Patents
Literature
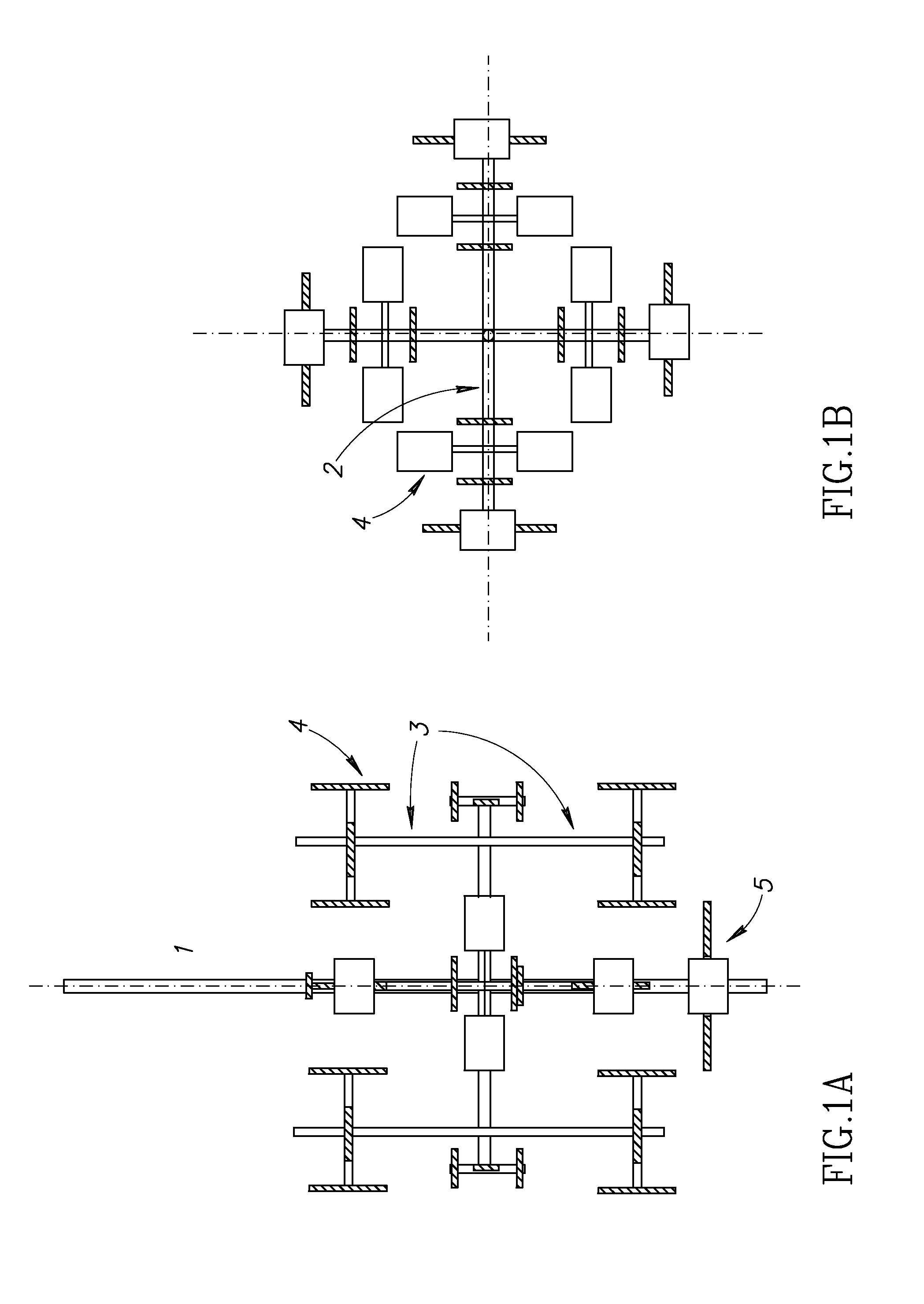
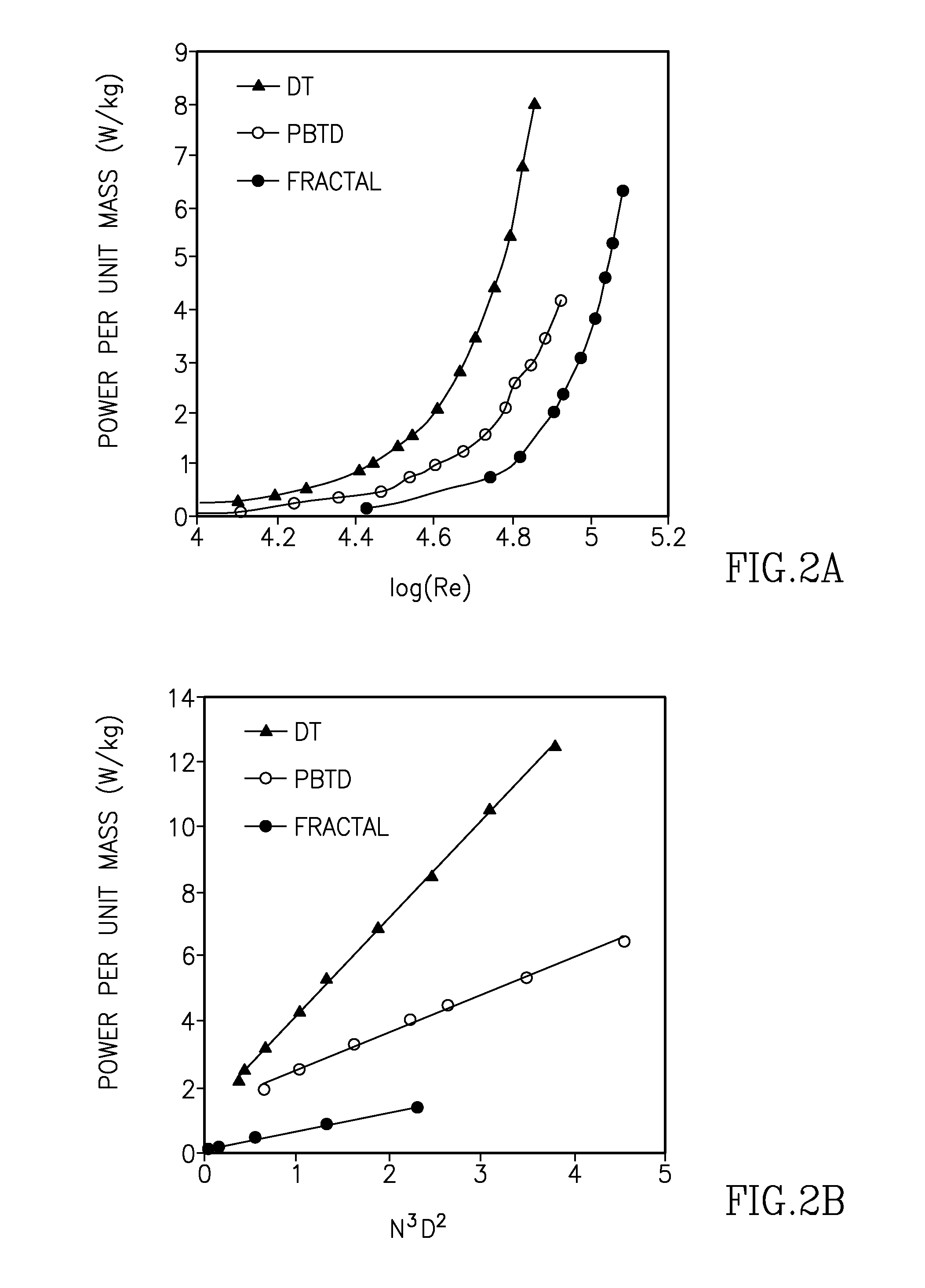
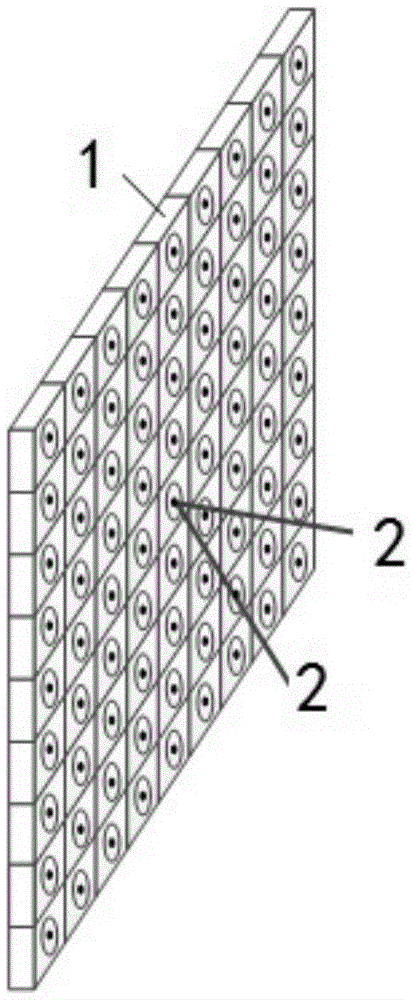
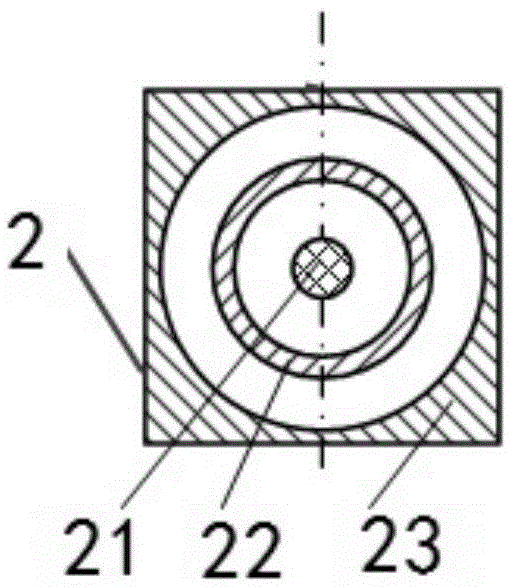
123 results about "Shear zone" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A shear zone is a very important structural discontinuity surface in the Earth's crust and upper mantle. It forms as a response to inhomogeneous deformation partitioning strain into planar or curviplanar high-strain zones. Intervening (crustal) blocks stay relatively unaffected by the deformation. Due to the shearing motion of the surrounding more rigid medium, a rotational, non co-axial component can be induced in the shear zone. Because the discontinuity surface usually passes through a wide depth-range, a great variety of different rock types with their characteristic structures are produced.
