A fungal fluorescent dye
A fluorescent dyeing and fluorescent whitening agent technology, applied in the field of fungal fluorescent dyes, can solve the problems of reduced detection sensitivity, long dyeing time, and inability to fungus, and achieve the goals of improving fungal detection efficiency, simplifying specimen staining steps, and good staining effects Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] The preparation of embodiment 1 fungal fluorescent dye
[0032] Reagent 1:
[0033] Solution A: Dissolve the fluorescent whitening agent 28 in a solution with a concentration of 10% (W / V) potassium hydroxide, and dissolve sufficiently so that the concentration of the fluorescent whitening agent is 0.1% (W / V).
[0034] Solution B: 1% Evans blue solution.
[0035] Before use, it is necessary to stain the sample with solution A, and then use solution B to stain the sample.
[0036] Reagent 2:
[0037] Fluorescent whitening agent 28 is dissolved in the solution that concentration is 10% (W / V) potassium hydroxide, and dissolving is sufficient, and the concentration that makes fluorescent whitening agent 28 is 0.1% (W / V), adds Evans blue dyestuff and Glycerol was used so that the concentration of Evans blue dye was 1% (W / V), and the concentration of glycerol was 30% (V / V).
[0038] Reagent 3:
[0039] Fluorescent whitening agent 28 is dissolved in the solution that conce...
Embodiment 2
[0044] The staining of embodiment 2 dander specimens
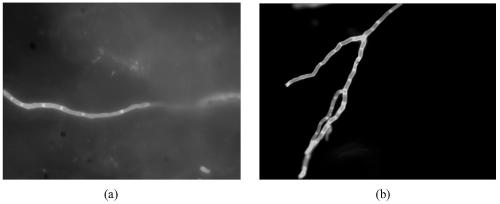
[0045] Select 5 dander specimens with similar size, shape and weight, place them on glass slides respectively, add a drop of ethanol to fix the tissue sections, leave them at room temperature for 5 minutes, wash the sections with water, blot the excess water with paper, and use reagent 1, 2,3,4,5 Stain for 1 minute, add a cover slip, absorb excess dye with paper, and then observe under a fluorescent microscope. Activated with 340nm–400nm UV light, the fungus will appear blue or yellowish green. The results showed that all the reagents could stain the fungus in the dander specimens. The dyeing effect is not much different, and the time required for dyeing is basically the same. Taking reagent 1 and reagent 3 as an example, the staining results of the two are as follows figure 1 As shown, the results show that both of them can stain the fungus in dander specimens, but the background contrast of reagent 3 to fungal stainin...
Embodiment 3
[0046] The dyeing of embodiment 3 foot skin samples
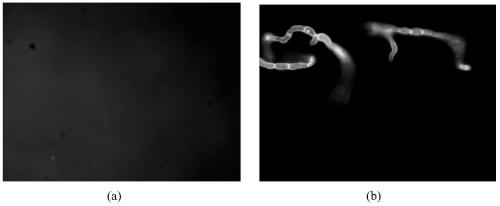
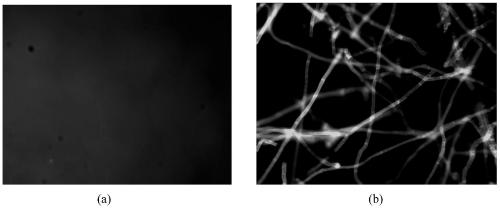
[0047] Select 5 small pieces of foot skin specimens with similar size, shape and weight, place them on glass slides, stain with reagents 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 respectively, and leave them at room temperature for staining. If the foot skin cannot be stained, the staining can be extended appropriately time, or increase the dyeing temperature to speed up the dyeing of the foot skin. A cover slip was added and observed under a fluorescent microscope. Activated with 340nm–400nm UV light, the fungus will appear blue or yellow-green. The results are shown in Table 1. The results show that reagents 3, 4, and 5 have the fastest staining speed, and fungi can be observed after 3 minutes of staining, while reagent 1 has the slowest staining speed, and only a small amount of fungi can be seen after 30 minutes of staining. It shows that the sensitivity of reagent 1 is not as high as that of reagents 2, 3, 4, and 5. Taking reagent 1 and re...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com