Ultrasonic vibration auxiliary micro-electrochemical electrical discharge wire-cutting machining method and device
An ultrasonic vibration and EDM wire technology, which is applied in the field of composite micromachining, can solve the problems of high-precision machining of structures that cannot have a depth-to-width ratio, mechanical stress and thermal stress, and difficulty in discharging wear debris, so as to improve machining efficiency, increase The effect of large maximum length and increased thickness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
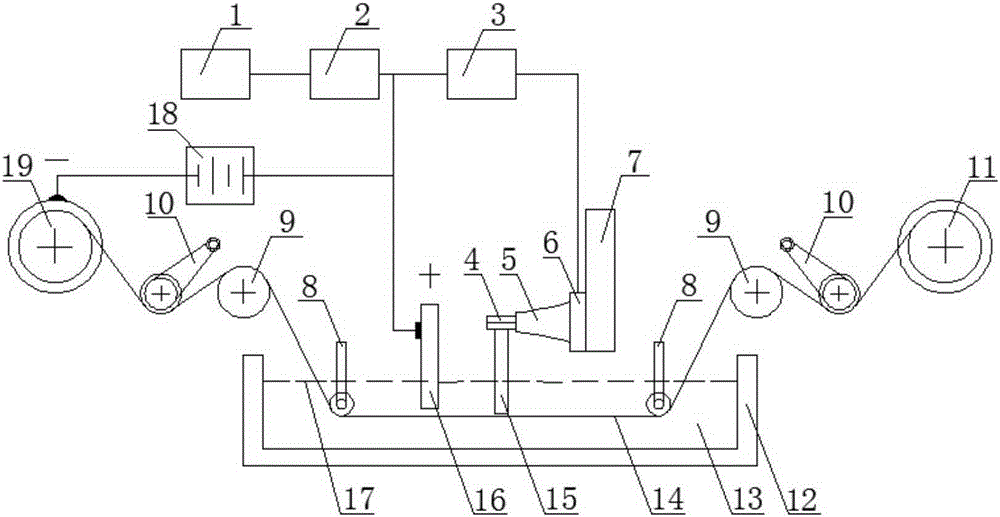
[0020] Such as figure 1 As shown, the ultrasonic vibration-assisted micro-electrolytic wire electric discharge processing method and device of the present invention mainly include an electrolysis-wire electric discharge device, an ultrasonic vibration unit and a workbench. Under the control of the control computer 1, the ultrasonic power supply 3 sends out an ultrasonic signal, which is converted into a mechanical vibration signal by the ultrasonic transducer 6, amplified by the horn 5 and transmitted to the workpiece 15 through the clamping device 4, so that the workpiece 15 Vibrate along the axial direction of the electrode wire 14; the horn 5 and the clamping device 4, and between the clamping device 4 and the workpiece 15 are fixedly connected by threads; the spindle 7 drives the workpiece 15 to perform feed motion (including Y and Z direction of feed), the feed speed is controlled by the control computer 1; the driving wheel 11 drives the electrode wire 14 out of the wire...
Embodiment 2
[0022] Such as figure 1 As shown, the electrolysis-electric spark power supply 18 adopts a DC pulse power supply, the electrolyte solution 13 adopts a sodium hydroxide solution, and the others are as in Example 1.
Embodiment 3
[0024] Such as Figure 1 As shown, the electrode wire 14 is made of steel wire, the horn 5 and the clamping device 4 , and the clamping device 4 and the workpiece 15 are all fixedly connected by bonding, and others are as in Example 1.
[0025]The invention is oriented to the micromachining of non-conductive hard and brittle materials, and has a good processing effect on high-aspect-ratio microstructure parts, and uses ultrasonic vibration to assist electrolysis-EDM. Since the workpiece is ultrasonically vibrated along the direction of the electrode wire, the electrolyte is accelerated. Renewal and chip removal can ensure machining accuracy and machining stability, and improve machining efficiency.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com