A method of screening a marker of renal toxicity caused by aristolochic acid by utilizing cell metabolic profiling in vitro
An aristolochic acid and cell metabolism technology, which is applied in the fields of analytical chemistry and medicinal chemistry, can solve the problems of unstable analysis sequences of instruments, difficulty in data modeling, and deviation of mass spectrometry response, and achieves less difficulty in clinical translation, high sensitivity, and high The effect of separation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
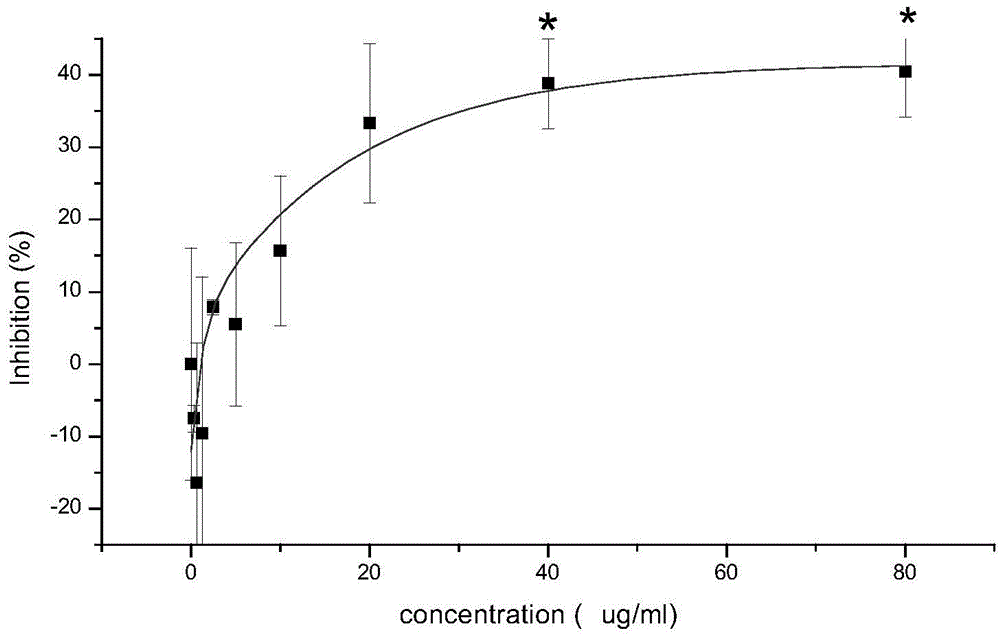
[0046] 1. Study on the effective dose of aristolochic acid-induced renal cell damage
[0047] Inoculate equal amounts of humanized normal kidney cells HL7702 suspended in K-SFM medium into 96-well plates (104 cells / well), add 200ul of K-SFM cell culture medium to each well, place at 37°C, 5% CO2 constant temperature cell incubator. Overnight, remove the original medium, add 200ul 0.312, 0.625, 1.25, 2.5, 5, 10, 20, 40, and 80 μg / ml of aristolochic acid respectively, and the aristolochic acid aqueous solution uses K-SFM cell culture medium Make a dilution. Three parallel wells were designed for each dose, and a cell control group (control group) without drug addition and only an equal volume of medium was set in parallel, and a blank group was not inoculated with cells but only an equal volume of medium was added. After culturing in a constant temperature cell incubator at 37°C and 5% CO2 for 24 hours, add 20 μL of 5 mg / ml MTT phosphate buffer solution (pH=7.0) to each well, ...
Embodiment 2
[0077] 1. Nephrotoxic dose study, cell sample collection, processing, analysis and metabolic profile analysis are similar to those in Example 1, the main difference parameters are as follows:
[0078] 1) Set up groups: control group, 24h aristolochic acid injury group. There are 12 parallel samples in each group, a total of 24 samples.
[0079] 2) The number of cells in each sample is about 50 mg after centrifugation. The mobile phase A of metabolic profiling was 0.2% formic acid aqueous solution.
