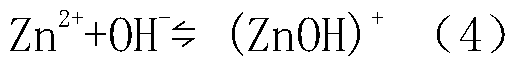Method for purifying zinc sulfate aqueous solution to remove nickel, cobalt and germanium
A zinc sulfate aqueous solution and nickel-cobalt technology are applied in the fields of purifying and removing nickel, cobalt and germanium, and in the fields of purifying and removing nickel, cobalt and germanium by hydro-smelting zinc, and can solve the problems of easy oxidation of cadmium and cobalt slag, poor adaptability of raw materials, and cobalt removal. The mechanism is unclear and other problems, so as to avoid re-dissolution, fast cobalt removal, and good cobalt removal effect.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
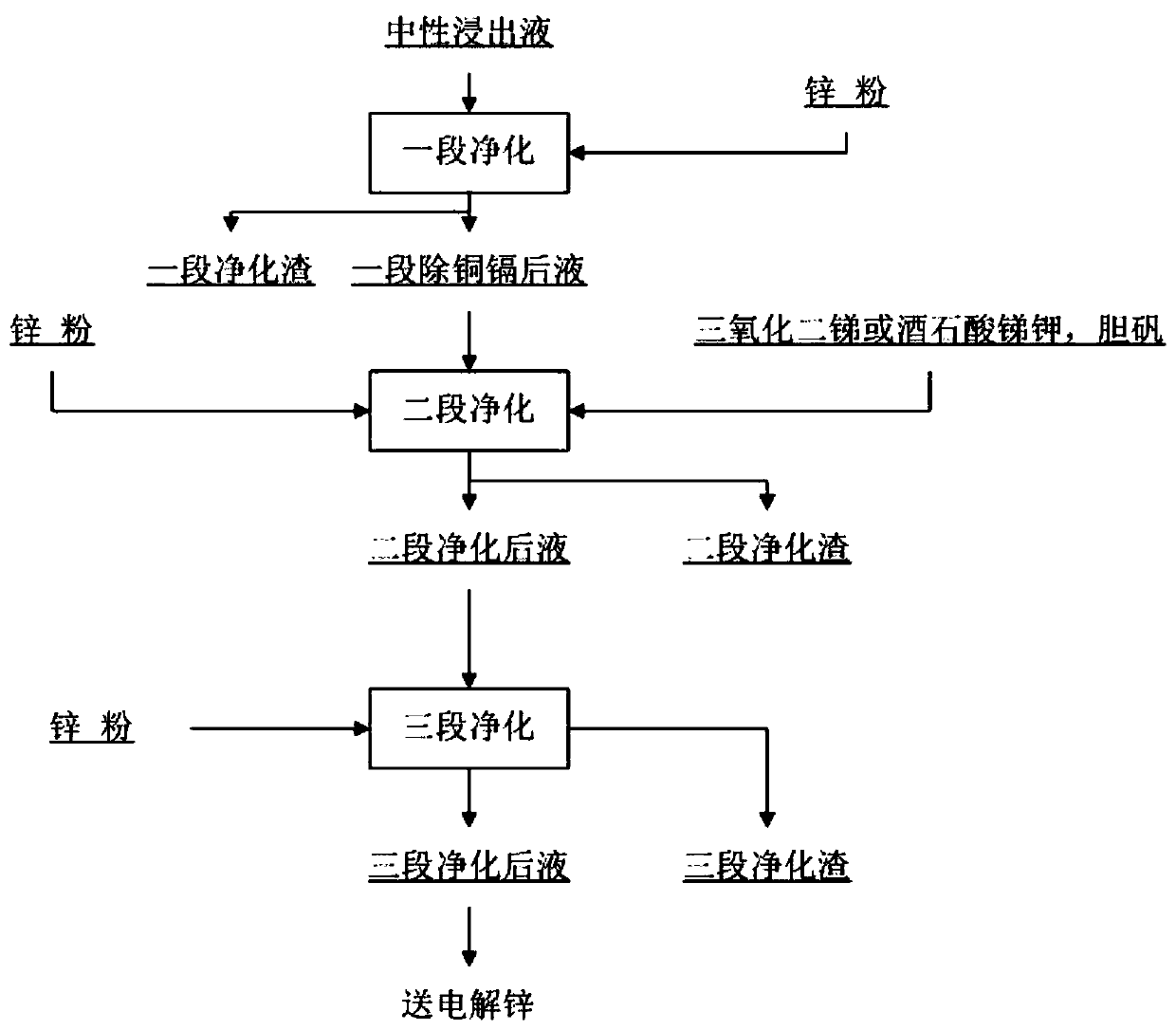
[0140] This embodiment adopts antimony potassium tartrate, Sb respectively 2 o 3 , Sb 4 o 5 Cl 2 Contrast experiment with cobalt and bile alum as activator for purification and removal of cobalt. The test temperature is 80°C, the test solution volume is 1 liter, and the test numbers are 1a, 1b, 1c, 1d, 1e.
[0141] The experimental equipment is a constant temperature water bath with a heating and temperature control device. The experiment is carried out in a beaker with an effective volume of 2 liters, and the stirring adopts a polytetrafluoro mechanical stirring paddle.
[0142] The experimental procedure is as follows: first heat a section of copper and cadmium removal solution to a certain temperature, add an appropriate amount of sulfuric acid, and at the same time add zinc powder, bile vitriol and antimony compound in solid form, maintain this temperature, and carry out cobalt removal experiment under stirring. After reacting for 60 minutes, start sampling to measure...
