Gene engineering bacteria capable of producing bile salt hydrolase and construction method and application thereof
A technology of genetically engineered bacteria and bile salt hydrolyzing enzymes, applied in genetic engineering, hydrolyzing enzymes, and methods based on microorganisms, can solve the problems of enzymatic substrate hydrolysis ability and low enzymatic properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Embodiment 1: Construction and identification of recombinant bacteria
[0034] 1) Synthesize the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.2; use the synthesized sequence as a template to design primers for PCR:
[0035] bsh-F: 5'-GGGAATTC CATATG ATGTGCACTGCAGTACGTTTCGATG-3'
[0036] bsh-R: 5'-CCG CTCGAG TTTGGACTGCAGCTGGTTGCTAGACG-3"
[0037] Add the following reagents in sequence to a 0.2mL PCR tube: 10×LA PCR buffer II (Mg 2+ plus) 5 μl; DNTP Mixture 8 μl; template DNA 1 μl; upstream and downstream primers 2 μl each; Taq enzyme 0.5 μl; add double distilled water to a final volume of 50 μl. The PCR reaction program was as follows: pre-denaturation at 95°C for 5 min, denaturation at 98°C for 10 s, annealing at 57°C for 30 s, extension at 72°C for 1 min, and finally extension at 68°C for 10 min, 30 cycles.
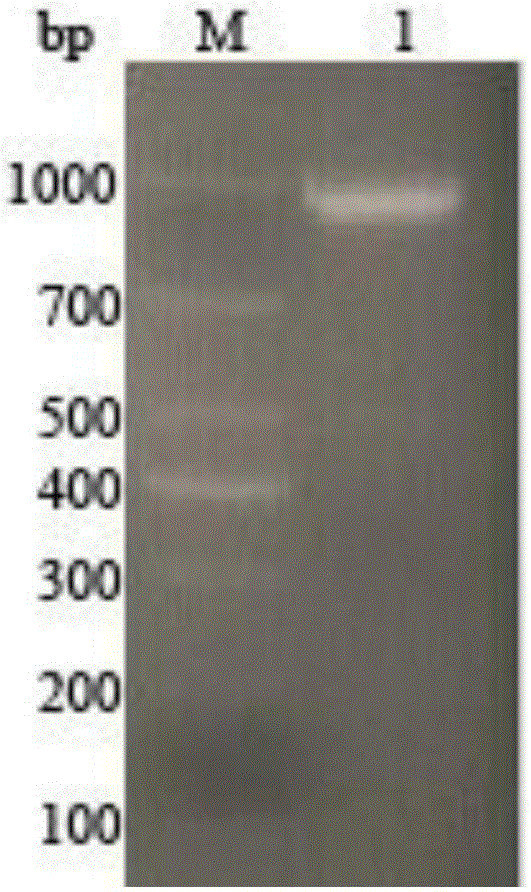
[0038] 2) Verify with 1% agarose gel electrophoresis and recover the PCR amplified product with 0.8% agarose gel electrophoresis, as a result, a bsh gene fragmen...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Embodiment 2: Enzyme activity assay and protein electrophoresis of recombinant bacteria
[0043] Culture method: Pick a single colony of Escherichia coli BL21(DE3)(pET-22b(+)-bsh) and inoculate it into LB liquid medium, inoculate at 37°C, 200r min -1 conditions overnight. The seeds were transferred to the basic fermentation medium with a 2% inoculation amount, and were incubated at 37°C and 200r min -1 cultivated under conditions;
[0044] Induction conditions: fermented broth cultured to OD 600 When it is 0.6, add IPTG (final concentration 1mmol L -1 ), induced for 10h. Samples were taken for the activity determination of recombinant bile salt hydrolase and SDS-PAGE detection.
