Method for total DNA extraction and diversity analysis of ship ballast water microorganisms
A technology for ship ballast water and microorganisms, which is applied in the field of environmental microbial molecular ecology to achieve the effects of simple operation, simple and convenient method, and avoiding DNA loss.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
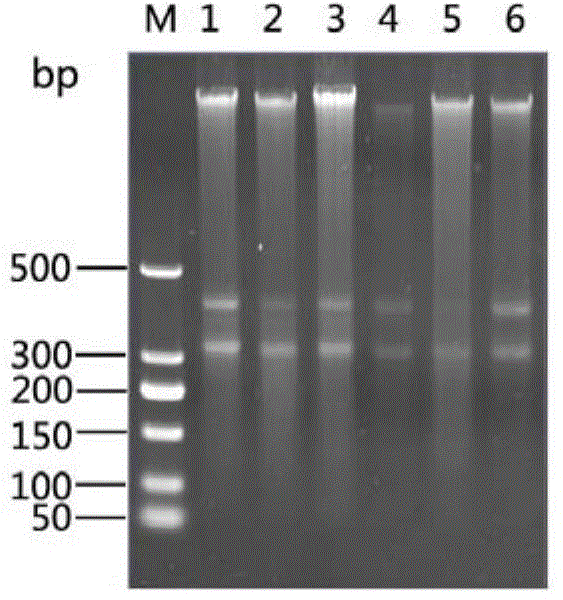
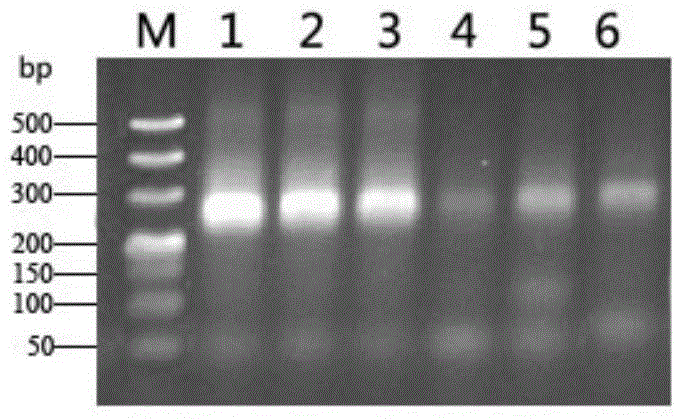
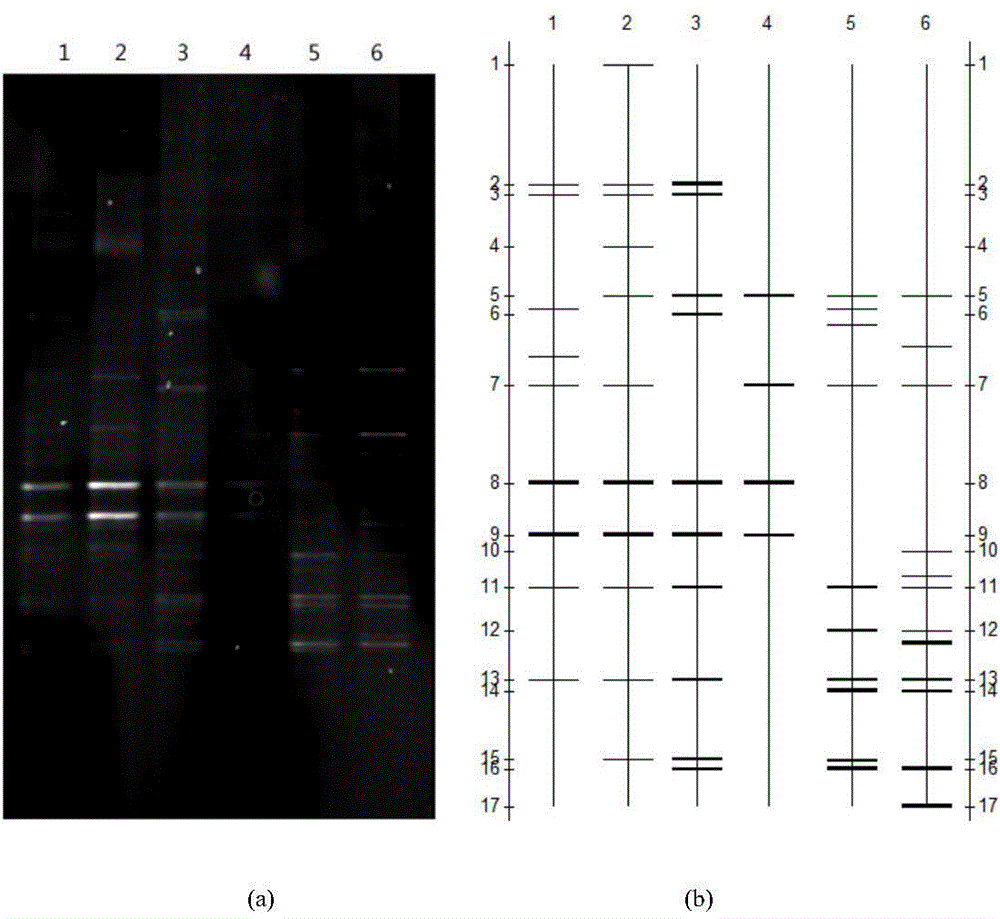
[0053] Select a ship, take samples, and take ballast water from ballast tanks in different spatial positions of the ship, analyze the bacterial population structure and determine the dominant bacterial group as follows
[0054] 1) Extraction and detection of microbial total DNA in ballast water:
[0055] Use water collectors to collect ballast water in different ballast tanks of ships, collect 2L samples in sterilized blue-necked glass bottles, and store them at 4°C; take ballast water samples and filter them through 3 μm and 0.22 μm microporous membranes (filter membranes) Prior sterilization treatment) After two-stage filtration, discard the 3 μm microporous filter membrane, and the ballast water microorganisms are on the 0.22 μm microporous filter membrane; use sterilized surgical forceps to transfer the 0.22 μm filter membrane to a 1.5mL centrifuge tube, Immediately freeze in a -80°C refrigerator for 4 hours; take out the centrifuge tube with the microbial filter membrane ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com