A colloidal slow-release material for in-situ restoration of groundwater and its preparation method
An in-situ repair and slow-release material technology, applied in the field of environmental pollution control and repair, can solve the problems of reducing the use efficiency of active repair agents, the influence of morphology, structure and particle size, and the short half-life of active repair agents, so as to improve the groundwater quality. In-situ remediation efficiency of chlorinated olefin pollution, easy-to-operate preparation method, and low operating condition requirements
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
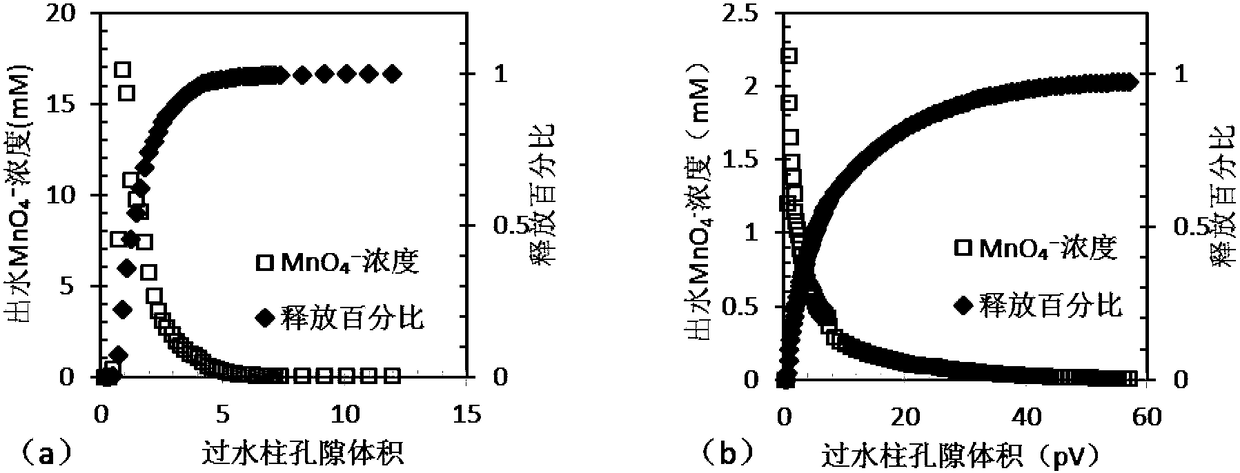
[0052] Slow release and effect of embodiment 1 permanganate oxidant
[0053] A permanganate solution with a concentration of 10g / L was prepared as the restorative solution, and then fumed silicon dioxide was added to make the mass fraction of the colloidal particles in the suspension be 7%, and mixed evenly to obtain the colloidal slow-release material.
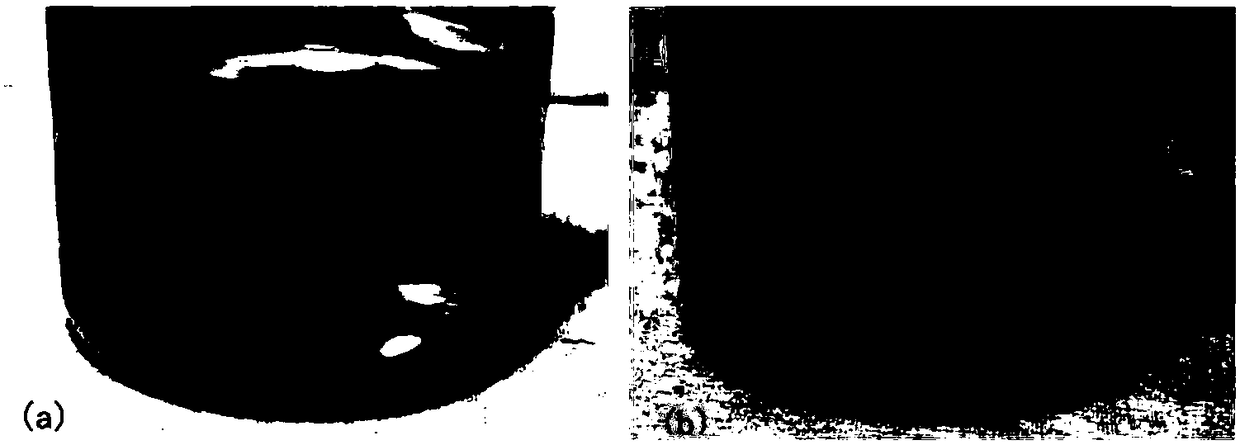
[0054] Place the prepared slow-release material at the bottom of a 250ml Erlenmeyer flask, and slowly inject 200ml of ultrapure water to avoid disturbing the surface morphology of the colloidal slow-release material. Keep the water in the Erlenmeyer flask at room temperature in a still state. Observing MnO through Visibility Observation 4 - Sustained release process, such as figure 1 As shown, the colloidal sustained-release material always maintains its original shape and size, and there is a clear interface between the colloid and the water phase. The color of the colloidal sustained-release material gradually changes fr...