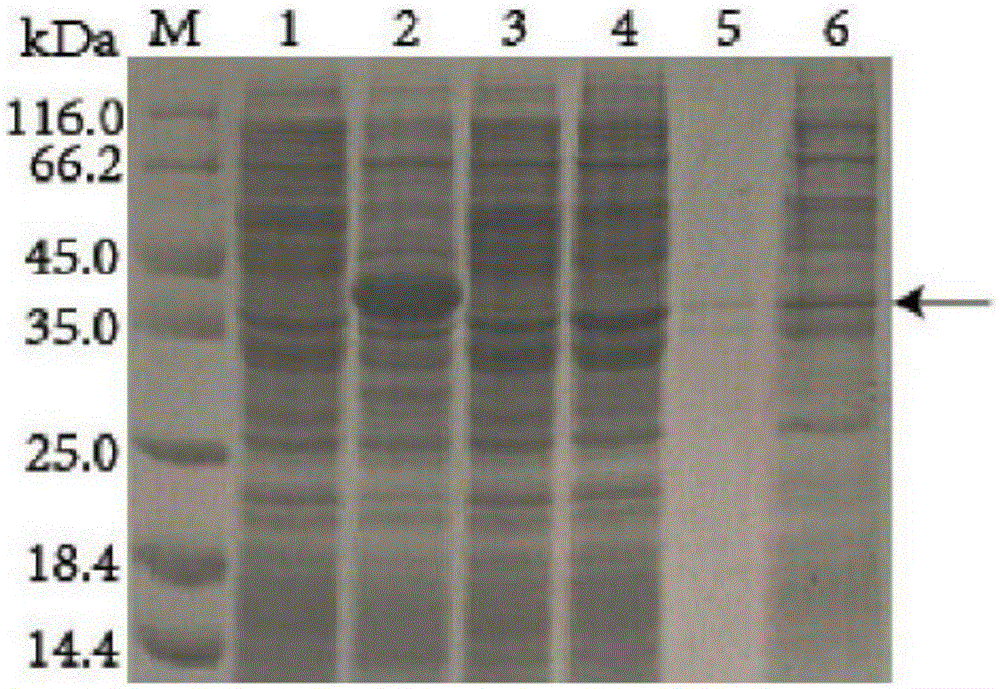
[0045] Using the empty vector as a control, a protein band with a molecular weight of about 37.5 kDa was obtained by protein electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) (see figure 2 ), indicating that the recombinant bacteria successfully expressed bile salt hydrolase.
Embodiment 3
[0046] Embodiment 3: the influence of culture condition on producing enzyme
[0047] (1) The genetically engineered bacteria seed liquid is transferred to the basic fermentation medium with an inoculum of 1%, and cultivated to OD 600 value is 1.5, then add the final concentration of 0.8mmol L -1 Induced by IPTG, cultured at 20°C for 26h. The activity of the obtained recombinant bile salt hydrolase on the two substrates of GDCA and TDCA was 105.3 U·mL -1 , 120.3U·mL -1 .
[0048] (2) Transfer the genetically engineered bacteria seed solution to the basic fermentation medium with an inoculum of 3%, and cultivate it to OD at 36-38°C 600 value is 2.0, then add the final concentration of 1.0mmol L -1 Induced by IPTG, cultured at 20°C for 36h. The activity of the recombinant bile salt hydrolase on the two substrates of GDCA and TDCA reached the highest, respectively 123.1U·mL -1 , 115.2U·mL -1 .
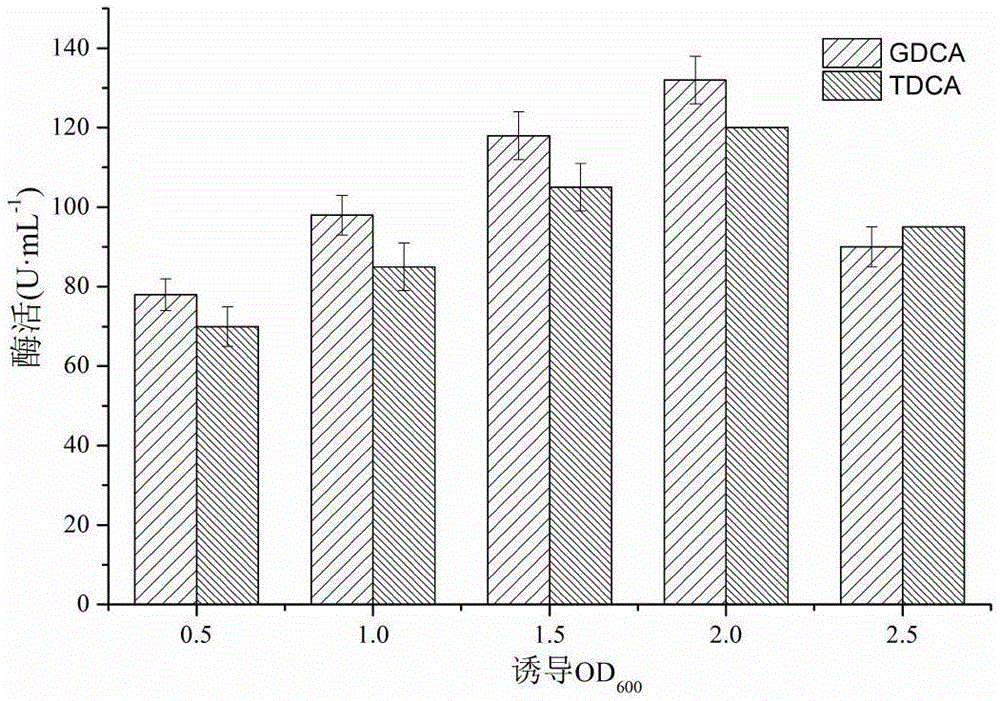
[0049] (3) compared different induced OD 600 The effect on enzyme production...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com