A method for evaluating oxidative stress in vivo based on detection of oxidative damage to mitochondrial DNA in peripheral blood
A technology for oxidative damage and mitochondria, applied in the field of molecular diagnosis, can solve the problems of low sensitivity, difficult promotion and application, and high cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Example 1 Primer Design
[0039]According to the standard sequence of human mtDNA (NC_012920) in the NCBI gene bank, primers were first designed for the mtDNA D-loop region (displacement loop). The D-loop region contains the replication initiation region for mtDNA heavy chain synthesis, is the control region for mtDNA replication, and is also the binding site for mtDNA and mitochondrial membranes. It is susceptible to lipid peroxides and is a high-incidence region for mtDNA mutations. The base mutation rate is 6-8 times higher than other regions. The D-loop region includes three hypervariable regions, hypervariable region I (np16024-16383), hypervariable region II (np57-372) and hypervariable region III (np438-574). Therefore, in order to ensure the specificity of amplification, these three hypervariable regions should be avoided when designing primers.
[0040] The fragment amplified by the DLP1 primer shown in Table 1 does not cover the hypervariable region, while t...
Embodiment 2
[0044] Example 2 Construction of cell model
[0045] HUEVC cell culture: RPMI 1640 medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum, 1% penicillin-streptomycin solution, 37°C, 5% CO 2 Cultivation; after the cells grow to the full of the culture dish, they are subcultured. When subcultured, wash the cells twice with PBS, digest with trypsin at 37°C for 1-2 minutes, add 1640 medium and blow the cells to make them fall off, collect the cells, wash the cells twice with PBS, and continue to cultivate;
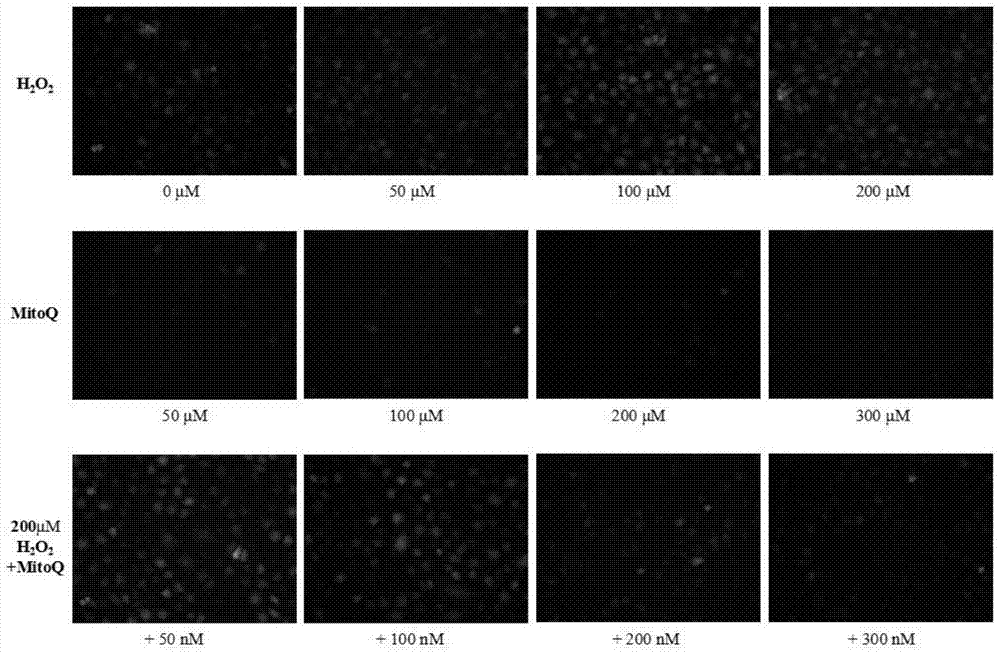
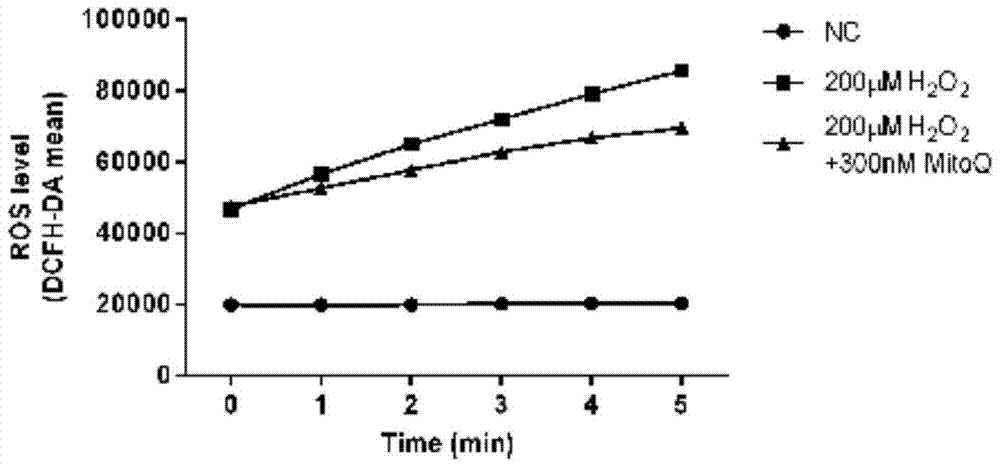
[0046] Oxidative stress cell model: add a certain amount of H 2 o 2 , so that the final concentration is 50, 100, 150, 200μM; antioxidant group: 200μM H 2 o 2 and antioxidant MtioQ, the final concentrations were 100, 200, 300nM; except H 2 o 2 , HUEVC cells under the same culture conditions as the control group. Cells were collected after 2 h of action, and after the protein concentration was measured by BCA method, MDA (malondialdehyde), SOD (superoxide dismutase), CAT (catalase), G...
