloses a metal electrolytic method in alkaline solutions, which comprises the following steps: casting deposited lead or deposited zinc or commercially available crude lead or crude zinc to a 0.2-6 cm thick anode plate, and preparing a lamelliform cathode through pure lead, pure zinc or an inert electrode; electrolytic refining in alkaline electrolyte, and finally obtaining high-purity electrolytic lead or electrolytic zinc on the cathode, wherein the metal electrolytic method further comprises: 1) dissolving a lead compound or a zinc compound into the alkaline electrolyte, and adding a reducing agent to reduce lead dioxide existing in the lead compound or the zinc compound to a soluble lead complex; and 2) selecting the lamelliform cathode prepared by the pure lead, pure zinc or inert electrode in the electrolysis process, selecting the anode as iron with purity larger than 94%, and finally obtaining the deposited lead or deposited zinc on the cathode. According to the metal electrolytic method disclosed by the invention, the lead compound or the zinc compound is dissolved under an alkaline condition through a complexing agent, the electrolytic lead or electrolytic zinc is obtained by electrolyzing the cathode, and a byproduct ferric oxide or ferric hydroxide is obtained by separation.
Owner:北京中金瑞丰环保科技有限公司
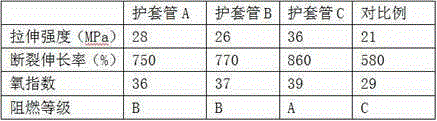
Cable sheath tube preparation method
ActiveCN105237867AReduce pollutionImprove flame retardant performanceInsulated cablesInsulatorsPolyolefinElectrolysis
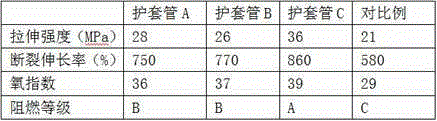
The invention discloses a cable sheath tube preparation method, and relates to the field of electricity facility. Raw materials of the cable sheath tube comprise, by weight, 80-90 parts of polyolefin, 2-5 parts of plant ash, 1-3 parts of gum, 0.5-0.8 parts of a silane coupling agent, 1-2 parts of stearic acid, 0.6-0.8 parts of white carbon black, and 3-5 parts of electrolytic zinc acid leaching residue. The cable sheath tube is prepared through the steps such as melt blending, crosslinking, granulation and molding. The tensile strength of the cable sheath tube is higher than 26 MPa. The breaking elongation of the cable sheath tube is higher than 750%. The oxygen index of the cable sheath tube is higher than 36. The flame retarding performance of the cable sheath tube reaches the A level. The cable sheath tube also has significant characteristics of high strength and high flame retarding performance. Also, plant ash and electrolytic zinc acid leaching residue are recycled, such that environment pollution is reduced, and production cost is reduced. The electric cable has significant economic and environmental benefits.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
Method for recovering Pb<2+> from electrolytic zinc rinsing wastewater with calcium-carbonate-modified kieselguhr
InactiveCN103159278AEfficient use ofHigh recovery rateOther chemical processesProcess efficiency improvementFiltrationSorbent
The invention discloses a method for recovering Pb<2+> from electrolytic zinc rinsing wastewater with calcium-carbonate-modified kieselguhr, which comprises the following steps:(1) adding 10g of fine kieselguhr into 50mL of 0.4-0.5 mol / L Na2CO3 solution, putting in a rotary thermostatic water bath oscillator, stirring, and dropwisely adding 5-5.2 mL of saturated CaCl2; after stirring, taking out, removing the supernatant solution, carrying out vacuum filtration, washing with pure water to a neutral state, centrifuging for solid-liquid separation, drying, pulverizing, and passing through a 200-mesh sieve to prepare a calcium-carbonate-modified kieselguhr adsorbent; and (2) adding 10mL of 0.1 g / L calcium-carbonate-modified kieselguhr adsorbent prepared in the step (1) into a 250 mL a conical flask with a stopper, adding 100mL of Pb<2+>-containing electrolytic zinc rinsing wastewater solution with the pH value of 4.83-4.85, adsorbing at 25-30 DEG C for 120-125 minutes, plugging, and oscillating in the rotary thermostatic water bath oscillator at the speed of 150 r / min to adsorption equilibrium. The invention can be used for recovering Pb<2+> from electrolytic zinc rinsing wastewater, and enhances the recovery rate.
Owner:GUILIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Preprocessing method of lead/lead-alloy inert anode for zinc electrowinning
InactiveCN102465314AReduce cut strengthYield advantagePhotography auxillary processesElectrodesPretreatment methodAlloy
