Preprocessing method of lead/lead-alloy inert anode for zinc electrowinning
An inert anode and pretreatment technology, applied in the direction of electrodes, electrolysis process, electrolysis components, etc., can solve the problems of cathode zinc products not meeting the standard of 0# zinc, reducing production efficiency and cutting strength, etc., which is beneficial to industrial application. , The effect of reducing the output rate and suppressing the falling off
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
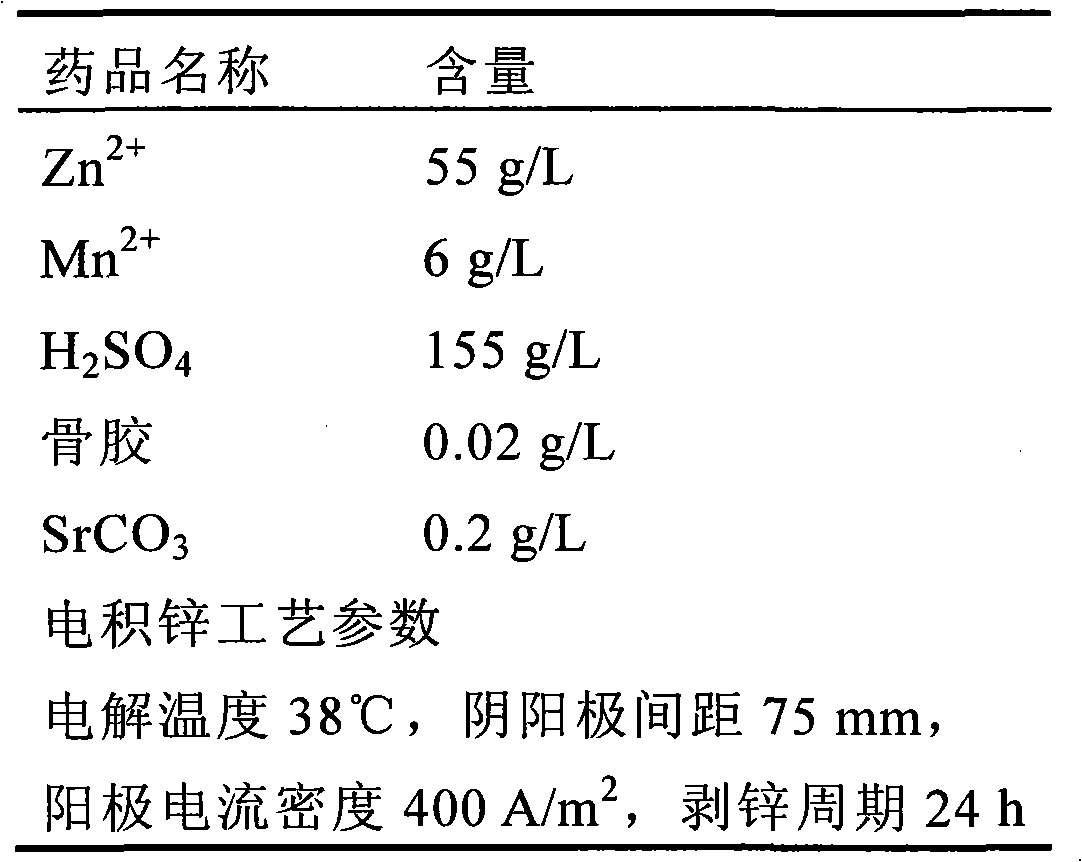
[0033] The composition of the pretreatment liquid of the present embodiment and the pretreatment process parameters are shown in Table 3
[0034] The pretreatment liquid composition of table 3 embodiment 1 and pretreatment process parameter
[0035]
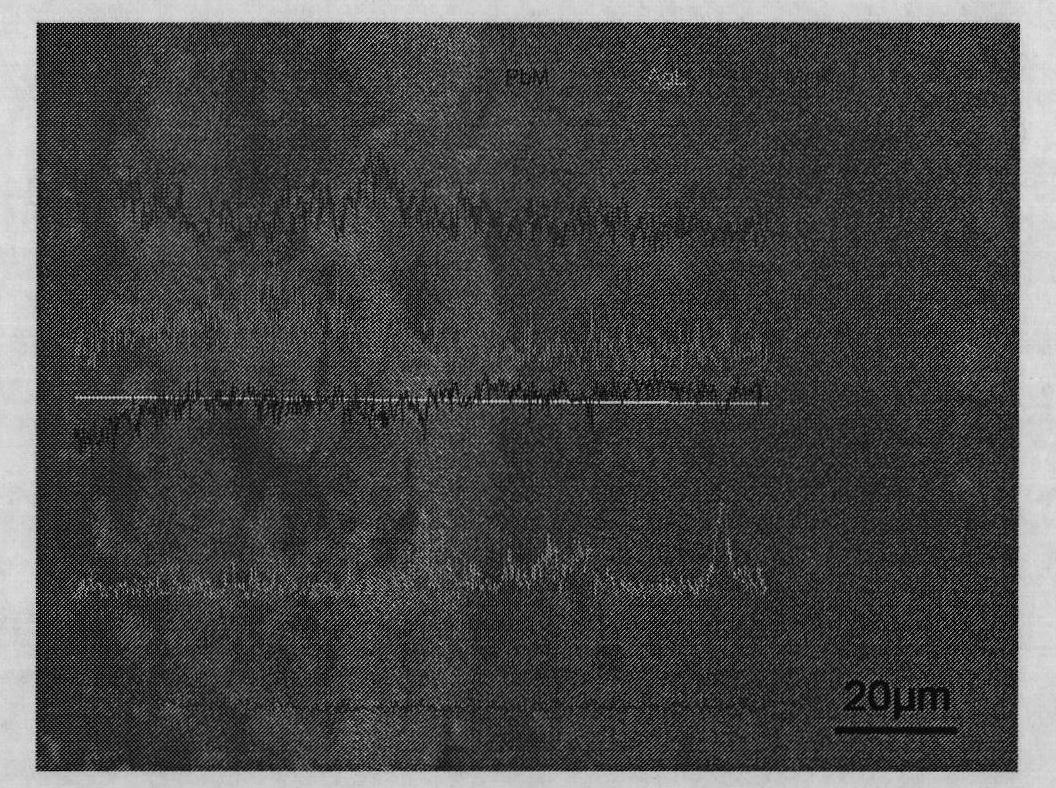
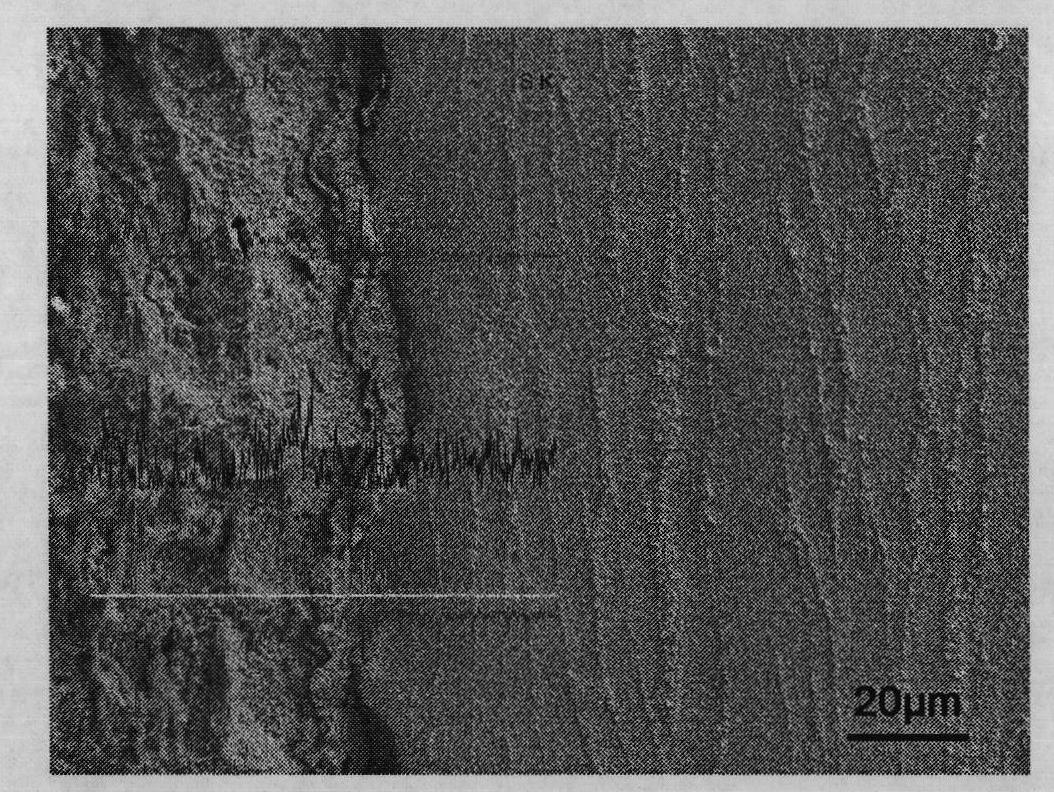
[0036] figure 2 It is the cross-sectional morphology of the lead-silver inert anode after pretreatment in this embodiment. The lead or lead alloy inert anode treated by the invention forms a dense transition layer of fluorine-containing products on the surface of the anode, thereby effectively suppressing the phenomenon that the anode slime is easy to fall off from the surface of the anode. The anode treated by this method has good corrosion resistance, and has obvious effects on reducing the zinc impurity lead content in the cathode and improving production efficiency.
[0037] The anode treated by this anode pretreatment process was used as the anode of electrolytic zinc. After 12 weeks (the anode was cleaned and cut at t...
Embodiment 2
[0042] The composition of the pretreatment solution and the parameters of the pretreatment process in this embodiment are shown in Table 5.
