Mg-Zn-Y directional solidification alloy and preparing method thereof
A directional solidification, mg-zn-y technology, applied in the field of Mg-Zn-Y alloy, can solve the problems of coarse solidification structure and insufficient quasi-crystal strengthening effect.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
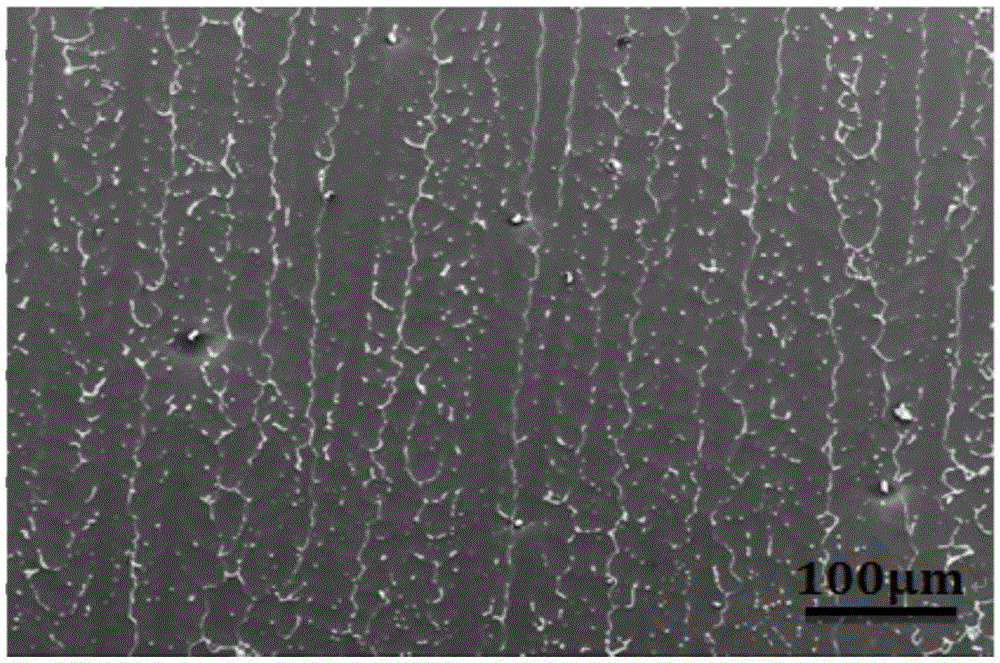
[0058] Embodiment 1 of the present invention: a kind of Mg-Zn-Y directionally solidified alloy is prepared by the following method (as Figure 13 shown):
[0059] a. Take 88g of Mg ingot, 12g of Zn ingot with a purity (mass fraction) of 99.9%, and 2.5g of Mg-30Y (30%, mass fraction) master alloy, mix the above-mentioned raw materials, heat and melt, and obtain an alloy liquid;
[0060] b. continue to heat the alloy liquid, and control the alloy liquid to be cast into the down-drawing system of the directional solidification equipment at different casting temperatures, and simultaneously control the down-drawing system to pull at different pulling speeds; wherein, the directional The vacuum in the furnace chamber of the solidification equipment is 2.4×10 -2 Pa;
[0061] c. Utilize the down rod, water-cooled copper ring and gallium-indium alloy to form the cold end of the quenching table capable of directional movement, the temperature of the alloy liquid and the cold end form...