The invention relates to a processing method of an lead / lead-alloy inert anode for zinc electrowinning, wherein a preprocessing solution consists of fluorides, sulfuric acid, MnSO4 and distilled water, and the temperature of the preprocessing temperature is 20-80 DEG C; the anode is an anode to be preprocessed, a cathode is a lead / lead-alloy electrode, a distance between the cathode and the anode is 3-6cm, and the circulation amount of the preprocessing solution is 0.05-0.5V tank / h, wherein V tank refers to volume of a preprocessing tank; and the preprocessing process parameters are as follows: the anode current density is 200-800A / m<2>, and the preprocessing time is 8-24h. According to the invention, the preprocessing solution containing fluorine ions is adopted, preprocessing process parameters are optimized, and the preprocessing process is simple and convenient to operation and is beneficial to industrial application. According to the preprocessing method disclosed by the invention, a period of forming a stable protection layer of the lead / lead-alloy anode for zinc electrowinning is shortened to be within 7 days from 3-6 months.
Owner:GENERAL RESEARCH INSTITUTE FOR NONFERROUS METALS BEIJNG
Zinc electrolysis technology of zinc ammonia complex aqueous solution
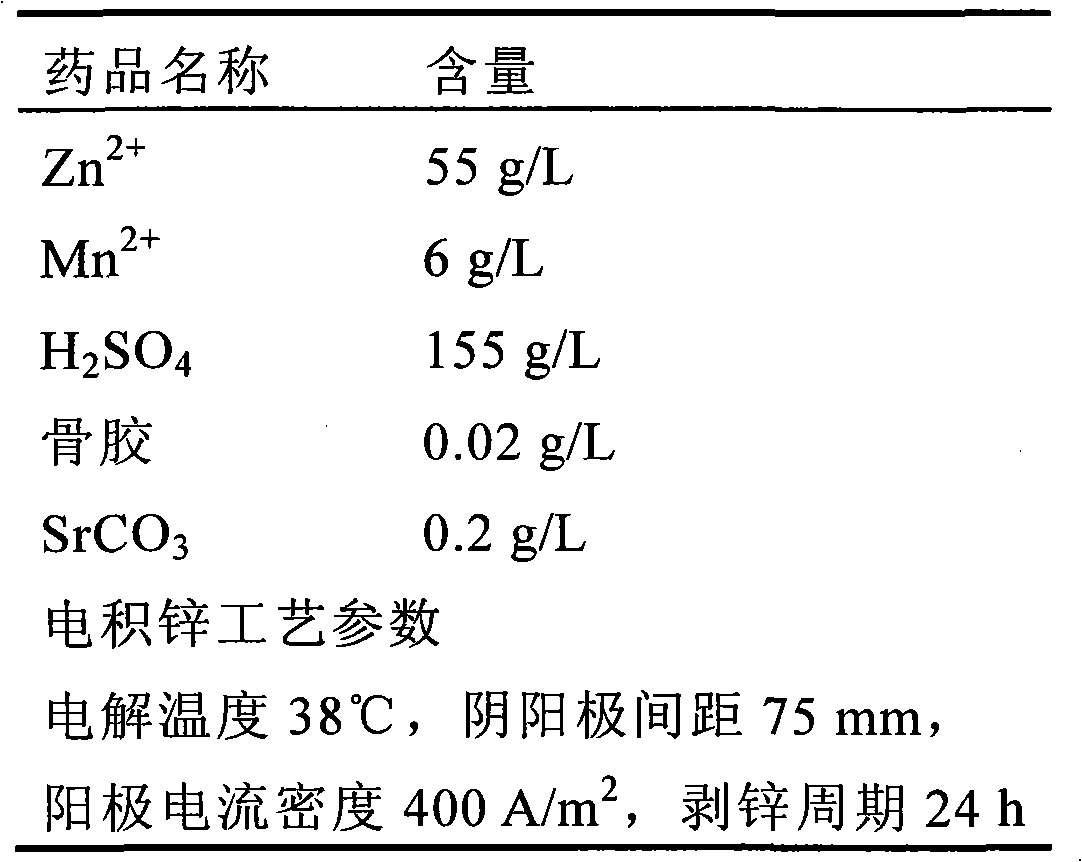
The invention relates to a zinc electrolysis technology of a zinc ammonia complex aqueous solution system. The zinc electrolysis technology is characterized in that in allusion to high-low grade zinc oxide ores, leaching is carried out with an aqua ammonia with the concentration of 20%-25%, and the zinc ammonia complex leachate is reduced and purified by a zinc powder and then goes into an electrolysis work section; a metal aluminum plate is used as a cathode, a ruthenium-coated metal titanium plate is used as an anode, and optimum process conditions determined through an orthogonal test method comprise: the temperature is controlled at 18-26 DEG C, the current is 6.5 A, the heteropole distance is 3.5 cm, the zinc concentration of an electrolysis solution is controlled at 60 g / L-160 g / L, the current efficiency is 94.33%, and the electric energy consumption is 2869 kW.h / t zinc, wherein the electric energy is saved by 10% compared with a traditional process; the electrolytic zinc product quality can be up to 99.84%-99.89%.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
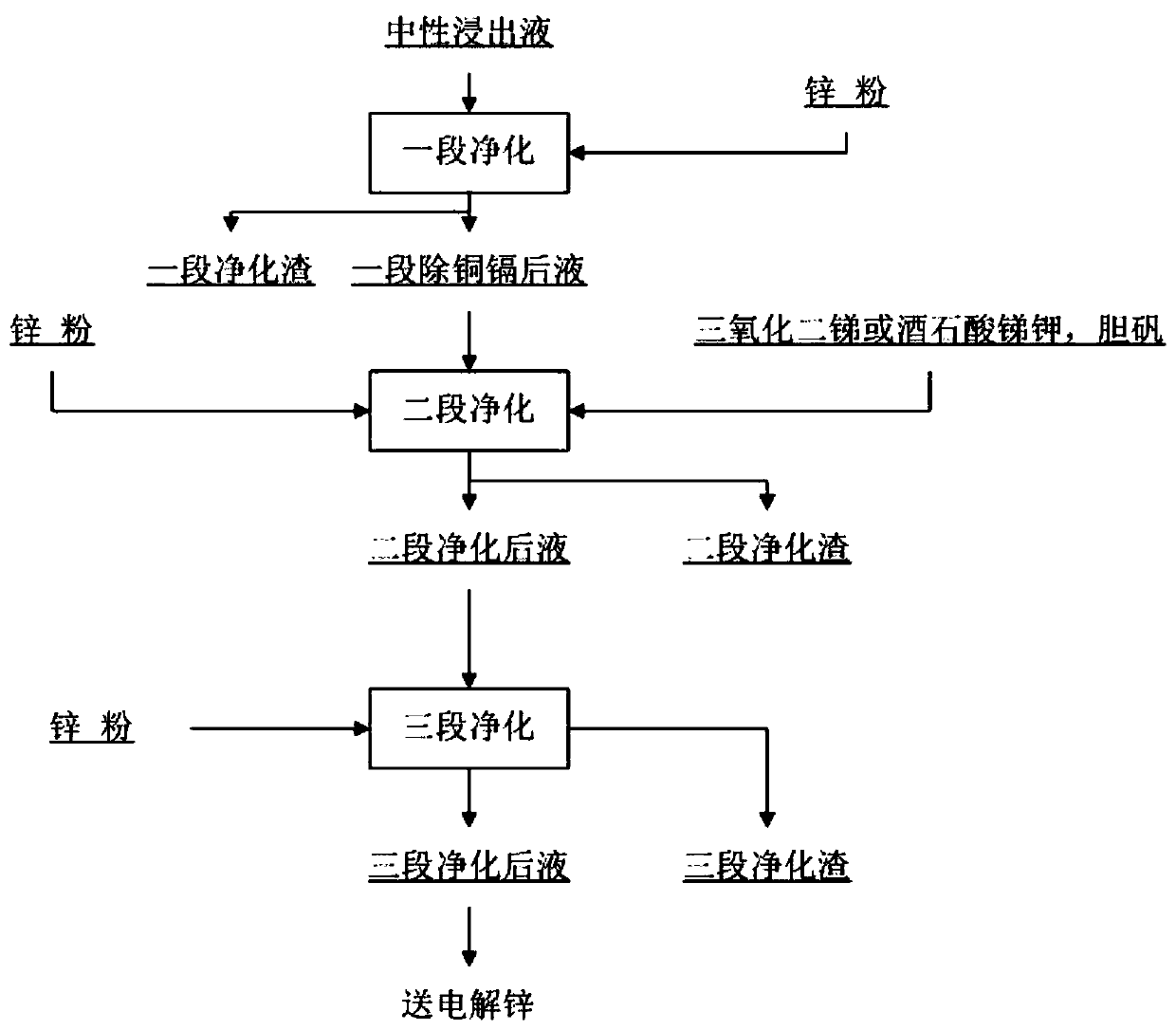
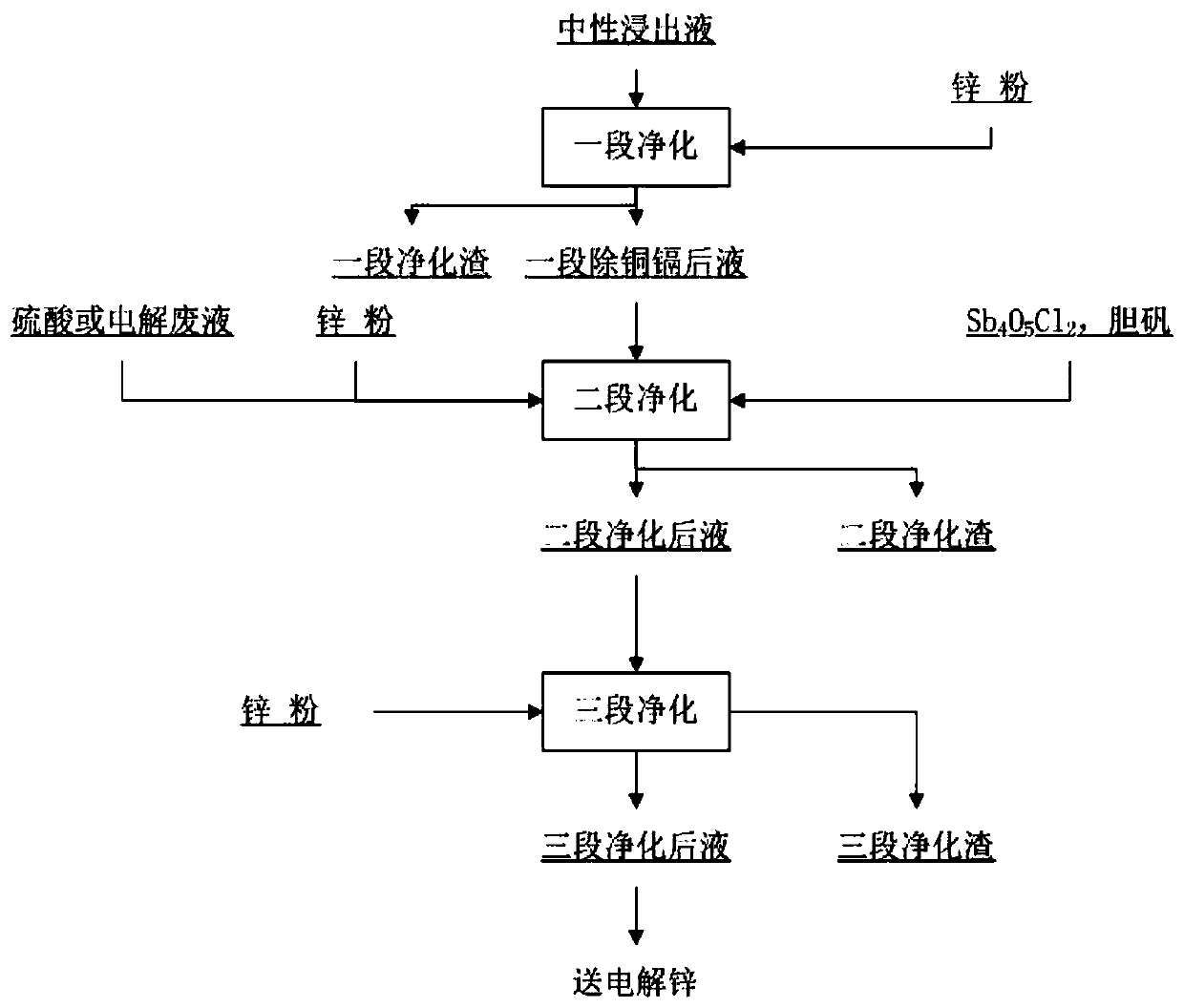
Method for purifying zinc sulfate aqueous solution to remove nickel, cobalt and germanium
ActiveCN111254292AAvoid reconstitutionGood cobalt removal effectPhotography auxillary processesElectrolysis componentsSulfate zincElectrolysis
The invention relates to a method for purifying a zinc sulfate aqueous solution. In a supernatant, a zinc powder is used to remove copper and cadmium. At a temperature of 80 to 95 DEG C, the zinc powder and a copper antimony activator are added to purify to remove cobalt, nickel and germanium. According to the cobalt concentration of the solution, the copper antimony activator, the zinc powder anda small amount of sulfuric acid or electrolytic waste liquid are added. For a section of waste solution after copper and cadmium removal, containing 2-120 mg / l of cobalt, 0.02-0.3 mg / l of germanium,0.02-4 mg / l of nickel, and 5-120 mg / l of cadmium, the purifying effect of the waste solution containing 0.1 mg / l of cobalt, 0.02 mg / l of germanium, and 0.1 mg / l of nickel can be realized after 90-150minutes. Various zinc powders are used to realize deep purification of the solution. The method is suitable for a purification system of an electrolytic zinc plant.
Owner:KUNMING HANCHUANG SCI & TECH CO LTD
Anode for use in zinc and cobalt electrowinning and electrowinning method
ActiveUS20110079518A1Reduce consumptionLow production costMachining electrodesPhotography auxillary processesElectrolysisManganese
The present invention aims to provide a zinc electrowinning anode capable of inhibiting manganese compound deposition on the anode and a cobalt electrowinning anode capable of inhibiting cobalt oxyhydroxide deposition on the anode.The zinc electrowinning anode according to the present invention is a zinc electrowinning anode having an amorphous iridium oxide-containing catalytic layer formed on a conductive substrate, and the zinc electrowinning method according to the present invention is an electrowinning method using that electrowinning anode. Also, the cobalt electrowinning anode according to the present invention is an electrowinning anode having an amorphous iridium oxide or ruthenium oxide-containing catalytic layer formed on a conductive substrate, and the cobalt electrowinning method according to the present invention is an electrowinning method using that electrowinning anode.
Owner:DOSHISHA CO LTD
Method and smelting furnace for processing high-iron multi-metal zinc concentrate
ActiveCN104060089AEfficient recyclingAdvanced technical indicatorsPhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementElectrolysisIndium
