Electromagnetic wave shielding composite film
A composite film and electromagnetic wave technology, applied in the direction of magnetic/electric field shielding, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of ineffective shielding of low-frequency electromagnetic waves, high equipment investment costs, etc., and achieve the effect of improving electromagnetic wave shielding effect, light weight, and saving thickness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
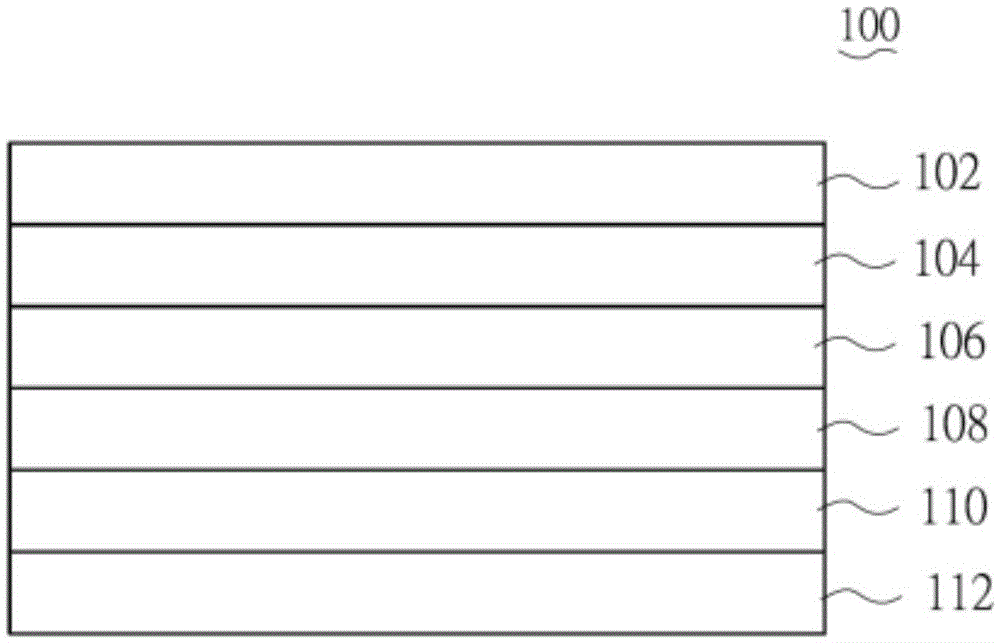
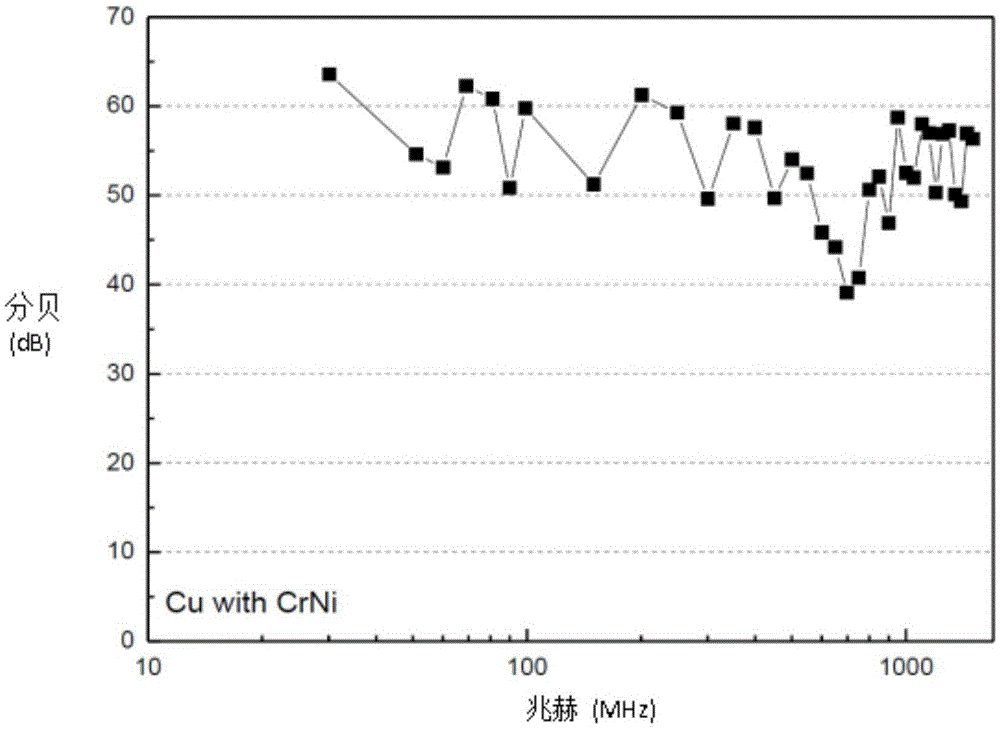
[0029] The electromagnetic shielding composite film of the present embodiment is completed by the following process steps: graphene is prepared by Mechanical Exfoliation, and its average thickness range can be from 0.2 nanometers to 300 nanometers, and then graphene (25% by weight), low Viscosity macromolecular binder (40 weight percent epoxy resin), hardener (15 weight percent polyamide hardener), dispersant (0.5 weight percent anionic dispersant), organic solvent (19 weight percent methyl ethyl ketone , a mixed solvent of toluene and ethyl acetate) and additives (0.5 weight percent defoamer), etc., are fully and evenly mixed, and coated and dispersed on the surface of the PET release film 112 to form an incident layer with a high conductive function 110, the thickness of which is about 15 micrometers; then, a wave-absorbing layer 108 of nickel-chromium alloy with a thickness of 50 nanometers and a reflective layer 106 of copper metal with a thickness of 300 nanometers are seq...
