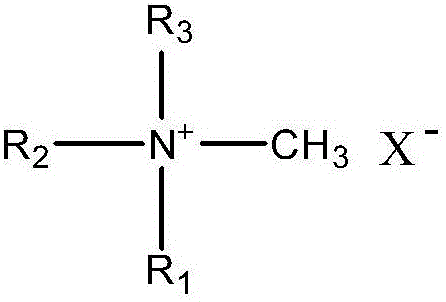
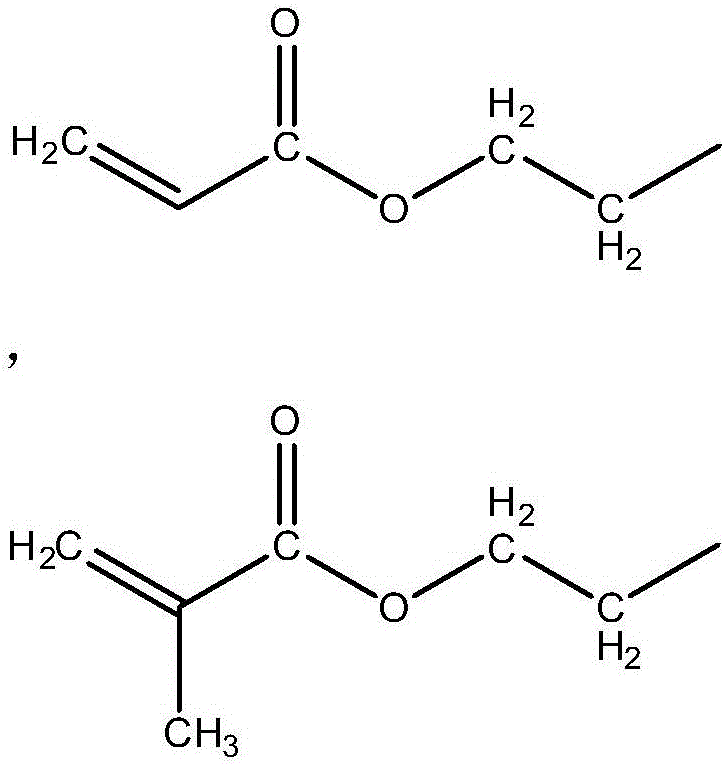
3D printing composite material for mouth rehabilitation and preparation and using method of 3D printing composite material
A technology of 3D printing and composite materials, applied in the field of composite materials, it can solve the problems of few types of 3D printing materials, limited 3D printing materials, and inability to meet industrial applications.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0070] The preparation method of the above-mentioned 3D printing composite material for dental restoration includes the following:
[0071] Step S110, mixing low-viscosity monomers, reinforcing monomers or oligomers, expanding monomers, polymerizable quaternary ammonium antibacterial monomers, and dispersants to obtain a premix.
[0072] Preferably, the low-viscosity monomer and the reinforcing monomer or oligomer are uniformly mixed before the expansion monomer is mixed and the dispersant and the polymerizable quaternary ammonium salt antibacterial monomer are added.
[0073] Preferably, if the expansion monomer is a mixture of two expansion monomers, mix the two expansion monomers evenly before adding the dispersant and the polymerizable quaternary ammonium salt antibacterial monomer to the resin monomer / oligomer.
[0074] Step S120, adding ceramic powder to the premix and then ball milling to obtain a mixture.
[0075] Preferably, the ceramic powder is gradually added to t...
Embodiment 1
[0087] The preparation of the 3D printing composite material for dental restoration of Example 1 comprises the following steps:
[0088] An electronic balance weighed 10 g of pentaerythritol tetramethacrylate and 10 g of urethane methacrylate oligomer, and mixed and stirred the two resins.
[0089] Measure 20g of spiro-orthocarbonate expansion monomer 3,9-diethyl-3,9-propenyloxymethyl-1,5,7,11-tetraoxaspiraundecane (BAOM), add into the above resin mixture.
[0090] Measure 5 g of the polymerizable quaternary ammonium salt antibacterial monomer methacryloyloxydodecylpyridine bromide (MDPB), and add it to the above mixture.
[0091] Measure 5 g of diethylpolypropoxymethylammonium chloride (VARIQUAT CC-59 from Degussa Company) as a dispersant and add it to the above mixture, and stir properly to obtain a liquid mixture.
[0092] After the spherical zirconia powder is sieved, the required powder is obtained, and the average diameter of the powder particles is 0.3 micron. Measur...
Embodiment 2
[0096] An electronic balance weighed 40 g of urethane dimethacrylate (UDMA) and 10 g of bisphenol A-glycidyl dimethacrylate (bis-GMA), and mixed and stirred the two resins.
[0097] Measure 5g of spirocyclic orthocarbonate expansion monomer 3,9-diethyl-3,9-propenyloxymethyl-1,5,7,11-tetraoxaspiraundecane (BAOM), add into the above resin mixture.
[0098] Measure 5 g of polymerizable quaternary ammonium salt antibacterial monomer methacryloyloxyethyl-n-hexadecyl-dimethylammonium hexafluorophosphate (DMAE-CH), and add it to the above mixture.
[0099] Measure 15 g of polyamide hyperdispersant (SOLSPERSE 32000 from Noveon Company) and add to the above mixture, and stir properly to obtain a liquid mixture.
[0100] After sieving the spherical glass-ceramic powder, the required powder is obtained, and the average diameter of the powder particles is about 0.1 micron. Measure 200g of glass-ceramic powder, gradually add into the above liquid mixture in three batches and stir after e...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com