The invention relates to a method and a smelting furnace for processing a high-iron multi-metal zinc concentrate. The method comprises the following steps of: adding the zinc concentrate which contains the following components in percentage by weight: 16%-24% of Fe, 0.02-0.40% of In, 0.2%-2.0% of Cu, 0.004%-0.04% of Ag and 36%-48% of Zn to the smelting furnace, successively carrying out three processes including oxygen-enriched oxidation smelting, weak reduction smelting and strong reduction smelting to product sulfur dioxide fume, a copper-silver alloy, smelting slag and zinc-indium smoke dust, wherein the sulfur dioxide fume is used for preparing sulfuric acid, the smelting slag is externally sold, the copper-silver alloy is separated to extract copper and silver, and the zinc-indium smoke dust is subjected to neutral leaching to obtain a neutral leaching solution and neutral leaching residues; producing electrolytic zinc through the neutral leaching solution according to a conventional process; carrying out two-stage acid counter current leaching on the neutral leaching residues to obtain a low-acid leaching solution and high-acid leaching residues; returning the high-acid leaching residues to the smelting furnace for smelting, producing fine indium by using the low-acid leaching solution according to a conventional P204 extraction process, and returning extraction raffinate to neutral leaching. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of short process flow, high production efficiency, low production cost, good integrated recovery and clean and environment-friendly production process.
Owner:LAIBIN CHINA TIN SMELTING
Recycling technology for valuable metals in electrolytic zinc leach residues and electrolytic cell adopted by same
InactiveCN104532295AHigh recovery rateImprove work efficiencyPhotography auxillary processesFiltrationMixing tank
The invention provides a recycling technology for valuable metals in electrolytic zinc leach residues. The technology comprises the steps that waste residues, water, sulfuric acid and hydrogen peroxide are added into a superfine grinding mill and then ground to be put into a stirring tank, water is added into the mixing tank, sulfuric acid and hydrogen peroxide are supplied sufficiently, stirring is carried out on the normal pressure condition, an extract is filtered, residues are washed, liquid obtained through filtration is heated and concentrated, solid zinc sulfate is obtained through cooling and filtration, and a zinc sulfate product is obtained through drying; then the liquid is heated, and sponge cadmium is generated after zinc powder is added to obtain a cadmium product; the solid obtained through filtration is placed into an electrolytic cell, a chloride and a catalyst are added, and lead is leached in a cathode region; then waste residues and wastewater are processed. The invention further provides the electrolytic cell adopted by the recycling technology for valuable metals in the electrolytic zinc leach residues. According to the recycling technology, metals of lead, zinc and cadmium can be efficiently recycled, the cost is greatly reduced, and harm to the environment is greatly lowered; The recycling technology has the wide development prospect and can be applicable to electrolytic zinc leach residues accumulated in different regions all the year round and some refractory oxidized ores.
Owner:HUAYUAN COUNTY HONGDA BIANCHENG TECH
Method for extracting germanium and removing chlorine in zinc sulfate solution
InactiveCN106834682ASimple processing methodImprove efficiencyProcess efficiency improvementKeroseneOctanol
The invention discloses a method for extracting germanium and removing chlorine in a zinc sulfate solution. The method includes the following steps that firstly, complexing is conducted, wherein a complexing agent is added into the low-germanium and high-chlorine zinc sulfate solution, sufficient mixing is conducted, and a mixed solution is obtained; secondly, a mixed extraction agent is prepared, wherein N235, octanol and sulfonated kerosene are evenly mixed to be prepared into the mixed extraction agent; thirdly, extracting is conducted, wherein the mixed extraction agent is added into the mixed solution, sufficient mixing is conducted, extracting is conducted, and an organic phase and raffinate are obtained through separation; and fourthly, washing and stripping are conducted, wherein the organic phase is washed through dilute acid or clean water, stripping is conducted through a stripping agent, strip liquid is obtained, then the strip liquid is neutralized and precipitated, and germanium is recycled. The method for extracting and recycling the heavy metal of germanium and removing the harmful element of chloride ions at the same time from the zinc sulfate solution in the production process for producing electrolytic zinc or zinc sulfate in a zinc sulfate system is provided, the germanium element is extracted and recycled effectively, meanwhile, the harmful element of chlorine in the zinc sulfate solution is removed, the technological method is simple, and efficiency is high.
