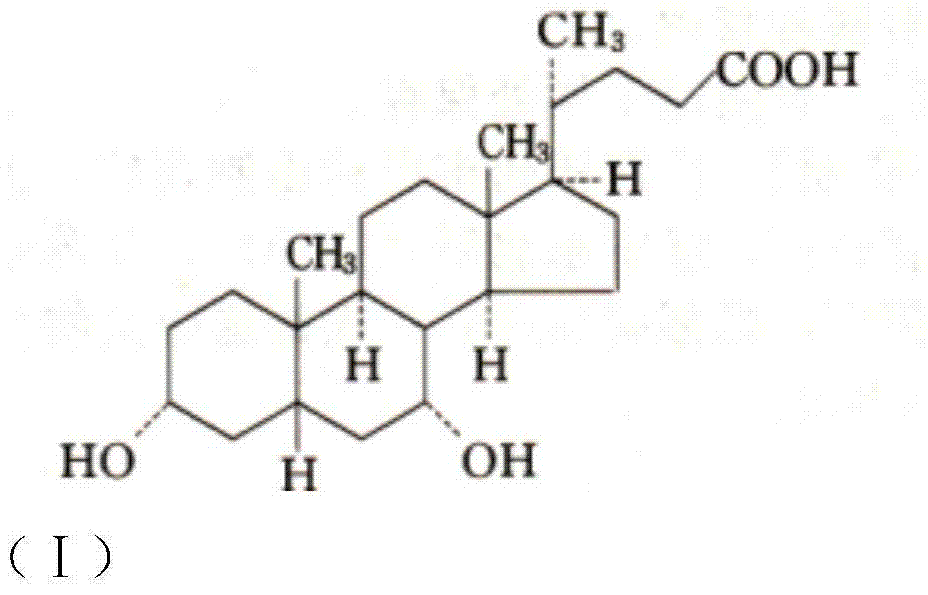
Chenodeoxycholic acid and application thereof
A kind of use, technology of compound, application field in preventing and treating arterial thrombosis disease
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
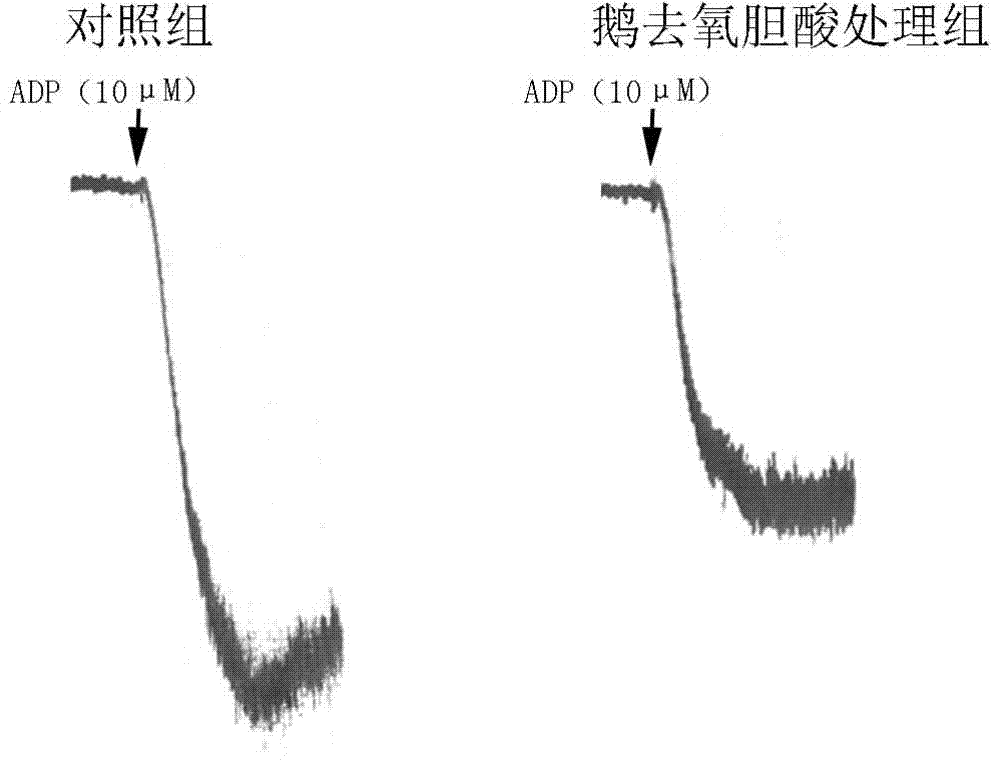
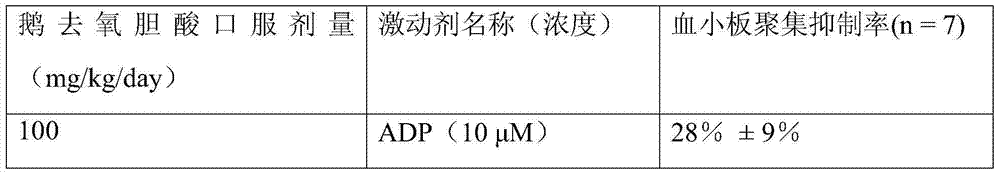
[0083] Example 1. Inhibitory effect of chenodeoxycholic acid on ADP-induced human platelet aggregation
[0084] The purpose of this example is to prove that chenodeoxycholic acid can inhibit ADP-induced human platelet aggregation.
[0085] In this example, the platelets were prepared as follows: platelets were obtained from healthy volunteers who signed informed consent, and the volunteers did not take any antiplatelet drugs such as aspirin and clopidogrel within 20 days before blood collection. Anticoagulant ACD (85mmol L -1 Sodium citrate, 71.38mmol L -1 Citric acid, and 27.78mmol L -1 glucose). Centrifuge at 300xg for 20 minutes to obtain platelet-rich plasma, take the upper layer of platelet-rich plasma and centrifuge at 900xg for 10 minutes to obtain platelets, and finally resuspend with Tyrode's buffer (138mmol L -1 Sodium chloride (NaCl), 2.7mmol L -1 Potassium chloride (KCl), 2 mmol L -1 Magnesium Chloride (MgCl 2 ), 0.42 mmol L -1 Sodium dihydrogen phosphate (...
Embodiment 2
[0090] Example 2. Inhibitory effect of 100 μM chenodeoxycholic acid on human platelet aggregation induced by other various agonists
[0091] The purpose of this example is to prove that chenodeoxycholic acid can inhibit the aggregation of human platelets induced by thrombin and collagen.
