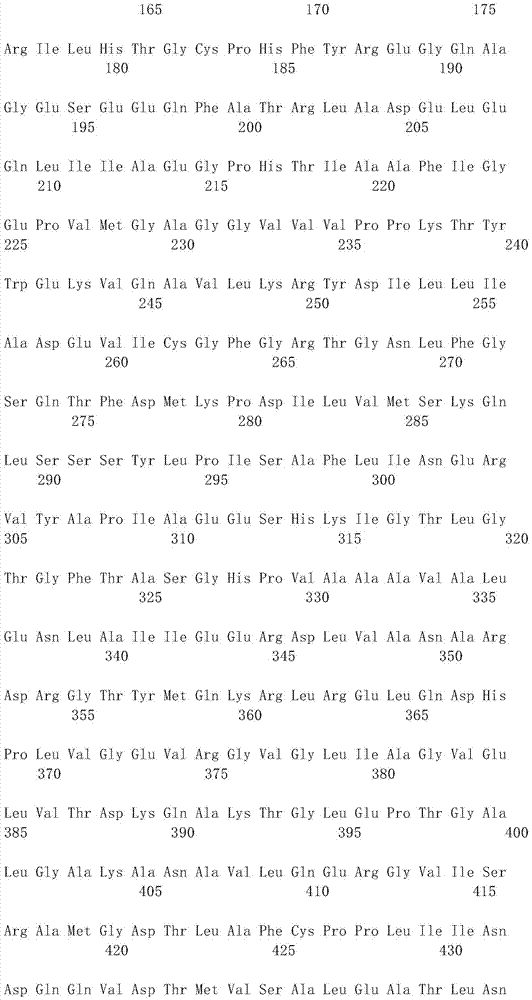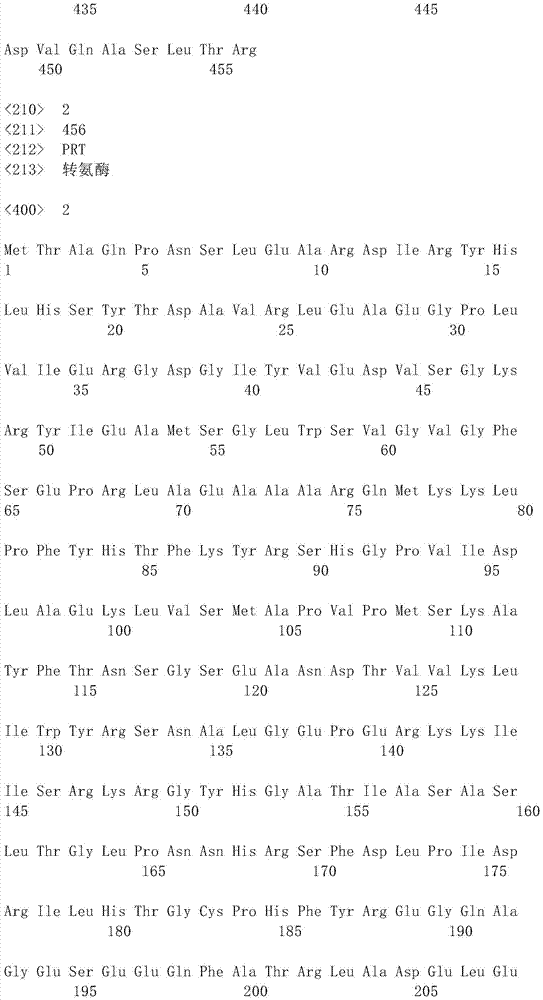Aminopherase for producing L-2-aminobutyric acid
A technology of aminobutyric acid and threonine deaminase, which is applied in the field of biocatalysis, can solve the problems of low conversion concentration and low enzyme activity, and achieve the effect of overcoming low conversion rate, improving enzyme activity and realizing industrialization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0060] 1.1 Construction of recombinant Escherichia coli expressing various sources of ω-transaminase (ω-TA)
[0061] Select Ochrobactrumanthropi, Aquamicrobiumdefluvii, Bradyrhizobiumsp.Ec3.3, Brucellaneotomae, Novosphingobiumacidiphilum, Ochrobactrumintermedium, Pseudaminobacteralicylatoxidans, Brucellaabortus, ParacoccusdenitrificansPD1222 sources of ω-transaminase, and synthesize the basic transaminase gene sequence as Restriction endonuclease sites NdeI and BamHI were designed at the end, subcloned into the corresponding sites of the vector pET24a (Novagen) to obtain recombinant plasmids, transformed into E. coli expression host BL21 (DE3), and obtained recombinant E. coli expressing ω-transaminase.
[0062] 1.2 Comparison of the ability of ω-transaminases from different sources to catalyze the production of L-2-aminobutyric acid
[0063] Shake flask fermentation of ω-transaminase expression strains: prepare liquid medium TB (pH7.0-7.5), containing 12g / L peptone, 24g / L imp...
Embodiment 2
[0069] Example 2 Site-directed mutagenesis
[0070] 2.1 Site-directed mutagenesis of ω-transaminase from multiple sources
[0071] Park et al. (2014) carried out molecular modeling of PDTA by X-ray diffraction technology, and obtained the active site and substrate-related information in the enzyme structure (PBDID: 4GRX). They found that the type of substrate recognized by Lpocket of PDTA is determined by the spatial structure of Spocket regulated by the V153 site. Subsequent site-directed mutation at this site resulted in the mutant V153A with improved enzymatic activity for specific substrates, further confirming the key role of the V153 site as the active site of the enzyme. [Park ES, et al., Advanced Synthesis & Catalysis, 2014, 356(1): 212–220]
[0072] Park et al. (2012) have reported that the V154 site of OATA corresponds to the V153 site of PDTA [ParkES, KimM, ShinJS., ApplMicrobiolBiotechnol, 2012, 93(6):2425-2435]. The inventors compared the amino acid sequences o...
Embodiment 3
[0082] Example 3 Site-directed saturation mutation
[0083] 3.1 Construction of site-specific saturation mutation library
[0084] After site-directed mutation, compared with the corresponding wild type, the catalytic ability of ADTA / V154A, BNTA / V154A, BSTA / V154A, OITA / V154A, PSTA / V154A was significantly improved, proving that the V154 site determines the activity of ω-transaminase key active sites. Use degenerate primers to make site-directed saturation mutations at these sites, and construct a mutation library.
[0085] Table 4 Site-directed saturation mutation sites and primer design of ω-transaminase from various sources
[0086] name
mutation site
Mutation Primer
Primer sequence (5'-3')
OATA
V154
OATA-V154-F
cgcggctatcacggtNNKacgattgcctctgcc
ADTA
V154
ADTA-V154-F
cgcggttatcatggcNNKaccattgcatcggct
BATA
V154
BATA-V154-F
cgcggttatcatggcNNKaccattgccagcgca
BSTA
V154
BSTA-V154-F
c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com