Owner:卜琰
Method for producing electrolytic lead powder through alkali immersion rotational flow electrolysis of wet electrolytic zinc acid dipping residues
ActiveCN102851508AImprove leaching rateAchieve separationProcess efficiency improvementElectrolysisRotational flow
The invention discloses a method for recovering lead powder through alkali immersion rotational flow electrolysis of wet electrolytic zinc acid dipping residues. The method is characterized in that acid dipping residues generated in the wet electrolytic zinc production are adopted as a raw material and are leached through a sodium hydroxide solution; metal ions with the reduction potential higher than lead are removed to purify the resultant leachate; and ultrafine electrolytic lead powder is produced through the electrodeposition of a rotational flow electrolytic device. The method which adopts the sodium hydroxide as an acid dipping residue leaching agent has the advantages of high lead leaching rate, no tin leaching, and realization of lead and tin separation; the method which adopts the rotational flow electrolysis to prepare the ultrafine lead powder has the advantages of high purity, large market value, high lead removal rate, and low labor intensity; and no wastewater discharge and environmental protection are realized in the whole production process.
Owner:江西自立环保科技有限公司
Method using wet method to treat high-fluorine and high-chlorine copper smelting dust containing zinc
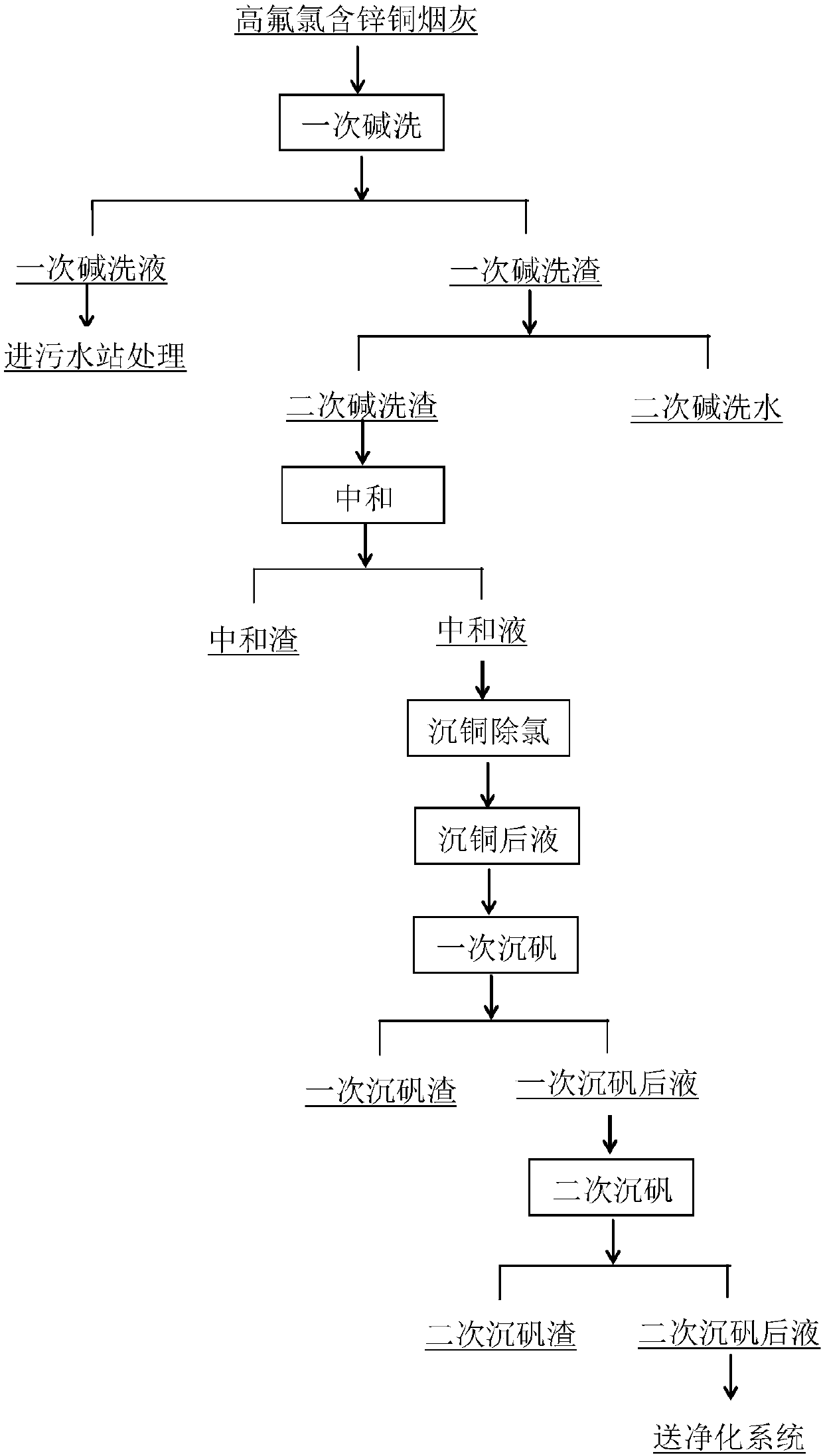
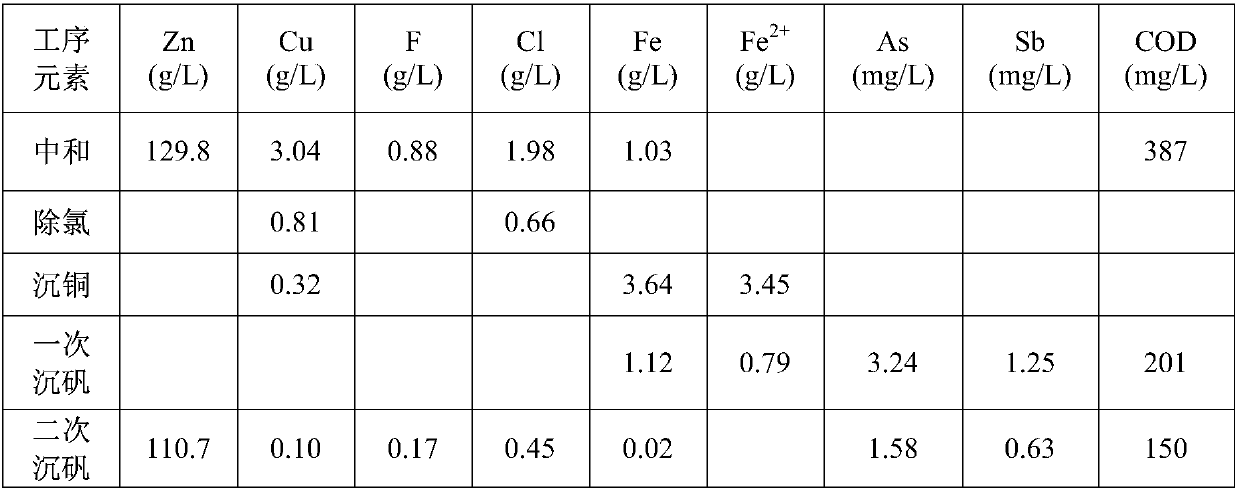
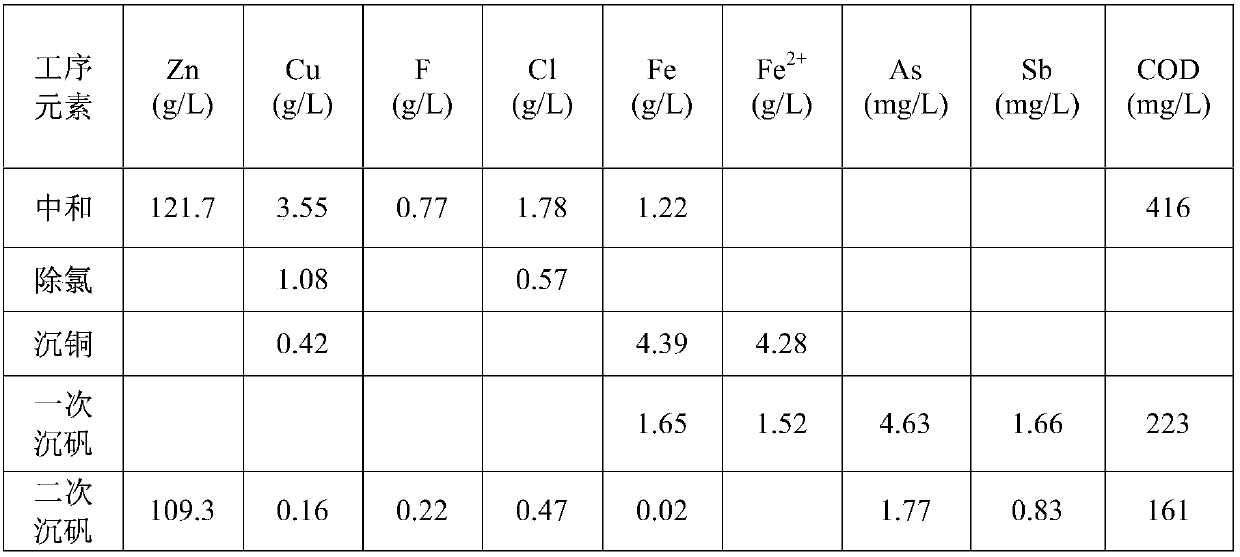
ActiveCN107779606AReduce the impactEasy to handleProcess efficiency improvementGoethiteZinc electrowinning
The invention a method using a wet method to treat high-fluorine and high-chlorine copper smelting dust containing zinc. The method includes: the copper smelting dust is subjected to alkali washing twice to remove fluorine and chlorine impurity elements in the copper smelting dust, the alkali washing residues of the copper smelting dust are subjected to neutralizing to leach valuable metal such aszinc and copper in the copper smelting dust, the solution after the neutralizing is subjected to copper precipitation and chlorine removing, the solution after the chlorine removing is subjected to