Fusion mixture
A mixture and biotinylation technology, which is applied in the direction of fusion cells, cells modified by introducing foreign genetic material, liposome delivery, etc., to achieve the effect of easy preparation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
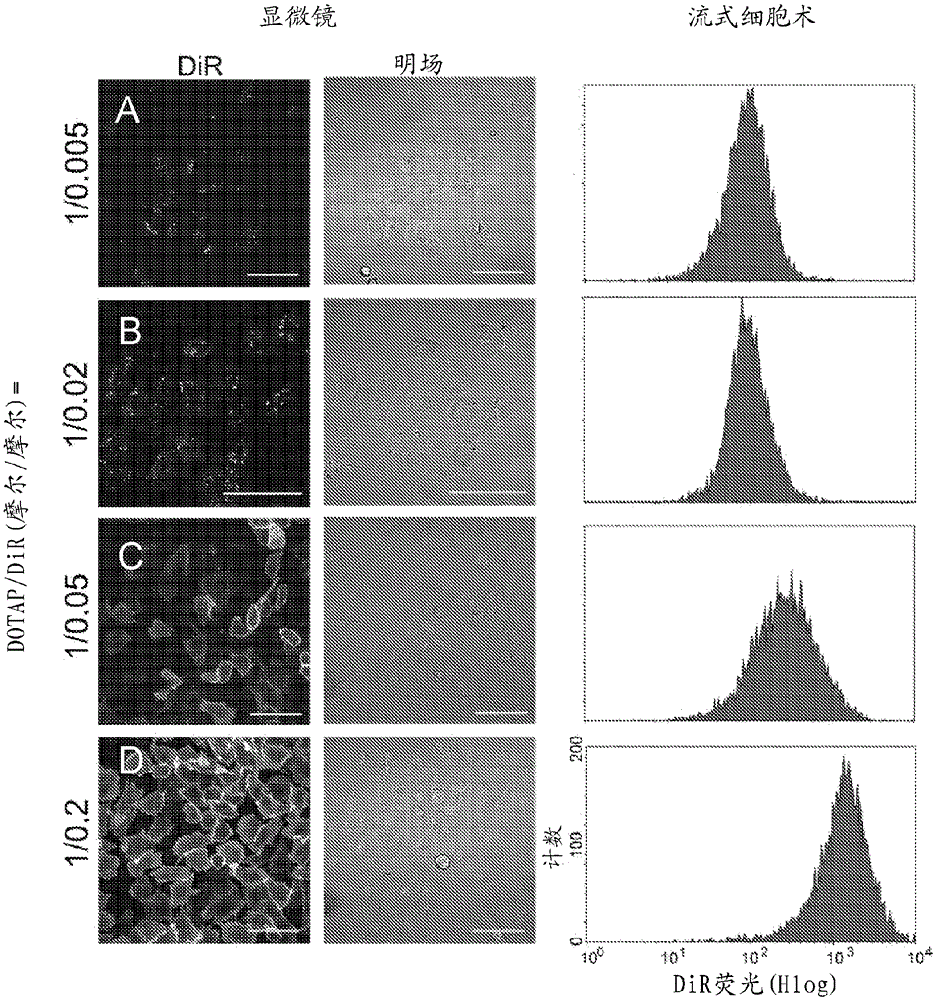
[0109] First embodiment ( figure 1 with 2 ): Fusion in cell suspension (1:0.005 to 1:0.2 mol / mol fusion mixture of molecular species A:B (DOTAP:DiR) with CHO-cells).
[0110] The first example confirms the correct molar ratio of molecular species A and B in the claimed fusion mixture.
[0111] In the case of flow cytometry measurements, the X- and Y-axis labels given in the diagram below are also used for the measurement results placed thereon.
[0112] The components of the fusion mixture, here DOTAP (molecular species A) and DiR (molecular species B) were mixed from a stock solution of 1 mg / ml in chloroform at a mixing ratio of 1:0.005 to 1:2 mol / mol to determine DiR-inducing fusion concentration range.