Embodiment 2
[0162] This example is an experiment on the influence of the amount of acid added to different types of zinc powder on the removal of cobalt. The experimental temperature is 80° C., and the amount of the experimental solution is 1 liter. The experimental equipment is the same as in Example 1.
[0163] a. Experiment on the amount of acid added to zinc powder in electric furnace
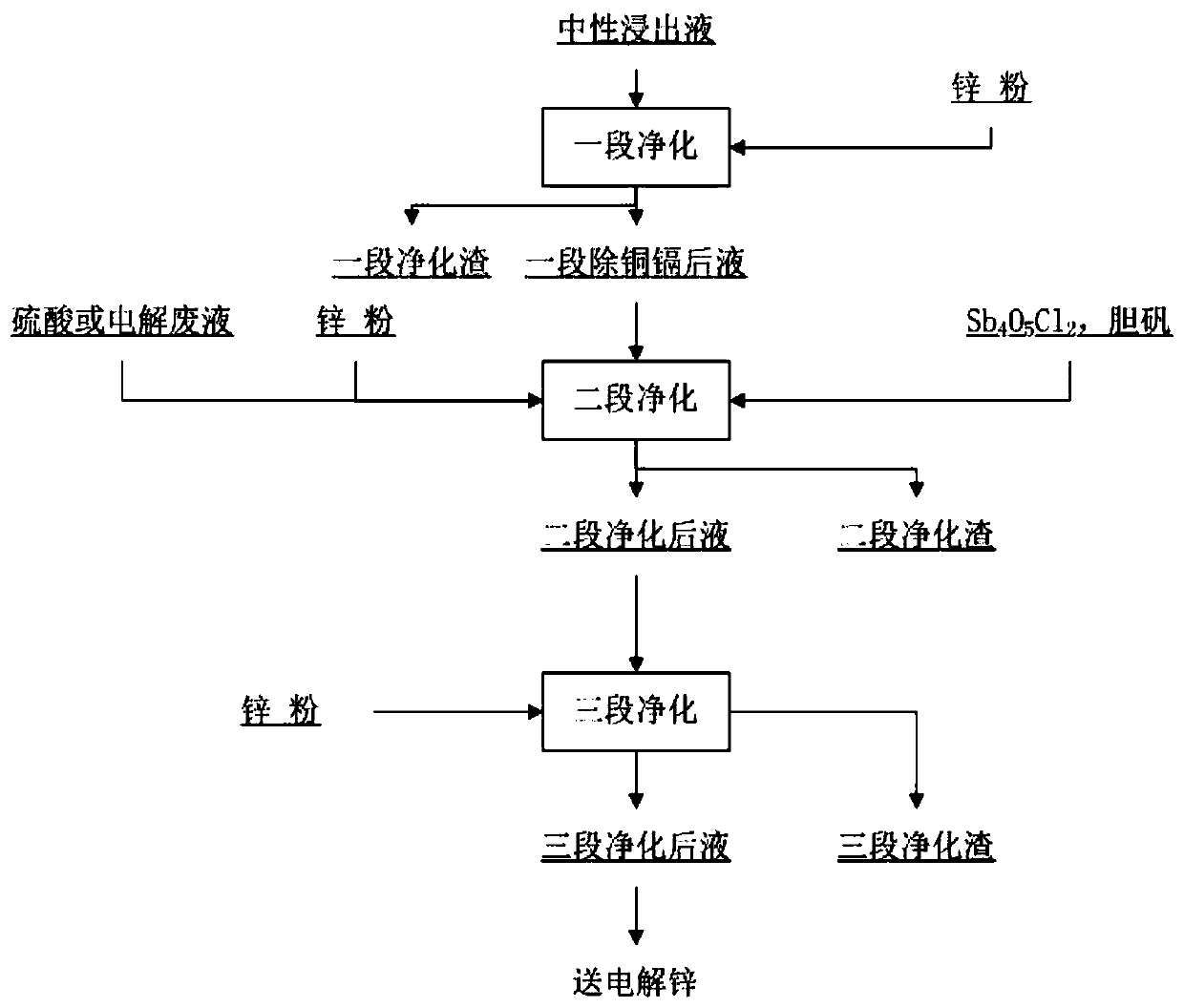
[0164] The main purpose of this experiment is to investigate the effect of the amount of acid added to the cobalt removal process of the electric furnace zinc powder on the removal of cobalt. The experiment numbers are 2a, 2b, 2c, and 2d. The experimental equipment and experimental procedures are the same as in Example 1. The difference is that sampling is only done at 90 minutes and 120 minutes, and no slag detection is performed. The zinc powder adopts the electric furnace zinc powder listed in Table 1, the zinc powder addition amount is 2g / l, and the activator adopts Sb 4 o 5 Cl 2 + bile vitrio...
Embodiment 3
[0177] This embodiment is an experiment of adding ways of bile vitriol and different antimony compounds and zinc powder. In the disclosed patents and some research papers, the addition method of the activator has not been paid attention to basically. The more addition method is to dissolve the activator into a solution first, then add it to the solution, and then add zinc powder. This addition method is conducive to precise control of the amount of reagent added. Surprisingly, the inventors found that different addition methods of the activator lead to significant differences in the experimental results. The experiment adopts two adding methods, the first one is to add the activator and dissolve it in the solution heated to the experimental temperature for 3 minutes, and then add zinc powder to remove cobalt; the second adding method is to use solid The activator and zinc powder are simultaneously added to the solution which has been heated to the experimental temperature. T...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com