goethite-method jarosite precipitation twice to remove impurity ions such as iron, arsenic, antimony, fluorine and chlorine in the solution and lower the COD of the solution, the solution after the jarosite precipitation enters a thickening tank for subsequent purification, and the purified solution finally enters a zinc electrowinning system; neutralizing residues are subjected to medium-acid leaching once and high-acid leaching once and then enter a lead pyrometallurgy system. The method has the advantages that the valuable metal such as the zinc and the copper is recycled effectively, and the fluorine and chlorine removing effects are above 90%; efficient and low-cost effective treatment of the high-fluorine and high-chlorine copper smelting dust is achieved, and the influence of high COD caused by the high-fluorine and high-chlorine copper smelting dust on zinc electrowinning is eliminated at the same time.
Owner:CHENZHOU FENGYUE ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH
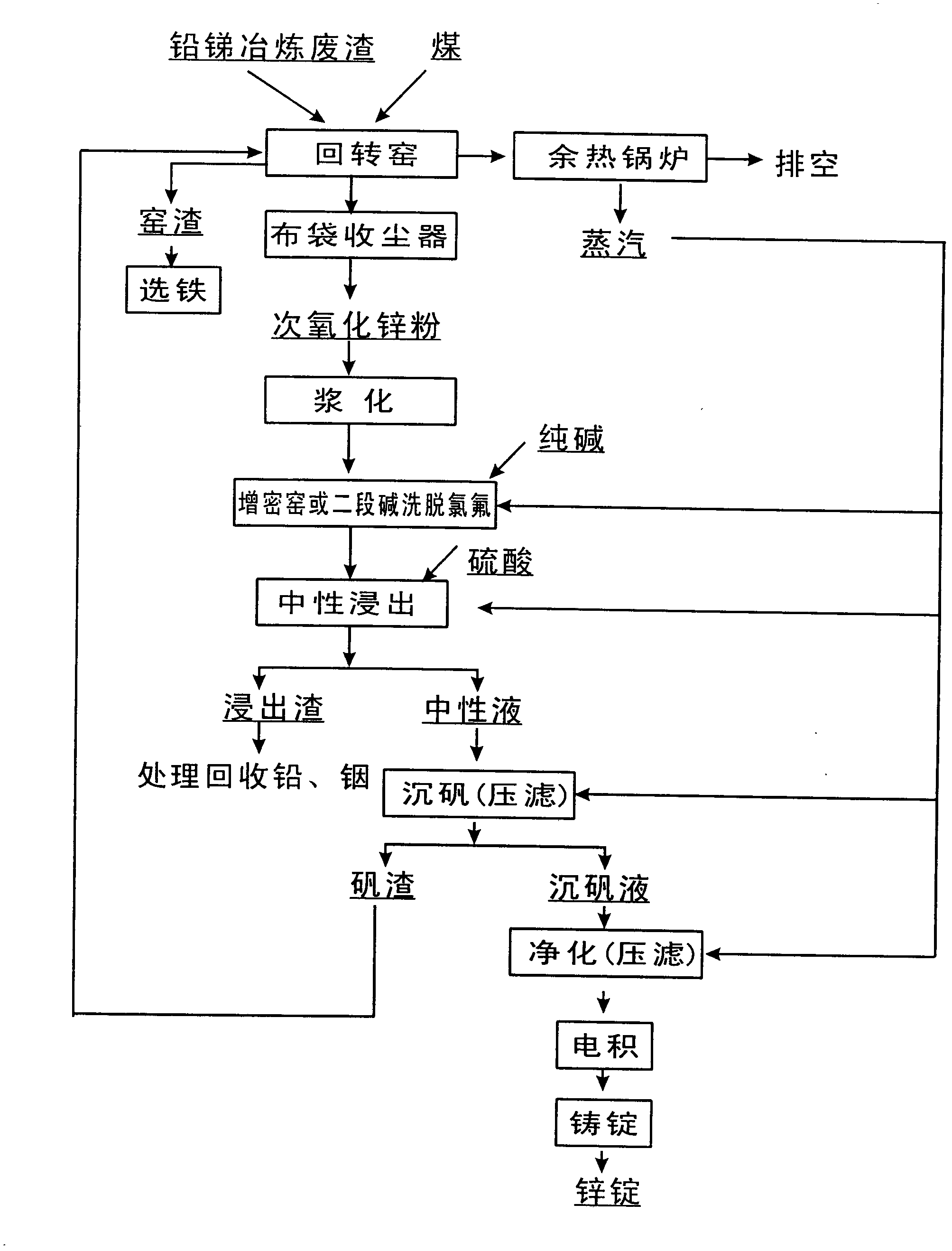
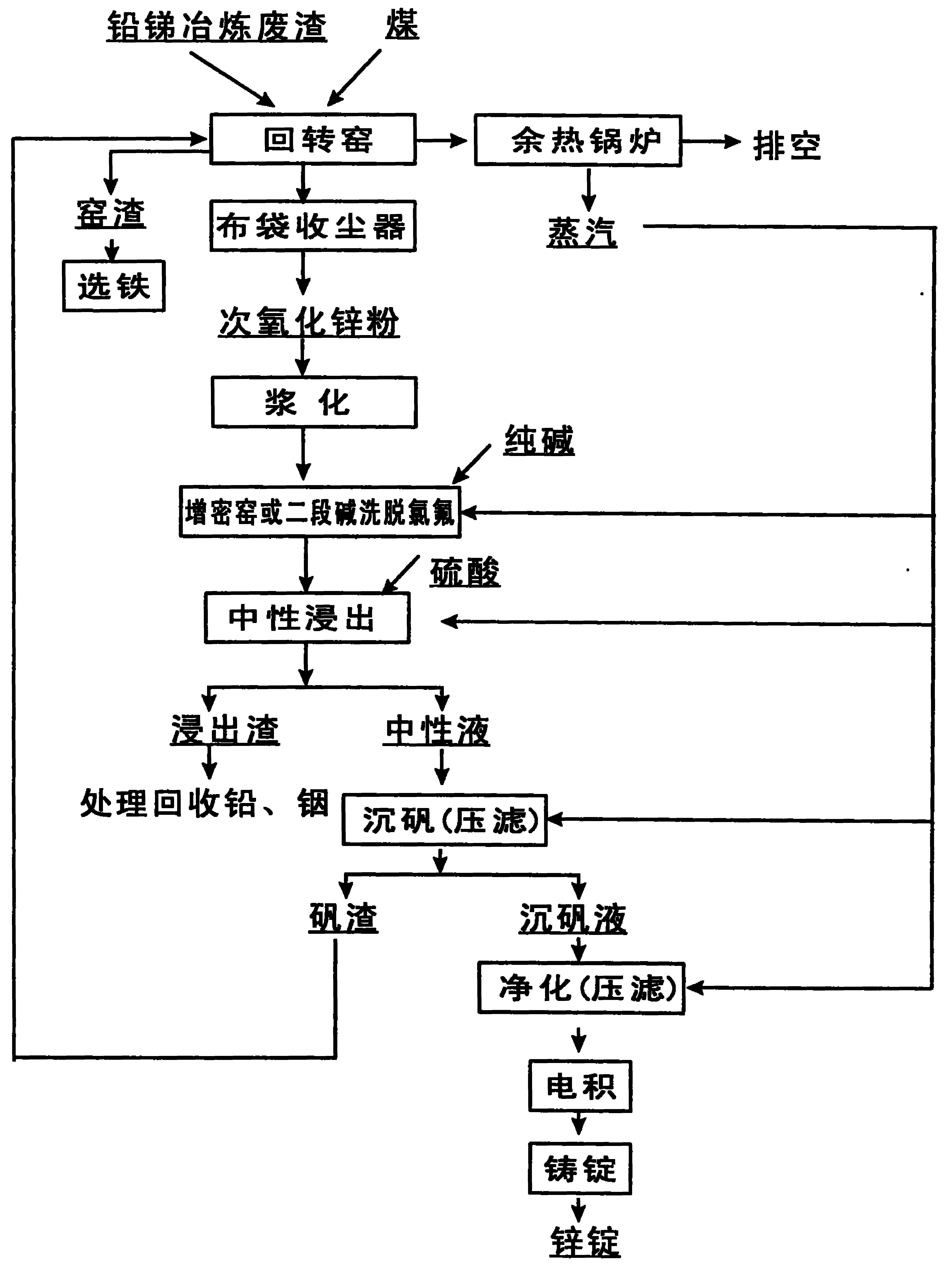
Method for producing electrolytic zinc by comprehensively recycling high-chlorine high-fluorine lead and antimony smelting waste residue
InactiveCN102586622AIncrease consumptionMeet the requirements of electrowinning processPhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementElectrolysisSludge
The invention discloses a method for producing electrolytic zinc by comprehensively recycling high-chlorine high-fluorine lead and antimony smelting waste residue. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: preparing zinc hypoxide powder from the high-chlorine high-fluorine lead and antimony smelting waste residue by using a rotary kiln, slurrying the zinc hypoxide powder, removing fluorine and chlorine through two-stage alkaline washing, neutrally leaching obtained caustic sludge by using sulfuric acid, performing alum settlement treatment to obtain a purified liquid, and treating by the conventional electrodeposition process to obtain the electrolytic zinc. The invention provides the preparation of the zinc hypoxide powder from lead and antimony waste residue by using the rotary kiln, and the removal of the fluorine and the chlorine through a densification kiln or two-stage alkaline