Fat-soluble tea polyphenol preparation method
A fat-soluble tea polyphenol and tea polyphenol technology, which can be applied in food preparation, medical preparations with inactive ingredients, and pharmaceutical formulations, etc., can solve the problems of highly toxic solvents, high cost of enzymes, low enzymatic hydrolysis efficiency, etc. The effect of shortening the reaction time and improving the lipid solubility of the product
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
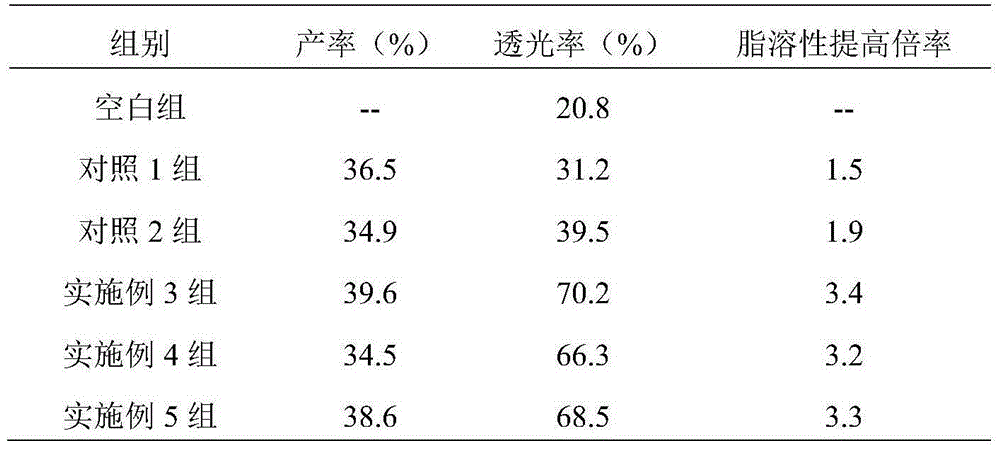
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] (1) Take tea polyphenols, add ethyl acetate, mix well, add lipase and protease, and finally add disodium hydrogen phosphate-sodium dihydrogen phosphate buffer to obtain a reaction solution;
[0024] (2) Microwave radiation was carried out to the above reaction solution, and the reaction was carried out at a temperature of 35° C. for 10 minutes;
[0025] (3) After the reaction is finished, add water to remove water-soluble impurities, stand to separate layers, take the ethyl acetate layer, distill under reduced pressure, and vacuum freeze-dry to obtain the product.
[0026] In step (1), ethyl acetate is food-grade ethyl acetate, and its addition is that every gram of tea polyphenols adds ethyl acetate 300ml.
[0027] In step (1), the mass ratio of the total mass of lipase and protease to tea polyphenol is 0.0625:1, wherein the mass of lipase accounts for 20% of the total mass.
[0028] In step (1), the amount of disodium hydrogen phosphate-sodium dihydrogen phosphate bu...
Embodiment 2
[0032] (1) Take tea polyphenols, add ethyl acetate, mix well, add lipase and protease, and finally add disodium hydrogen phosphate-sodium dihydrogen phosphate buffer to obtain a reaction solution;
[0033] (2) Microwave radiation was carried out to the above reaction solution, and the reaction was carried out at a temperature of 45° C. for 20 minutes;
[0034] (3) After the reaction is finished, add water to remove water-soluble impurities, stand to separate layers, take the ethyl acetate layer, distill under reduced pressure, and vacuum freeze-dry to obtain the product.
[0035] In step (1), ethyl acetate is food-grade ethyl acetate, and its addition is that every gram of tea polyphenols adds 400ml of ethyl acetate.
[0036] In step (1), the mass ratio of the total mass of lipase and protease to tea polyphenol is 0.1875:1, wherein the mass of lipase accounts for 50% of the total mass.
[0037] In step (1), the amount of disodium hydrogen phosphate-sodium dihydrogen phosphate...
Embodiment 3
[0041] (1) Take tea polyphenols, add ethyl acetate, mix well, add lipase and protease, and finally add disodium hydrogen phosphate-sodium dihydrogen phosphate buffer to obtain a reaction solution;
[0042] (2) Microwave radiation was carried out to the above reaction solution, and the reaction was carried out at a temperature of 40° C. for 15 minutes;
[0043] (3) After the reaction is finished, add water to remove water-soluble impurities, stand to separate layers, take the ethyl acetate layer, distill under reduced pressure, and vacuum freeze-dry to obtain the product.
[0044] In step (1), ethyl acetate is food-grade ethyl acetate, and its addition is that every gram of tea polyphenols adds ethyl acetate 350ml.
[0045] In step (1), the mass ratio of the total mass of lipase and protease to tea polyphenol is 0.125:1, wherein the mass of lipase accounts for 35% of the total mass.
[0046] In step (1), the amount of disodium hydrogen phosphate-sodium dihydrogen phosphate buf...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com