Embodiment 2
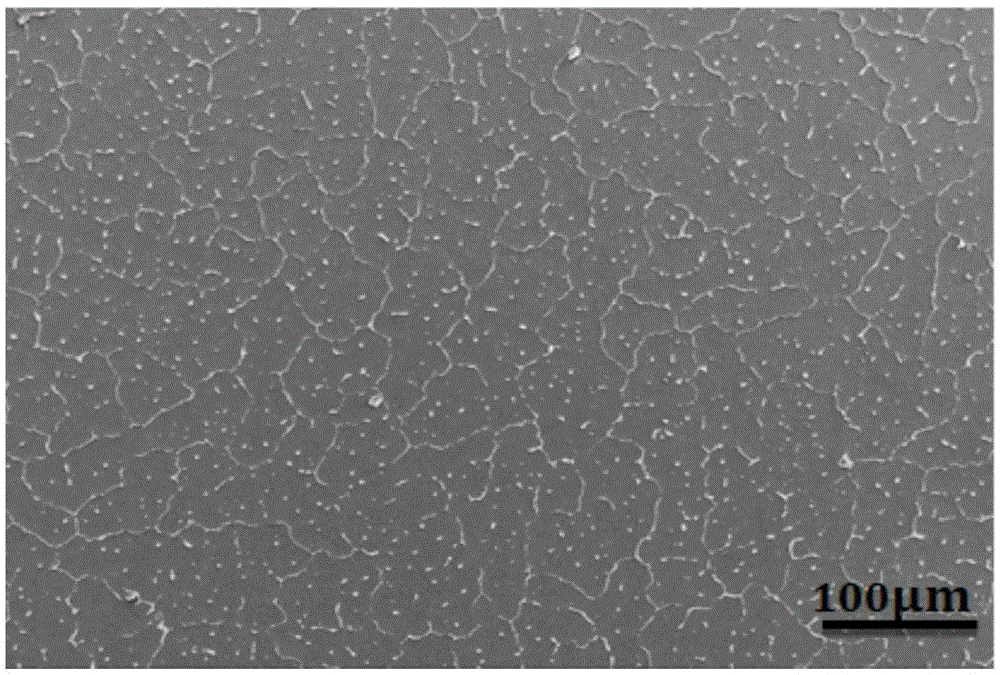
[0065] Embodiment 2: a kind of Mg-Zn-Y directionally solidified alloy is prepared by the following method (as Figure 13 shown):
[0066] a. Take 92g of Mg ingot with a purity (mass fraction) of 99.9%, 8g of Zn ingot, and 1.2g of Mg-30Y (30%, mass fraction) master alloy, mix the above-mentioned raw materials, heat and melt, and obtain an alloy liquid;
[0067] b. continue to heat the alloy liquid, and control the alloy liquid to be cast into the down-drawing system of the directional solidification equipment at different casting temperatures, and simultaneously control the down-drawing system to pull at different pulling speeds;
[0068] c. Utilize the down rod, water-cooled copper ring and gallium-indium alloy to form the cold end of the quenching table capable of directional movement, the temperature of the alloy liquid and the cold end form a temperature gradient, and maintain the solid-liquid interface at the beginning of casting through the insulation jacket and the pulli...
Embodiment 3
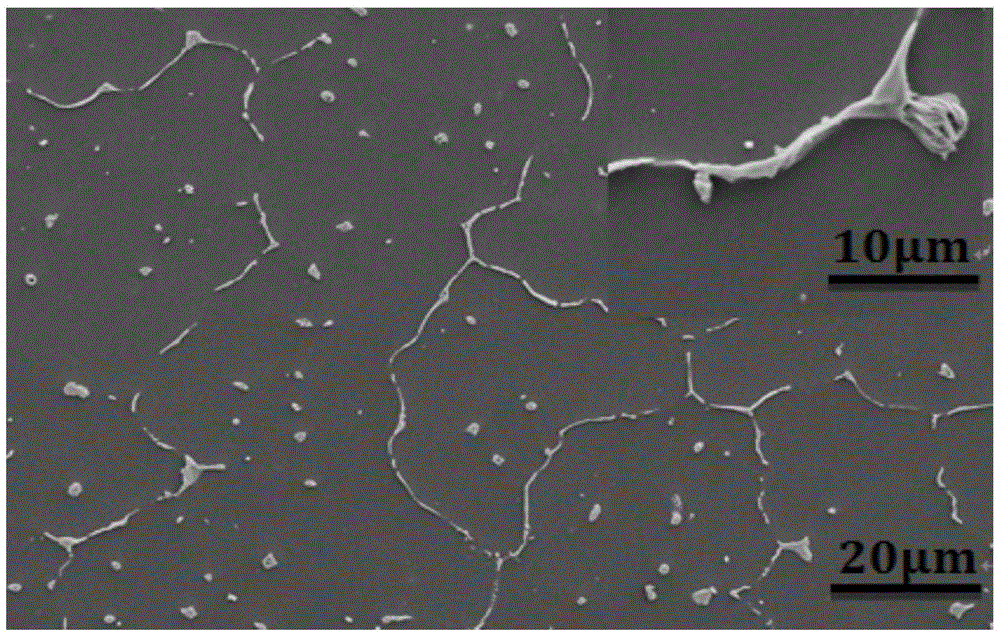
[0072] Embodiment 3: A Mg-Zn-Y directionally solidified alloy prepared by the following method:
[0073] a. Take 89.2 g of Mg ingots with a purity (mass fraction) of 99.9%, 9 g of Zn ingots, and 1.8 g of Mg-30Y (30%, mass fraction) master alloy, mix the above-mentioned raw materials, heat and melt them, and obtain an alloy liquid;
[0074] b. continue to heat the alloy liquid, and control the alloy liquid to be cast into the down-drawing system of the directional solidification equipment at different casting temperatures, and simultaneously control the down-drawing system to pull at different pulling speeds;
[0075] c. Utilize the down rod, water-cooled copper ring and gallium-indium alloy to form the cold end of the quenching table capable of directional movement, the temperature of the alloy liquid and the cold end form a temperature gradient, and maintain the solid-liquid interface at the beginning of casting through the insulation jacket and the pulling speed The formed t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com