Embodiment 3
[0050] Example 3 Detection of Oxidative Damage Levels of Intracellular and Extracellular mtDNA
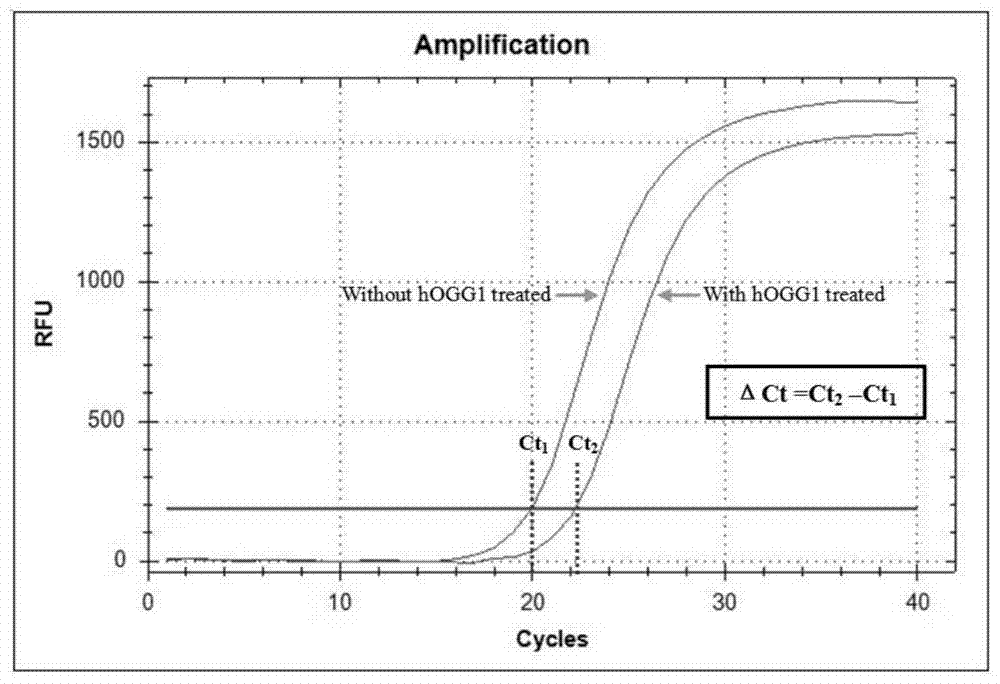
[0051] Extract various H 2 o 2 Cell DNA treated with MitoQ concentration, the cell supernatant free DNA was extracted by magnetic bead method. A certain amount of DNA and hOGG were bathed in water at 137°C for 2h. The same amount of DNA was used as a control without adding hOGG1, and other conditions were the same. Then use the above 5 pairs of primers to carry out qPCR reaction respectively, and calculate the difference of Ct value between the DNA samples from the same source with and without hOGG1, so as to reflect the content of 8-OH-dG, and indirectly reflect the level of DNA oxidative damage .
[0052] Preparation of hOGG1 enzyme digestion reaction system
[0053]
[0054] Mix well, 37°C water bath for 2h, 65°C enzyme inactivation 15mim
[0055] Fluorescent quantitative PCR
[0056] 1) Prepare PCR reaction system
[0057]
[0058] 2) PCR reaction conditions:
[...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com