Regenerated cellulose fiber and preparation method thereof
A technology of regenerated cellulose and fiber, applied in the direction of single-component cellulose rayon, fiber chemical characteristics, rayon manufacturing, etc., can solve the problems of shortage of regenerated cellulose fiber raw materials, poor operability, etc., and achieve short dissolution time , Improve the uniformity of reaction and reduce the effect of reaction time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
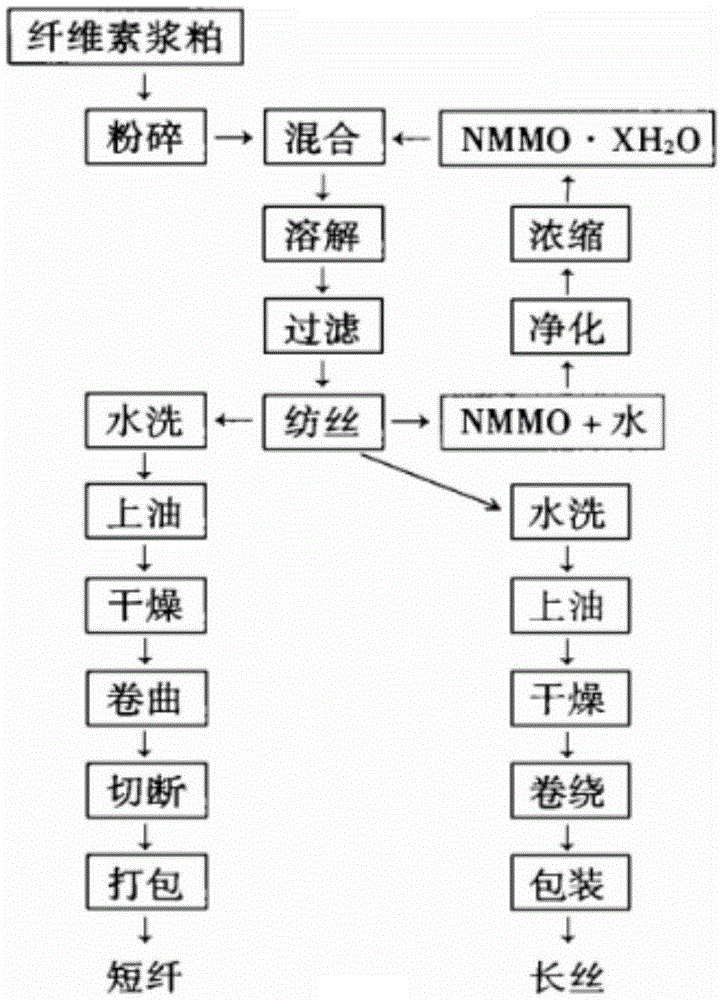
[0032] The invention provides a kind of preparation method of regenerated cellulose fiber, it is characterized in that, comprises the steps:
[0033] 1) After mixing and dissolving the corn cob fiber pulp and the chelating agent in the NMMO solution, the spinning dope is obtained;
[0034] 2) Spinning the spinning dope obtained in the above steps to obtain regenerated cellulose fibers.
[0035] In the present invention, firstly, the corncob fiber pulp and the chelating agent are mixed and dissolved in the NMMO solution to obtain the spinning dope; the degree of polymerization of the corncob fiber pulp is preferably 400-800, more preferably 400-750, and more preferably 400-700, more preferably 400-650, most preferably 400-600. In the corn cob fiber pulp, the cellulose is preferably 80% to 95%, more preferably 83% to 92%, most preferably 85% to 90%; the whiteness is preferably 70% to 90% , more preferably 75%-85%, most preferably 78%-82%; the ash content is preferably 0-0.5%, ...
Embodiment 1
[0075] The corncob fiber pulp and the chelating agent are dissolved with NMMO solution to obtain a spinning stock solution, and the spinning stock solution is used to prepare regenerated cellulose fibers.
[0076] Among them, corncob pulp accounts for 12% of the total material weight. The addition amount of the chelating agent (ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid) is 0.1% of the cellulose pulp.
