High xylose tolerance bifunctional hemicellulose degrading enzyme, its coding gene and its preparation method
A hemicellulose and dual-function technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of low tolerance to xylose and difficulty in meeting industrial needs, and achieve the effects of reducing anti-nutritional effects, increasing fragrance, and increasing concentration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] Example 1: Cloning of the gene XylRBM26
[0048] Extraction of Massilia sp.RBM26 genomic DNA: Centrifuge the bacterial liquid from the liquid culture for 2 days, add 1 mL of lysozyme, treat at 37 °C for 1 h, and then add lysate. The lysate consists of: 50mM Tris, 20mM EDTA, NaCl 500mM, 2 % SDS (w / v), pH 8.0, lysed in a water bath at 70°C for 1 h, mixed every 10 min, and centrifuged at 10,000 rpm for 5 min at 4°C. The supernatant was extracted with phenol / chloroform to remove impurity proteins, and then the supernatant was added with an equal volume of isopropanol, and after standing at room temperature for 5 min, centrifuged at 10,000 rpm for 10 min at 4°C. The supernatant was discarded, the precipitate was washed twice with 70% ethanol, dried under vacuum, dissolved in an appropriate amount of TE, and placed at -20°C for later use.
[0049]The genome of 5 μg of Massilia sp.RBM26 was fragmented into fragments of 400-600bp using the ultrasonic fragmentation instrument B...
Embodiment 2
[0051] Example 2: Preparation of recombinant bifunctional hemicellulose degrading enzyme XylRBM26
[0052] Primers for amplifying mature peptides were designed according to the sequence analysis of the bifunctional hemicellulose degrading enzyme gene XylRBM26:
[0053] XylRBM26F: ATGATCCACAACCCGATCCTGC
[0054] XylRBM26R: CAGCCCGGCTGAGGTAGGGCC