Embodiment 2
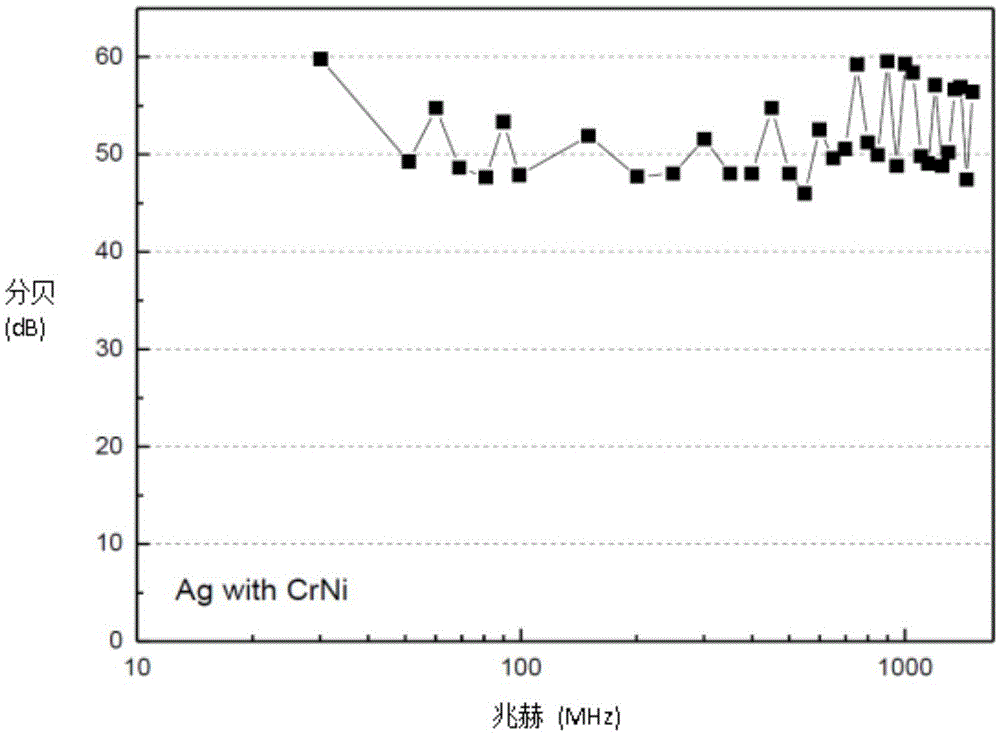
[0031] The electromagnetic shielding composite film of the present embodiment is completed by the following process steps: graphene is prepared by Mechanical Exfoliation, and its average thickness range can be from 0.2 nanometers to 300 nanometers, and then graphene (25% by weight) and low Viscosity macromolecular binder (40 weight percent epoxy resin), hardener (15 weight percent polyamide hardener), dispersant (0.5 weight percent anionic dispersant), organic solvent (19 weight percent methyl ethyl ketone , a mixed solvent of toluene and ethyl acetate) and additives (0.5 weight percent defoamer), etc., are fully and evenly mixed, and coated and dispersed on the surface of the PET release film 112 to form an incident layer with a high conductive function 110, the thickness of which is about 15 micrometers; then, a wave-absorbing layer 108 of nickel-chromium alloy with a thickness of 50 nanometers and a reflective layer 106 of silver metal with a thickness of 200 nanometers are ...
Embodiment 3
[0033] The electromagnetic shielding composite film of the present embodiment is completed by the following process steps: graphene is prepared by Mechanical Exfoliation, and its average thickness range can be from 0.2 nanometers to 300 nanometers, and then graphene (25% by weight) and low Viscosity macromolecular binder (40 weight percent epoxy resin), hardener (15 weight percent polyamide hardener), dispersant (0.5 weight percent anionic dispersant), organic solvent (19 weight percent methyl ethyl ketone , a mixed solvent of toluene and ethyl acetate) and additives (0.5% by weight defoamer) etc. are fully and evenly mixed and coated and dispersed on the surface of the PET release film 112 to form an incident layer 110 with a high conductive function. The thickness is about 15 microns; then, a wave-absorbing layer 108 of nickel-chromium alloy with a thickness of 50 nanometers and a reflective layer 106 of aluminum metal with a thickness of 300 nanometers are sequentially forme...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com