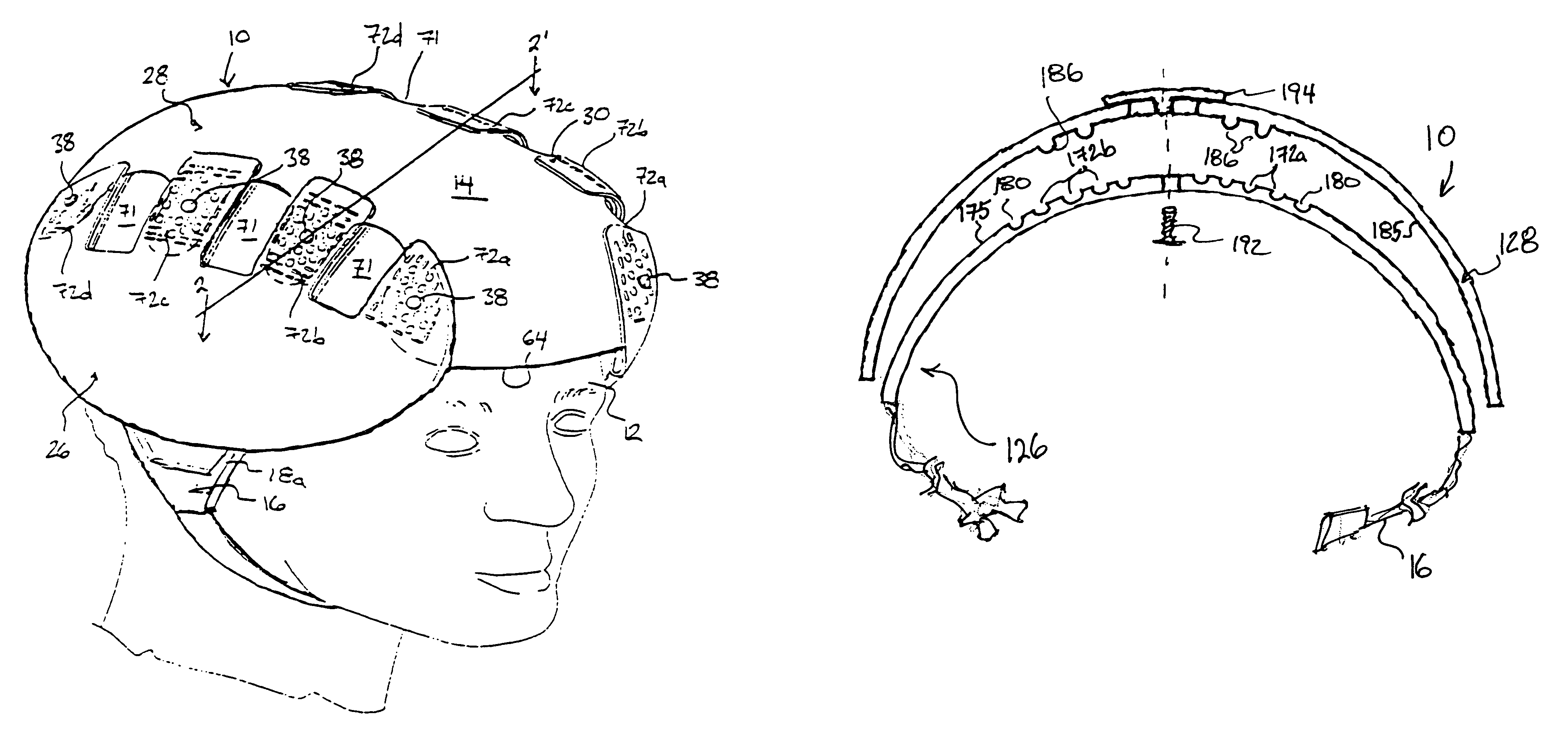
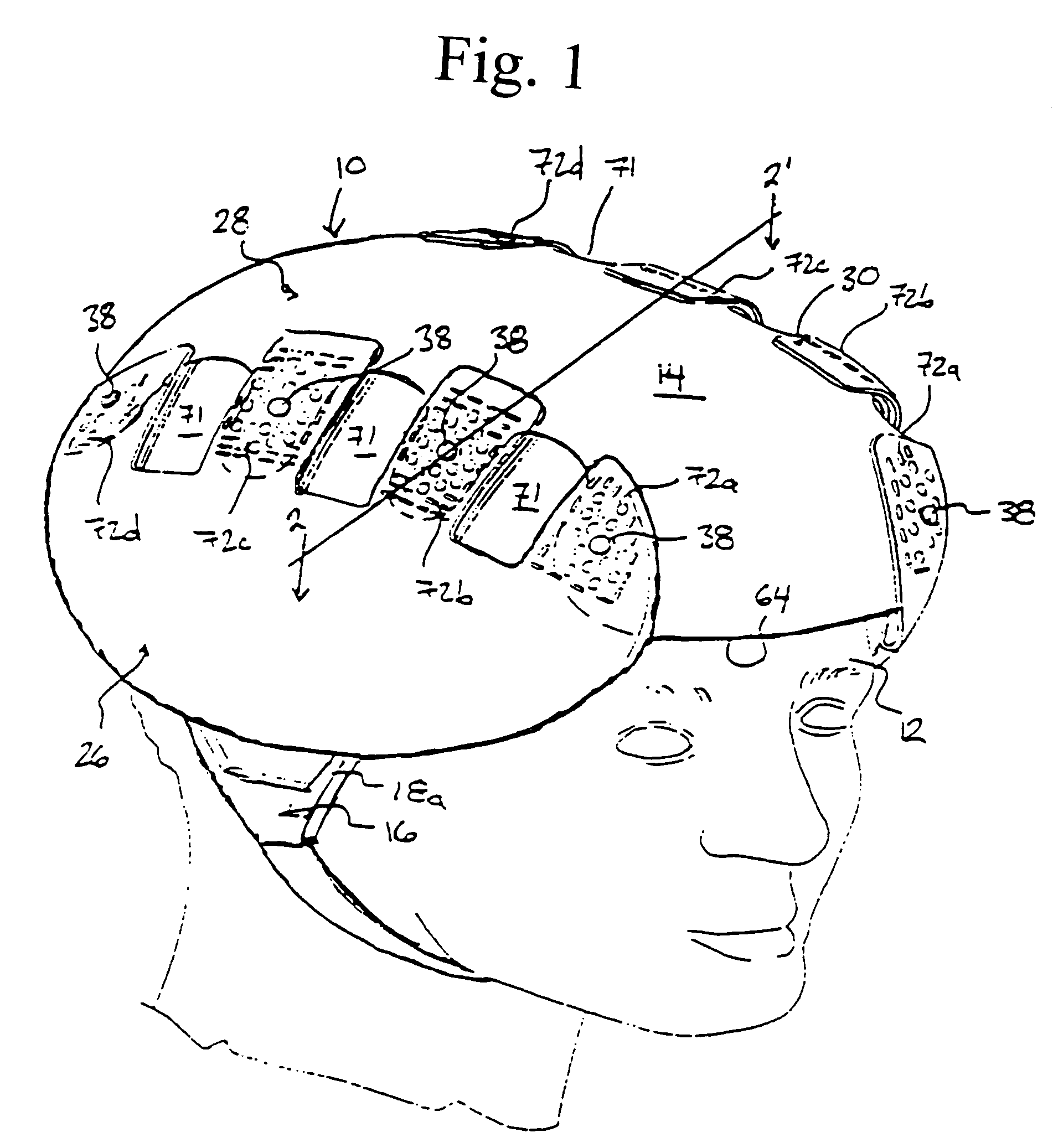
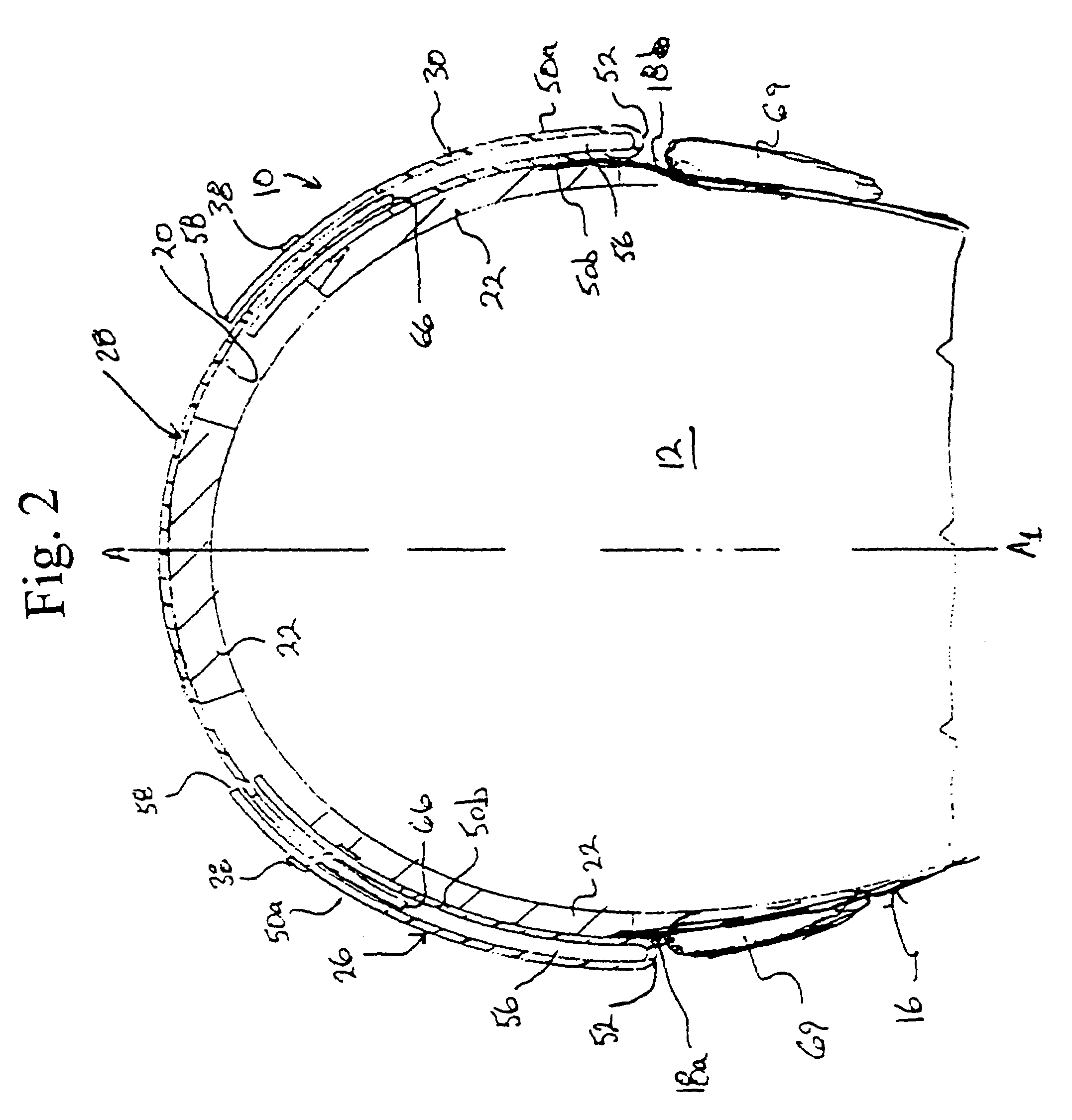
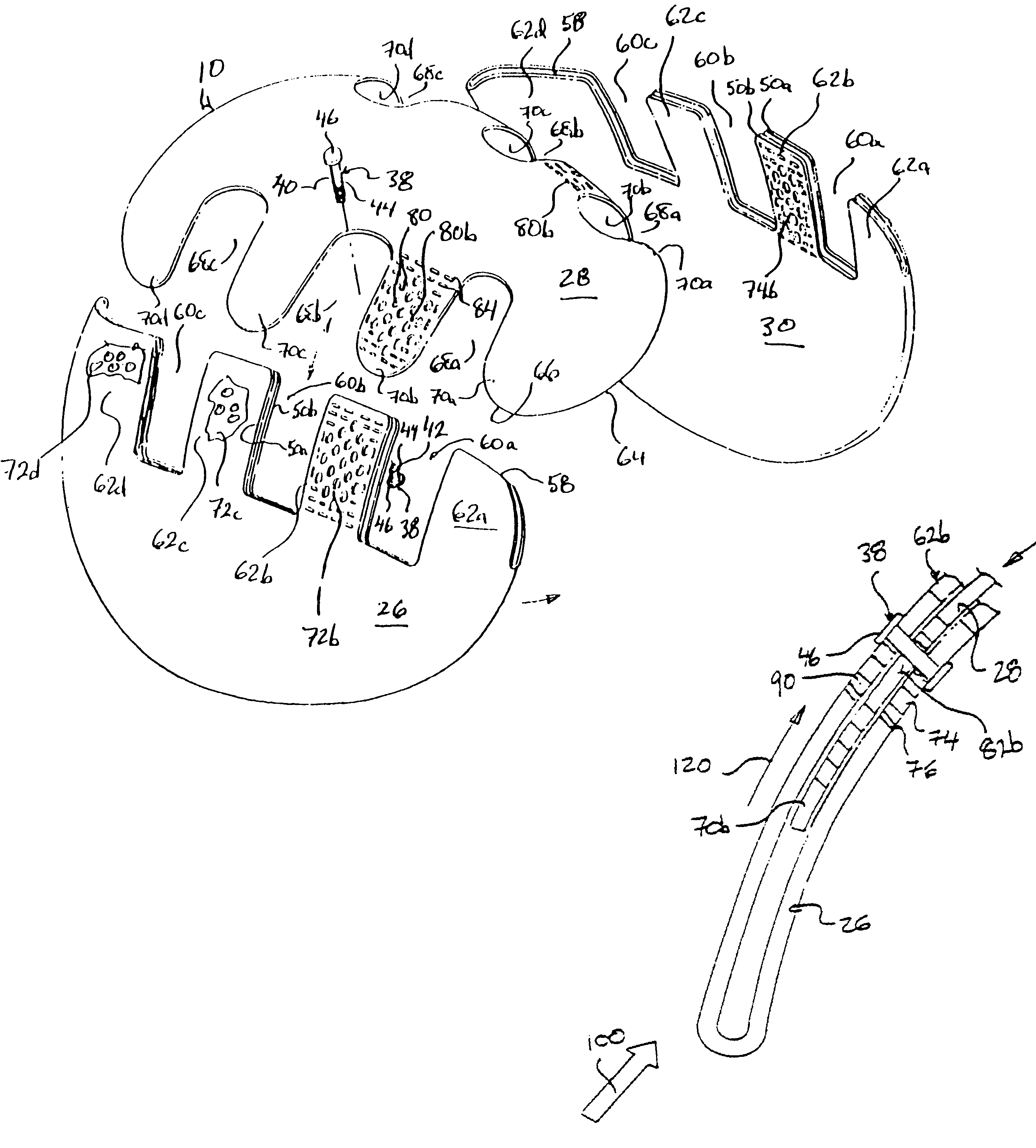
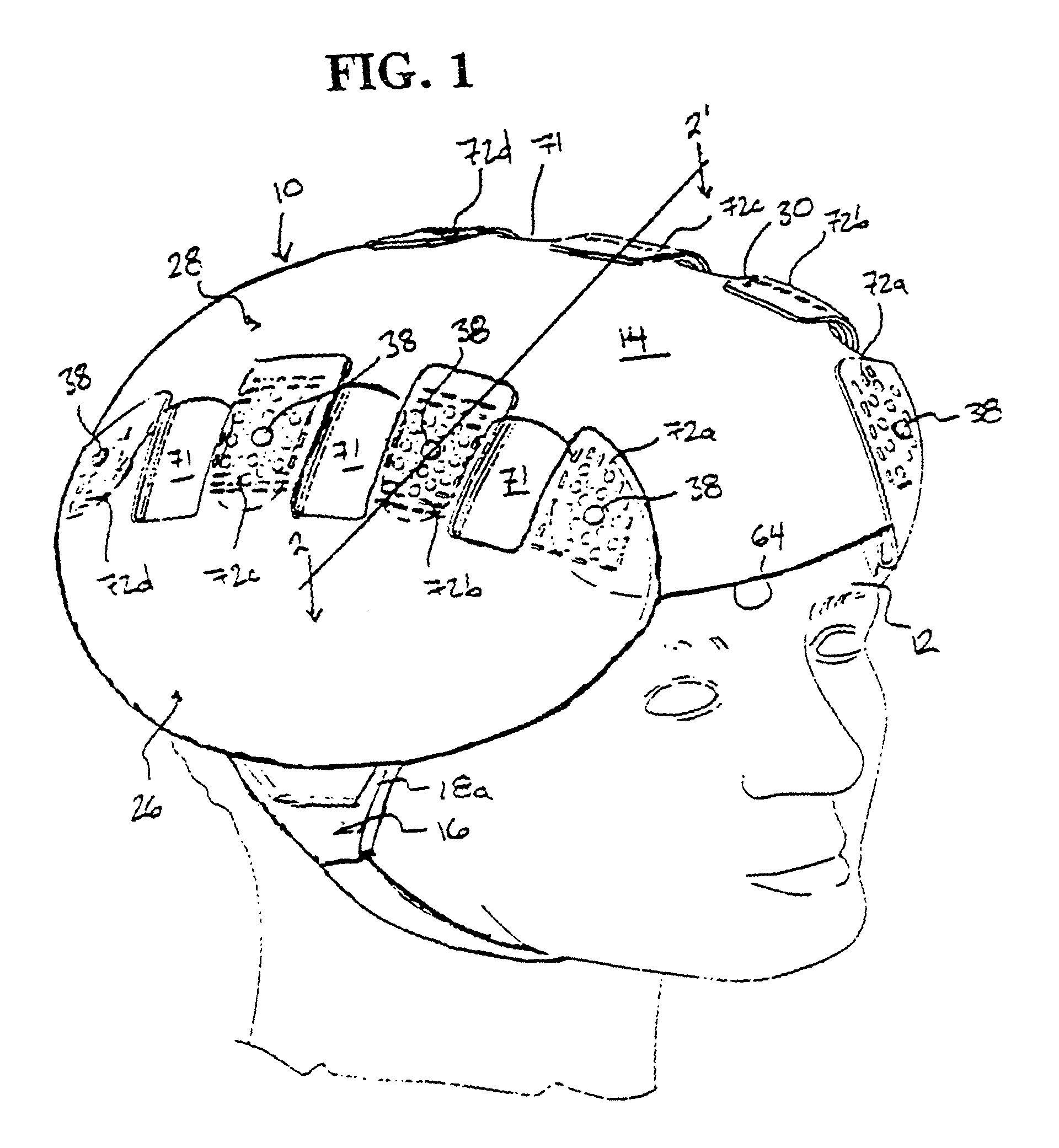
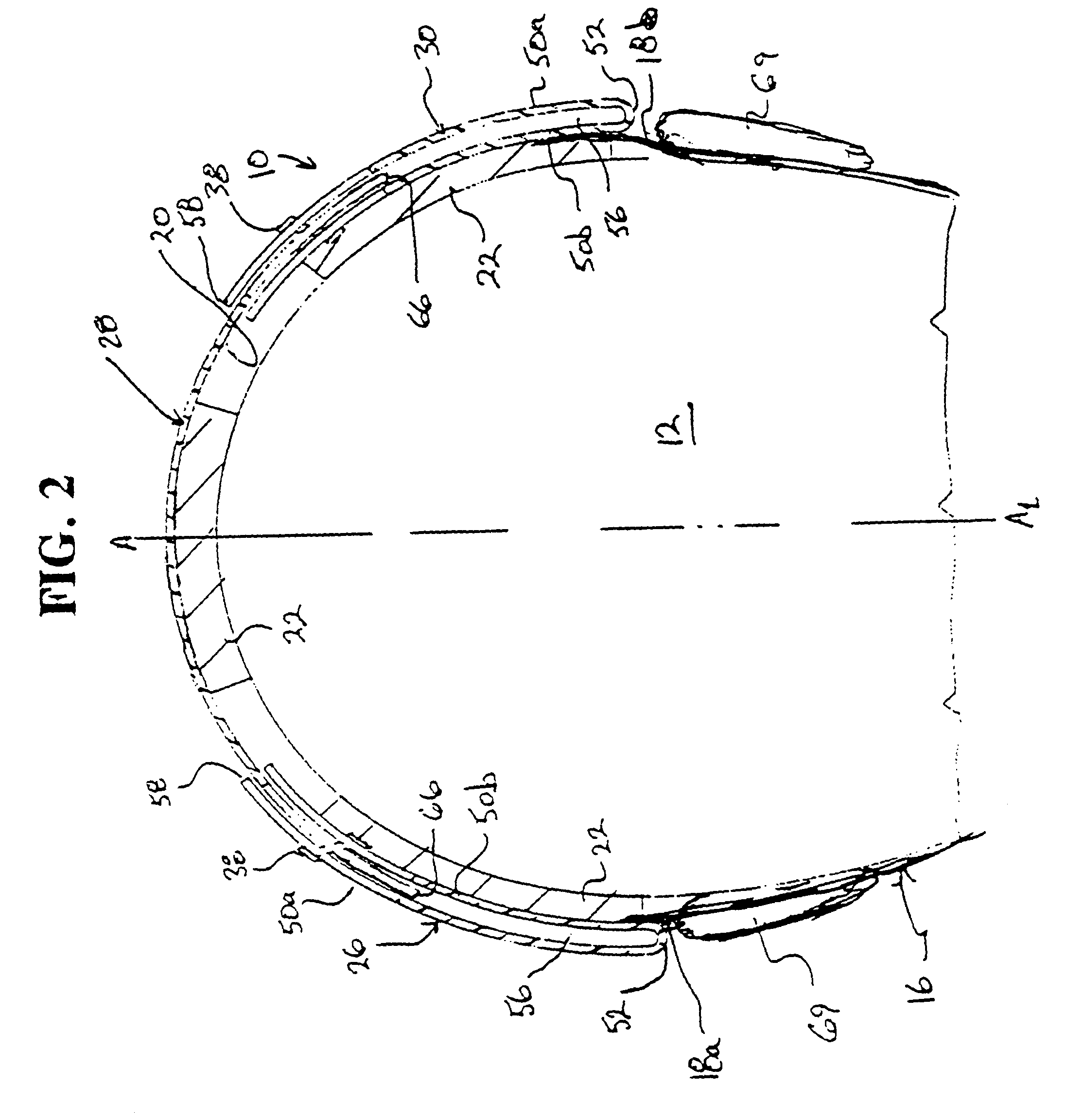
Protective head covering having impact absorbing crumple zone
InactiveUS6996856B2Closer in weight and sizeMinimizing resultant disproportionHatsSport apparatusMostly TrueEngineering
A helmet construction for protecting a user's head, and the brain within the cranium from impact forces, includes a shell contoured to the shape of the user's head, with cushioning along at least part of the shell interior and a chinstrap. The shell consists of three (or more) discrete panels that are physically and firmly coupled together providing rigid protection under most circumstances, but upon impact the panels move relative to one another, but not relative to the user's head, thereby permitting impact forces to be dissipated and / or redirected away from the cranium and brain within. Upon impact to the helmet, there are sequential stages of movement of the panels relative to each other, these movements initially being recoverable, but with sufficient vector forces the helmet undergoes structural changes in a pre-determined fashion, so that the recoverable and permanent movements cumulatively provide a protective ‘crumple zone’ or ‘shear zone’. The first two stages of protection arise from the design of the fasteners that have the ability to invaginate and collapse within themselves, and their design having a 45 degree angle, which will allow movement of a region of connected panels to translate along the fastener shaft. Both of these movements will be recoverable and provide a ‘functional crumple zone’. The final stage of protection arises from the braking function of the pins, as they are forced from one aperture through to the next, the direction and extent of which is determined by the impact force and direction. This final level of panel movement and protection is not recoverable and thus provides a ‘structural crumple zone’. Finally the fastener size and thickness, together with the thickness of webbing and distance between apertures, functions to provide varying degrees of resistance to impact forces, thus making the helmet design suitable for activities with different levels of impact speed and risk potential.
