Near infrared spectrum-based mathematical model and detection method for heat-treated wood color
A technology of near-infrared spectroscopy and mathematical models, applied in the direction of material analysis, measuring devices, and scientific instruments through optical means, can solve problems such as uneven color of heat-treated wood and affect processing quality, so as to increase added value and improve product quality. Effect of adding value and expanding application fields
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] This embodiment is a mathematical quantitative model building method for detecting heat-treated wood color, specifically comprising the following steps:
[0038] (1) Sample pretreatment: treat southern pine wood into wood blocks (80 pieces in total) with a fiber direction of 20 mm x a radius direction of 20 mm x a chord direction of 20 mm;
[0039] (2) Heat treatment: Take 20 pieces of wood respectively, and use water vapor as a protective gas in an electric blower drying box, and carry out heat treatment at 120°C×4h, 180°C×4h, 220°C×4h, plus untreated A group of (20) together as the experimental material.
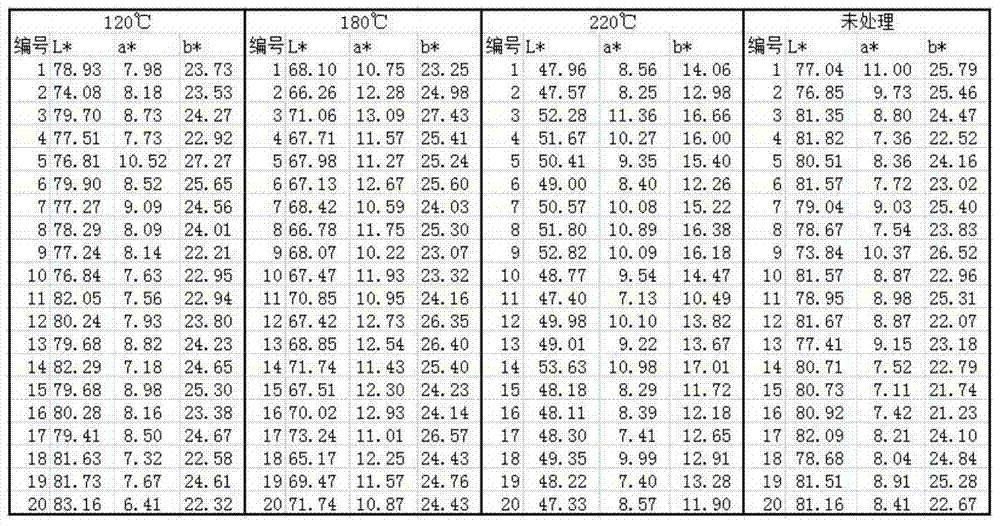
[0040] (3) Measure the colorimetric parameters of the wood block (the data are shown in the column of L*, a*, b* in Table 1);
[0041] Table 1 Colorimetric parameter data of each wood block
[0042]
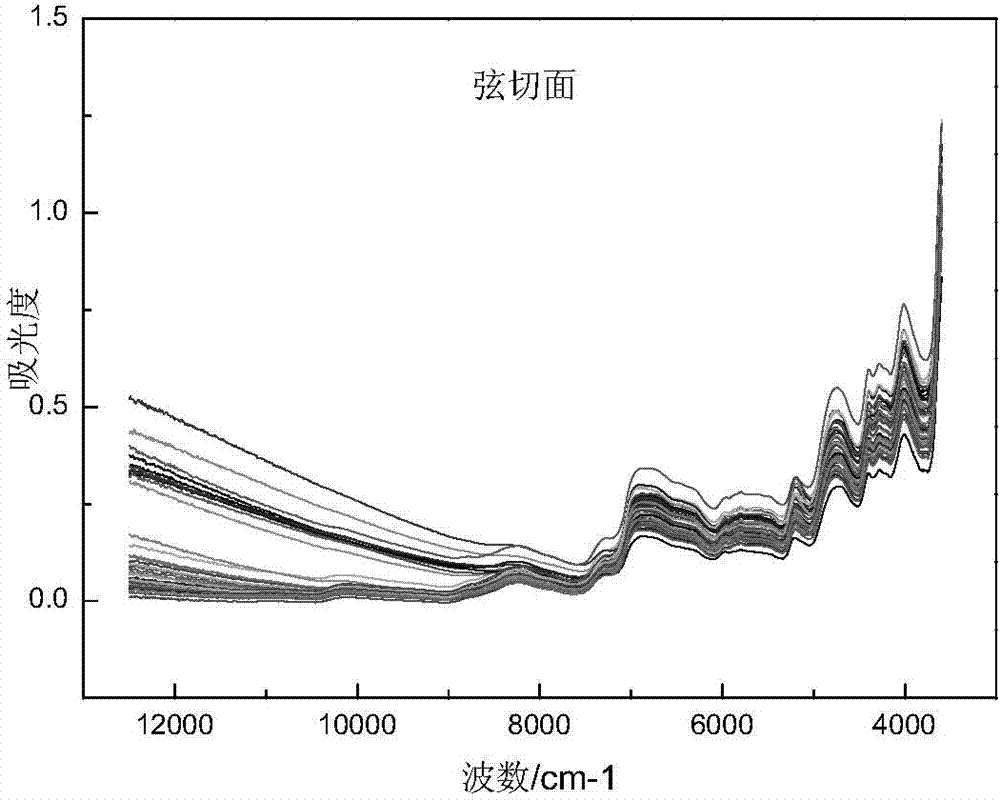
[0043] (4) Gather near-infrared spectrum: Get step (3) and carry out the wooden piece after the colorimetric parameter measurement, utilize German Bruker to have ...