washing after the zinc hypoxide powder is slurried for the first time; the invention is characterized in that: the method is high in production capacity, the fluorine and the chlorine are completely removed, the treated purified liquid can remove a large number of harmful elements and meet electrodeposition requirements, the qualified electrolytic zinc is produced, the recovery rate of zinc reaches 84 percent, various kinds of valuable elements can be recovered, and the like; and the method can be used for the smelting and recovery industry of the lead and antimony waste residue.
Owner:广西成源矿冶有限公司
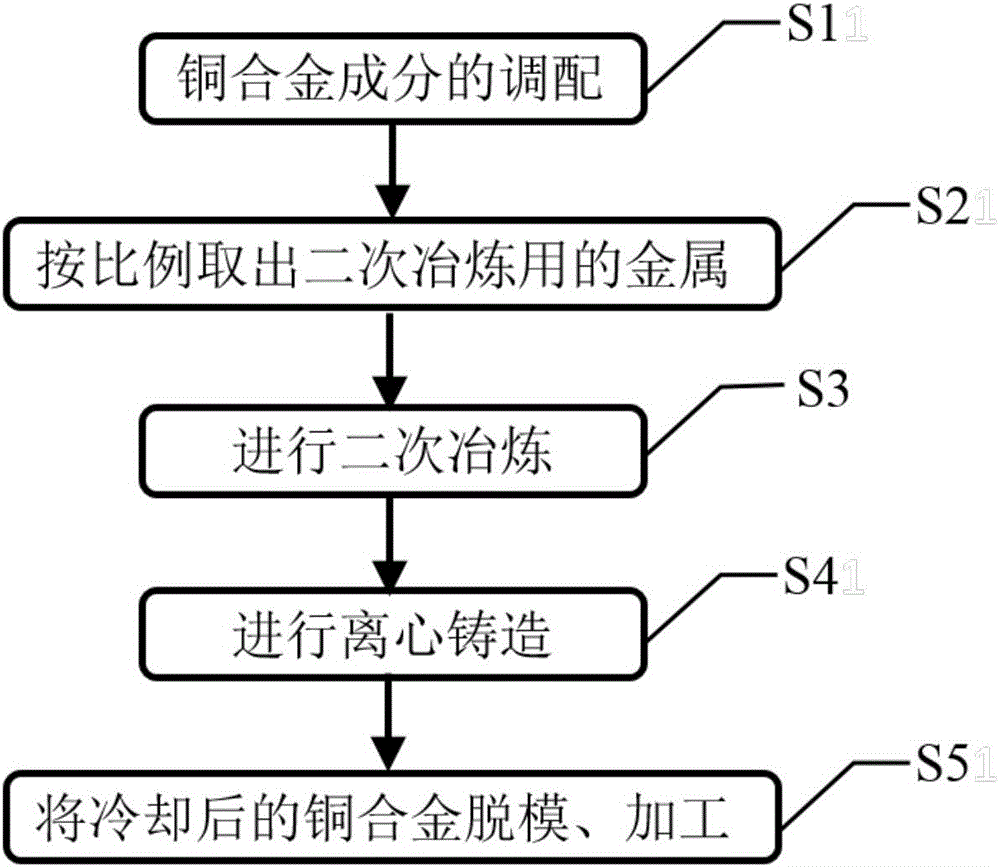
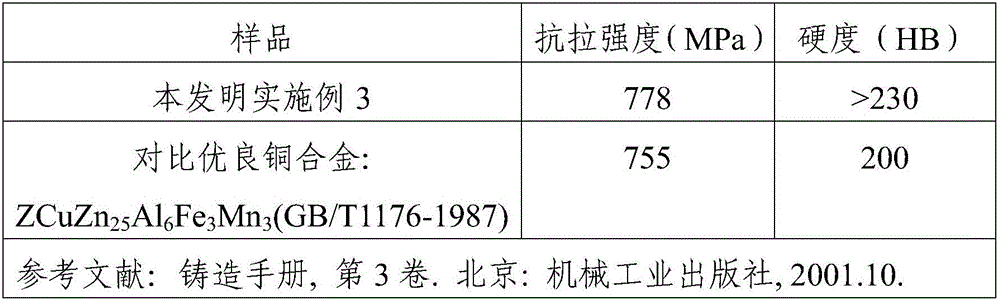
High-strength super-wear-resisting copper alloy and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a high-strength super-wear-resisting copper alloy which consists of the following chemical components in percentage by mass: 55%-65% of Cu, 2%-6% of Al, 0.5%-5% of Fe, 0.2%-3% of Mn and the balance Zn. A preparation method for the high-strength super-wear-resisting copper alloy comprises the following steps of: separately weighing electrolytic copper, electrolytic aluminum, electrolytic iron, electrolytic manganese and electrolytic zinc according to chemical components; taking out part of the electrolytic copper and electrolytic zinc according to certain mass percent; melting residual electrolytic copper and electrolytic zinc as well as electrolytic aluminum, electrolytic iron and electrolytic manganese to smelt; after raw materials are completely molten, adding the taken-out electrolytic copper and electrolytic zinc into a furnace to carry out secondary smelting until all of the taken-out electrolytic copper and electrolytic zinc are molten again, thereby obtaining a molten copper alloy; and casting and molding the molten copper alloy in a centrifugal mould, thereby obtain the high-strength super-wear-resisting copper alloy. The high-strength super-wear-resisting copper alloy can solve the technical problems such as high product cost, poor product quality, short product service life and the like in the existing domestic nuclear power industry, the existing domestic aerospace industry and the existing domestic military industry very well to adapt to the technical requirements.