[0092] In this example, the preparation of platelets and the aggregation induction and measurement methods of platelets are the same as those in Example 1. The results are shown in Table 2. Chenodeoxycholic acid inhibits thrombin (Chrono-log Company, Havertown, PA) (0.1 U / mL) and collagen (Chrono-log Company, Havertown, PA) (1 μg / mL) at 100 μM Induced aggregation of human platelets.
[0093] Table 2: Chenodeoxycholic acid inhibits thrombin- and collagen-induced aggregation of human platelets.
[0094] Chenodeoxycholic acid concentration (μM)
Embodiment 3
[0095] Example 3. Inhibitory effect of chenodeoxycholic acid on platelet spreading.
[0096] The purpose of this example is to demonstrate that chenodeoxycholic acid can inhibit platelet spreading.
[0097] In this embodiment, the preparation of platelets is the same as in Example 1, and the experimental process of platelet spreading is as follows:
[0098] 1) Coating of coverslips or culture plates: Coat coverslips or disposable culture plates with 20 μg / mL fibrinogen (fibrinogen, Chrono-log Company, Havertown, PA) (dissolved in PBS), 4°C Overnight, 2% bovine serum albumin blocked non-specific binding sites at 37°C for 1 hour, and washed once with PBS.
[0099] 2) Adjust the concentration of platelets in the control group or chenodeoxycholic acid treatment group to 1.8×10 with HEPES-Tyrode buffer 6 / 500 μL, inoculated on the fibrinogen-coated coverslips in a 24-well plate, 500 μL per well, and incubated at 37°C for 2 hours.
[0100] 3) Take out the above coverslip, wash once...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com