Method of separating high-molecular film from liquid crystal glass through microwave heating
A liquid crystal glass, polymer film technology, applied in nonlinear optics, instruments, optics, etc., can solve the problems of slow heat transfer effect of glass, long processing time, high processing cost, and achieve low microwave processing cost, short cooling time, The effect of short processing time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
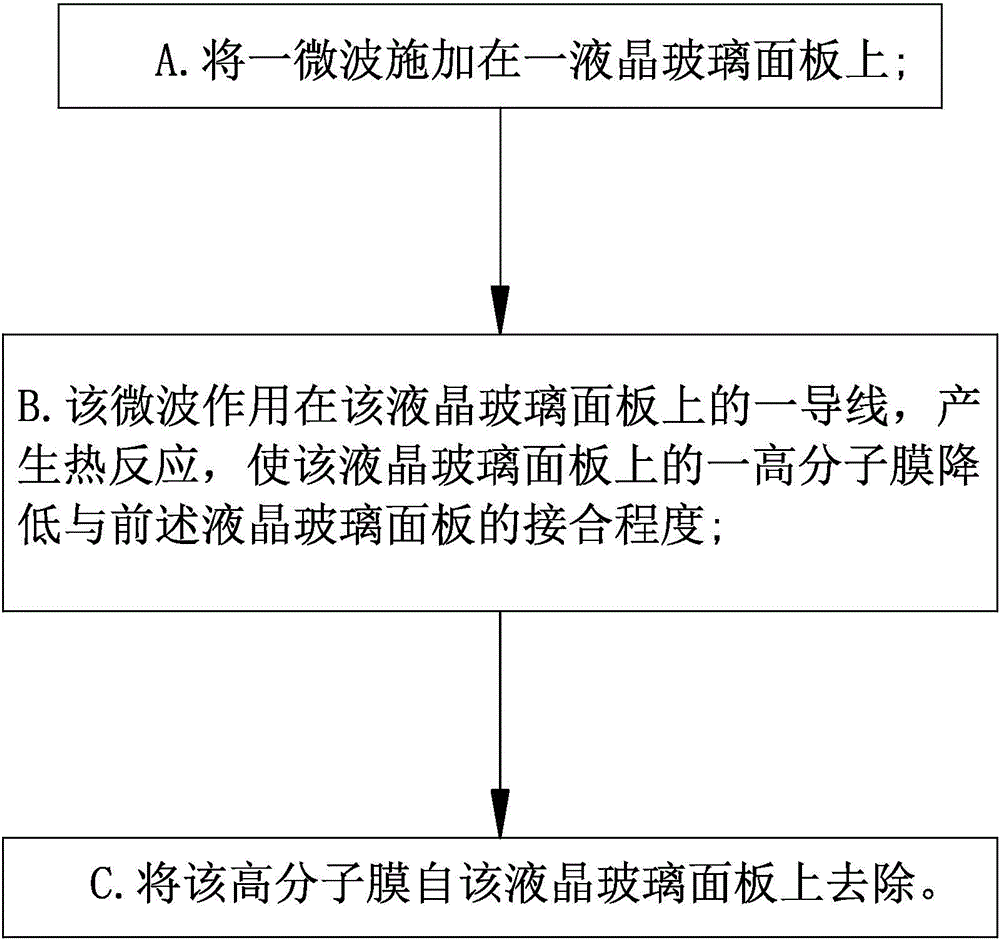
[0029] Based on the above-mentioned technical features, the main functions of the method of microwave heating and separating the polymer film of liquid crystal glass of the present invention will be clearly presented in the following examples.
