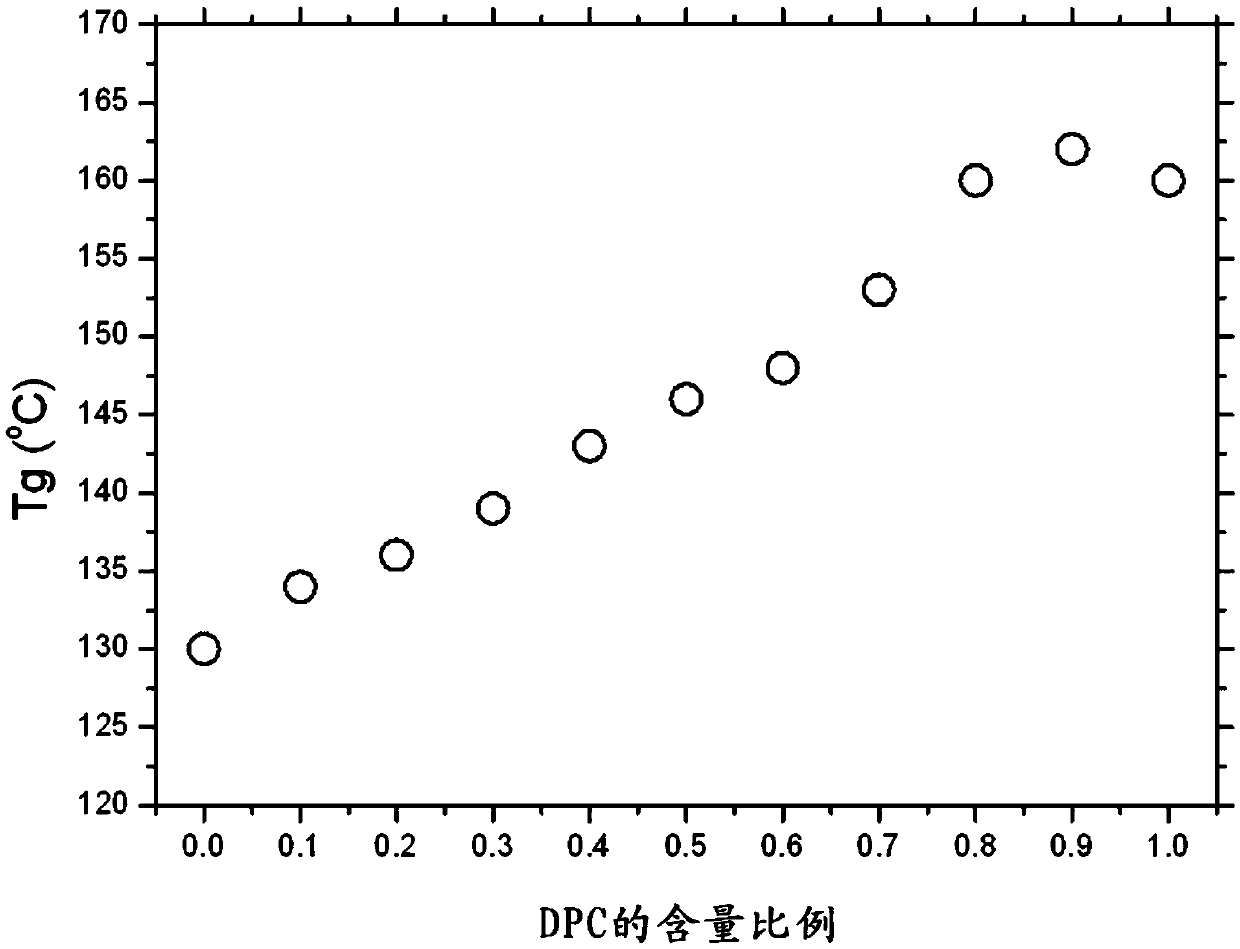
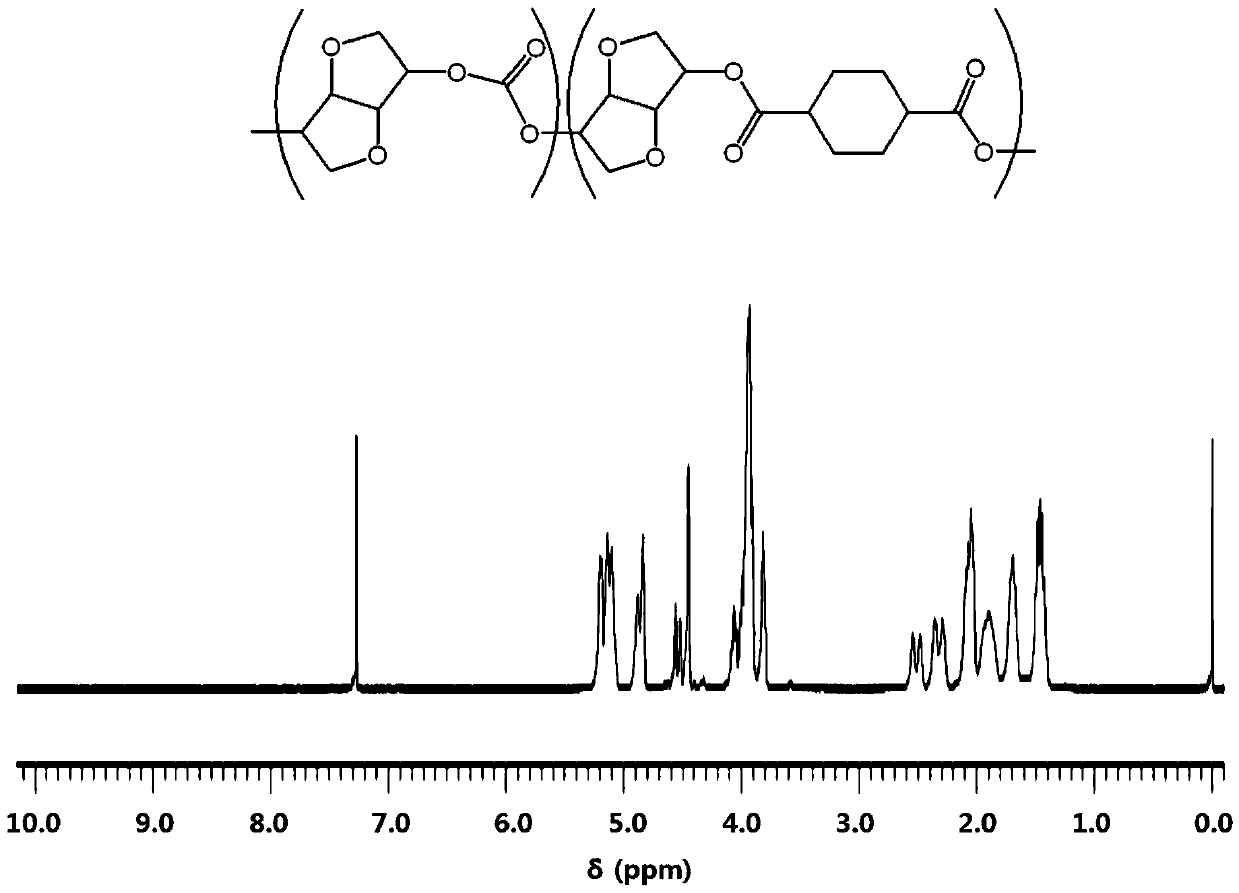
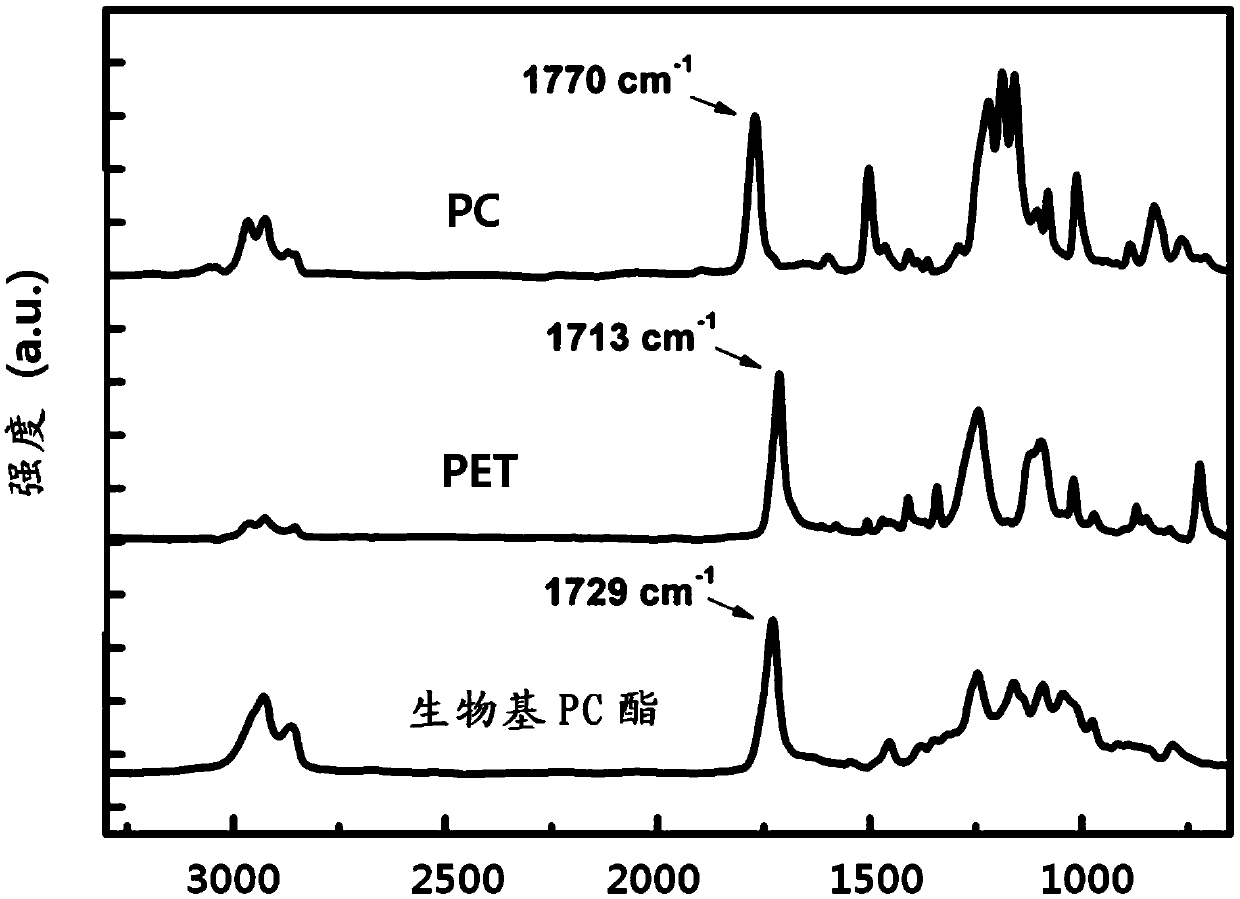
Highly heat-resistant and highly transparent polycarbonate ester, and preparation method therefor
A technology of polycarbonate and carbonate, applied in the field of polycarbonate and its preparation, to achieve the effect of high transparency and high heat resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation Embodiment 1
[0097] Preparation Example 1: Synthesis of DPCD by using CHDA
[0098] 100 g (0.58 mol) CHDA (SK Chemicals), 218 g (2.32 mol) phenol, 0.1 g (0.55 mmol) Zn(OAc) with a cis / trans ratio of 95 / 5% 2 The catalyst and magnetic stir bar were introduced into a 500 mL single-necked flask. The flask was equipped with a distillation head, a thermometer and a condenser, and the flask was heated to 200°C. The reaction was allowed to proceed at the same temperature for 24 hours, and water generated as a by-product of the reaction was removed from the flask. After the reaction was completed, the reactant thus obtained was cooled to room temperature, and excessively introduced phenol was removed therefrom by using an