Preparation method of cellulose-modified modified nano-iron particles
A technology of modification and nano-iron, which is applied in the field of water treatment, can solve the problems of loss of reactive sites of nano-zero-valent iron particles, reduction of effective contact area of pollutants, unfavorable environmental pollution restoration work, etc., to achieve easy engineering The effect of chemical application, good environmental friendliness, and good particle uniformity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
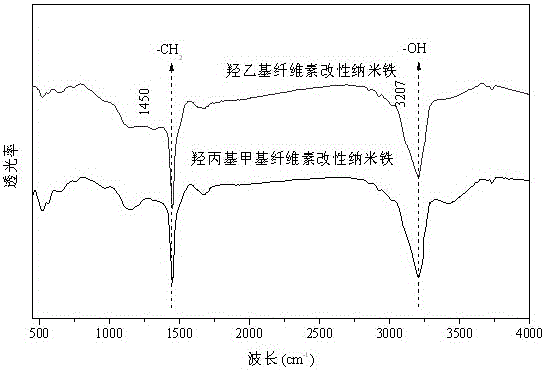
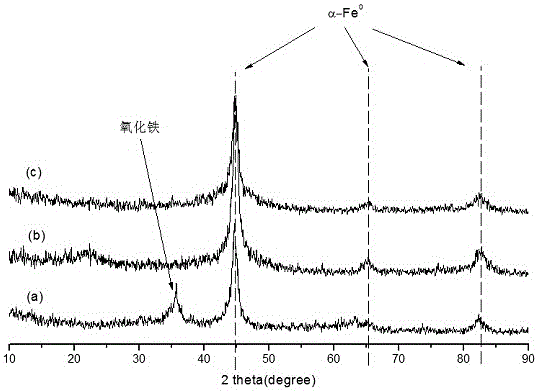
[0029] Example 1: Preparation and crystal structure analysis of nanometer zero-valent iron
[0030] (1) Preparation of unmodified nano zero-valent iron
[0031] 100ml of 5.0 mol / L potassium borohydride solution was dropped into 100ml of FeSO with a concentration of 0.9 mol / L 4 In the solution, stir while dripping, and continue stirring for 15 minutes after the addition of the solution is complete, filter the solution that has completely reacted, and rinse the obtained filter cake with deionized water for 3 times and then filter dry to obtain nanometer zero-valent iron particles; use acetone and After rinsing the nano-iron particles with anhydrous ethanol mixture (volume ratio of acetone and absolute ethanol: 1:5), the nano-iron particles were filtered and vacuum-dried, and the dried particles were ground and sealed to obtain unmodified nano-zero-valent iron .
[0032] (2) Preparation of hydroxyethyl cellulose modified nanometer zero-valent iron
[0033] Mix 10 g / L hydroxyet...
Embodiment 2
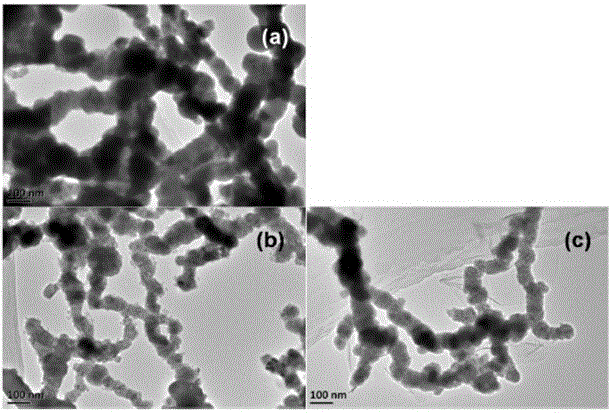
[0038] Example 2: Analysis of agglomeration degree of nano-zero-valent iron and cellulose-modified modified nano-iron particles
[0039] (1) Preparation of unmodified nano zero-valent iron particles
[0040] 100ml of 3.0 mol / L potassium borohydride solution is dropped into 100ml of FeSO with a concentration of 1.5mol / L 4 In the solution, stir while dripping, continue to stir for 40min after the addition of the solution is completed, filter the solution that has reacted completely, and filter the obtained filter cake to rinse with deionized water for 5 times to obtain nanometer zero-valent iron particles; use acetone and The nano-iron particles obtained by washing with anhydrous ethanol mixture (acetone and ethanol volume ratio 1:9) were washed twice, then vacuum-dried after suction filtration, and the dried particles were ground and sealed to obtain unmodified nano-sized zero-valent iron.
[0041] (2) Preparation of hydroxyethyl cellulose modified nanometer zero-valent iron ...
Embodiment 3
[0047] Example 3: Specific surface area (BET) analysis of cellulose-modified modified nano-iron particles
[0048] (1) Preparation of unmodified nano zero-valent iron particles
[0049] 100ml of 1.0 mol / L potassium borohydride solution was dropped into 100ml of FeSO with a concentration of 0.5 mol / L 4 In the solution, stir while dripping, and continue stirring for 5 minutes after the addition of the solution is complete, filter the solution that has completely reacted, and rinse the obtained filter cake with deionized water for 3 times and then filter dry to obtain nanometer zero-valent iron particles; use acetone and After rinsing the nano-iron particles with anhydrous ethanol mixture (volume ratio of acetone and ethanol: 1:5), the nano-iron particles were filtered and vacuum-dried, and the dried particles were ground and sealed to obtain unmodified nano-sized zero-valent iron.
[0050] (2) Preparation of hydroxyethyl cellulose modified nanometer zero-valent iron
[0051] M...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com