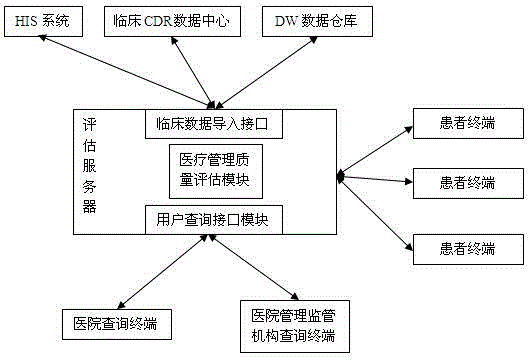
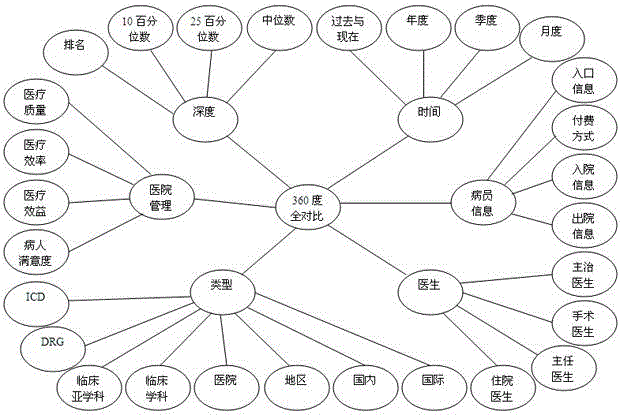
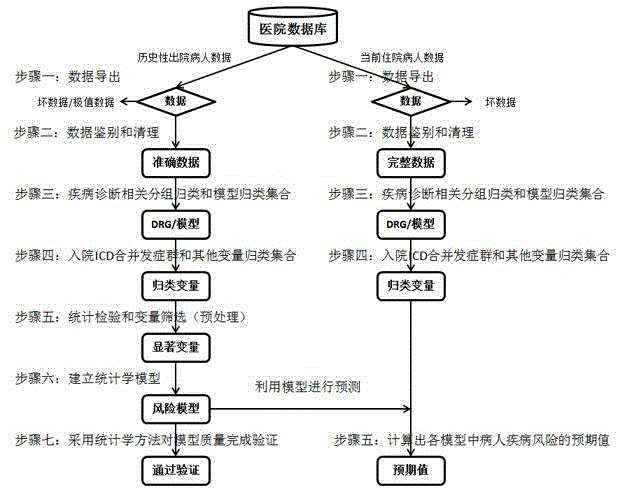
Intelligent analysis and assessment system for disease management in hospital
A technology of intelligent analysis and evaluation system, applied in the field of intelligent analysis and evaluation system of hospital disease management, can solve the problems of increasing model instability, artificially high cost treatment, deviation of judgment results, etc., to improve medical quality and operational efficiency, increase Patient Satisfaction, Improve the Effect of Clinical Research
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0093] Example 1: Categorical variables for disease coding and population information
[0094]
[0095] Bacterial endocarditis complex group (ICD9 code)
[0096] The patient's basic demographic information and admission status variables (partial) are as follows:
[0097]
[0098]
[0099] S5: Within the same DRG cohort, statistically significant comorbidities and other categorical variables were pretreated by statistical tests for patient mortality, length of hospital stay, and cost.
[0100] S6: In the step of establishing a statistical model, regression analysis is performed on the model to quantify the degree of influence of variables;
[0101] Use the independent variables to quantitatively describe the predictive variables. In the disease risk adjustment, the predictive variables are patient mortality, hospitalization days and hospitalization costs, and the independent variables are combined complication variables and other variables; the regression analysis of ...
example 2
[0104] Example 2: DMIAES Mortality Model #22: (patient age ≥ 18) acute ischemic stroke and use of thrombolytic agents with severe complications (MSDRG 61), with complications (MSDRG 62), without complications ( MSDRG 63).
[0105] Data source: Memorial Hermann Hospital, Texas Medical Center, USA
[0106] Number of patients in modeling sample: 996 Sample time 7 / 1 / 2004-6 / 30 / 2014
[0107] Model Category: Logistic Regression Model
[0108] Explanatory variables for combined complications
intercept
-4.159
pressure on the brain
2.272
Female, aged 75-80 years
1.547
1.488
On a ventilator within 48 hours of admission
1.392
give up rescue
1.388
1.344
1.285
Female, over 85 years old
1.092
0.943
Arrhythmia
0.906
[0109] acute respiratory failure
0.322
atri...
example 3
[0117] Example 3: Model quality verification results and comparative analysis
[0118] 1. Mortality rate
[0119] Model #22: Acute Ischemic Stroke DRG 61,62,63
[0120] Data source: Memorial Hermann Hospital, Texas Medical Center, USA
[0121] Test Sample Patient Number: 66 Discharge Time 7 / 1 / 2004-6 / 30 / 2014
[0122] Comparing models: our DMIAES model and the American equivalent model (referred to as U model)
[0123] C-Index test of model fit: DMIAES model in modeling data: 0.890, DMIAES model in test data: 0.964, U model: 0.933.
[0124]
[0125]
[0126] Model #328: Multiple Surgical Trauma DRG 957,958,959
[0127] Data source: Memorial Hermann Hospital, Texas Medical Center, USA
[0128] Number of test samples: 212 Discharge time 7 / 1 / 2004-6 / 30 / 2014
[0129] Comparing models: our DMIAES model and the American equivalent model (referred to as U model)
[0130] C-Index test of model fit: DMIAES model in modeling data: 0.955, DMIAES model in test data: 0.987, U mod...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com