A hole sealing method for a powder metallurgy chromium alloy fuel cell connector
A powder metallurgy and fuel cell technology, applied in the direction of fuel cell components, etc., can solve the problems such as the inability to use battery connectors, achieve the effect of convenient operation, simple process, and solve the problem of air tightness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
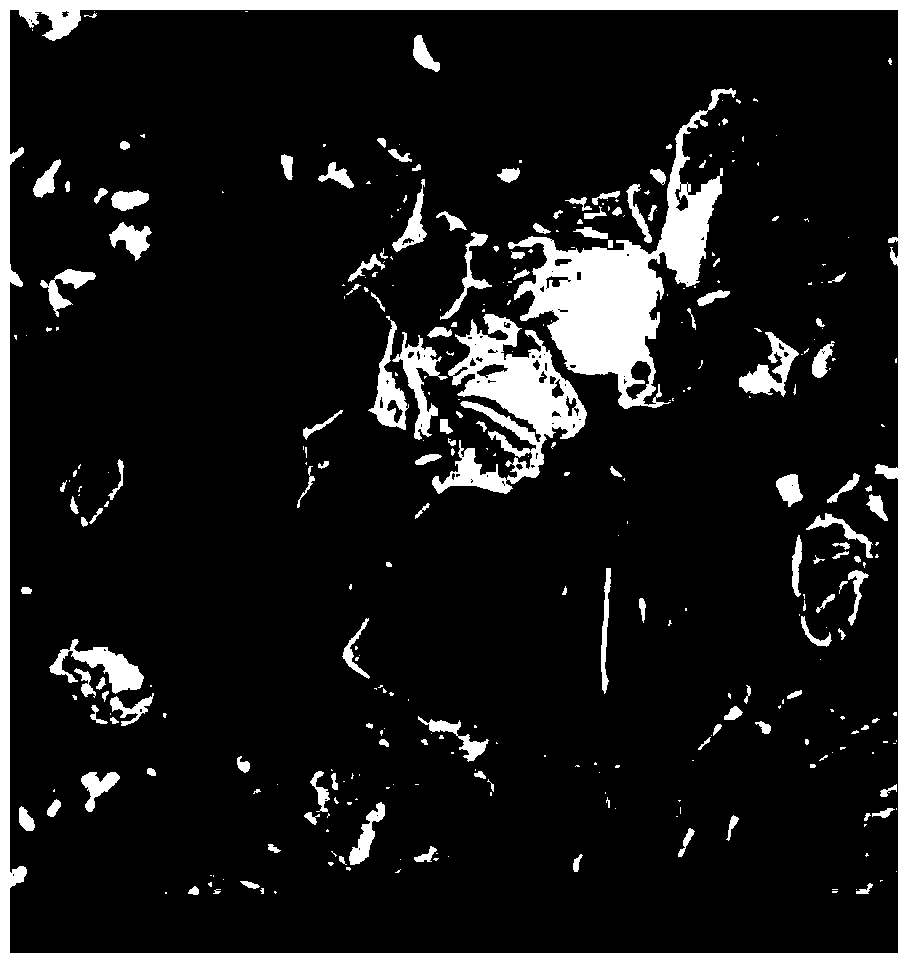
[0020] The chromium content is 85%, the porosity is 10%, and the powder metallurgy chromium alloy connector with a thickness of 3mm is placed in a heat treatment furnace at 800°C for 3 hours, and then heated to 900°C for 1 hour, carbon potential Cp: 1.0%, It is then cooled in air and finally sandblasted. Pore morphology before sealing figure 1 As shown, the pore morphology after sealing is as follows figure 2 shown. The depth of the compound layer immersed in the internal pores of the part is 1.5mm, the thickness of the compound layer is 0.8-1.0μm, and the compound is dense and continuous.
Embodiment 2
[0022] The chromium content is 95%, the porosity is 12%, and the powder metallurgy chromium alloy connector with a thickness of 3mm is placed in a heat treatment furnace at 880°C for 3 hours, and the carbon potential Cp: 1.0%, then cooled in the air, and finally Sandblasting. The pore morphology after sealing is as follows: image 3 shown. The depth of the compound layer immersed in the internal pores of the part is 1.5mm, the thickness of the compound layer is 1.5-2.0μm, and the compound is dense and continuous.
Embodiment 3
[0024] The chromium content is 75%, the porosity is 15%, and the powder metallurgy chromium alloy connector with a thickness of 3mm is placed in a heat treatment furnace at 850°C. Carbon potential Cp: 0.8 and kept for 3 hours, then heated to 980°C. , keep warm for 1 hour, then cool in the air, and finally perform sandblasting. The morphology of the compound in the pores after sealing is as follows: Figure 4 shown. The depth of the compound layer immersed in the internal pores of the part is 0.5mm, the thickness of the compound layer is 2-3μm, and the compound is relatively loose.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| depth | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com