High-xylose-tolerance difunctional hemicellulolytic enzyme and encoding gene and preparation method thereof
A hemicellulose and dual-function technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of low xylose tolerance and difficulty in meeting industrial needs, and achieve the effects of reducing anti-nutritional effects, increasing fragrance, and increasing concentration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] Example 1: Cloning of gene XylRBM26
[0048] Extract Massiliasp.RBM26 genomic DNA: centrifuge the bacterial liquid cultured in liquid for 2 days to get the thallus, add 1mL lysozyme, treat at 37°C for 1h, then add the lysate, the lysate consists of: 50mM Tris, 20mM EDTA, NaCl500mM, 2% SDS (w / v), pH 8.0, lysed in a water bath at 70°C for 1 hour, mixed every 10 minutes, and centrifuged at 10,000 rpm for 5 minutes at 4°C. The supernatant was extracted in phenol / chloroform to remove impurity proteins, and then an equal volume of isopropanol was added to the supernatant. After standing at room temperature for 5 minutes, centrifuge at 10,000 rpm for 10 minutes at 4°C. The supernatant was discarded, the precipitate was washed twice with 70% ethanol, dried in vacuum, dissolved by adding an appropriate amount of TE, and stored at -20°C for later use.
[0049]5 μg of Massiliasp.RBM26 genome was broken into fragments of 400-600 bp with an ultrasonic breaker Biorupter, and the br...
Embodiment 2
[0051] Example 2: Preparation of recombinant bifunctional hemicellulose degrading enzyme XylRBM26
[0052] According to the sequence analysis results of the bifunctional hemicellulose degrading enzyme gene XylRBM26, the primers for amplifying the mature peptide were designed:
[0053] XylRBM26F: ATGATCCACAACCCGATCCTGC
[0054] XylRBM26R: CAGCCGGCTGAGGTAGGGCC
[0055] Using the genome of strain Massiliasp.RBM26 as a template, the above primers amplify the target gene by PCR. The PCR reaction parameters were pre-denaturation at 94°C for 5 minutes; denaturation at 94°C for 30S, annealing at 72°C for 30S, extension at 72°C for 1min30S, a total of 20 cycles; denaturation at 94°C for 30S, annealing at 52°C for 30S, and extension at 72°C for 1min30S, a total of 10 cycles; After amplification at 72°C, it was extended for 7 minutes; the temperature was decreased by 1°C for each cycle from 72°C to 52°C.
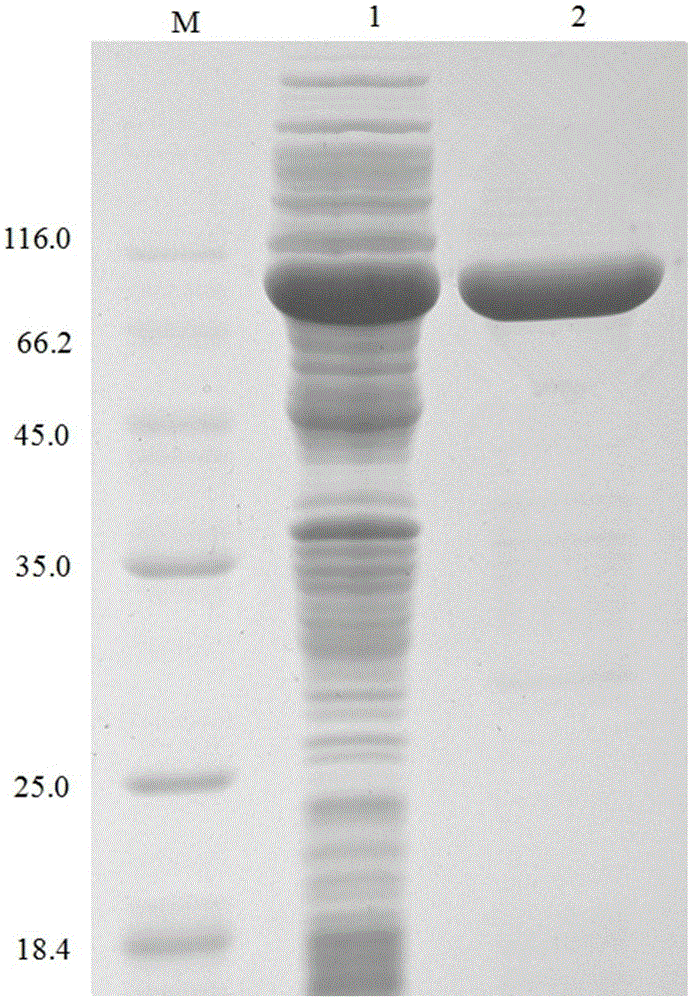
[0056] The bifunctional hemicellulose degrading enzyme gene XylRBM26 and the ex...