Owner:PUCHALSKI TECHN
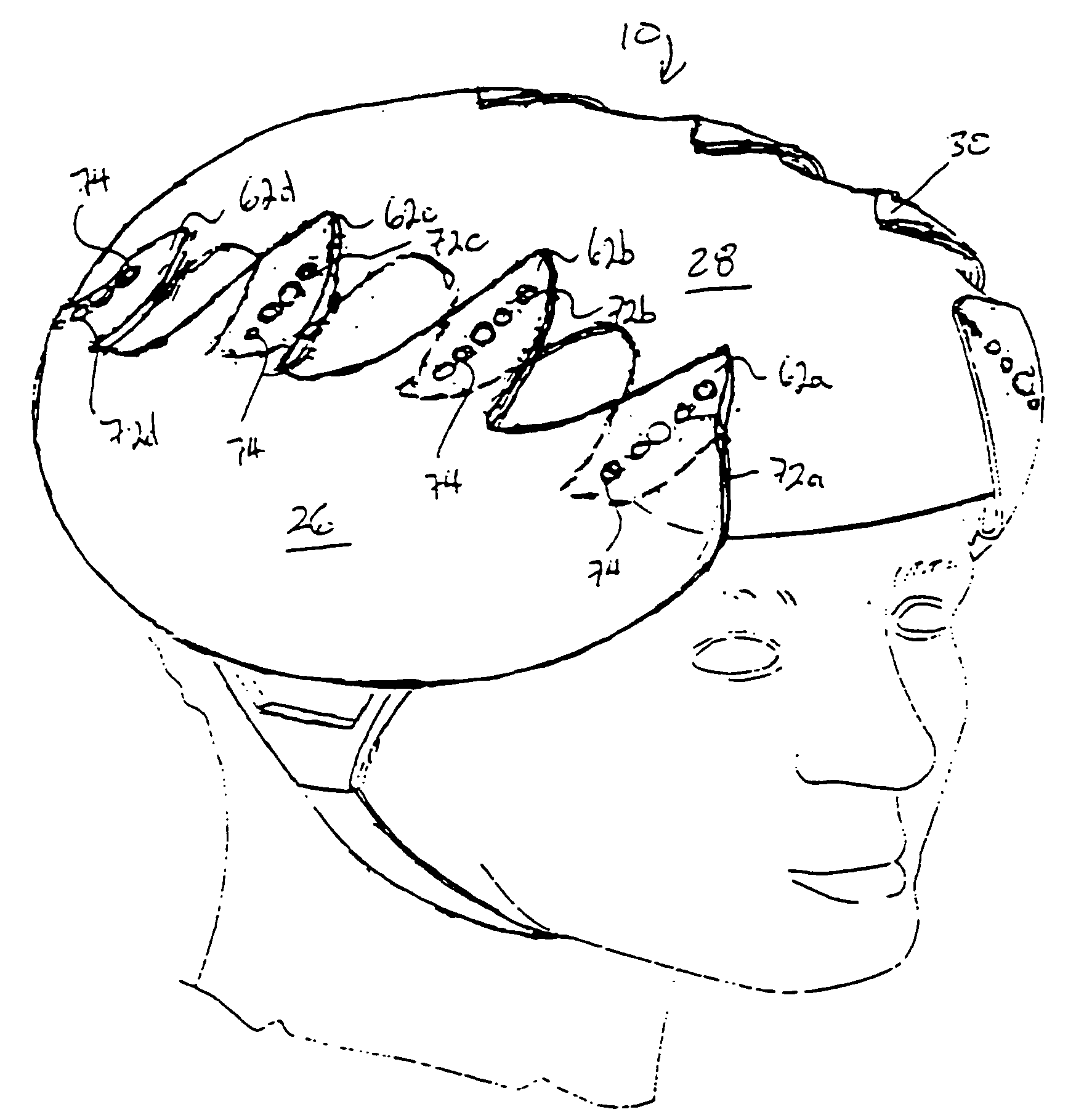
Protective head covering having impact absorbing crumple or shear zone
A helmet construction for protecting a user's head, and the brain within the cranium from impact forces, includes a shell contoured to the shape of the user's head, with cushioning along at least part of the shell interior and a chinstrap. The shell consists of three (or more) discrete panels that are physically and firmly coupled together providing rigid protection under most circumstances, but upon impact the panels move relative to one another, but not relative to the user's head, thereby permitting impact forces to be dissipated and / or redirected away from the cranium and brain within. Upon impact to the helmet, there are sequential stages of movement of the panels relative to each other, these movements initially being recoverable, but with sufficient vector forces the helmet undergoes structural changes in a pre-determined fashion, so that the recoverable and permanent movements cumulatively provide a protective ‘crumple zone’ or ‘shear zone’. The first two stages of protection arise from the design of the fasteners that have the ability to invaginate and collapse within themselves, and their design having a 45 degree angle, which will allow movement of a region of connected panels to translate along the fastener shaft. Both of these movements will be recoverable and provide a ‘functional crumple zone’. The final stage of protection arises from the braking function of the pins, as they are forced from one aperture through to the next, the direction and extent of which is determined by the impact force and direction. This final level of panel movement and protection is not recoverable and thus provides a ‘structural crumple zone’. Finally the fastener size and thickness, together with the thickness of webbing and distance between apertures, functions to provide varying degrees of resistance to impact forces, thus making the helmet design suitable for activities with different levels of impact speed and risk potential.
Owner:PUCHALSKI TECHN
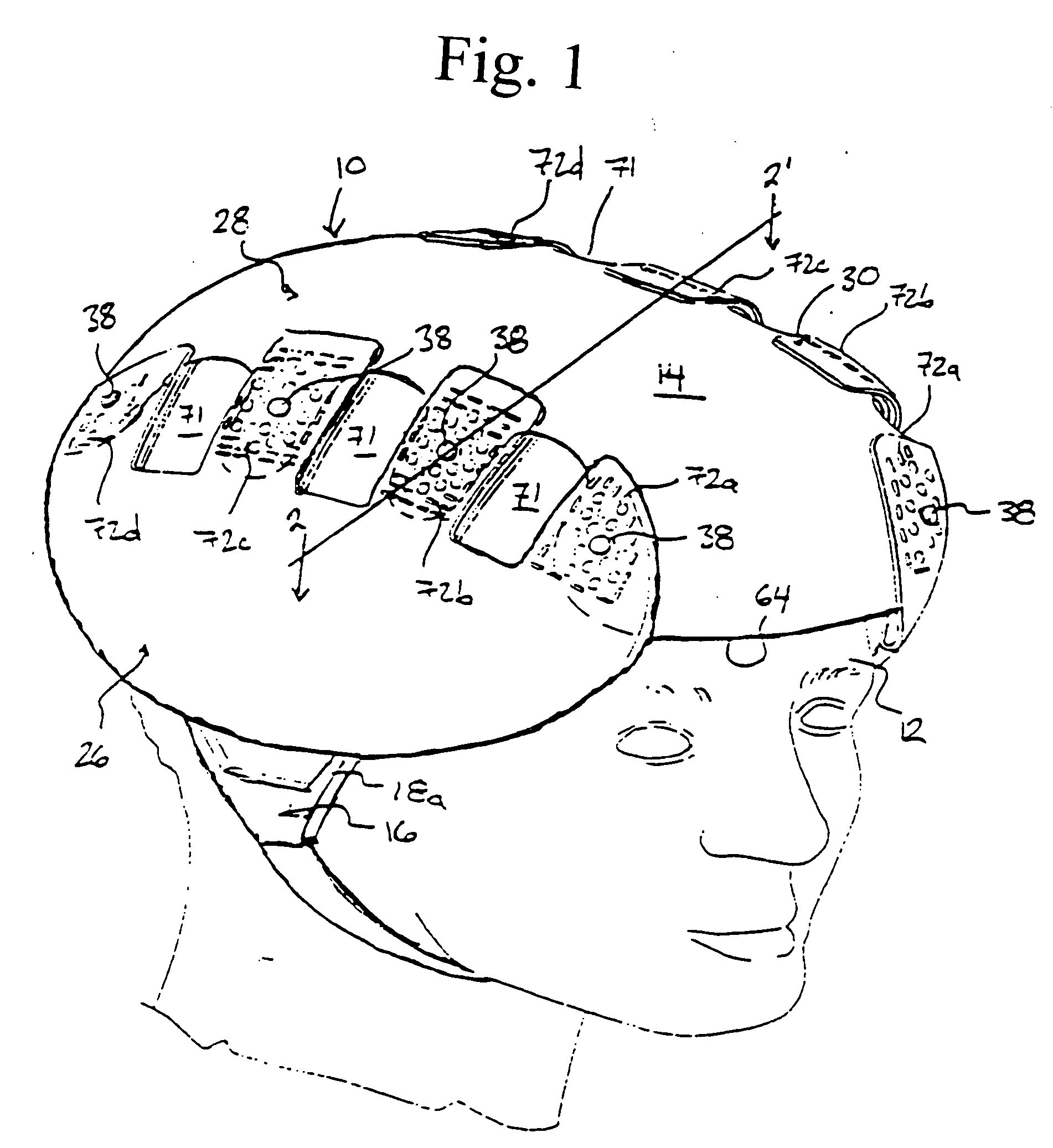
Protective head covering having impact absorbing crumple zone
InactiveUS20050257312A1Closer in weight and sizeMinimizing resultant disproportionHatsSport apparatusMostly TrueEngineering