evaporator. To the solid compound thus obtained was added excess water and mechanically stirred to remove residual phenol. After vacuum drying at 90° C. for 24 hours, 111 g of DPCD was obtained (yield: 59%). As a result of the reaction with phenol under the reaction conditions...
preparation Embodiment 2
[0099] Preparation Example 2: Synthesis of DPCD by using DMCD
[0100] 100 g (0.50 mol) DMCD (SK Chemicals), 188 g (2.00 mol) phenol, 100 mL water and 1.0 g (5.81 mmol) p-toluenesulfonic acid catalyst with a cis / trans ratio of 77 / 23% were introduced together with a magnetic stirring bar 500mL single-necked flask. The flask was equipped with a condenser, heated to 100°C, and refluxed for 10 hours with stirring. After the reaction was completed, the reactant thus obtained was cooled to room temperature, and then water and phenol were removed therefrom by distillation. Subsequently, the remaining reactants were heated to 200° C., and the reaction was performed at the same temperature for 24 hours, followed by removal of water generated as a by-product of the reaction. After the reaction was completed, the reactant thus obtained was cooled to room temperature, and excessively introduced phenol was removed therefrom using an evaporator. To the solid compound thus obtained was ad...
Embodiment 1
[0101] Embodiment 1: the preparation of bio-based polycarbonate
[0102] A 500 mL three-necked flask was equipped with a distillation head, thermometer, condenser and mechanical stirrer. 102.3g (0.7mol) of isosorbide (RoquetteFreres), 97.3g (0.3mol) of DPCD obtained in Preparation Example 1, 85.7g (0.4mol) of DPC (Aldrich) and 5.9×10 -4 g(1.8×10 -3 mmol) cesium carbonate (Cs) as catalyst 2 CO 3 ) was added to the flask and the flask was heated to 150°C. Once the temperature reached 150°C, the pressure was reduced to 400 Torr and the temperature was raised to 190°C within 1 hour. During the temperature increase, phenol begins to form as a by-product of the polymerization reaction. When the temperature reached 190°C, the pressure was reduced to 100 Torr, held for 20 minutes, and then the temperature was raised to 230°C over 20 minutes. Once the temperature reached 230°C, the pressure was reduced to 10 Torr, then the temperature was raised to 250°C within 10 minutes. The p...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com