Embodiment 3
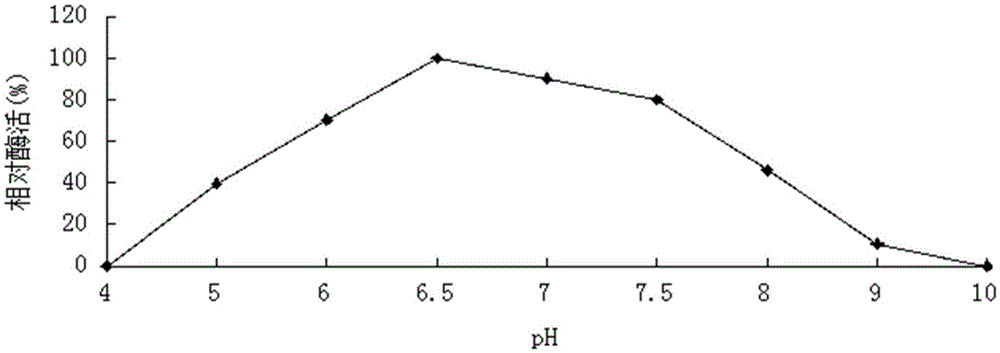
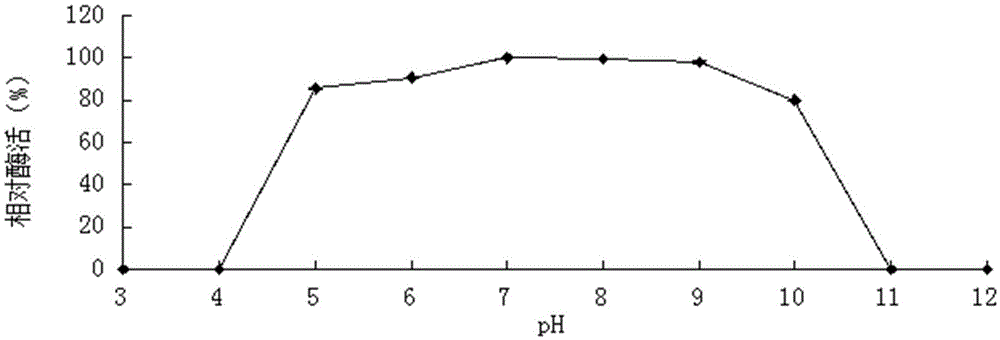
[0058] Example 3 Determination of the properties of the purified recombinant bifunctional hemicellulose degrading enzyme XylRBM26
[0059] 1. Activity analysis of purified recombinant bifunctional hemicellulose degrading enzyme XylRBM26
[0060] The method for measuring the activity of the recombinant bifunctional hemicellulose-degrading enzyme XylRBM26 adopts the pNPX method: pNPX is dissolved in 0.1M buffer to make the final concentration 2mM. 450μL of 2mM substrate; after preheating at the reaction temperature for 5min, add 50μL of an appropriate amount of diluted enzyme solution, and after 10min of reaction, add 2mL of 1M Na 2 CO 3 Terminate the reaction, measure the released pNP at a wavelength of 405nm after cooling to room temperature; 1 enzyme activity unit (U) is defined as the amount of enzyme required to decompose pNPX to produce 1 μmol pNP per minute (the enzyme activity determination method of the pNP substrate is the same as that of pNPX) . 3,5-dinitrosalicyli...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com