Embodiment 2
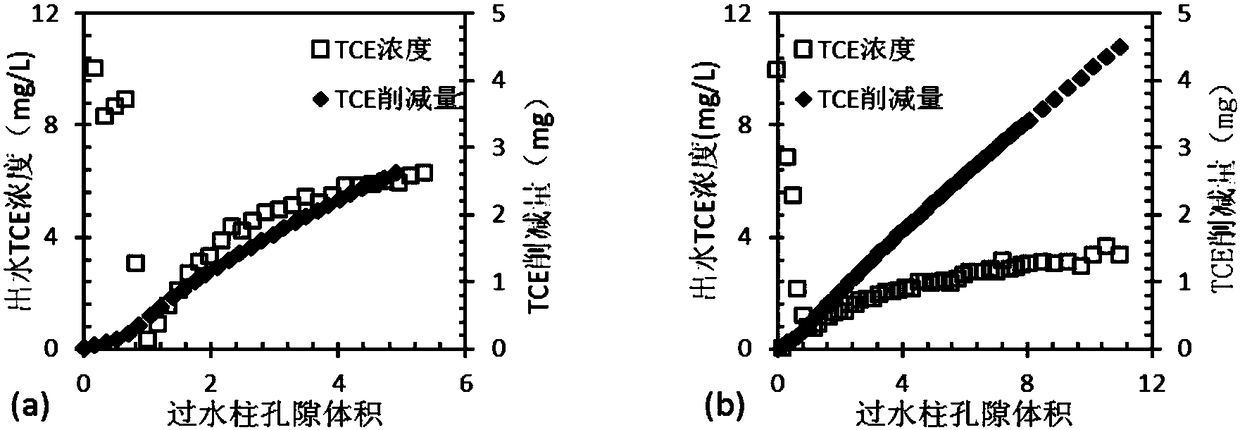
[0057] Embodiment 2 Colloid slow-release material oxidized trichlorethylene effect
[0058] A permanganate solution with a concentration of 4g / L was prepared, and fumed silica was added to make the mass fraction of the colloidal particles in the suspension to be 7%, and the mixture was evenly mixed. The suspension was stirred on a stirrer at a speed of 600 rpm for 1 h, and the viscosity was reduced by 95% compared with before.
[0059] 10ml of permanganate solution or permanganate colloid slow-release material (containing MnO 4 - The same quantity) was injected into the bottom of the water-saturated sand column through a syringe. The peristaltic pump controls the flow rate to 2.56m / d, rinses the entire packed column with 10mg / L trichlorethylene (TCE) solution from bottom to top, and begins to collect effluent samples. The sample taken was injected directly via needle into a 20ml headspace vial already filled with 10ml of methylene chloride. The headspace bottle was placed ...
Embodiment 3
[0063] The sustained release of embodiment 3 sodium persulfate oxidant
[0064] Prepare a sodium persulfate solution with a mass concentration of 10%, and then add silicon dioxide aerosol to make the mass fraction of colloidal particles in the suspension be 5%, and mix evenly. The suspension was stirred on a stirrer at a speed of 600rpm for 1 hour, and the viscosity was reduced by 95% compared with before to obtain a sodium persulfate colloid slow-release material.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| clearance rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com