Molecular markers co-separated with bruchid resistance genes VrPGIP of vigna radiate and application of molecular markers
A technology of molecular markers and anti-weevil, which is applied in the fields of genetic engineering, molecular biology and genetic breeding, can solve the problems of weak research at the molecular level and lagging research on mung bean weevil, and achieve the effect of accurate cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Example 1 TC1966 / Zhonglv No. 1 F1 and F2 population construction and phenotypic identification
[0033] Using TC1966 as the male parent and Zhonglu No. 1 as the female parent, we prepared hybrids and constructed a segregation population of TC1966 / Zhonglu 1 containing 150 individuals. Each F2 individual The corresponding TC1966 / Zhonglv 1 F2:3 family was obtained by selfing, and the insect resistance was identified. The specific method is as follows:
[0034] 30 healthy seeds were randomly selected for each material, including 2 copies of Gandouxiang Zhonglu No. 1 and Kangdouxiang TC1966 control, placed in a plastic box in the Kangdouxiang identification room, the temperature was kept between 25°C and 29°C, and the humidity was low. Control it between 70%-80%. Put 400-500 mung bean weevil adults that have just emerged for 1-3 days in each plastic box, let it lay eggs at random, and remove the adults when the amount of eggs dropped by each seed is more than 5. After 40-...
Embodiment 2
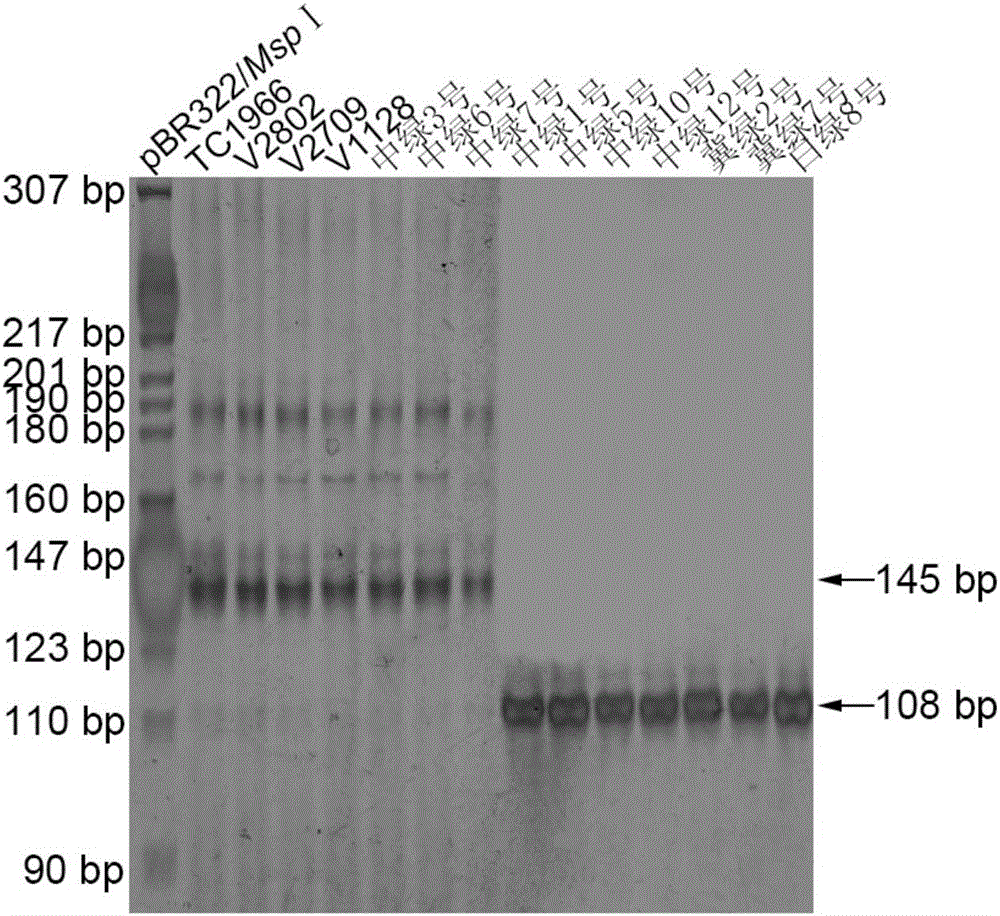
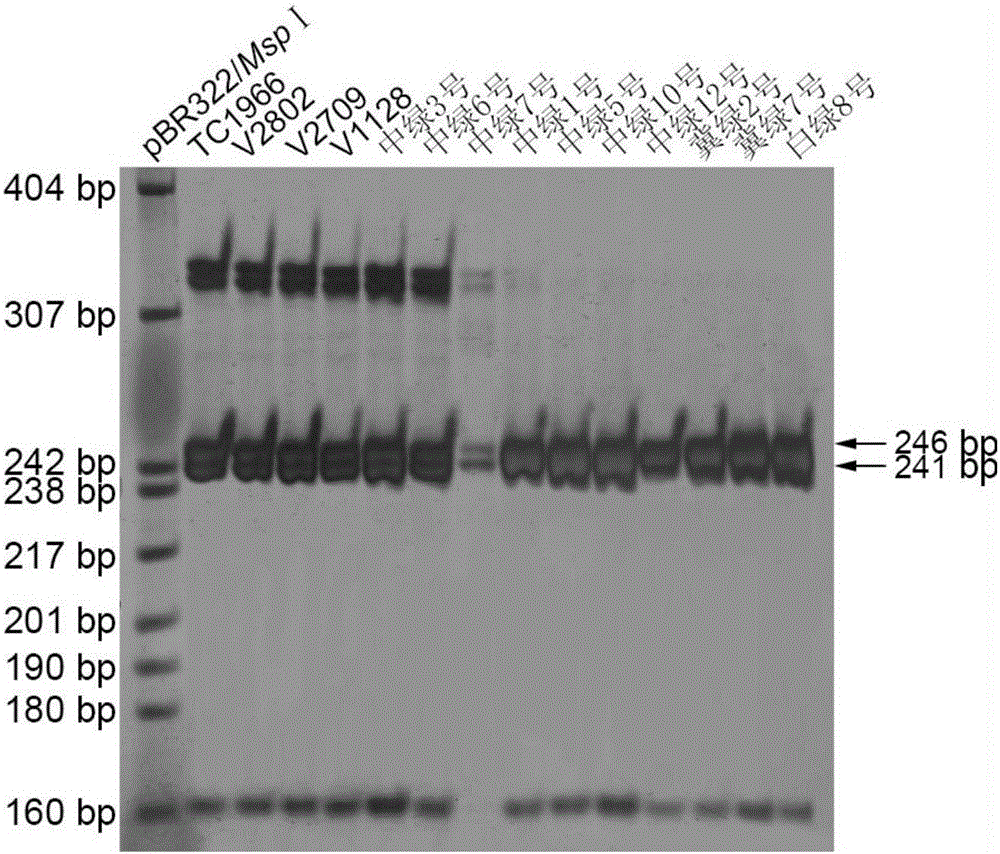
[0038] Example 2 Development of SSR Molecular Marker Linked to Mung Bean Anti-Elephant Gene VrPGIP
