High-affinity aptamers specifically binding to lactoxins 1 and 4 and their applications
A technology of lactoxin and aptamer, which is applied in the field of biotechnology and biotechnology, and can solve the problems of identification, optimization and application of affinity constants that have not yet been reported.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Example 1. Construction of random ssDNA library and primers thereof
[0031] 1. Construct a random ssDNA library with a length of 80 nucleotides
[0032] 5′-AGCAGCACAGAGGTCAGATG-N 40 -CCTATGCGTGCTACCGTGAA-3'; wherein, N represents any one of the bases A, T, C, G, N 40 Represents a random sequence of length 40bp.
[0033] 2. Construction of primers
[0034] Upstream primer: 5'-AGCAGCACAGAGGTCAGATG-3', SEQ ID NO: 15
[0035]Downstream primer 1: 5'-TTCACGGTAGCACGCATAGG-3', SEQ ID NO: 16
[0036] Downstream primer 2: 5′-poly(dA20)-Spacer18-TTCACGGTAGCACGCATAGG-3′
Embodiment 2
[0037] Example 2. Screening of GTX1 and GTX4 nucleic acid adaptation
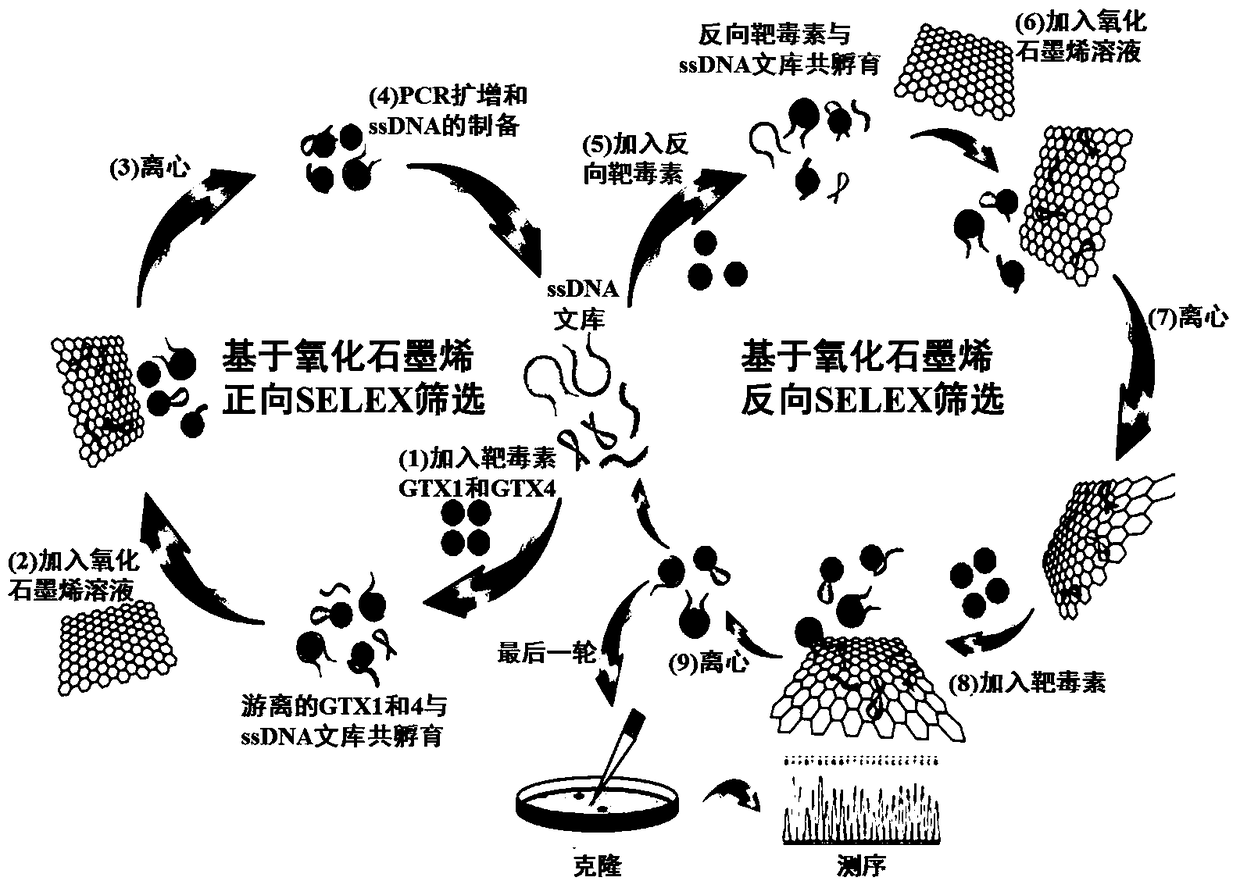
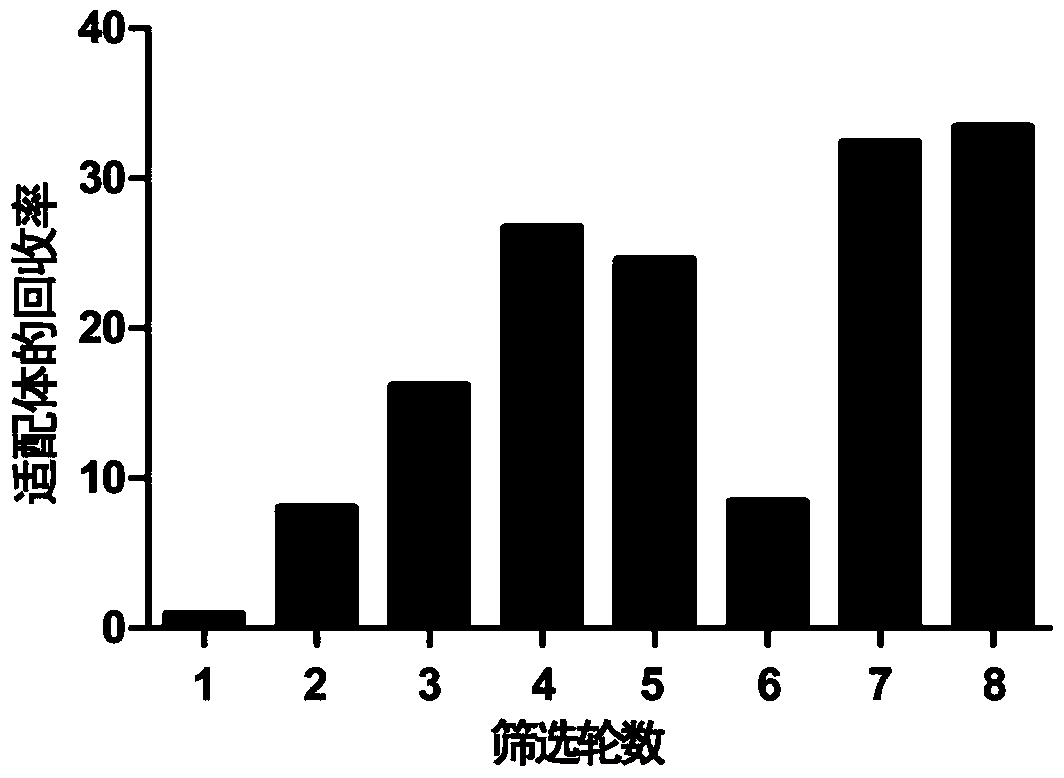
[0038] In order to obtain nucleic acid aptamers with high affinity and high specificity for GTX1 and GTX4, eight rounds of screening were carried out based on graphene oxide’s ability to non-specifically adsorb ssDNA, as shown in figure 1 shown; where the reverse screening was introduced from the sixth round, that is, the ssDNA library was first incubated with the reverse targets (GTX2, GTX3, STX and neoSTX), and then an appropriate amount of graphene oxide was added for co-incubation; after the supernatant was removed by centrifugation, Add free target toxins GTX1 and GTX4 and incubate again; finally, aptamers that specifically bind to GTX1 and GTX4 are recovered. In each round of screening, the recovery rate of aptamers binding to target toxins GTX1 and GTX4 was as follows: figure 2 shown.
[0039] Take 1 nmol of the initial ssDNA library, add 200 μL of binding buffer (20 mM Tris-HCl, 100 mM NaCl, 2 mM...
