Device for detecting the organ origin of free epithelial cells in blood
A detection device and blood technology, applied in the direction of biological testing, material inspection products, microbial measurement/inspection, etc., to achieve the effect of simple structure, easy operation, and accurate early diagnosis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] Example 1 Detection device for rare cell proteome in blood
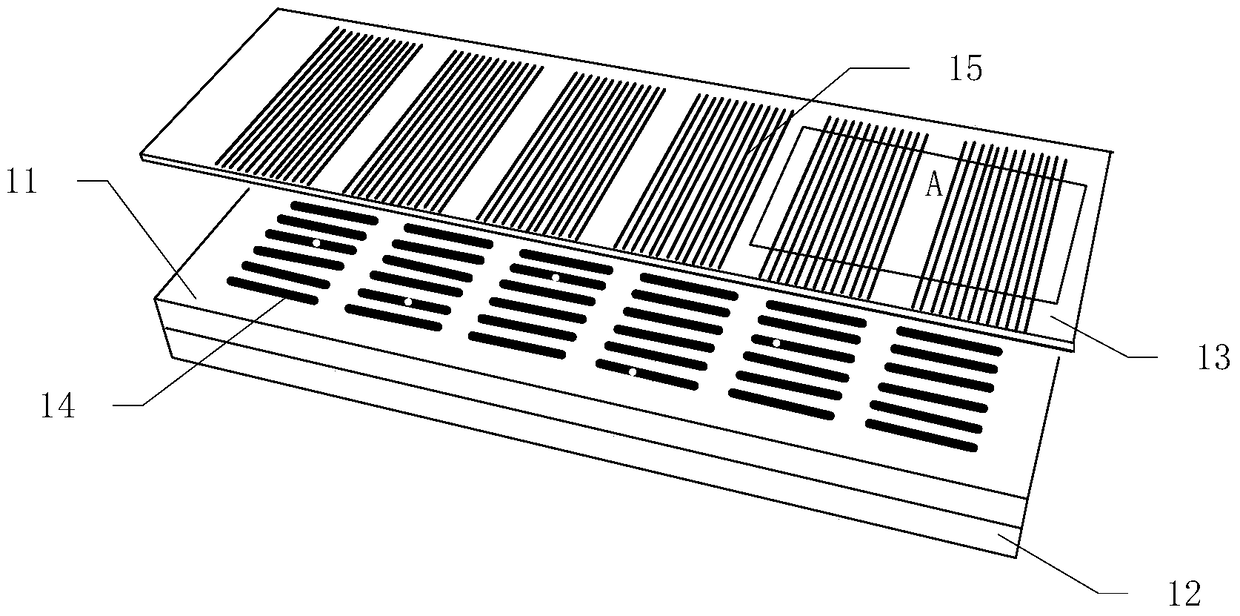
[0043] Such as figure 1 As shown, the detection device for rare cell protein groups in blood according to the present invention includes a microgroove chip 11, a magnet 12 and an antibody-loaded glass slide 13.
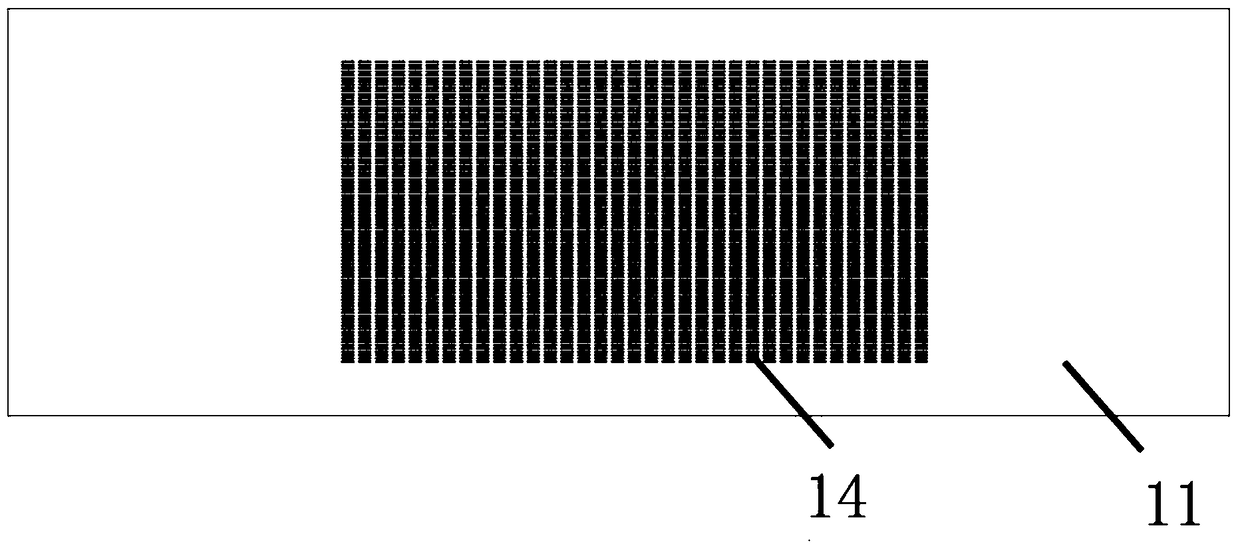
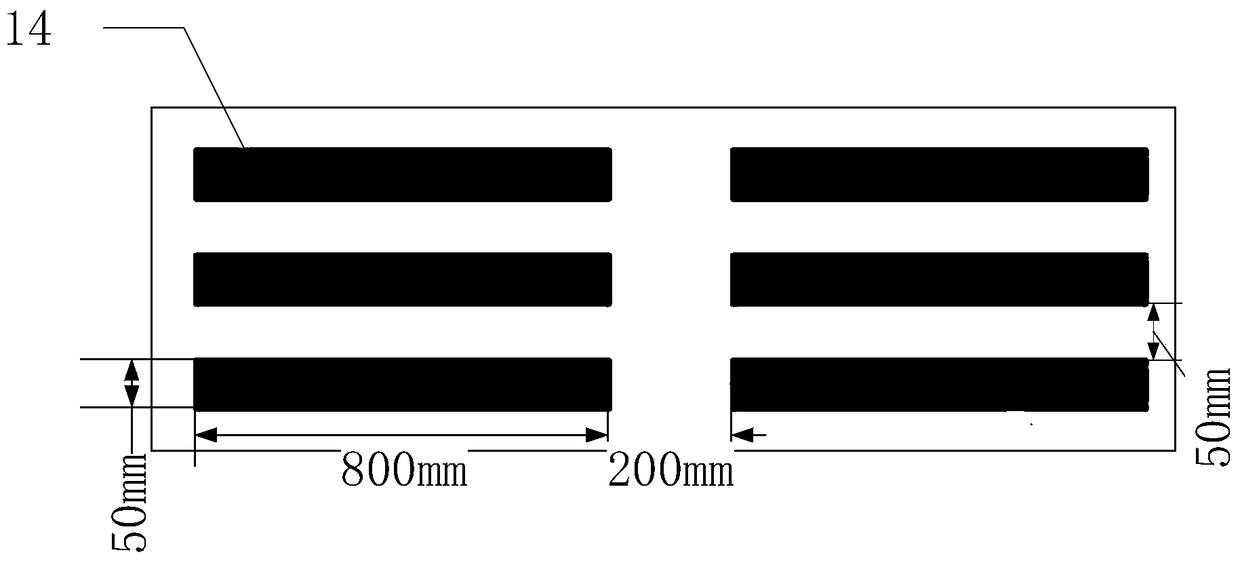
[0044] Such as figure 2 As shown, the microgroove chip 11 is provided with 3220 (35×92) microgrooves 14 with a volume of 1 nanoliter arranged in a matrix. Such as image 3 As shown, the cross-section of a single microgroove 14 is rectangular, with a length of 800 microns, a width of 50 microns, and a depth of 25 microns. During fabrication, a mask is first printed on a film substrate, a photoresist template is obtained through a photolithography process, and then a chip made of PDMS, that is, a microgroove chip 11 , is fabricated by using the photoresist template as a template.
[0045] Such as figure 1 As shown, the antibody-loaded glass slide 13 is loaded with an antibody microarray 15 , and t...
Embodiment 2
[0049] Example 2 Detection of multiple organ-specific protein markers in circulating epithelial cells in human peripheral blood
[0050] In order to identify the organ source of the epithelial cells isolated from blood, this example designs a set of 8 organ-specific protein markers for identification.