Embodiment 2
[0053] The difference between embodiment 2 and embodiment 1 is that the preprocessing method of the near-infrared spectral information of the step (5) chord section is different. In embodiment 2, the preprocessing method is: use OPUS software to eliminate the near-infrared spectral data of the chord section The constant bias preprocessing method selects the range of the spectral region, 9-point smoothing, 10 principal components, and uses partial least squares and cross-validation methods.
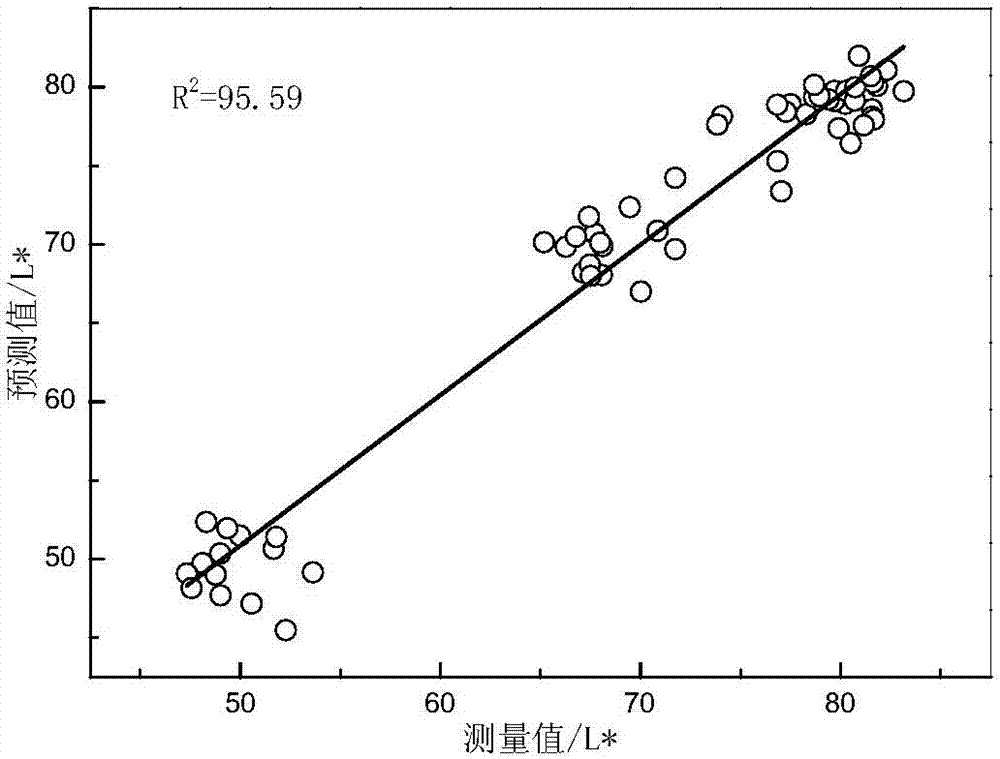
[0054] The mathematical quantitative model of the obtained chromaticity parameter lightness L* is, the coefficient of determination R 2 =91.97, root mean square error RMSECV=3.35, relative analytical error RPD=3.53.
Embodiment 3
[0056] The difference between embodiment 3 and embodiment 1 is only that the preprocessing method of the near-infrared spectral information of the step (6) chord section is different, and the preprocessing method in embodiment 2 is: utilize OPUS software to carry out a Order derivative and vector normalization preprocessing method, select the range of spectral region, 15-point smoothing, 3 principal component scores, use partial least square method and cross-check method.
[0057] The obtained mathematical quantitative model of a* has coefficient of determination R2=89.38, root mean square error RMSECV=0.692, and relative analysis error RPD=2.46.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com