Method for removing chloride ions in copper sulphate solution
A copper sulfate solution, chlorine removal technology, applied in the chemical industry, can solve the problems of high cost and complicated operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
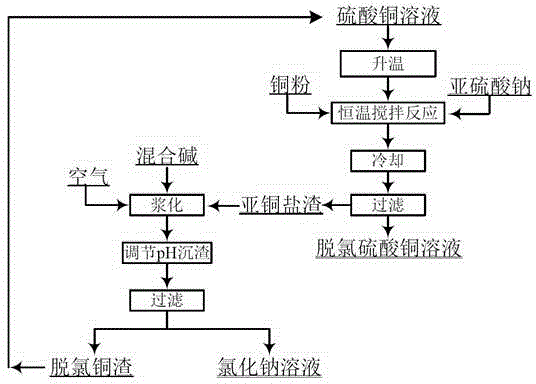
[0032] 1) Take 4L of chlorine-containing copper sulfate solution, put it in a 5L beaker, check that the original solution contains Cu=55.65g / L, Cl=18.64g / L; weigh 110g of copper powder; weigh 4g of solid sodium sulfite.
[0033] 2) Put the beaker in a constant temperature water bath and raise the temperature to 80°C, start stirring and add the weighed sodium sulfite and copper powder, and stir for 2.5 hours;
[0034] 3) Take out the beaker from the water bath, let it cool down to room temperature naturally, and filter;
[0035] 4) Obtain 271g of white cuprous salt filter residue and 3800ml of sky-blue copper sulfate solution; the detected filtrate Cu=57.26g / L, Cl=800mg / L; the primary removal rate of chloride ions is 95.93%.
Embodiment 2
[0037] 1) Take 4L of chlorine-containing copper sulfate solution, put it in a 5L beaker, check that the original solution contains Cu=50.65g / L, Cl=4.7g / L; weigh 25g of copper powder; weigh 4g of solid sodium sulfite.
[0038] 2) Put the beaker in a constant temperature water bath and raise the temperature to 80°C, start stirring and add the weighed sodium sulfite and copper powder, and stir for 2.5 hours;
[0039] 3) Take out the beaker from the water bath, let it cool down to room temperature naturally, and filter;
[0040] 4) Obtain 64.6g of white cuprous salt filter residue and 3950ml of sky blue copper sulfate solution; the detected filtrate Cu=52.32g / L, Cl=27mg / L; the solution meets the needs of traditional electrodeposition copper solution, and can also prepare copper sulfate pentahydrate crystals.
Embodiment 3
[0042] 1) Take 4L of chlorine-containing copper sulfate solution, put it in a 5L beaker, and detect that the original solution contains Cu=27.44g / L, Cl=12.7g / L; weigh 75g of copper powder; weigh 4g of solid sodium sulfite.
[0043] 2) Put the beaker in a constant temperature water bath and raise the temperature to 80°C, start stirring and add the weighed sodium sulfite and copper powder, and stir for 2.5 hours;
[0044] 3) Take out the beaker from the water bath, let it cool down to room temperature naturally, and filter;
[0045] 4) Obtain 184.6g of white cuprous salt filter residue and 3920ml of sky blue copper sulfate solution; test filtrate Cu=31.26g / L, Cl=128mg / L; chloride ion removal rate is 99.01%.
[0046] Reuse of dechlorination slag:
[0047] 1) Collect a total of 500g of white cuprous salt wet slag, prepare 500ml mixed alkali slurry with sodium carbonate and caustic soda with a mass ratio of 2:1, add the cuprous salt wet slag into the mixed alkali slurry, and conti...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com