[0043] The pretreatment liquid composition of table 5 embodiment 2 and pretreatment process parameter
[0044]
[0045] The anode treated by this anode pretreatment process was used as the anode of electrolytic zinc. After 12 weeks (among which the anode was cleaned and cut at the sixth weekend), the average lead content in the cathode zinc per week is shown in Table 6.
[0046] Table 6 Weekly average and 12-week total average (ppm) of lead content in cathode zinc products
[0047]
[0048] It can be seen from Table 6 that except that the lead content of cathode zinc in the first week did not reach the standard of 0# zinc, the rest of the period was lower than the 0# zinc standard of 20ppm. When anode cleaning and gouging are performed, the lead content of the cathode zinc stabilizes at around 5ppm.
Embodiment 3
[0050] The pretreatment liquid composition and pretreatment process parameters of this embodiment are shown in Table 7.
[0051] The pretreatment liquid composition of table 7 embodiment 3 and pretreatment process parameter
[0052]
[0053] The anode treated by this anode pretreatment process was used as the anode of electrolytic zinc. After 12 weeks (the anode was cleaned and cut at the end of the 9th week), the average lead content in the cathode zinc per week is shown in Table 8.
[0054] Table 8 Weekly average and 12-week total average (ppm) of lead content in cathode zinc products
[0055]
[0056] It can be seen from Table 8 that except that the lead content of cathode zinc in the first week did not reach the standard of 0# zinc, the rest of the period was lower than the 0# zinc standard of 20ppm. When anode cleaning and gouging are performed, the lead content of the cathode zinc stabilizes at around 10ppm.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com