[0113] As a result it can be determined that starting from a molar ratio of molecular species A:B of 1:2 or greater (i.e. e.g. 1:3 mol / mol molecular species A:B), homogenization of the two substances in a fusion mixture is Difficult because these substances clump to...
no. 2 example ( pic 3)
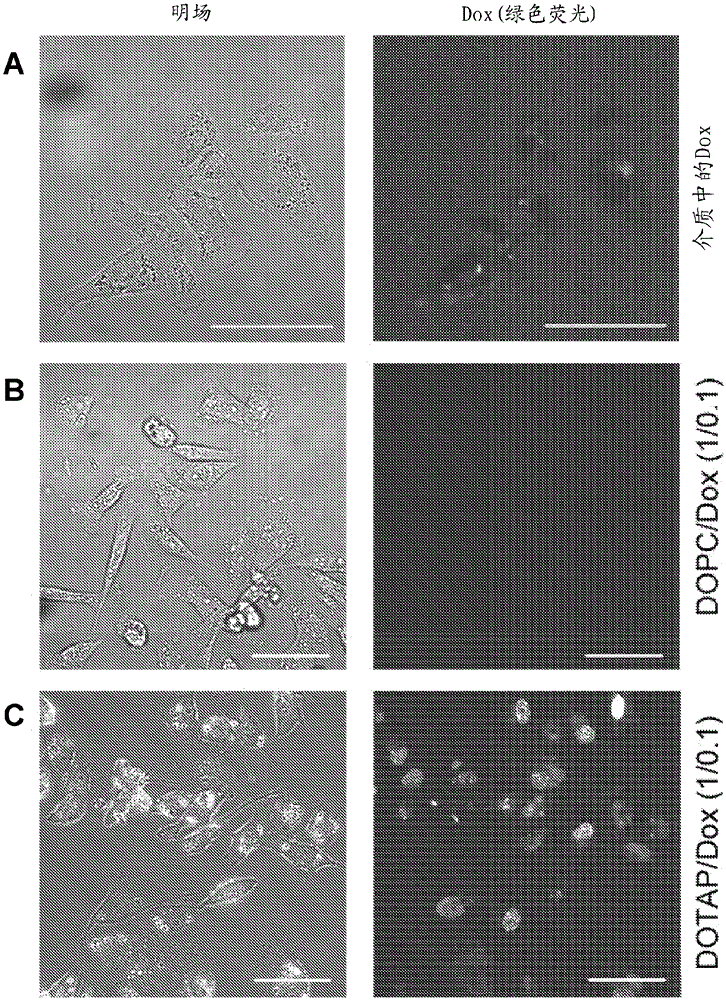
[0123] The second embodiment ( image 3 ): Fusion with model membrane (Fusion of fusion mixture of molecular species A:B (DOTAP:DiO) with DOPC model membrane and A:B molar ratio of 1:0.1 mol / mol)
[0124]Large unilamellar vesicles composed of 1,2-dioleoyl-sn-glyceryl-3-phosphocholine swell in 250 mM sucrose solution (pH 7.4, adjusted with 4 mM imidazole / HCl) under alternating current at 1.3 V and 10 Hz . 100 μl of vesicle solution was transferred into the measurement chamber, which was previously coated with avidin and filled with 1.8 ml of 250 mM glucose solution. In addition, 100 μl of fused vesicles (DOTAP:DiO=1:0.1 mol / mol) were added. Fused vesicles were prepared as in Example 1. Cover the sample holder with a cover glass and increase the temperature to 37°C.
