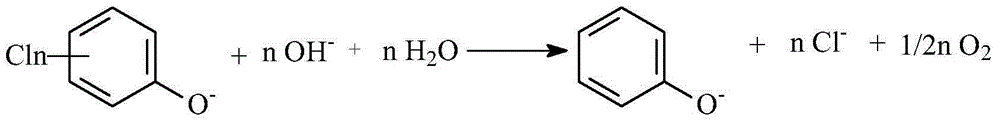
Electrochemical method for hydrodechlorination of chlorinated organic pollutant
An organic pollutant, electrochemical technology, applied in the direction of electrolytic organic production, electrolytic process, electrolytic components, etc., can solve the problems of low current density, low current efficiency, low utilization rate of palladium, etc., to achieve simplified structure, high current efficiency, The effect of reducing the volume
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
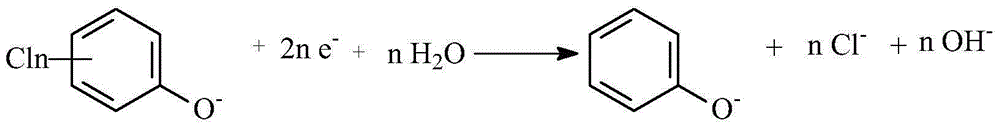
[0035] Embodiment 1 Palladium catalyzes the electrochemical hydrogenation dechlorination of 4-chlorophenol sodium into phenol
[0036] In a diaphragmless electrolyzer, a palladium-modified expanded silver screen was used as the cathode (1g Pd / m 2 ), the Hastelloy C 276 nickel alloy mesh is used as the anode, and the distance between the cathode and the anode is 0.5cm. The aqueous solution of 1000mL 1mol / L NaOH + 250g 4-chlorophenate sodium is the electrolyte. During the electrolysis process, the temperature is controlled at 20-25°C, and the current density is controlled at 10A / dm 2 , the electrolysis voltage is 2.8-3.2V, the pH of the catholyte is controlled at 13.5-14, and the cathode potential is -0.8--1.2V vs. Ag / AgCl (3.0M KCl). Stop the electrolysis after feeding 2F / mol 4-chlorophenol sodium electricity. After the catholyte was transferred to the beaker, sulfuric acid was added to adjust the pH=4, and then the yield of phenol was analyzed by high performance liquid pha...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Embodiment 2 Palladium catalyzes the electrochemical hydrogenation dechlorination of chlorinated phenol mixture into phenol
[0039] In a diaphragmless electrolyzer, a palladium-modified expanded silver screen was used as the cathode (1g Pd / m 2 ), the Hastelloy C 276 nickel alloy mesh is used as the anode, and the distance between the cathode and the anode is 0.5cm. 1000mL 1mol / L NaOH+15g sodium 2-chlorophenate+18.5g sodium 2,4-dichlorophenol+131.6g sodium 2,4,6-trichlorophenol+25.4g sodium 2,3,5,6-tetrachloro The aqueous solution of sodium phenate+28.9 grams of sodium pentachlorophenate is electrolyte. During the electrolysis process, the temperature is controlled at 20-25°C, and the current density is controlled at 10A / dm 2 , the electrolysis voltage is 2.8-3.3V, the pH of the catholyte is controlled at 13.5-14, and the cathode potential is -0.8--1.2V vs. Ag / AgCl (3.0M KCl). Stop the electrolysis after feeding 200AH of electricity. After the catholyte was transfer...
Embodiment 3
[0040] Example 3 Palladium-catalyzed electrochemical hydrogenation dechlorination of 2,4-dichlorophenate sodium, 2,4-dichlorophenoxy sodium acetate, 3,6-dichloropicolinate sodium, and dichloroacetate sodium mixture into phenol and phenoxyacetic acid , picolinic acid and acetic acid
[0041] In a diaphragmless electrolyzer, a palladium-modified expanded silver screen was used as the cathode (1g Pd / m 2 ), the Hastelloy C 276 nickel alloy mesh is used as the anode, and the distance between the cathode and the anode is 0.5cm. The aqueous solution of 1000mL 1mol / L NaOH+37g sodium 2,4-dichlorophenate+48.8g sodium 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetate+43g sodium 3,6-dichloropicolinate+60.4g sodium dichloroacetate is electrolyte. During the electrolysis process, the temperature is controlled at 20-25°C, and the current density is controlled at 10A / dm 2 , the electrolysis voltage is 2.9-3.4V, the pH of the catholyte is controlled at 13.5-14, and the cathode potential is -0.8--1.2V vs. Ag / AgCl ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| current efficiency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com