Owner:刘芳
Process for ensuring zinc electrowinning safety driving in case of overproof copper mass through forced low-temperature method
ActiveCN103320814AReduce the problem of long waiting time for drivingElectrolysis componentsPhotography auxillary processesElectrolysisEconomic benefits
The invention provides a process for ensuring zinc electrowinning safety driving in case of overproof copper mass through a forced low-temperature method. A refrigeration fan is arranged on an electrolytic bath, the temperature during driving is 20-22 DEG C, the acid-zinc ratio is adjusted to 1.8-2.0, and the total load of current is 30%-40%; when the time reaches 24h, the concentration of copper ions is reduced to 2.8-3.2mg / l and the total load of the current is 40%-50%; when the time reaches 48h, the concentration of the copper ions is reduced to below 2.0mg / l, the total load of the production current is 50%-70%, and the temperature of the bath is ensured to be 20-30 DEG C; and when the time reaches 72h, the concentration of the copper ions is reduced to below 0.3mg / l and the normal production is restored. The process disclosed by the invention adopts a forced cooling segmental operation method, safety driving can be realized when the copper ions in a zinc electrolysis circulation solution are 5.0-1.5mg / l in concentration, ablation of a plate by copper can be avoided, the new method can be popularized and applied to other zinc wet smelters to improve the range of applications of a copper content standard in a zinc electrolyte in factories and reduce the problems that waiting time for driving is too long and the like because of overhaul or temporary parking of the factories and workshops, the technical and economic benefits are obvious, and the process has actual application value in production.
Owner:BAIYIN NONFERROUS GROUP
Filling resin of electrolytic zinc negative plate stripping mouth and processing technology thereof
The invention discloses a filling resin of an electrolytic zinc negative plate stripping mouth and a processing technology thereof. The filling resin is prepared by mixing component A and component B at a weight ratio of 2:1; the component A comprises bisphenol-F-epoxy resin, a epoxy resin diluent, a flexibilizer, silicon carbide filling material, a hydrolytic stabilizer and an adhesion promoter; and the component B comprises polyamide 650 curing agent, polysulfide rubber flexibilizer, mica and a color paste. Optimized selection and reasonable combination of raw materials with different performances, and a double-component mixing process are employed in the preparation of the filling resin, so that the filling resin is capable of solidifying quickly at room temperature, and possesses high bonding strength and peeling resistance after solidification, and also possesses excellent acid corrosion resistance, high temperature resistance, ageing resistance, and current shock resistance. The insulativity is high, cost is low, and storage requirements are few. The filling resin is easy to produce, is non-toxic, and is appropriate to be used as the filling resin of the electrolytic zinc negative plate stripping mouth.
Owner:云南曲靖润扬商贸有限公司
Method of recovering Pb<2+> from electrolytic zinc rinsing waste water by using manganese oxide modified diatomite
InactiveCN103030188AHigh recovery rateEfficient use ofWaste water treatment from metallurgical processWater/sewage treatment by sorptionAdsorption equilibriumElectrolysis
The invention discloses a method of recovering Pb<2+> from electrolytic zinc rinsing waste water by using manganese oxide modified diatomite. The method comprises the steps that (1), refined purified diatomite is taken, added to an NaOH solution, vibrated at 90-95 DEG C for 100-120 minutes, subjected to upper layer solution removal, added with an MnCl2 solution, placed for 120 minutes after a pH value is adjusted to 1-2 with analytical pure HCl, stirred for 60 minutes, then placed for 24 hours, and subjected to supernate removal; (2), the MnCl2 solution is added to a substance obtained in Step (1), stirred and placed; (3), operational processes in Step (2) are repeated; supernate is removed; the substance is washed to be neutral with pure water; centrifugation is performed for solid-liquid separation; solid is taken, dried and smashed; the manganese oxide modified diatomite is prepared; and (4), the manganese oxide modified diatomite is added to a 100mL Pb<2+> electrolytic zinc rinsing waste water solution, adsorbed at 25-30 DEG C for 80-85 minutes, subjected to capping, and then vibrated in a rotary water-bath constant-temperature vibrator at 200r / min till adsorption equilibrium is achieved. The method is simple in technology, and the recovery rate of Pb<2+> is high.
Owner:GUILIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Electric cable
ActiveCN105237866AReduce pollutionImprove flame retardant performancePlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsInsulated cablesPolyolefinElectrolysis
The invention discloses an electric cable, and relates to the field of electricity facility. Raw materials of the sheath tube of the cable comprise, by weight, 85 parts of polyolefin, 3 parts of plant ash, 2 parts of gum, 0.6 parts of a silane coupling agent, 1.5 parts of stearic acid, 0.7 parts of white carbon black, and 4 parts of electrolytic zinc acid leaching residue. The tensile strength of the cable sheath tube is higher than 26 MPa. The breaking elongation of the cable sheath tube is higher than 750%. The oxygen index of the cable sheath tube is higher than 36. The flame retarding performance of the cable sheath tube reaches the A level. The cable sheath tube also has significant characteristics of high strength and high flame retarding performance. Also, plant ash and electrolytic zinc acid leaching residue are recycled, such that environment pollution is reduced, and production cost is reduced. The electric cable has significant economic and environmental benefits.
Owner:正规电线电缆(东莞)有限公司
Anode for use in zinc and cobalt electrowinning and electrowinning method
ActiveUS8357271B2Reduce consumptionLow production costMachining electrodesPhotography auxillary processesElectrolysisManganese
The present invention aims to provide a zinc electrowinning anode capable of inhibiting manganese compound deposition on the anode and a cobalt electrowinning anode capable of inhibiting cobalt oxyhydroxide deposition on the anode.The zinc electrowinning anode according to the present invention is a zinc electrowinning anode having an amorphous iridium oxide-containing catalytic layer formed on a conductive substrate, and the zinc electrowinning method according to the present invention is an electrowinning method using that electrowinning anode. Also, the cobalt electrowinning anode according to the present invention is an electrowinning anode having an amorphous iridium oxide or ruthenium oxide-containing catalytic layer formed on a conductive substrate, and the cobalt electrowinning method according to the present invention is an electrowinning method using that electrowinning anode.
Owner:DOSHISHA CO LTD
Method for recovering valuable metals
Owner:METSO OUTOTEC (FINLAND) OY
Method for reducing ferric ions in pickle liquor containing Ge, In and Zn into ferrous ions
InactiveCN105039697AReduce contentOvercoming difficult flawsProcess efficiency improvementIndiumSlag
The invention relates to the technical field of wet metallurgy, in particular to a method for reducing ferric ions in pickle liquor containing Ge, In and Zn into ferrous ions. The method comprises the steps that firstly, stirring treatment is conducted for 40-60 minutes in the environment with the temperature ranging from 60 DEG C to 70 DEG C through ZnSO3; secondly, scrap iron is added, and a stirring reaction is conducted continuously for at least 30 minutes, so that the content of the ferric ions in an extraction pre-solution is reduced to the level below 200 mg / L. By means of the method, the problems that the cost is high by purely adopting zinc to reduce the ferric ions, the slag discharge amount is large and the cost is high by purely adopting the scrap iron to reduce the ferric ions and crystals produced by ferrous sulfate blocks a pipeline are solved, and the difficulty of consequent reactions is reduced; moreover, the defect that the difficulty of subsequently electrolyzing zinc is large when ferrous sulfate is adopted to reduce the ferric ions in the prior art is overcome; the germanium and indium content in the extraction pre-solution is prevented from being reduced; the extraction recovery rate of germanium and indium is guaranteed, and the additional value is increased.