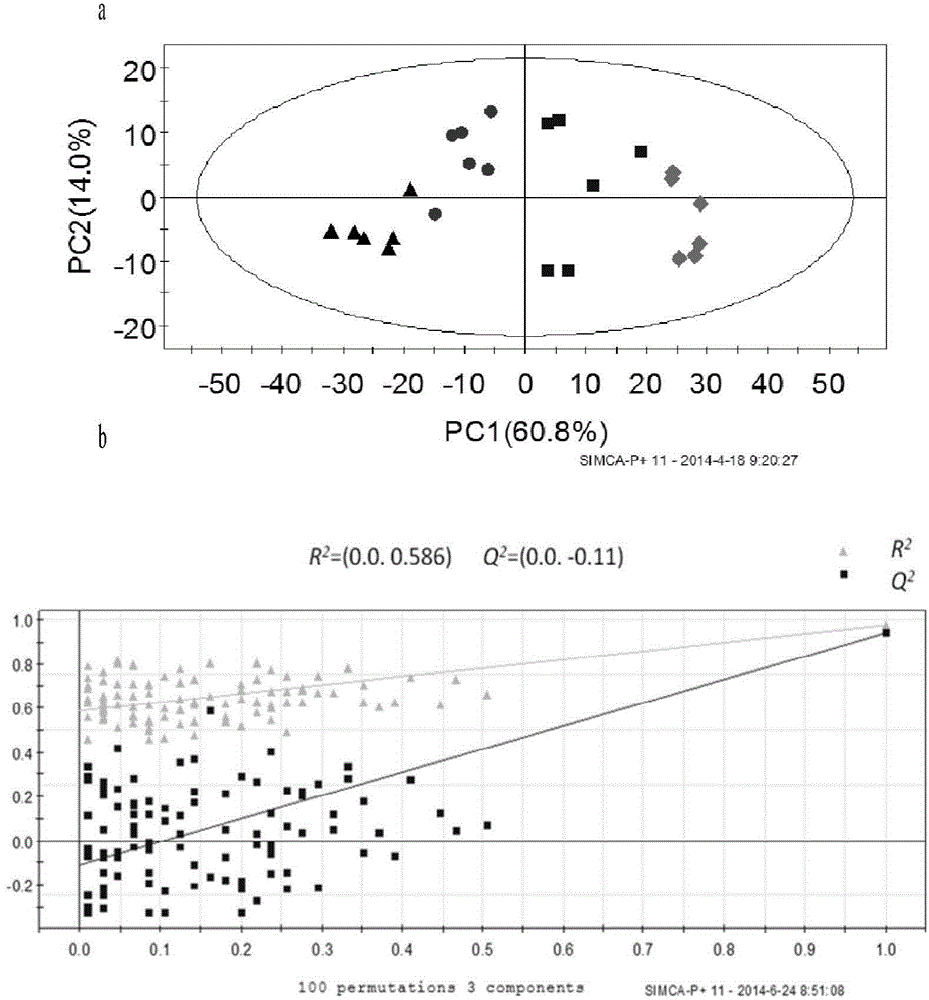
[0080] 3) The main parameters of the PLSDA model (model 2) are A (principal component number) = 2, R2X = 0.609, R2Y = 0.985, and Q2 = 0.96.
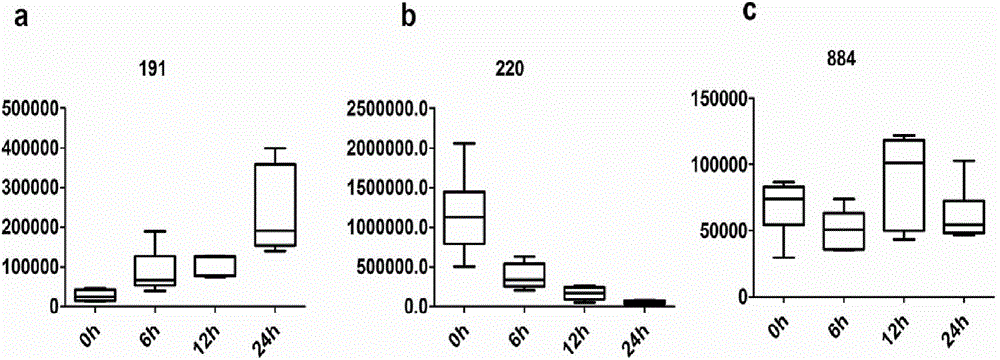
[0081] The normal group and the injury group were also well separated in model 2. And the ions in Table 1 are included in the candidate markers screened out by Model 2. It shows that the markers screened by this method have the characteristics of stability and reproducibility.
[0082] The predictive ability of the potential markers of m...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com