[0039] Acquisition of mung bean resistance gene VrPGIP: polymorphic SSR markers were screened out by using the F2 segregation population crossed by the resistant parent TC1966 and the sensitive parent Zhonglu 1 and the resistant and sensitive pools. The anti-weevil gene was preliminarily located on Chromosome No. 5 of mung bean. According to the mung bean genome sequence published by NCBI (GenBank accession number: JJMO00000000), primers were designed with the software Primer3.0, and a total of 3143 pairs of SSR primers were generated on chromosome 5 of mung bean. The DNA of mung bean leaves was extracted, and the success rate of primers was tested. The results showed that a total of 1254 pairs of SSR primers detected clear bands at 100-300 bp, indicating that the success rate of primer design was high.
Embodiment 3
[0040] Example 3 Fine Mapping of Mung Bean Anti-Elephant Gene VrPGIP
[0041] The DNA of each strain of the parent and F2 population was extracted by the improved CTAB method, the concentration was measured by a UV spectrophotometer, and then diluted to 25 ng / μL, and stored in a -20°C refrigerator for later use.
[0042] Referring to the method of Chen et al. (2015), the mung bean genomic DNA was used as a template for PCR reaction. 10μl PCR reaction system includes: 40ng DNA, 1×Taq enzyme buffer (10mmolL -1 Tris-HCl, pH8.8; 10mmol L -1 KCl; 10 mmol L -1 (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 ; 1.5mmolL -1 MgCl 2 ; 0.1% Triton X-100), 1 mmol L -1 dNTPs, 0.25 μmol L each for upstream and downstream primers -1 and 1U Taq DNA polymerase, ddH 2 O to make up to 10 μl. Reaction program: pre-denaturation at 95°C for 5min; denaturation at 95°C for 30s, annealing at 55°C for 45s, extension at 72°C for 45s, 32-35 cycles; final extension at 72°C for 5min. The whole reaction was carried out on Dongsh...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com