A helmet construction for protecting a user's head, and the brain within the cranium from impact forces, includes a shell contoured to the shape of the user's head, with cushioning along at least part of the shell interior and a chinstrap. The shell consists of three (or more) discrete panels that are physically and firmly coupled together providing rigid protection under most circumstances, but upon impact the panels move relative to one another, but not relative to the user's head, thereby permitting impact forces to be dissipated and / or redirected away from the cranium and brain within. Upon impact to the helmet, there are sequential stages of movement of the panels relative to each other, these movements initially being recoverable, but with sufficient vector forces the helmet undergoes structural changes in a pre-determined fashion, so that the recoverable and permanent movements cumulatively provide a protective ‘crumple zone’ or ‘shear zone’. The first two stages of protection arise from the design of the fasteners that have the ability to invaginate and collapse within themselves, and their design having a 45 degree angle, which will allow movement of a region of connected panels to translate along the fastener shaft. Both of these movements will be recoverable and provide a ‘functional crumple zone’. The final stage of protection arises from the braking function of the pins, as they are forced from one aperture through to the next, the direction and extent of which is determined by the impact force and direction. This final level of panel movement and protection is not recoverable and thus provides a ‘structural crumple zone’. Finally the fastener size and thickness, together with the thickness of webbing and distance between apertures, functions to provide varying degrees of resistance to impact forces, thus making the helmet design suitable for activities with different levels of impact speed and risk potential.
Owner:PUCHALSKI TECHN
Cutting tool retainer
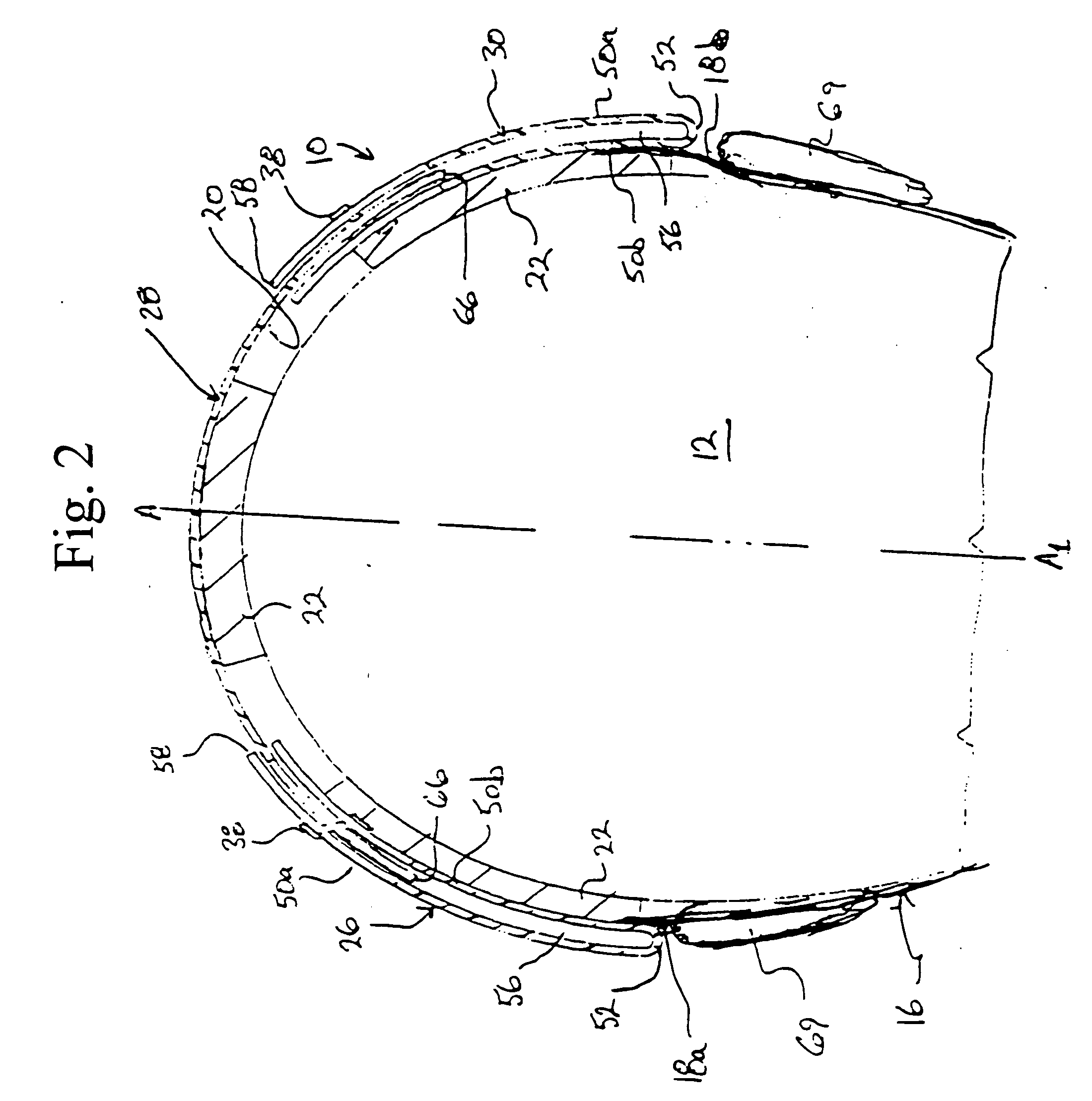
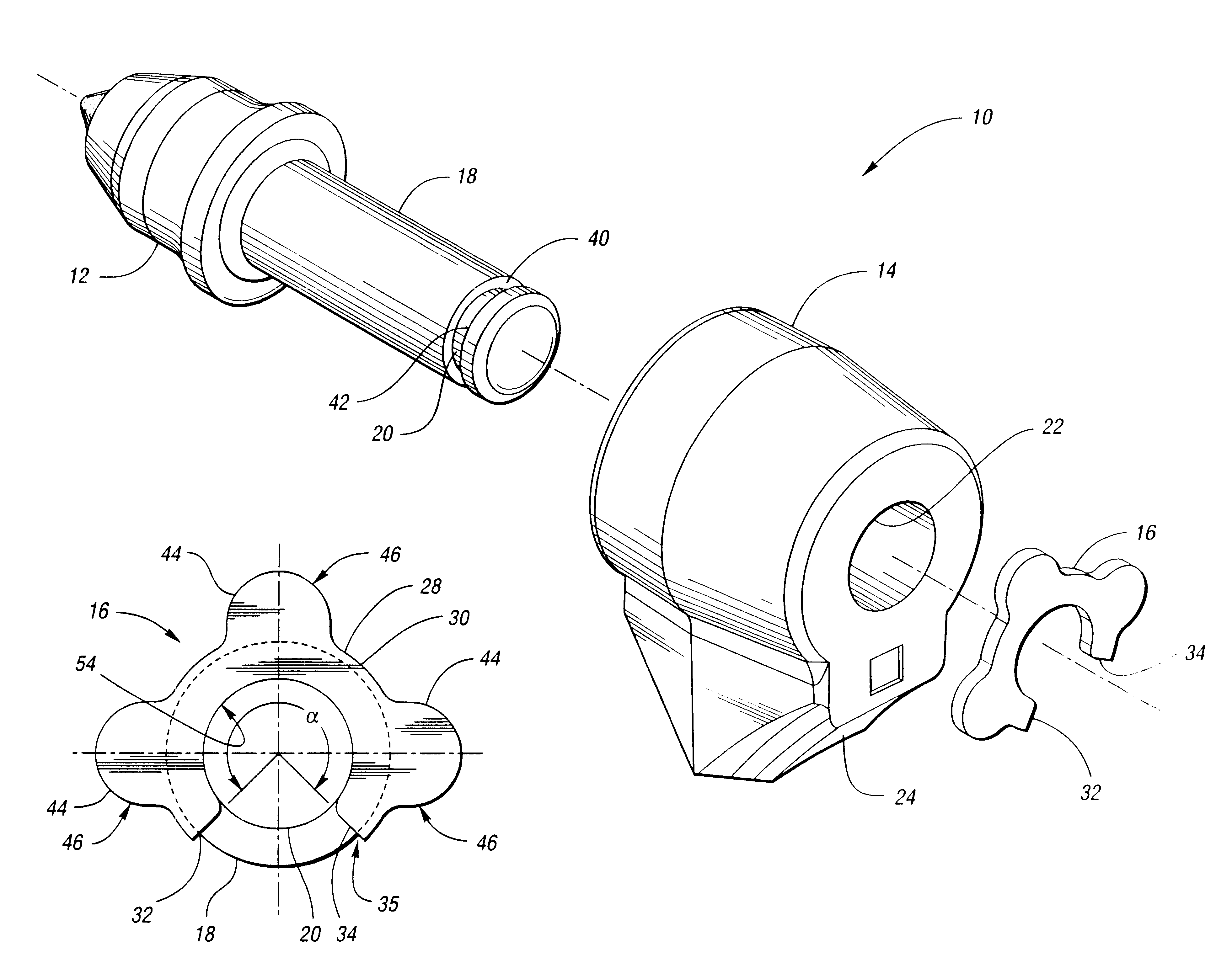
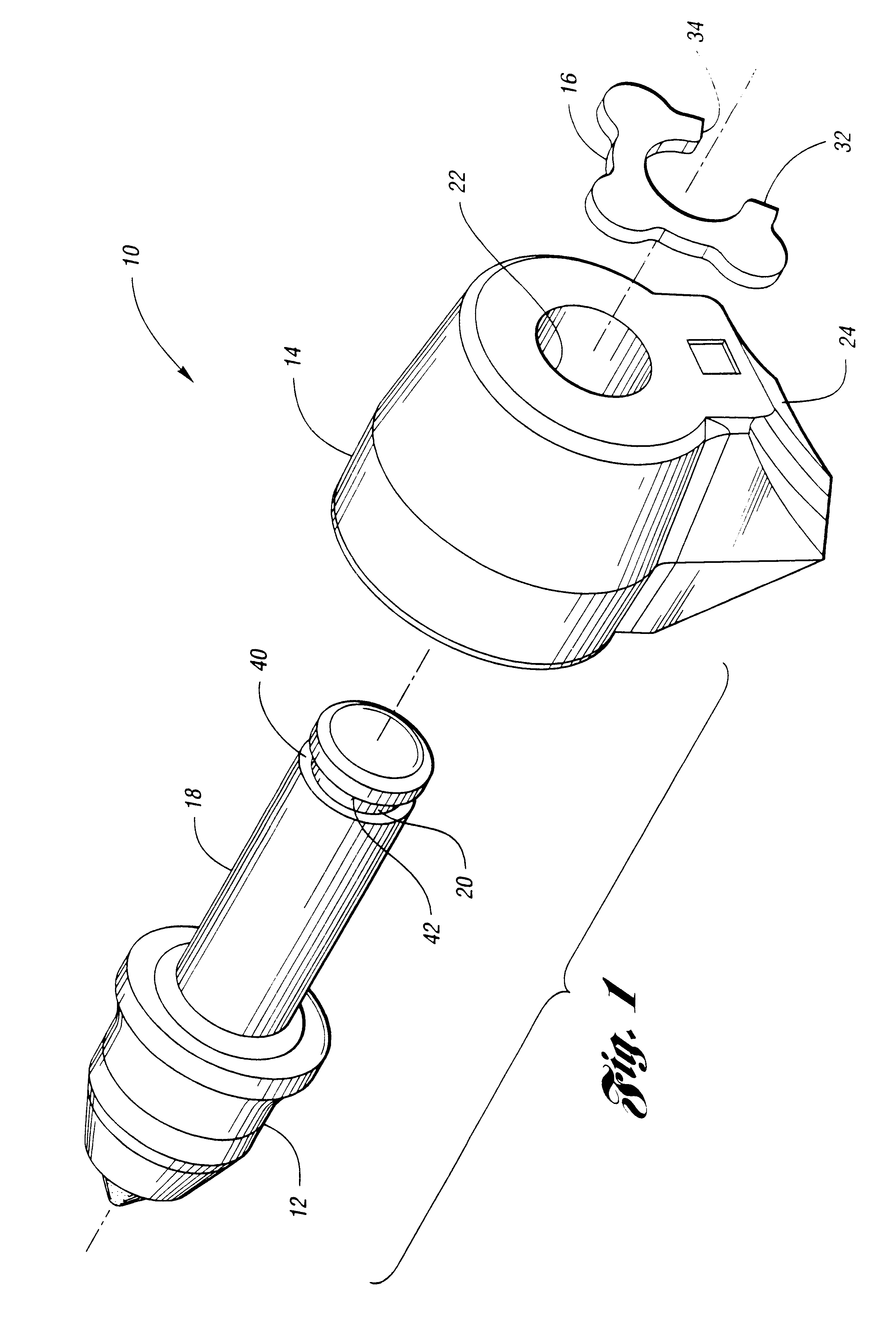
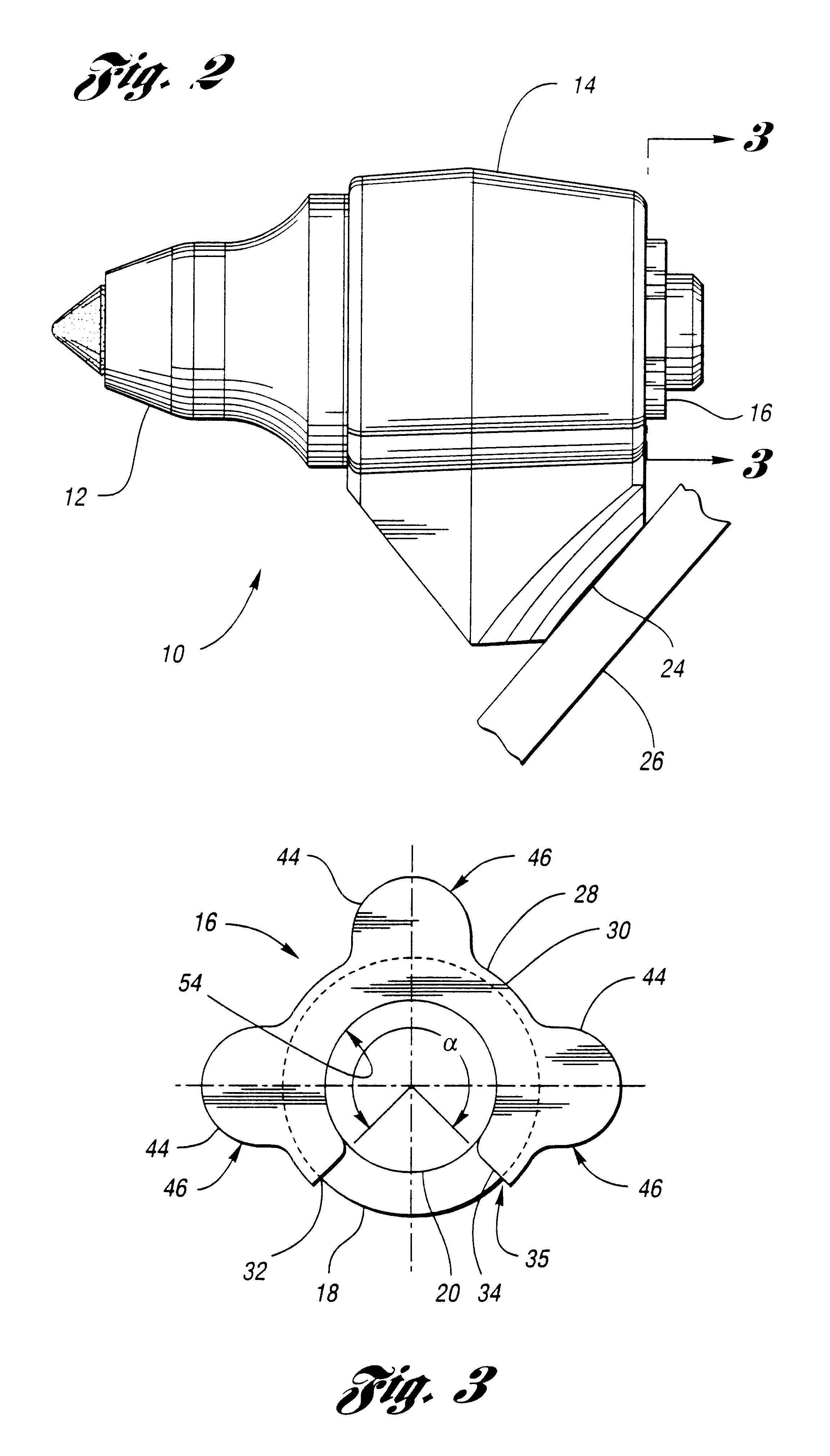
InactiveUS6428110B1Smooth connectionHigh strengthSnap fastenersSlitting machinesMechanical engineeringShear zone
A retainer, adapted to engage a recess in a cutting tool for securing the cutting tool to a support block, includes a retainer body having a main portion with first and second ends. The main portion defines a continuous shear zone having first and second ends. The retainer body further includes a protruding portion disposed between the ends of the continuous shear zone and spaced away from the ends of the main portion. The protruding portion extends radially from the main portion and is adapted to overlap the support block when the retainer is engaging the recess.