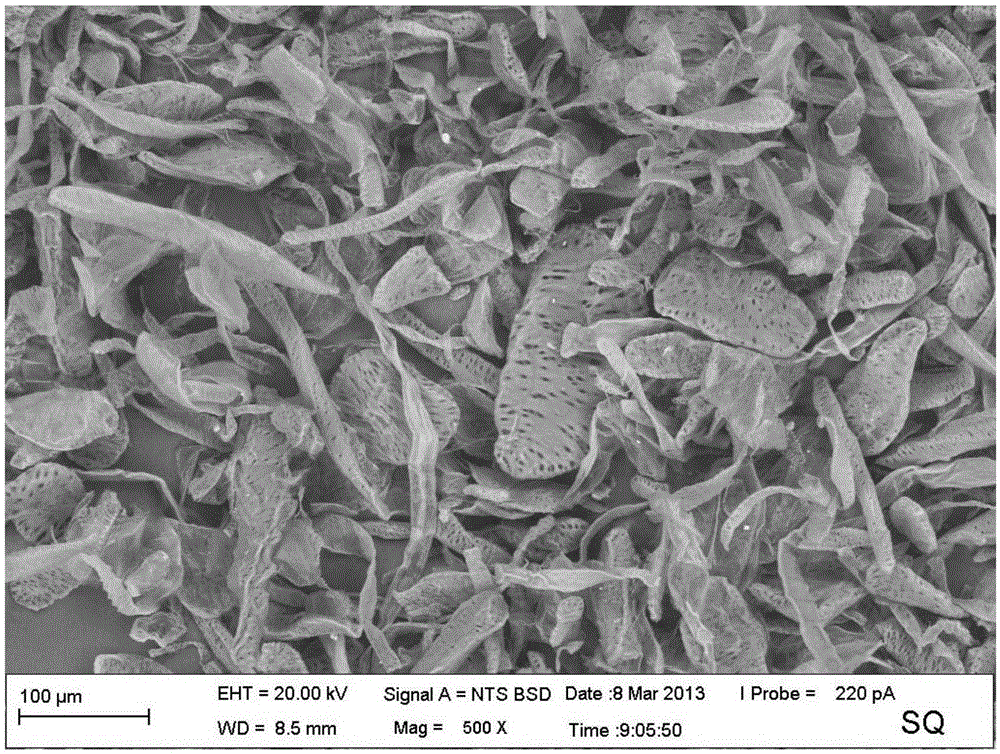
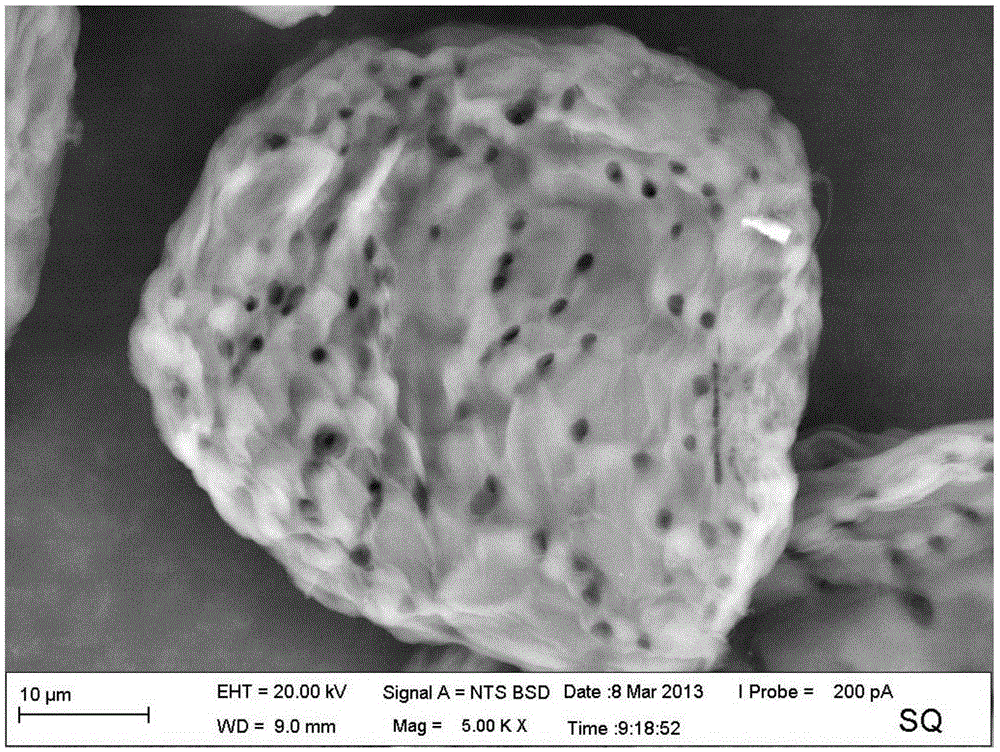
[0077] see image 3 , image 3 It is a 5000 times SEM photo of the corncob cellulose pulp in Example 1 of the present invention.
Embodiment 2~15
[0079] Embodiment 2-13 is the same as embodiment 1, only limited to the change of corn cob pulp content and the change of chelating agent, the corn cob pulp of embodiment 14 is impregnated with acetic acid before mixing with NMMO, then dried, then added to NMMO solution middle. In Example 15, after the corncob pulp and the NMMO solution were mixed, carbon dioxide gas was passed into the mixed slurry. The carbon dioxide introduced at this time is simultaneously removed in the defoaming step before spinning.
[0080] In Examples 1 to 15, the timing of adding the chelating agent is when the water content of NMMO is 10% to 30%, the properties of the corn cob fiber pulp selected in Examples 1-15 and Comparative Document 1: corn cob fiber pulp The medium cellulose content is 80-95%, the whiteness is 70-90%, the ash content is 0-0.5%, and the water content is 5-50%.
[0081] The preparation method of the corn cob fiber pulp is:
[0082] method one
[0083] (1) After crushing the ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| degree of polymerization | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| aggregation | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| elongation at break | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com