Embodiment 3
[0048] Example 3. Truncation optimization of GO18 aptamers
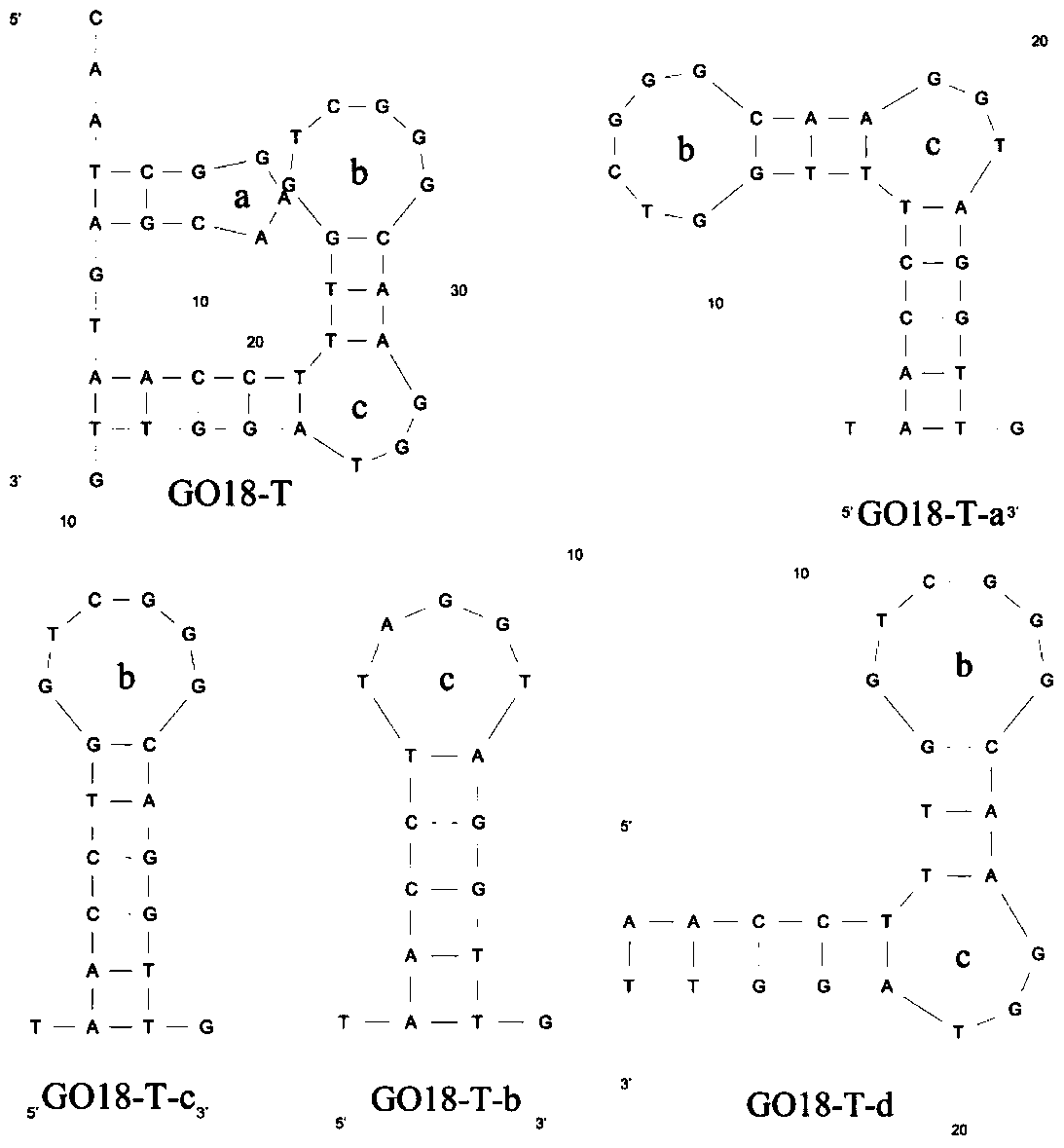
[0049] All truncated sequences are shown in Table 2. After the primers at both ends of the aptamer GO18 were truncated, the binding affinity was determined by biomembrane interferometry. affinity. Based on the secondary structure of GO18-T such as image 3 , forming three diameter rings a, b, c. The binding affinity of the aptamer GO18-T-a to the target toxin was significantly increased, while GO18-T-b and GO18-T-c showed no binding. It may be that the radial loop a on the aptamer GO18-T-a is fully exposed after the truncated rings b and c, and binds more tightly to the target molecules GTX1 and GTX4, resulting in a significant increase in the affinity of the two. Therefore, the aptamer GO18-T-d containing only 25 nucleotides was obtained after further truncation.
[0050] Table 2: Aptamer GO18 truncated sequence and its affinity constant Kd value
[0051]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com