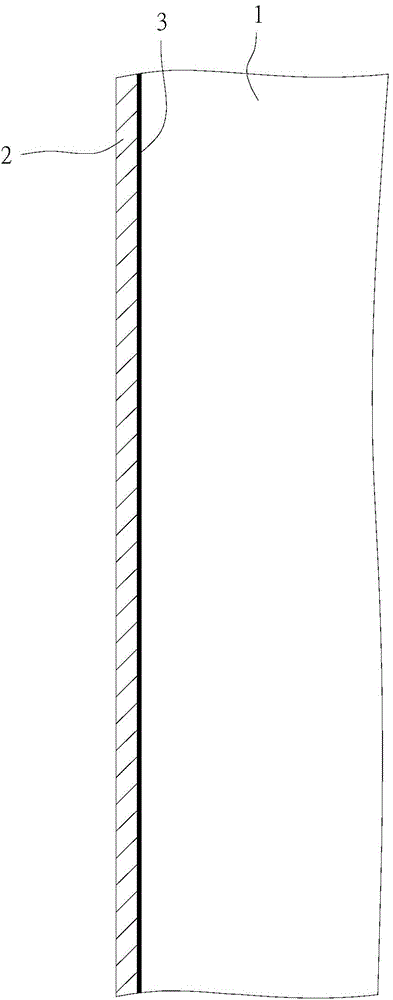
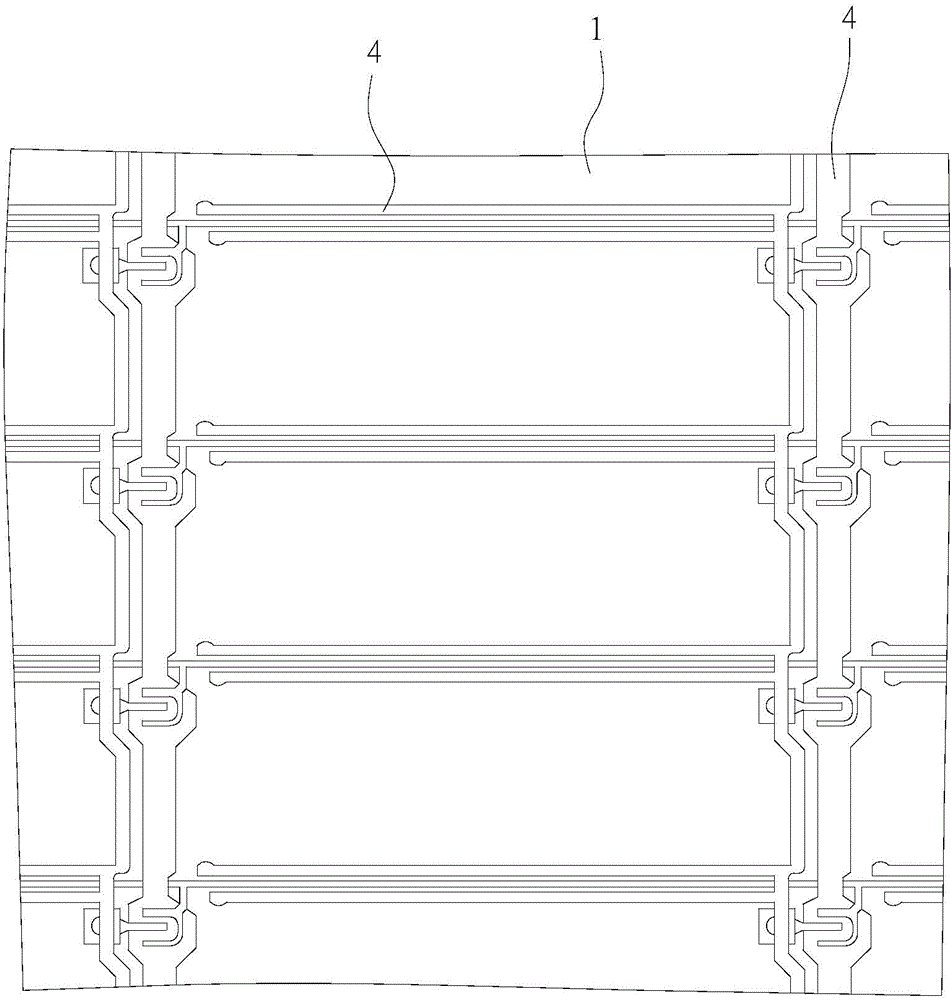
[0030] see figure 1 and figure 2 As shown, in this embodiment, a microwave is applied on a liquid crystal glass panel 1 to remove a polymer film on the liquid crystal glass panel 1. In this embodiment, the polarizing film 2 is taken as an example, wherein the polarizing film 2 passes through a joint Layer 3 is combined on the liquid crystal glass panel 1, and the bonding layer 3 is, for example, glue:
[0031] A. The power of the microwave acting on the liquid crystal glass panel 1 is between 800 watts and 1000 watts, and the microwave action time is between 10 seconds and 40 seconds; preferably, the microwave power is 900 watts, and the microwave action time is 30 seconds . In this embodiment, the liquid crystal glass panel 1 with...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com