Full-biodegradation bacterial cellulose/polylactic acid composite material and preparing method thereof
A technology of bacterial cellulose and composite materials, which is applied in the field of fully biodegradable bacterial cellulose/polylactic acid composite materials and its preparation, can solve the problems affecting the performance of composite materials, large anisotropy of composite materials, and limited enhancement effect of polylactic acid, etc. problems, to achieve the effect of high product dimensional stability, excellent tensile strength, and outstanding thermal stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
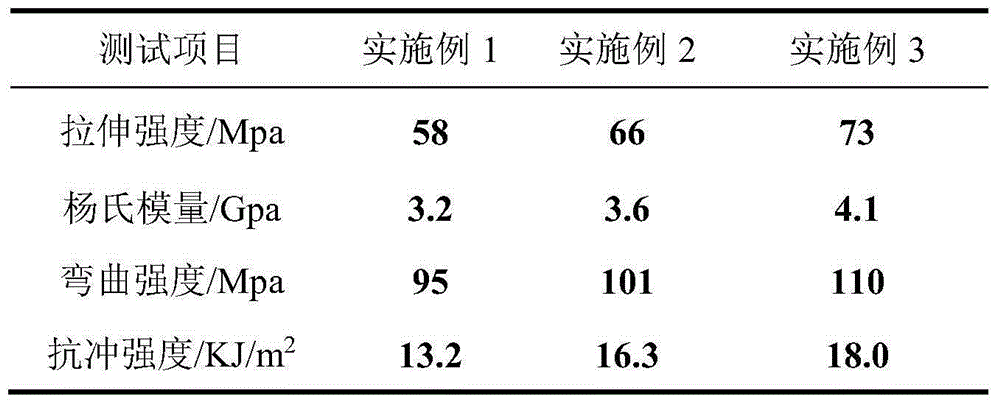
[0050] Accurately weigh 95 parts of polylactic acid and 5 parts of bacterial cellulose processed by the above method by weight, carry out shear melt blending with 50-60rpm in a twin-screw blending extruder for a period of time until uniform, and process The temperature is 180°C. After the mixture is extruded and cooled, it is vacuum-packed for use. After equilibrating for a period of time, the vacuum-dried blend is put into a compression molding machine and molded into a standard spline. The obtained samples were subjected to various performance tests. Some test properties of the obtained composite products are shown in Table 1.
Embodiment 2
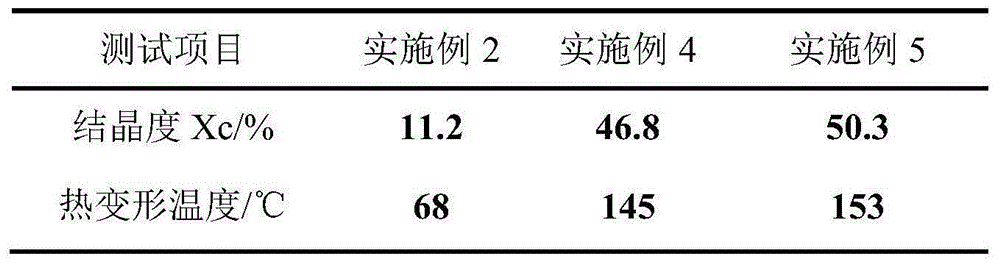
[0052] Accurately weigh 85 parts of polylactic acid and 15 parts of bacterial cellulose by weight, carry out shear melt blending with 50-60rpm in a torque internal mixer for 5 minutes to uniformity, and the melt blending temperature is 180 ° C. After extrusion and cooling, vacuum packaging is carried out for use. After equilibrating for a period of time, the vacuum-dried blend was injection molded into standard splines. The obtained samples are finally subjected to various performance tests. Some test properties of the obtained composite products are shown in Table 1.
Embodiment 3
[0054] Accurately weigh 85 parts of polylactic acid, 15 parts of bacterial cellulose and 2 parts of coupling agent HMDI in parts by weight, carry out shear melt blending with 50-60rpm in a torque internal mixer for 5min to uniformity, melt blending The mixing temperature is 180°C. After the mixture is extruded and cooled, it is vacuum-packed for use. After equilibrating for a period of time, the vacuum-dried blend was injection molded into standard splines. The obtained samples are finally subjected to various performance tests. Some test properties of the obtained composite products are shown in Table 1.
[0055] Table 1 Comparison of properties of composite materials prepared by different contents and different processes
[0056]
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com