Screening and domesticating method of composite microbial system for low-temperature degradation of straws
A technology of composite bacteria and straw, applied in the agricultural field, can solve the problems of limited promotion, poor decomposition effect, slow decomposition, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] Example 1 Screening of Composite Bacteria for Low Temperature Degradation of Corn Stalks
[0022] The experiment was carried out in the microbiology laboratory of Sarazi Experimental Base of Inner Mongolia Agricultural University from 2011 to 2012.
[0023] 1. Sources of materials and strains
[0024] Collect cellulose-rich sawdust, rotten grass, rotten straw, cattle, sheep, chickens, ducks, pigeons and rabbits, meadow soil, forest soil, wood mushroom, and soil that has been returned to the field for many years in the alpine area with an average annual temperature of -0.6-8°C 100 materials.
[0025] 2. Enrichment culture
[0026] In this experiment, filter paper laying method, filter paper disintegration method, and natural corn stalk powder shaking table enrichment culture were adopted.
[0027] Filter paper tiling method: Mix and enrich the collected materials for static culture, rotten corn stalks, rotten wheat stalks, rotten rice stalks, rotten fallen leaves, rot...
Embodiment 2
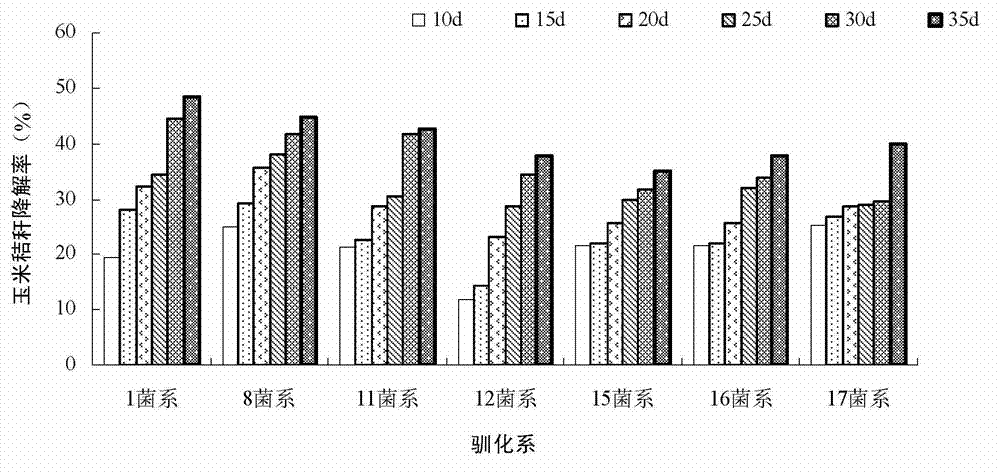
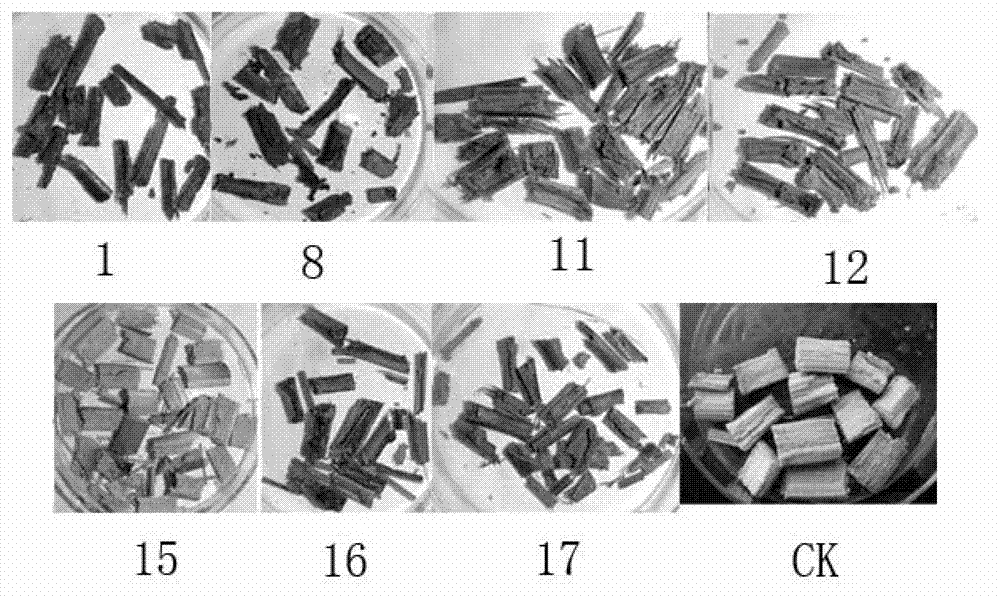
[0051] Example 2 Degradation Effect Determination of Domesticated Composite Bacteria Lines Corn Stalks
[0052] 1. Growth status of domesticated composite bacteria on corn stalk solid medium and its effect on corn stalk degradation
[0053] According to the inoculum amount of 5% (volume ratio), inoculate the liquid culture solution of the compound bacterial strain on the corn stalk, and cultivate the acclimatization line under the condition of 20 ℃, and observe that 1-2mm mycelium grows on the corn stalk on the 2nd day; On the 3rd day, the mycelia basically covered the upper part; on the 5th day, the mycelia still grew vigorously; on the 7th day, the mycelium grew slowly; on the 10th day, the mycelia showed autolysis, and most of them stopped growing. Cultivated at 15°C, 1, 8, 11, and 16 strains were observed to grow 1-2mm mycelia on the corn stalks on the second day; on the fourth day, the mycelia had basically covered the upper part; on the eighth day, the mycelium was still...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com