Method for fixing flocculated and settled lipid yeast through microbial flocculant cooperating with activated carbon
A microbial flocculant and oil yeast technology, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve the problems of complex process and high cost, and achieve the effects of high-efficiency flocculation and sedimentation, simple operation and increasing particle size.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0025] (3) Preparation of Starley's Lipoyeast Culture Fluid
[0026] Inoculate Lipoyces studii with the bacterial strain number CGMCCNO: 2.1560 stored on the slant into a sterile seed medium, and the dosage of each component in the seed culture of Lipostaria studii is: glucose; (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 ; Yeast powder; KH 2 PO 4 ;MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O; pH=6.0; cultivated on a shaker at 22°C at 150rpm for 1 day to obtain a cultured L. starii suspension, and stored the obtained suspension in a refrigerator at 4°C for future use;
[0027] (4) The immobilization of activated carbon to the strain No. CGMCCNO: 2.1560 Lipoyeast yeast
[0028] Take the suspension of L. starii obtained in step (3) and put it into a sterile nitrogen-limited medium. The dosage of each component in the nitrogen-limited medium is: glucose; (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 ; Yeast powder; KH 2 PO 4 ;MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O; pH=6.5; take the activated carbon obtained in step (1), add it to the above-mentioned nitrogen-limited medium that ...
Embodiment 1
[0031] (1) Treatment of activated carbon
[0032] Take 20g of activated carbon with a specification of 300 mesh and dry it at 200°C for 2 hours; after cooling to room temperature, weigh the activated carbon and water according to the volume ratio of activated carbon and water as 1:3; Sulfuric acid; fully stirred for 2 hours at a water bath temperature of 80°C; then suction filtered, and the activated carbon was washed several times with desalted water until the pH value of the filtrate was neutral; the filtered activated carbon was dried at 200°C; the activated carbon was taken out and placed in Baked in a muffle furnace at 300°C for 2.5 hours and then placed in a desiccator for later use;
[0033] (2) Preparation of microbial flocculant by Aspergillus sojae
[0034] Inoculate Aspergillus sojae (Aspergillus sojae) stored on the slant with the strain number CGMCCNO: 3.5231 into 100 mL of sterile fermentation medium. The dosage of each component in the Aspergillus sojae ferment...
Embodiment 2
[0045] Including the same steps (1), (2) and (3) as in Example 1, the difference steps are:
[0046] (4) The immobilization of activated carbon to the strain No. CGMCCNO: 2.1560 Lipoyeast yeast
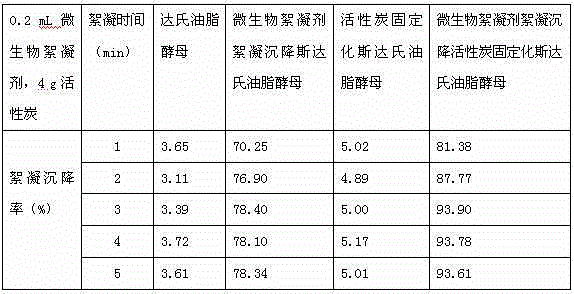
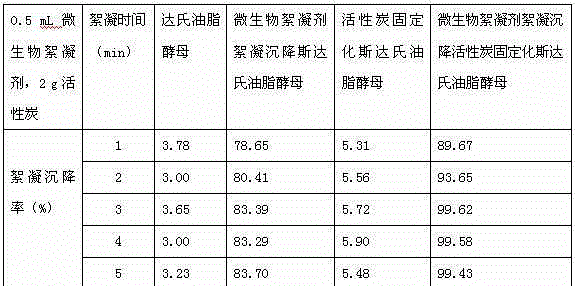
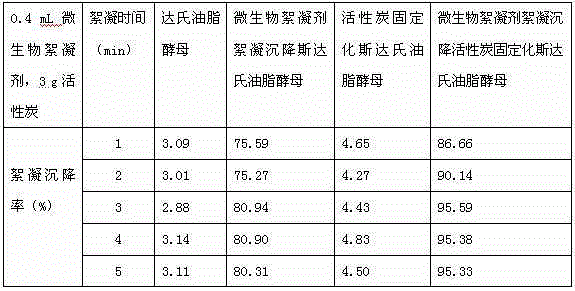
[0047] Take 10mL of the suspension of L. starii obtained in step (3) and put it into 100mL of sterile nitrogen-limited medium. The dosage of each component in the nitrogen-limited medium is: glucose 80.0g / L; (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 1.0g / L; yeast powder 0.8g / L; KH 2 PO 4 1.0g / L; MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O1.0g / L; pH=6.5; take 4g of activated carbon obtained in step (1), add it to the above 100mL nitrogen-limited medium that has been inoculated with L. studley yeast, and cultivate it on a shaker at 22°C at 150rpm for 3 days. Obtain activated carbon-immobilized Liposaccharomyces starii suspension;
[0048] (5) Microbial flocculant flocculation and sedimentation activated carbon immobilized strain No. CGMCCNO: 2.1560 Lipoyeast sp.
[0049] Take 0.2mL of the microbial flocculant obtained in step (2), p...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| sedimentation rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com