Owner:KENNAMETAL INC
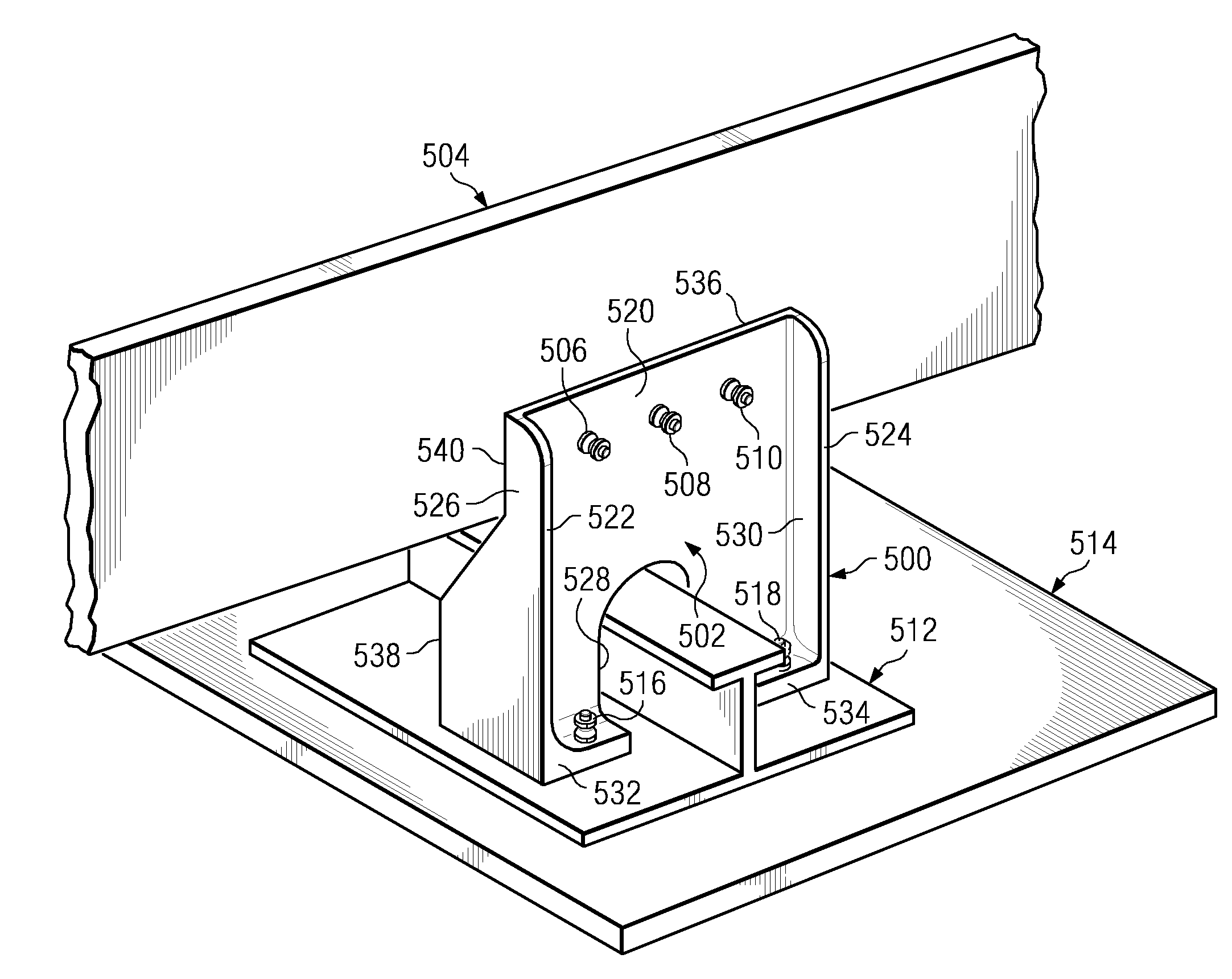
Composite shear tie
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Forming method for composites
ActiveUS8142181B2Minimizes the shear zoneReducing or eliminating out-of-plane fiber bucklingLayered productsConfectioneryFiberComposite laminates
A method for forming composite materials is presented, including providing a composite charge wider than a first surface of a mandrel, and positioning the composite charge across the first surface of the mandrel. The portion of the composite charge overhanging the first surface of the mandrel is supported and urged against the mandrel while supporting the unbent portion of the composite charge substantially parallel to the first surface of the mandrel. The invention also provides a system, using a compression mold of forming bladders and heater plates, to form a composite charge over a mandrel, while supporting the unbent portions of the composite charge during forming substantially parallel to the upper surface of the mandrel. The present invention minimizes the shear zone where plies in the composite laminate charge slide past one another during the forming process reducing or eliminating out-of-plane fiber buckling.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Composite shear tie
A composite shear tie for connecting a rib in a wing of an aircraft to a skin panel. The shear tie includes a web section having a first edge, a second edge, and a third edge. The web section is formed from a composite material. The first edge is parallel to the second edge, and the web section is configured to be connected to the rib in the wing of the aircraft. The shear tie also has a first free flange extending from the first edge, wherein the first free flange is around perpendicular to the web section and wherein the first free flange is formed from the composite material. A second free flange is present in the shear tie in which the second free flange extends from the second edge, wherein the second free flange is around perpendicular to the web section and wherein the second free flange is formed from the composite material. The shear tie has a base flange section extending from the third edge, wherein the first base flange is configured for attachment to the skin panel and wherein the first base flange is formed from the composite material.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Continuous casting method of liquid-phase composite slab
The invention provides a continuous casting method of a liquid-phase composite slab. A continuous casting device comprises a composite casting system, a roll type crystallizer, a pinch and bending device, a withdrawing-straightening device, a shearing device and a dummy bar system. A base material metal pouring ladle and a composite material metal pouring ladle pour metal solution into a roll type crystallizer molten pool formed by crystallizing rolls and side seal plates via submerged nozzles. An intermediate diaphragm separates the molten pool into a base material dissolved cavity and a composite material dissolved cavity. The base material metal solution and the composite material metal solution are respectively solidified into slab shells on the crystallizing rolls, the crystallizing rolls synchronously rotate in the reverse direction and the metal slab shells move downward along with rotation of the crystallizing rolls. The base material metal liquid interacts with the composite material metal solid-liquid interface to realize metallurgical fusion and composition of the interface, and is bonded into the composite slab at the exit of the roll crystallizer. The composite casting slab is transferred by pinch rolls and bent into arc by a bending roll, and then enters the withdrawing-straightening section through a guide roll to be horizontally straightened. The composite casting slab keeps on moving forward to the roll way in a shear zone to be cut to length by swinging shears and then is moved out.
Owner:CHINA FIRST HEAVY IND +1
Method for quantitatively measuring inhomogeneous deformation of nano-crystal material
InactiveCN101526453ALow costMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesUsing optical meansStress–strain curveEngineering
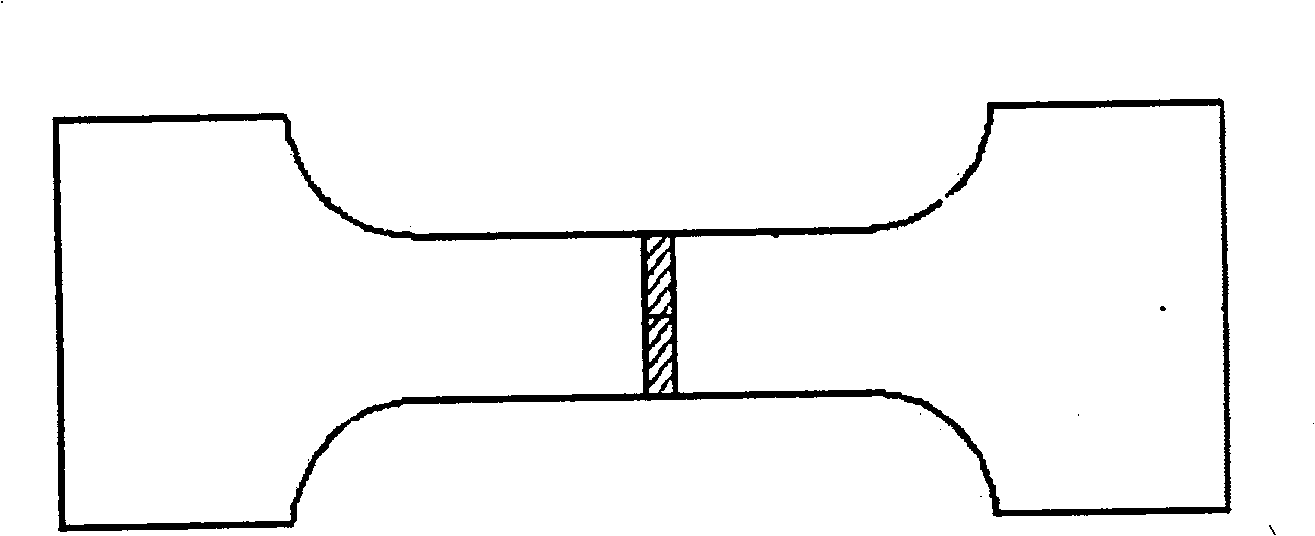
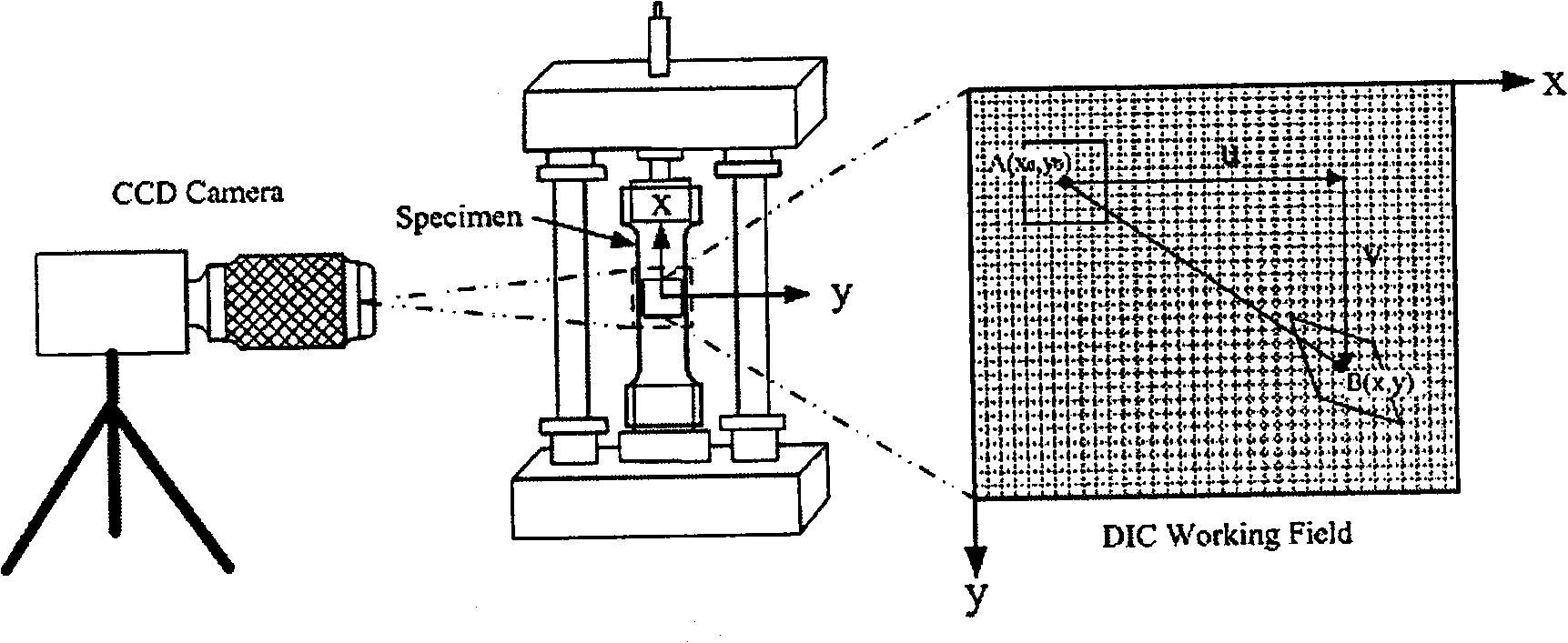
