Magnetic molecular imprinting electrochemical sensor used for detecting trace sulfadimidine
A magnetic molecular imprinting and sulfamethazine technology, which is applied in the fields of material electrochemical variables, measuring devices, scientific instruments, etc., can solve the problems such as the lack of relevant research on the detection of trace sulfamethazine, and improve the sensitivity and selectivity. , easy to automate effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Embodiment 1: The construction of the magnetic molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor for detecting trace amounts of sulfamethazine according to the present invention is characterized in that the magnetic molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor is prepared by the following method:
[0023] (1) Processing of magnetic core electrodes:
[0024] Put the magnetic core glassy carbon electrode in 0.2M sulfuric acid to activate for 20min, then use 1.0, 0.3 and 0.05μm α-alumina powder to polish the surface, rinse it with ultrapure water and dry it, then put the electrode on the K at 5mM 3 [Fe(CN) 6 ] solution, a cyclic voltammetry (CV) scan was performed at a rate of 100 mV / s in the potential range of -0.2V to 0.6V until a stable cyclic voltammetry was obtained.
[0025] (2) Modification of core electrodes:
[0026] Weigh 10 mg magnetically reduced graphene Fe 3 o 4 @rGO was ultrasonically dispersed in 4mL water for 10min to form a dispersion. Use a micropipette...
Embodiment 2
[0031] Example 2: Cyclic voltammetry characterization of the magnetic molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor for detecting trace amounts of sulfamethazine according to the present invention
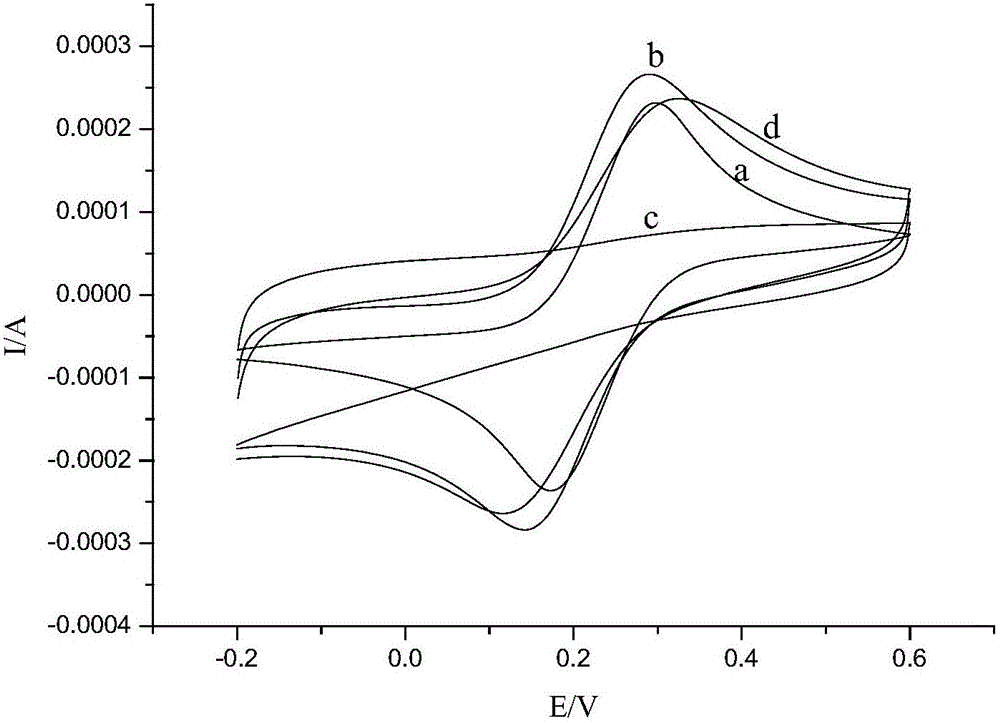
[0032] Since the imprinted holes in the membrane can serve as channels for electron transfer, using K 3 [Fe(CN) 6 ] as a probe, according to the magnitude of its current to characterize the surface properties of various electrodes. Such as figure 1 shown, different electrodes at 5mM K 3 [Fe(CN) 6 ] The cyclic voltammograms in the solution are significantly different. Curve a is the cyclic voltammogram of the bare magnetic core electrode, and the redox peak is obvious. As shown in curve b, when a layer of Fe is modified on the surface of the magnetic glassy carbon electrode 3 o 4 After the @rGO composite, the peak current increases significantly, which is due to the Fe 3 o 4 The @rGO composite is very conductive, which can promote electron transfer on the electrode surface a...
