A Simulation Test Method for Landslide Disaster in Soft Soil Layer
A technology for simulating experiments and disasters, applied in the field of geotechnical engineering, it can solve problems such as the inability to understand the law of influence, the complexity of the device structure, and the inability to analyze
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 2
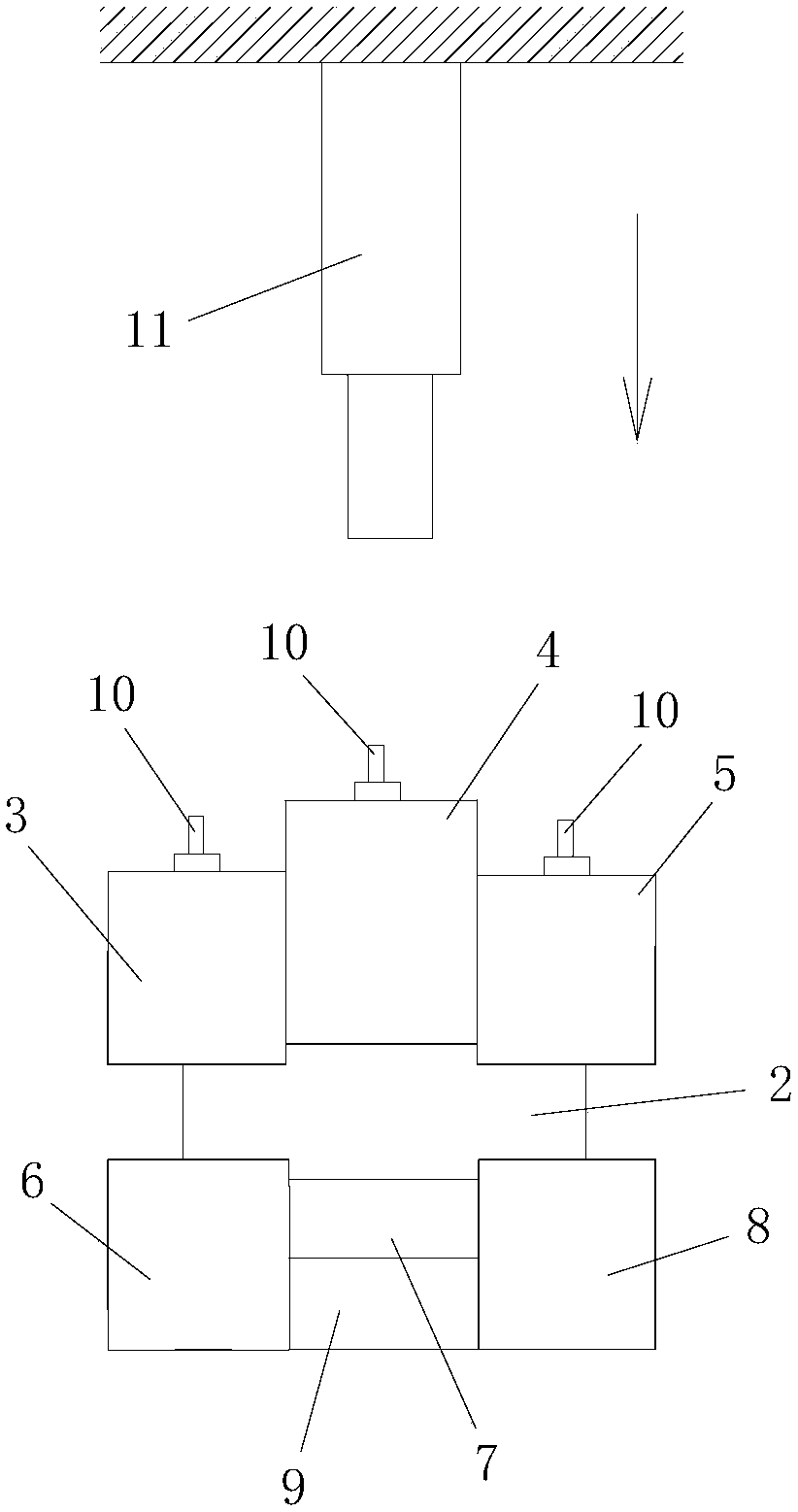
[0200] Such as Figure 5 As shown, in this embodiment, the difference from Embodiment 1 is that the shearing jig in step 201 further includes a limiting sleeve 12 fitted on the upper jig and outside the lower jig.