Owner:GUIZHOU HONGDA ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
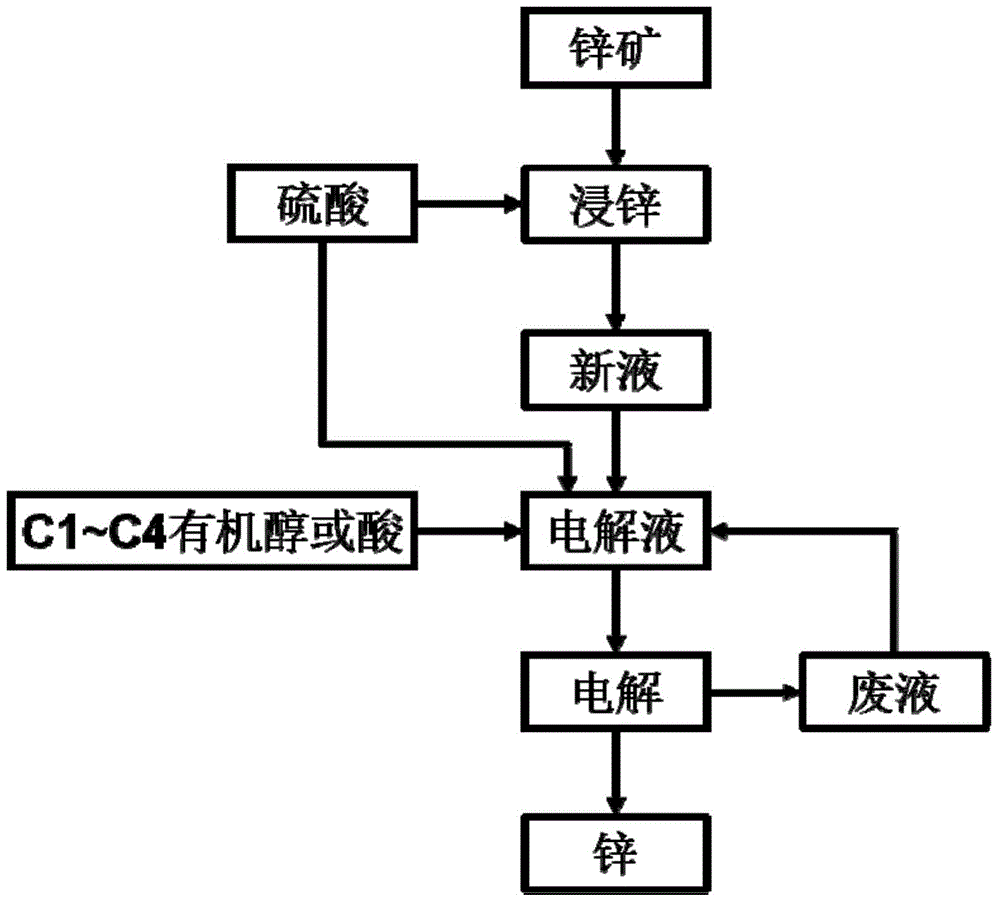
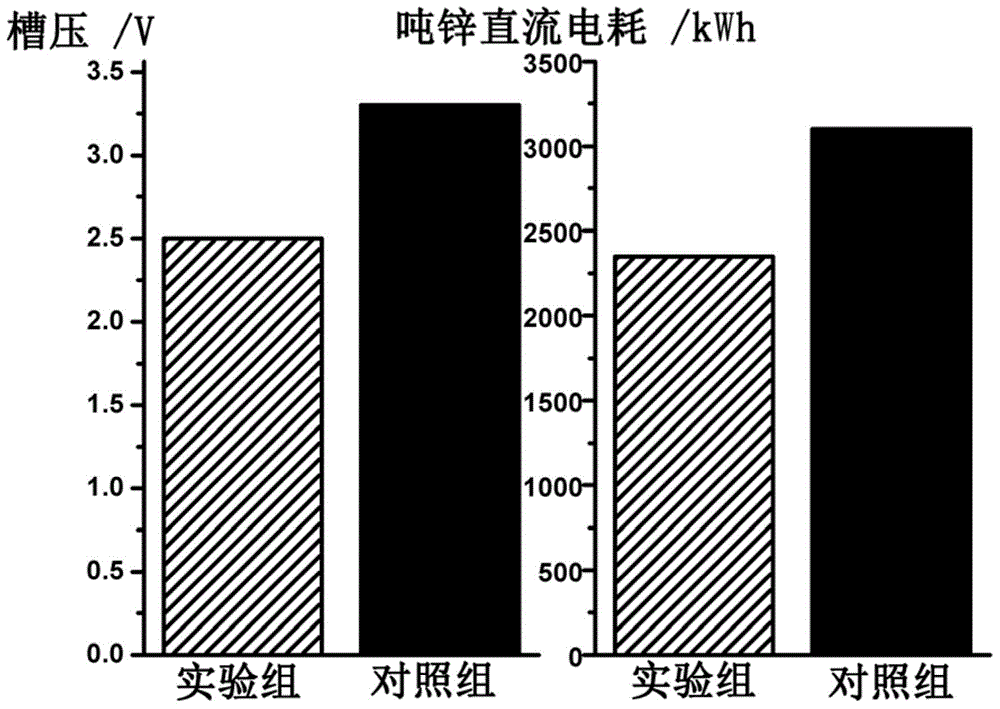
Low bath voltage zinc electrolysis method
InactiveCN104911630AReduce tank pressureChange the electrode reaction processPhotography auxillary processesElectrolysisAlcohol
A low bath voltage zinc electrolysis method relates to the field of zinc hydrometallurgy and solves the problem of large energy consumption of zinc electrolysis to adapt to industrial low energy and emission reduction production development demands. A certain concentration of C1-C4 organic linear acid or organic liner alcohol is added to an electrolyte, and the oxidation reaction potential of the C1-C4 organic linear acid or organic liner alcohol is lower than an anodic oxygen evolution potential, so the anodic reaction is characterized in that an organic matter oxidation reaction is preferentially carried out, and the electrode reaction process is fundamentally changed, thereby the bath voltage of a reaction system is reduced, and the problem of large energy consumption in the electrolysis process is effectively alleviated.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH +1
Sticking glue for sticking electrolytic zinc cathode plate insulation bar and production process of sticking glue
ActiveCN103242789AHigh bonding strengthGood sealingNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesEpoxy resin adhesivesChemistryPolyamide
The invention discloses sticking glue for sticking an electrolytic zinc cathode plate insulation bar and a production process of the sticking glue. The sticking glue consists of a component A and a component B, which are mixed according to a weight ratio of 1:1, wherein the component A comprises polyfunctional epoxy resin, HTBN (hydroxy-terminated butadiene-acrylonitrile), hydroxyl-terminated polysulfide rubber, a filler, an antioxidant, gas-phase silicon dioxide, body pigment and a defoaming agent, and the component B comprises polyamide, a filler, an amine curing agent, polyamine-thiourea polycondensate, an aminosilane coupling agent, a curing promoter, a flexibilizer, gas-phase silicon dioxide and a defoaming agent. By optically selecting and reasonably matching raw materials of different properties, the prepared sticking glue can be rapidly cured at the room temperature, the sticking strength of the sticking glue after being cured is high, and the sealing property is good; meanwhile, the sticking glue has excellent acid corrosion resistance, excellent aging resistance and excellent current impact resistance; and moreover, the sticking glue is low in cost, simple and convenient to construct, low in storage requirement, non-toxic, harmless and very suitable for sticking the electrolyte zinc cathode plate insulation bar.
Owner:云南曲靖润扬商贸有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com