The invention relates to a method for quantitatively measuring the inhomogeneous deformation of a nano-crystal material. The method comprises the following steps: firstly processing the measured nano-crystal material into a stretching sample, selecting a marking area on the stretching sample and marking the stretching sample; secondly, putting the stretching sample into a mechanics testing machine, and loading the stretching sample under the condition that the quasistatic strain rate of a displacement control mode at room temperature is 10<-4>s<-1>; obtaining data and displaying a stress strain curve by a material testing system of the mechanics testing machine, adopting a digital camera to acquire the image on the surface of the sample at the same time of loading, and recording the image by connecting the digital camera with a computer; and finally, carrying out digital image processing on the image acquired by the digital camera in the process of stretching to obtain the surface displacement and a stain field image of the tested image in the process of stretching. The method measures the cause of formation of a shear zone in a simple mode with low cost, so the method can have wide application prospect in the fields of modern mechanics, microelectronic technology, ultraprecise processing technology, nanometer technology, and the like.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Fractal impeller for stirring
InactiveUS20130208560A1Well mixedReduce shearRotary stirring mixersTransportation and packagingImpellerMain branch
A fractal impeller design for stirred tank reactors comprising plurality of main branches, each of which further having plurality of sub-branches with each sub branch having plurality of blades to distribute / dissipate energy in uniform manner and to achieve uniform temperature throughout the reactor while operating it at lower impeller speed to avoid high shear zones; wherein, the angular distances covered by the blades vary and yield variation in the local blade passage velocity for a given impeller rotation speed.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
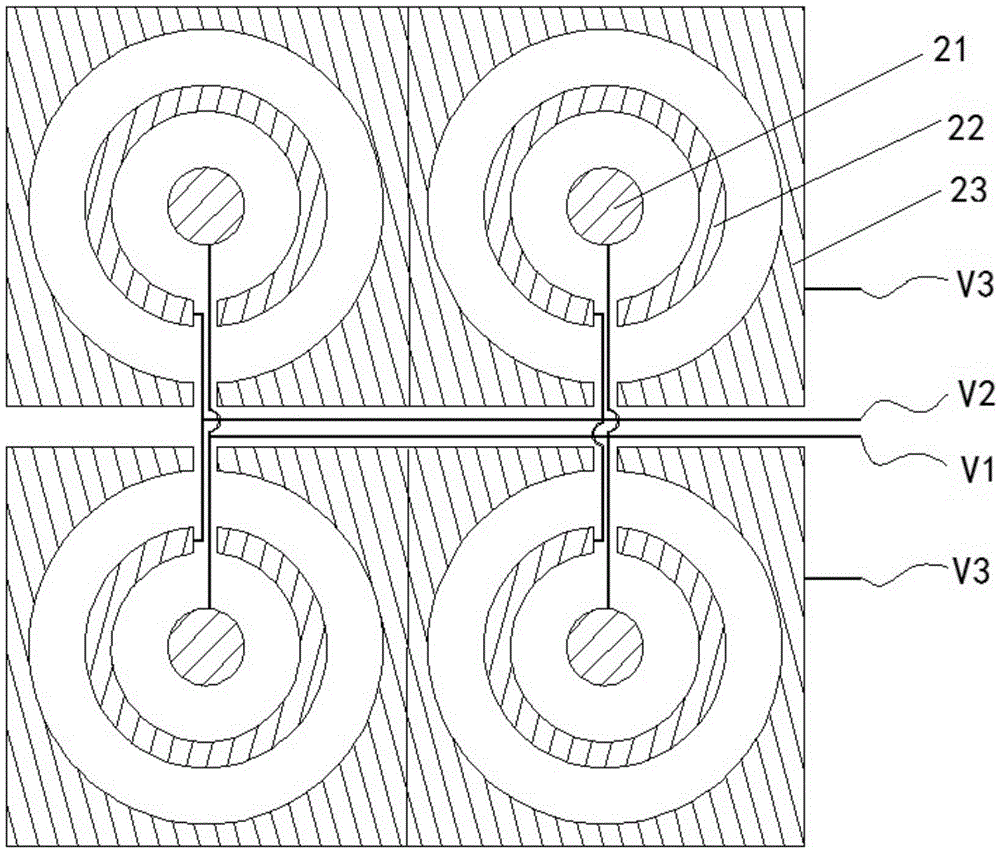
Liquid crystal lens array and stereoscopic display apparatus
ActiveCN105572885AHas rotational symmetry3D display effect is goodSteroscopic systemsNon-linear opticsLiquid crystalConcentric ring
The invention provides a liquid crystal lens array and a stereoscopic display apparatus, and relates to the technical field of stereoscopic display. The liquid crystal lens array includes a plurality of liquid crystal microlens units, wherein each liquid crystal microlens unit includes a first glass substrate and a second glass substrate; the first glass substrate is plated with a first electrode; the second glass substrate is plated with a second electrode; liquid crystal is filled between the first glass substrate and the second glass substrate; and the first electrode includes a circular electrode at the center position, and at least two annular electrodes which are arranged in the shape of a concentric ring and take the circular electrode as the center. As the 3D display effect formed by the liquid crystal lens array has no directionality, a user can watch the required 3D effect from a wider angle, and the watching angle is more continuous, so that the 3D display effect of a stereoscopic display apparatus using the liquid crystal lens array becomes better and has no shear zones and the problem that the watcher becomes giddy because of being in the shear zone is effectively avoided.
Owner:洪煦 +1
Forming method for composites
ActiveUS20050053762A1Minimizes shear zoneReducing and eliminating out-of-plane fiber bucklingLayered productsConfectioneryFiberComposite laminates
A method for forming composite materials is presented, including providing a composite charge wider than a first surface of a mandrel, and positioning the composite charge across the first surface of the mandrel. The portion of the composite charge overhanging the first surface of the mandrel is supported and urged against the mandrel while supporting the unbent portion of the composite charge substantially parallel to the first surface of the mandrel. The invention also provides a system, using a compression mold of forming bladders and heater plates, to form a composite charge over a mandrel, while supporting the unbent portions of the composite charge during forming substantially parallel to the upper surface of the mandrel. The present invention minimizes the shear zone where plies in the composite laminate charge slide past one another during the forming process reducing or eliminating out-of-plane fiber buckling.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Method for preparing essence by employing extrusion technology