[0201] In this embodiment, the remaining method steps are the same as those in Embodiment 1.
Embodiment 3
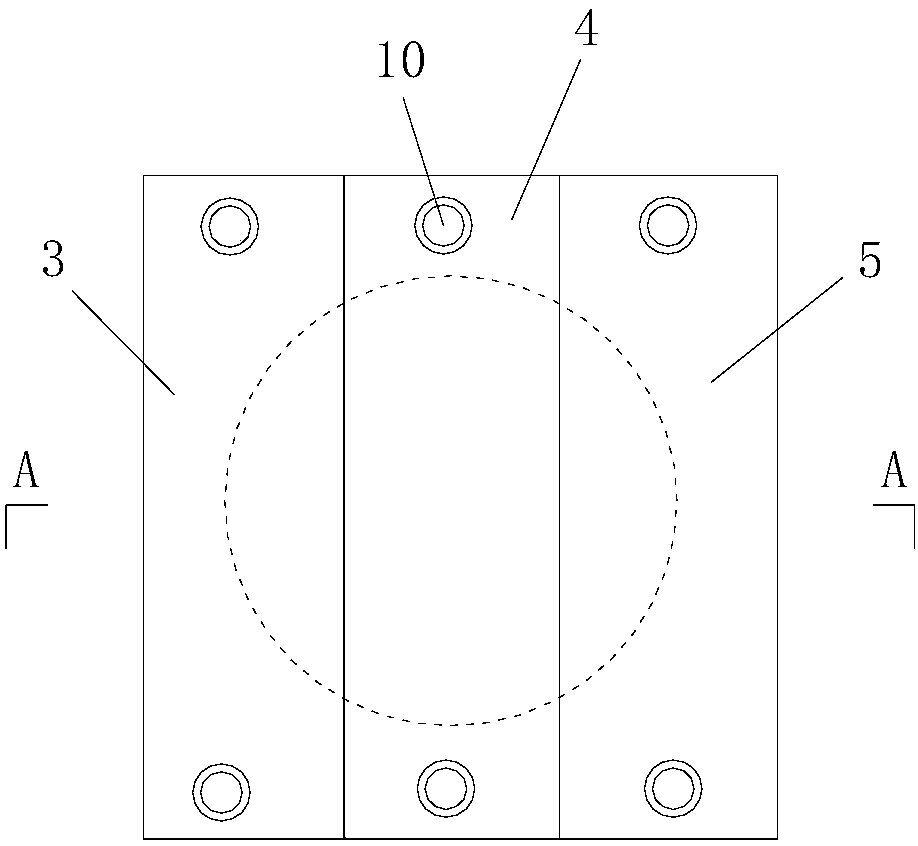
[0203] Such as Figure 6 , Figure 7 As shown, in this embodiment, the difference from Embodiment 1 is that the widths of the upper clamp and the lower clamp in step 201 are the same as the inner diameter of the earth taking ring cutter 2; the middle and lower clamping blocks only include Upper clamping block 7; the length, width and height of the upper left clamping block 3, the upper right clamping block 5, the lower left clamping block 6 and the lower right clamping block 8 are all the same, and the middle and upper clamping blocks 4 and The width and height of upper clamping block 7 are all identical with left upper clamping block 3, and the length of described middle upper clamping block 4 and upper clamping block 7 is identical and the length of both is greater than the length of left upper clamping block 3.
[0204] During actual processing, the lengths of the upper left clamping block 3, the upper right clamping block 5, the upper middle clamping block 4, the lower le...
Embodiment 4
[0212] In this example, the difference from Example 1 is that the curing solution described in step 203 is uniformly composed of epoxy resin, acetone, ethylenediamine and dibutyl phthalate in a volume ratio of 100:170:6:2.2 mixed.
[0213] In this embodiment, the remaining method steps are the same as those in Embodiment 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com