[0051] Anti-TTF-1 (thyroid transcription factor 1), anti-GCDFP-15 (gross cystic disease fluid protein 15), anti-CDX2, anti-CK7, anti-CK20, anti- SMAD4, anti-CEA, anti-CD45, anti-CD105 (or anti-CD146) and single-stranded polynucleotide M are passed into different microchannels 19 of the antibody-loaded chip described in Example 1, respectively. Among them, anti-TTF-1 (thyroid transcription factor 1), anti-GCDFP-15 (gross cystic disease fluidprotein 15), anti-CDX2, anti-CK7, anti-CK20, anti-SMAD4 and anti-CEA are used for specific binding Organ-specific protein markers, anti-CD45 is used to specifically bind leukocyte markers, anti-CD105 (or anti-CD146) is used for specific stru...
Embodiment 3
[0054] Example 3 Identification of Organ Source of Circulating Epithelial Cells
[0055] Adopt the method for embodiment 2 to have lung (100 examples), stomach (30 examples), colon (30 examples), ovary (10 examples), pancreas (10 examples) and breast ( 20) samples from patients with malignant lesions were tested and organ-of-origin identified.
[0056] Cluster analysis was performed on the results of protein marker detection, combined with the existing biological knowledge about organ-specific markers and the location of malignant lesions in patients, the following protein-based identification method for epithelial cell organ localization was obtained.
[0057] First, remove the data of CD45+ cells (leukocytes) and CD105+ (or CD146+) cells (endothelial cells) in the test results;
[0058] Then, according to the rules in Table 1, the results of epithelial cell origin were obtained.
[0059] Table I
[0060]
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com