Embodiment 3
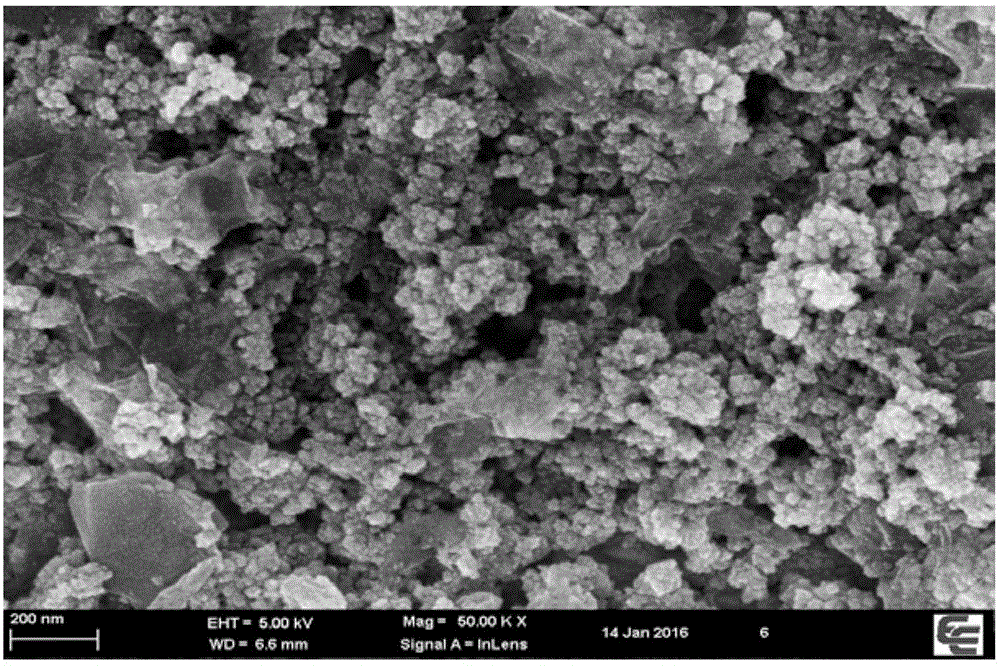
[0033] Example 3: Scanning electron microscopy characterization of different modified electrodes for magnetic molecular imprinting electrochemical sensing of the present invention for detecting trace amounts of sulfamethazine
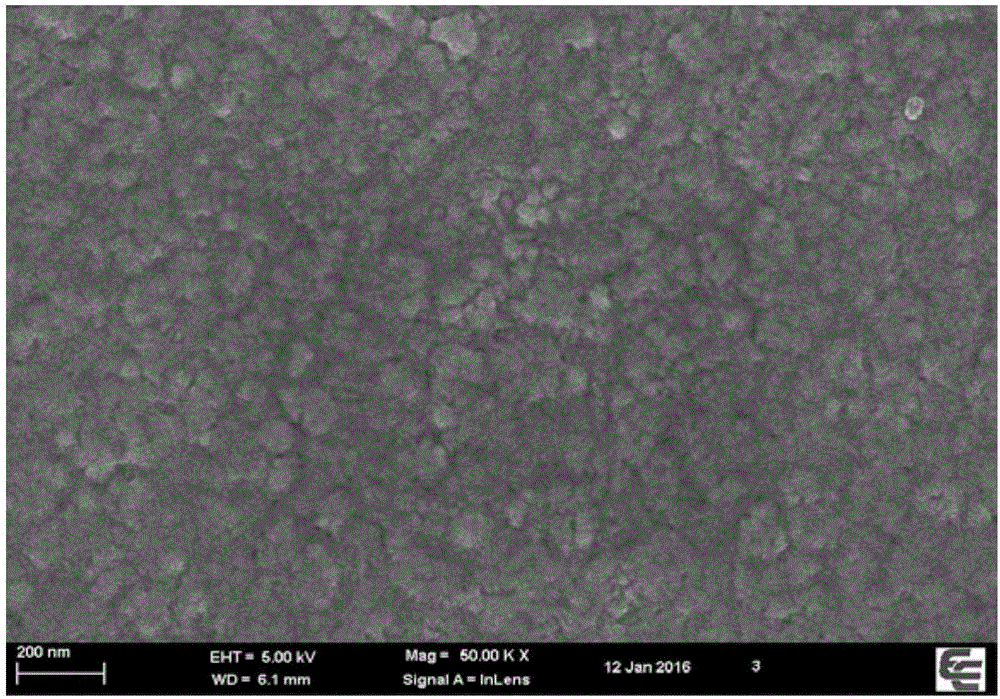
[0034] The microstructure of different modified electrodes was characterized by scanning electron microscopy. Such as Figure 2a As shown, the electrode surface is smooth after the molecular imprinted membrane is modified on the surface of the electrode, indicating that the imprinting effect is good; rough (see Figure 2b ).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com