Polarized RFID system without chips
A chipless, horizontally polarized technology, applied to collaborative devices, instruments, computing, etc., can solve the problems of increased difficulty in circuits and signal processing circuits, high price of SAW tags, and large size of tag antennas to improve anti-interference capability, production cost reduction, and system cost reduction effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
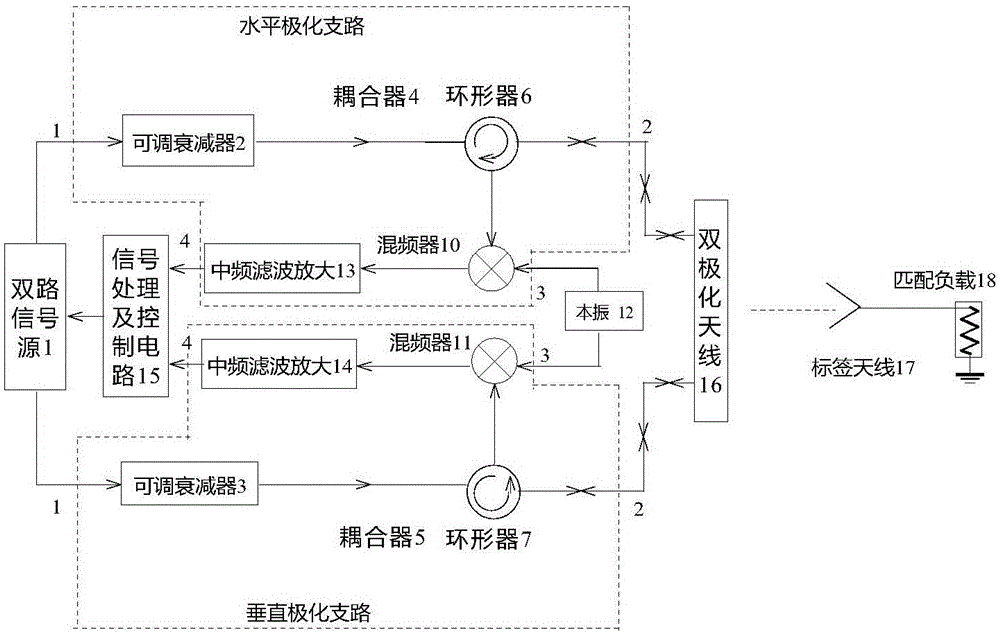
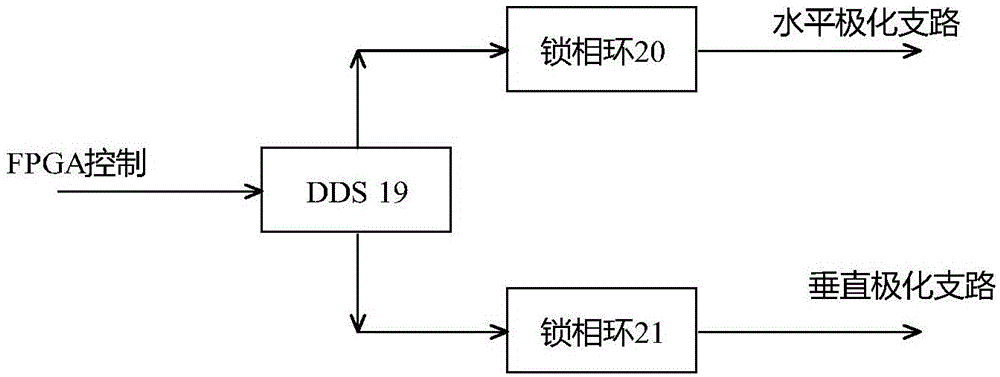
[0024]A chipless RFID system with variable polarization, including a dual signal source 1, a horizontal polarization branch, a vertical polarization branch, a signal processing and control circuit 15, a local oscillator 12, a dual-polarization antenna 16, and a tag antenna 17 , matching load 18. The horizontal polarization branch includes a first adjustable attenuator 2 , a first circulator 6 , a first mixer 10 , and a first intermediate frequency filter amplifier 13 . The vertical polarization branch includes a first adjustable attenuator 3 , a first circulator 7 , a first mixer 11 , and a first intermediate frequency filter amplifier 14 . The two output terminals of the dual signal source 1 are respectively connected to the input terminals of the first adjustable attenuator 2 and the second adjustable attenuator 3 . The output end of the second adjustable attenuator 2 is connected with the first port of the first circulator 6, and the second port of the first circulator 6 i...
Embodiment 2
[0028] A chipless RFID system with variable polarization, including a dual signal source 1, a horizontal polarization branch, a vertical polarization branch, a signal processing and control circuit 15, a local oscillator 12, a dual-polarization antenna 16, and a tag antenna 17 , matching load 18. The horizontal polarization branch includes a first adjustable attenuator 2 , a first circulator 6 , a first mixer 10 , and a first intermediate frequency filter amplifier 13 . The vertical polarization branch includes a first adjustable attenuator 3 , a first circulator 7 , a first mixer 11 , and a first intermediate frequency filter amplifier 14 . The two output terminals of the dual signal source are respectively connected to the first port of the horizontal polarization branch and the first port of the vertical polarization branch, and the second terminal of the horizontal polarization branch and the second terminal of the vertical polarization branch are respectively Connected t...
Embodiment 3
[0034] A chipless RFID system with variable polarization, including a dual signal source 1, a horizontal polarization branch, a vertical polarization branch, a signal processing and control circuit 15, a local oscillator 12, a dual-polarization antenna 16, and a tag antenna 17 , matching load 18. The horizontal polarization branch includes a first adjustable attenuator 2 , a first circulator 6 , a first mixer 10 , and a first intermediate frequency filter amplifier 13 . The vertical polarization branch includes a first adjustable attenuator 3 , a first circulator 7 , a first mixer 11 , and a first intermediate frequency filter amplifier 14 . The two output terminals of the dual signal source 1 are respectively connected to the input terminals of the first adjustable attenuator 2 and the second adjustable attenuator 3 . The output end of the second adjustable attenuator 2 is connected with the first port of the first circulator 6, and the second port of the first circulator 6 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com