[0055] Using the genome of the strain Massilia sp.RBM26 as a template, the above-mentioned primers were used to amplify the target gene by PCR. PCR reaction parameters were pre-denaturation at 94°C for 5 min; denaturation at 94°C for 30S, annealing at 72°C for 30S, extension at 72°C for 1min30S, a total of 20 cycles; denaturation at 94°C for 30S, annealing at 52°C for 30S, extension at 72°C for 1min30S, a total of 10 cycles; After amplification at 72°C, the extension was performed for 7 min; the temperature decreased by 1°C in each cycle from 72°C to 52°C.
[0056] The bifunctional hemicellulose degrading enzyme gene XylRBM26 was co...
Embodiment 3
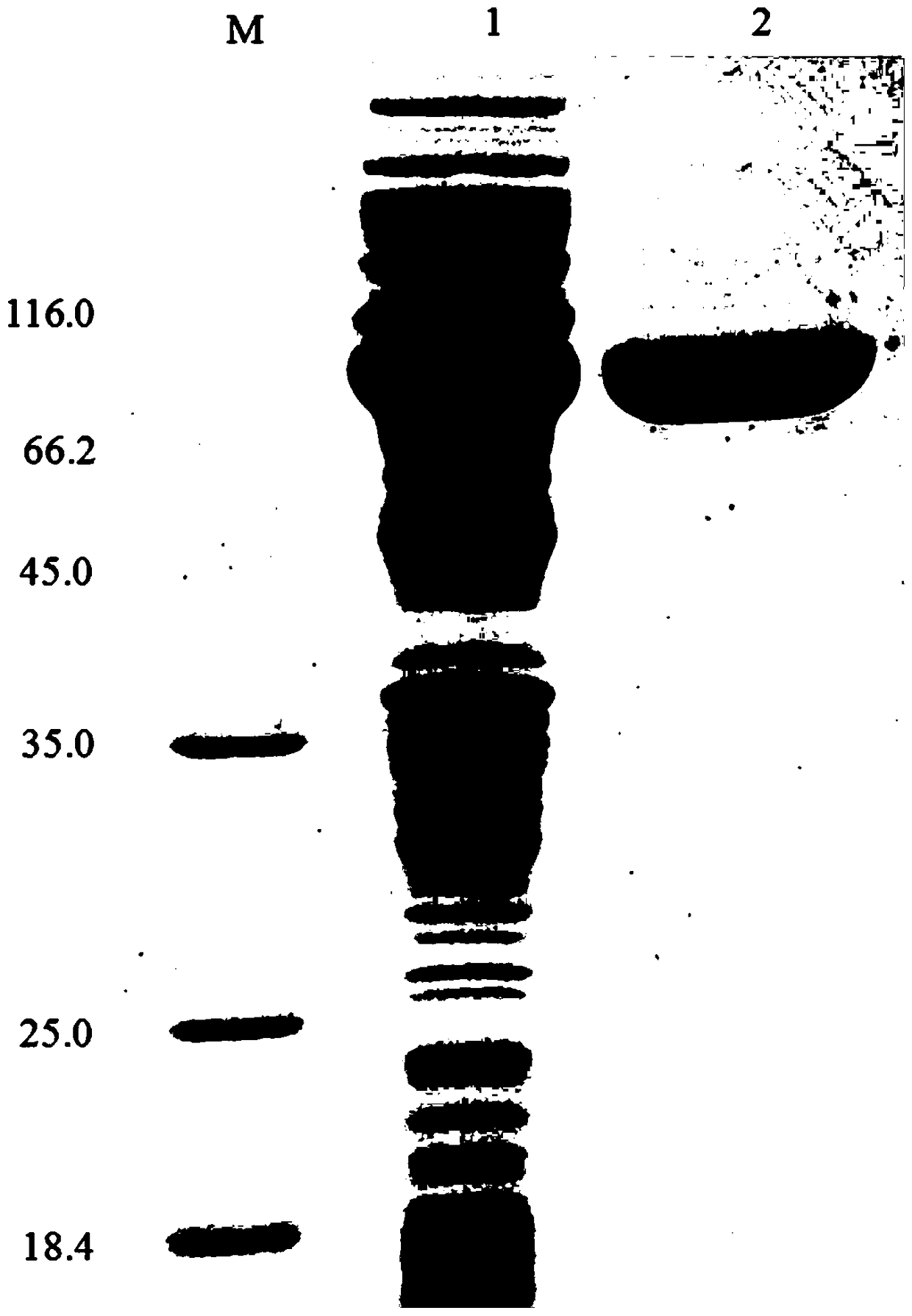
[0058] Example 3 Characterization of the purified recombinant bifunctional hemicellulose degrading enzyme XylRBM26
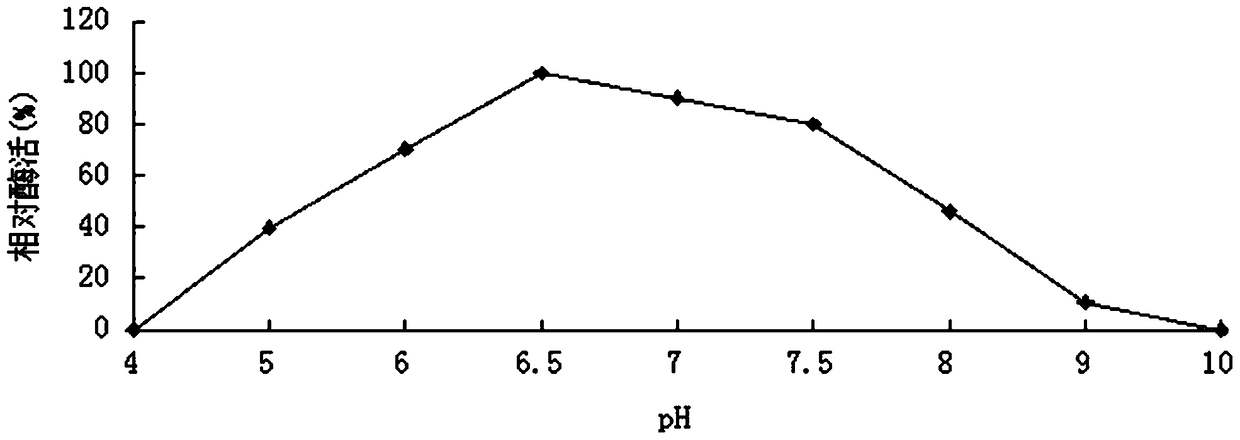
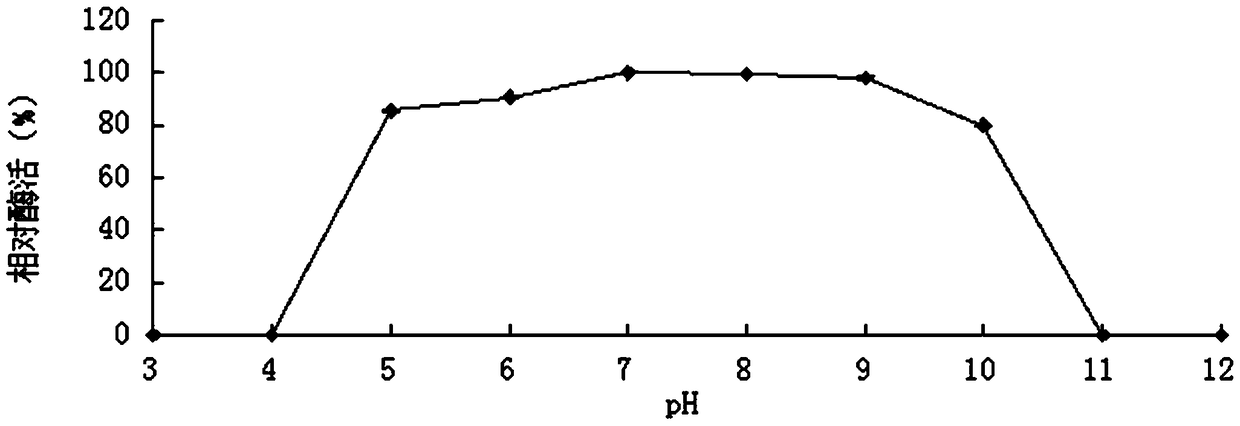
[0059] 1. Activity analysis of purified recombinant bifunctional hemicellulose-degrading enzyme XylRBM26
[0060] The activity assay method of the recombinant bifunctional hemicellulose degrading enzyme XylRBM26 adopts the pNPX method: pNPX is dissolved in 0.1M buffer to make the final concentration 2mM. 450μL of 2mM substrate; after preheating at the reaction temperature for 5min, add 50μL of appropriately diluted enzyme solution, after 10min of reaction, add 2mL of 1M Na 2 CO 3 The reaction was terminated, and the released pNP was measured at a wavelength of 405 nm after cooling to room temperature; 1 unit of enzyme activity (U) was defined as the amount of enzyme required to decompose pNPX to generate 1 μmol of pNP per minute (the method for measuring the enzyme activity of pNP substrates is the same as that of pNPX). ). The activity of the substrates oat ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com