[0125] image 3 A shows DOPC-large vesicles (arrows) after membrane fusion has occurred. Fluorescence transfer from small microscopically indistinguishable fused vesicles to large monolayer DOPC-model membr...
no. 3 example (
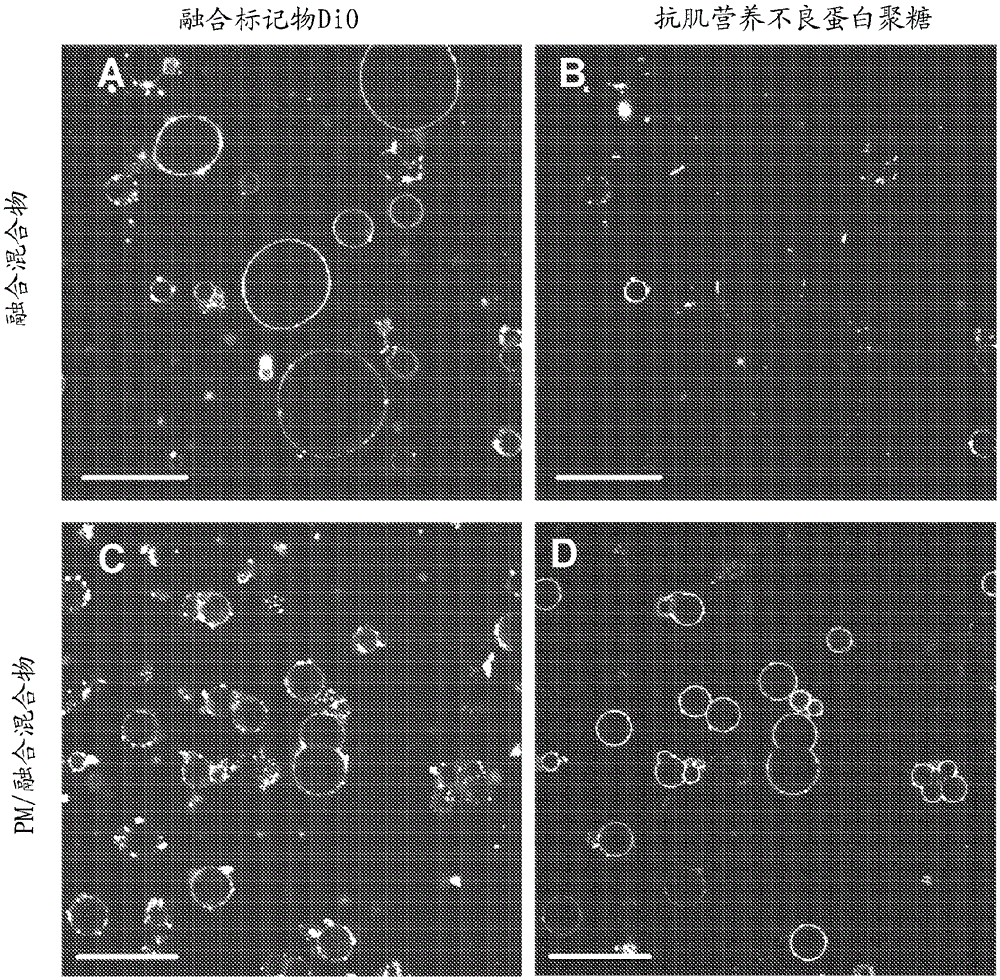
[0127] The third embodiment ( Figure 4 ): fusion with cell membrane fragments - fusion of molecular species A:B (DOTAP:DiO) in a ratio of 1:0.1 mole / mole to isolated HL-1 cell plasma membrane and further fusion of this fused membrane fraction with DOPC-macrovesicles fusion.
[0128] HL1-cells (myocyte-cell line) swell osmotically in PBS-buffer with 200 mOsm. Thereafter, the cells were crushed in a homogenizer. Nuclei and mitochondria can be separated from remaining membranes by centrifugation. The remaining fractions contain cytoplasmic membranes with Dystroglykan, ER-membranes and lysosomal membranes. This fraction was dissolved in a buffer solution of 250 mM sucrose / imidazole / HCl.
[0129] It was fused with fusion liposomes of DOTAP / DiO (1:0.1 mol / mol) at a volume ratio of 1 / 10 to generate plasma membrane-containing fusion liposomes.
[0130] A second fusion is initiated between the plasma membrane-containing fused liposome and the DOPC-macrovesicle (C, D).
[0131]...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com