A preparation method of salt-resistant and detergent-resistant seaweed fiber
A technology resistant to detergents and seaweed fibers, which is applied in fiber treatment, plant fibers, alginate artificial filaments, etc., can solve the problems of salt and detergent resistance, and achieve textiles with complete structures, environmentally friendly production processes, and good The effect of salt resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] (1) auxiliary agent is selected as boric acid solution (soaking solution), the preparation of boric acid soaking solution:
[0025] Dissolve 8g of boric acid in deionized water to prepare 400g of soaking solution, heat to 70°C, add Na 2 CO 3 Adjust the pH of the solution to 8;
[0026] (2) Preparation of boric acid modified seaweed fiber
[0027] Immerse 40g of calcium alginate fibers in the boric acid soaking solution obtained in the first step for 10 minutes, rinse the soaked seaweed fibers with deionized water, and dry to obtain boric acid modified seaweed fibers.
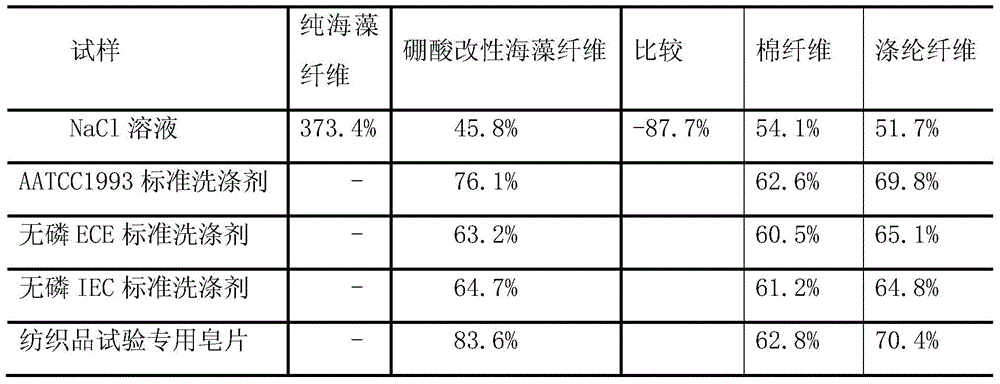
[0028] Table 1 shows the fiber swelling data of the modified seaweed fiber prepared in this example.
[0029] Table 1
[0030]
[0031] *: "-" indicates dissolution, and it has the same meaning in the following tables.
Embodiment 2
[0033] (1) auxiliary agent is selected as sodium tetraborate solution (soaking solution), the preparation of sodium tetraborate soaking solution:
[0034] Dissolve 0.5g of sodium tetraborate in deionized water to make 500g of soaking solution, heat to 50°C, add NaOH to adjust the pH of the solution to 10;
[0035] (2) Preparation of sodium tetraborate modified seaweed fiber
[0036] Immerse 50g of lead alginate fiber in the sodium tetraborate soaking solution obtained in the first step, soak for 300 minutes, rinse the soaked seaweed fiber with deionized water, and obtain sodium tetraborate modified seaweed fiber after drying. The swelling degree test data is as follows: Table 2 shows.
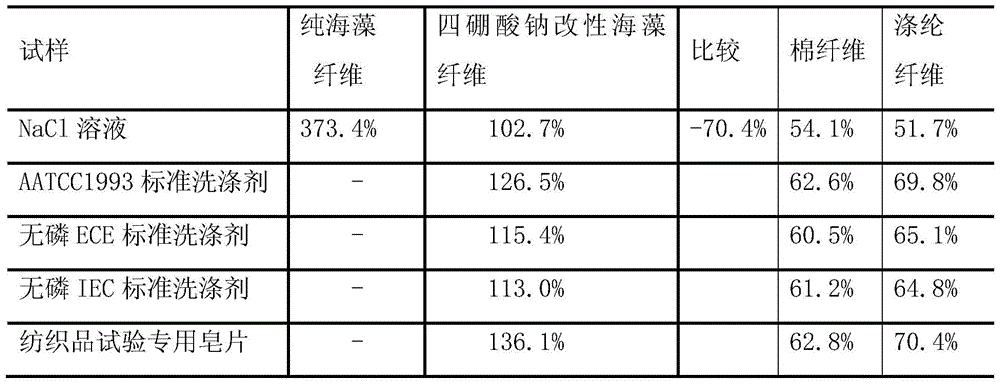
[0037] Table 2
[0038]
Embodiment 3
[0040] (1) auxiliary agent solution is selected as ammonium pentaborate solution (soaking liquid), the preparation of ammonium pentaborate soaking liquid:
[0041] Dissolve 1kg of ammonium pentaborate in deionized water to prepare 35Kg of soaking solution, heat to 60°C, add ammonia water to adjust the pH value of the solution to 9;
[0042] (2) Preparation of ammonium pentaborate modified seaweed fiber
[0043] Immerse 5 kg of zinc alginate fiber in the ammonium pentaborate soaking solution obtained in the first step, soak for 20 minutes, rinse the soaked seaweed fiber with deionized water, and dry it to obtain ammonium pentaborate modified seaweed fiber. The swelling degree test data is as follows: Table 3 shows.
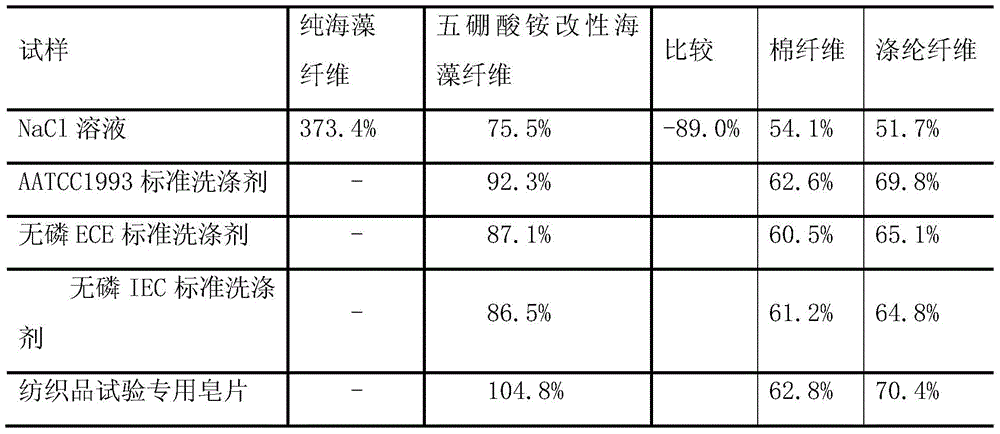
[0044] table 3
[0045]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com