The invention provides a method for preparing a flavor essence by employing an extrusion technology. The method comprises the following steps: (1) raw materials mixing: adding the raw materials used to prepare the essence according to a proportion of a formulation into an auto mixing machine to be mixed uniformly and obtaining a raw mix; (2) extrusion reaction: preheating a twin screw extruding machine to the following appointed temperatures: the temperature of a mixing zone is 60-130 DEG C, the temperature of a shear zone is 90-160 DEG C, the temperature of a melting zone is 120-190 DEG C; adding the raw mix into a loading hopper of the extruding machine, starting a screw and adjusting the rotation speed of the screw to be 100-400 rotation / minute; evenly adding the materials and controlling the speed of adding materials to be 20-500 kg / hour; transmitting and extruding the raw materials in the extruding machine, then squeezing out the raw materials from the port of a mould in the extruding machine, cooling extruded samples to room temperature and obtaining the powdered essence after being pulverized by a pulverizer.
Owner:TIANJIN CHUNFA BIO TECH GRP
Viscous fan drive having modified land design and armature venting
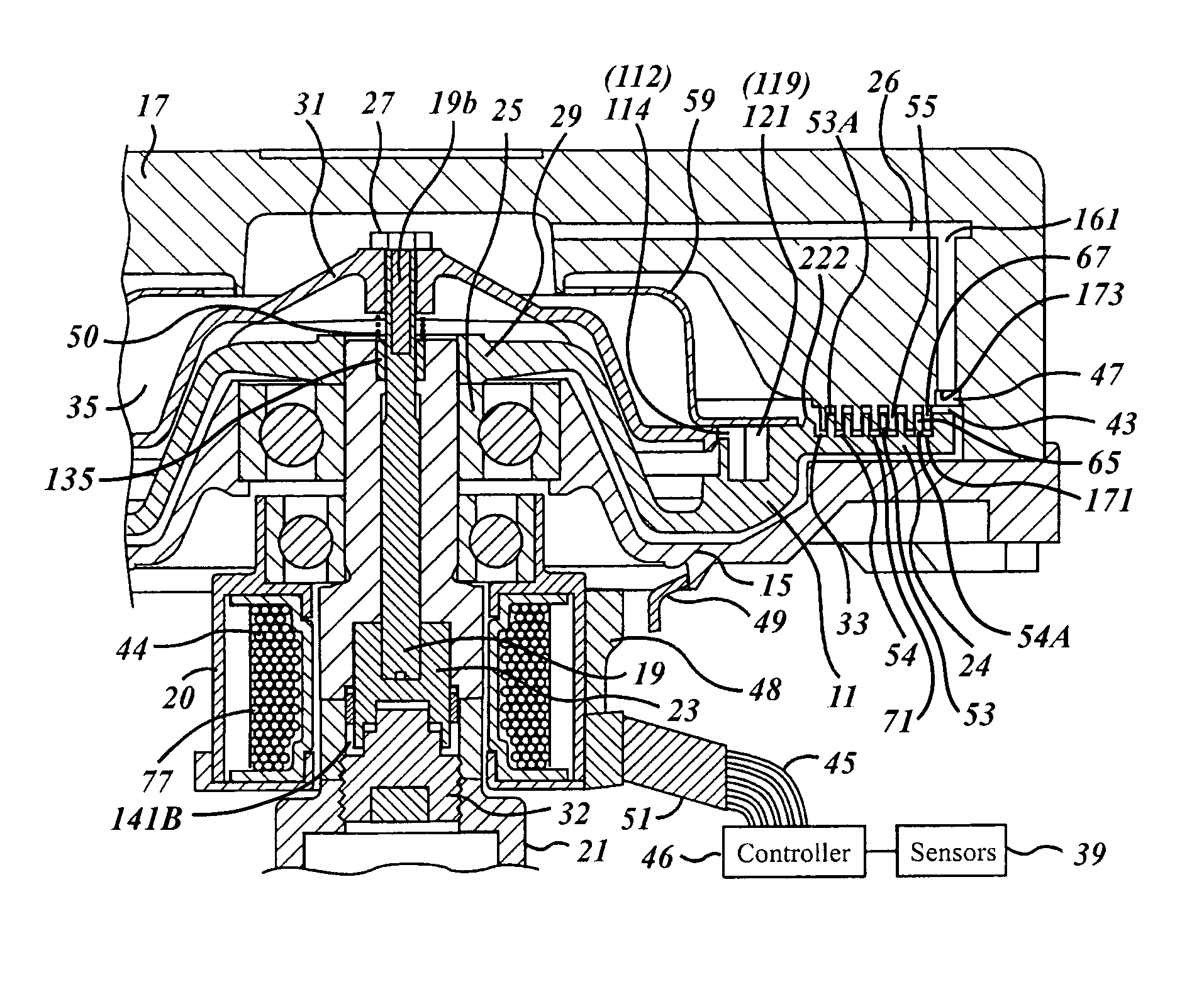
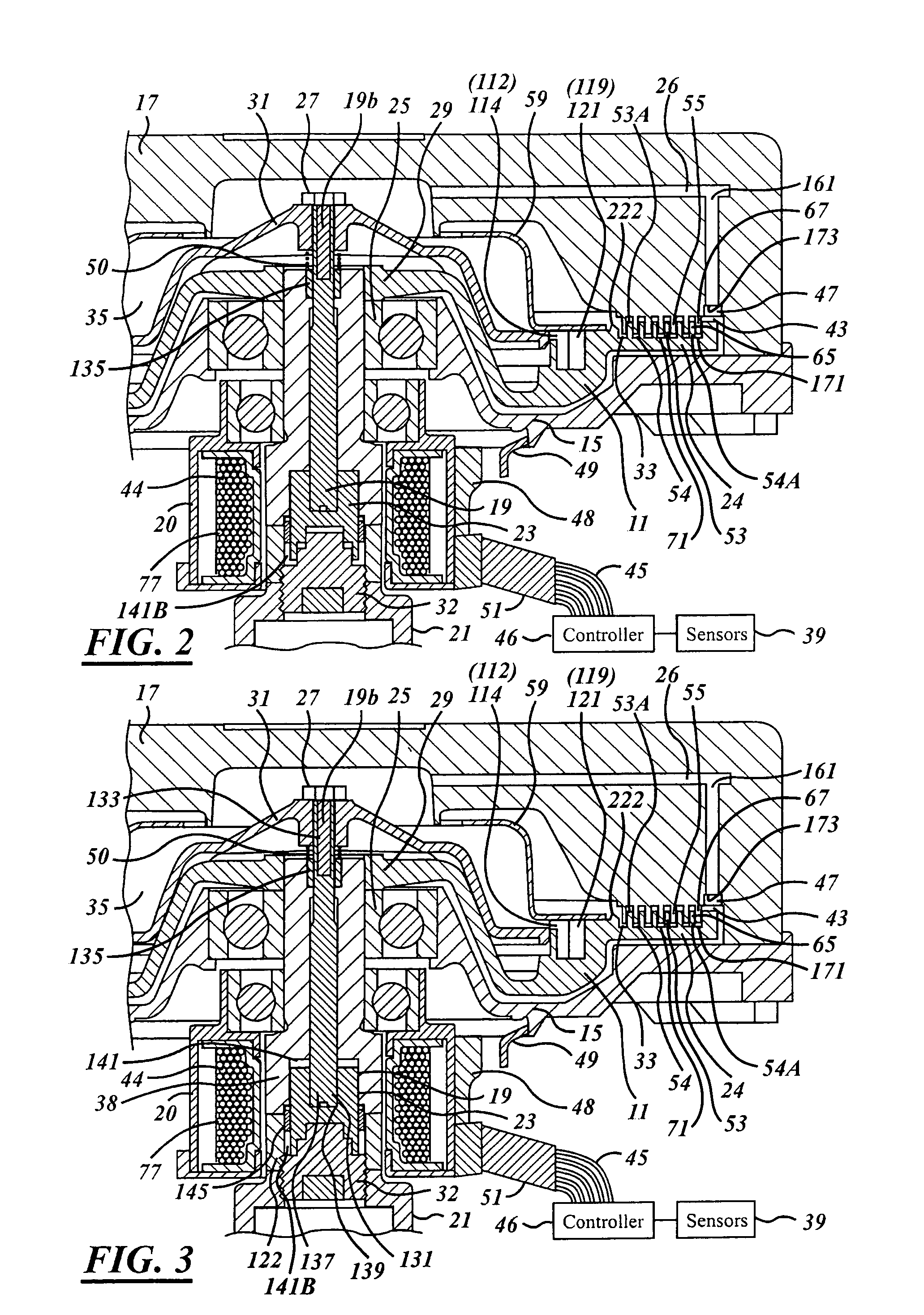
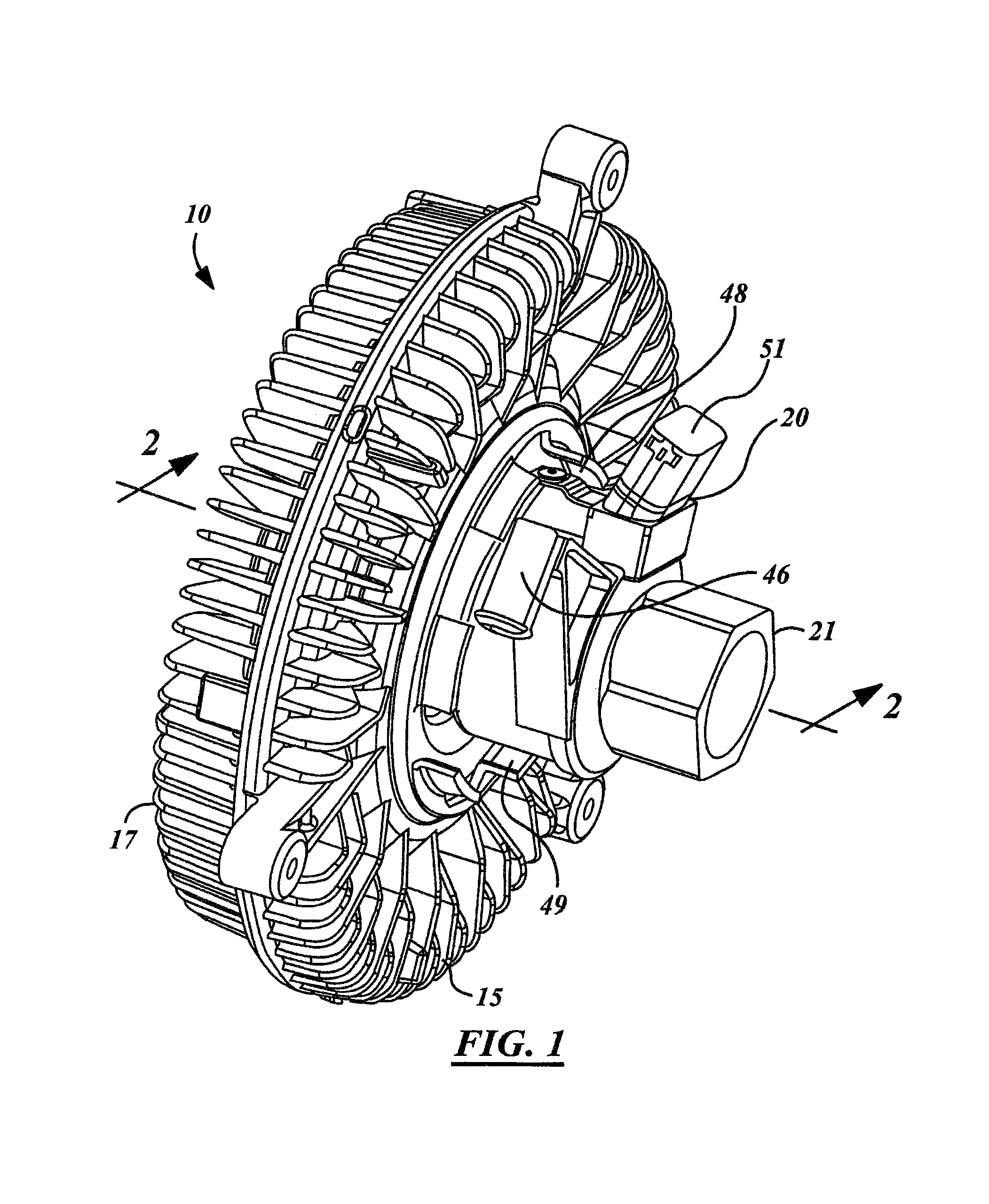
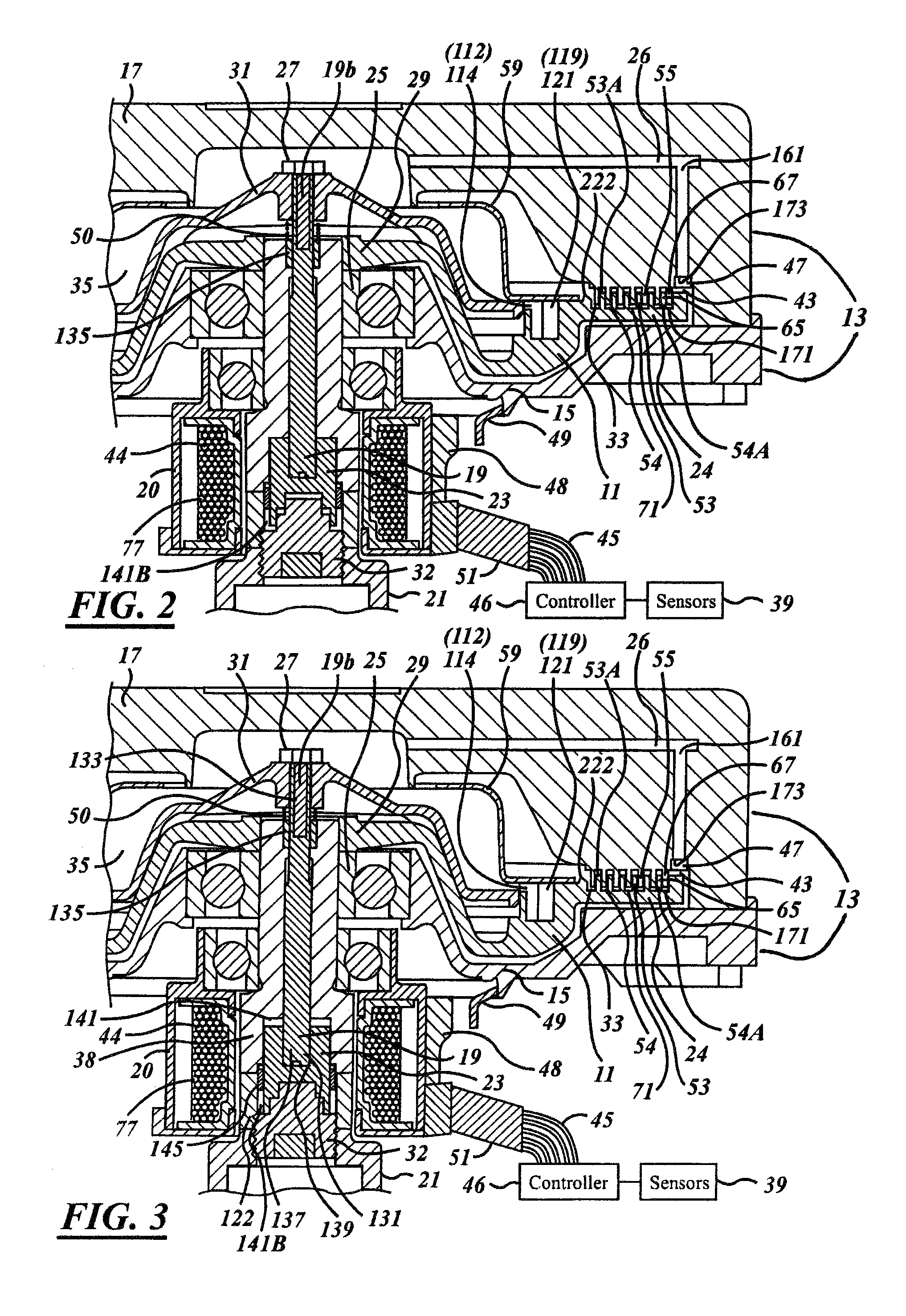
ActiveUS20070205071A1Large torque generationTravel can be limitedFluid couplingsFluid clutchesCouplingEngineering
A viscous fan drive in which the output drive to the fan is controlled by the movement of viscous fluid from a fluid reservoir and into the operating and working chamber of the coupling during normal operation. The input-coupling assembly and cover member are formed with a unique combination of continuous and non-continuous radially extending lands and grooves designed to distribute the viscous fluid in a continuous film throughout the shear zone so as to maximize output fan speed at a given input speed. An armature-venting feature is designed to simplify the opening and closing of the valve disk in an electronic version of the viscous fan drive depending upon the desired operating condition.
Owner:BORGWARNER INC
Beef flavor essence prepared by extrusion technology
The invention provides a beef flavor essence prepared by an extrusion technology. The preparation method of the essence comprises the following steps: mixing raw materials: adding the raw materials used to prepare the beef flavor essence according to a proportion of a formulation into an auto mixing machine to be mixed uniformly and obtaining a raw mix; extruding reaction materials: preheating a twin screw extruding machine to the following appointed temperatures: the temperature of a mixing zone is 60-130 DEG C, the temperature of a shear zone is 90-160 DEG C, the temperature of a melting zone is 120-190 DEG C; adding the raw mix into a loading hopper of the extruding machine, starting a screw and adjusting the rotation speed of the screw to be 100-400 rotation / minute; evenly adding the materials and controlling the speed of adding materials to be 20-500 kg / hour; transmitting and extruding the raw materials in the extruding machine and generating Maillard reaction and changes like sugar degradation, fat oxidation and the like in a high-temperature and high-pressure state; then squeezing out the raw materials from the port of a mould in the extruding machine, cooling extruded samples to room temperature and obtaining the powdered beef flavor essence after being pulverized by a pulverizer.
Owner:TIANJIN CHUNFA BIO TECH GRP
Powder compacting apparatus for continuous pressing of pharmaceutical powder
InactiveUS20050084560A1Improve compactionIncrease the friction surfaceDough-sheeters/rolling-machines/rolling-pinsConfectioneryMechanical engineeringPhysical property
Improved powder compacting apparatus for feeding powder between rollers to form a compressed material with enhanced physical properties including uniformity to facilitate forming tablets and similar items therefrom. Side seals confine the powder between the rollers and can be movable independently from the rollers and optionally independently from one another to enhance even compaction. A housing defines a guide channel with a linear feed and shearing zone immediately prior to the nip zone for smoothing and leveling powder flow. One or more vents are provided for releasing gases generated.
Owner:ROLAND EDWARD J
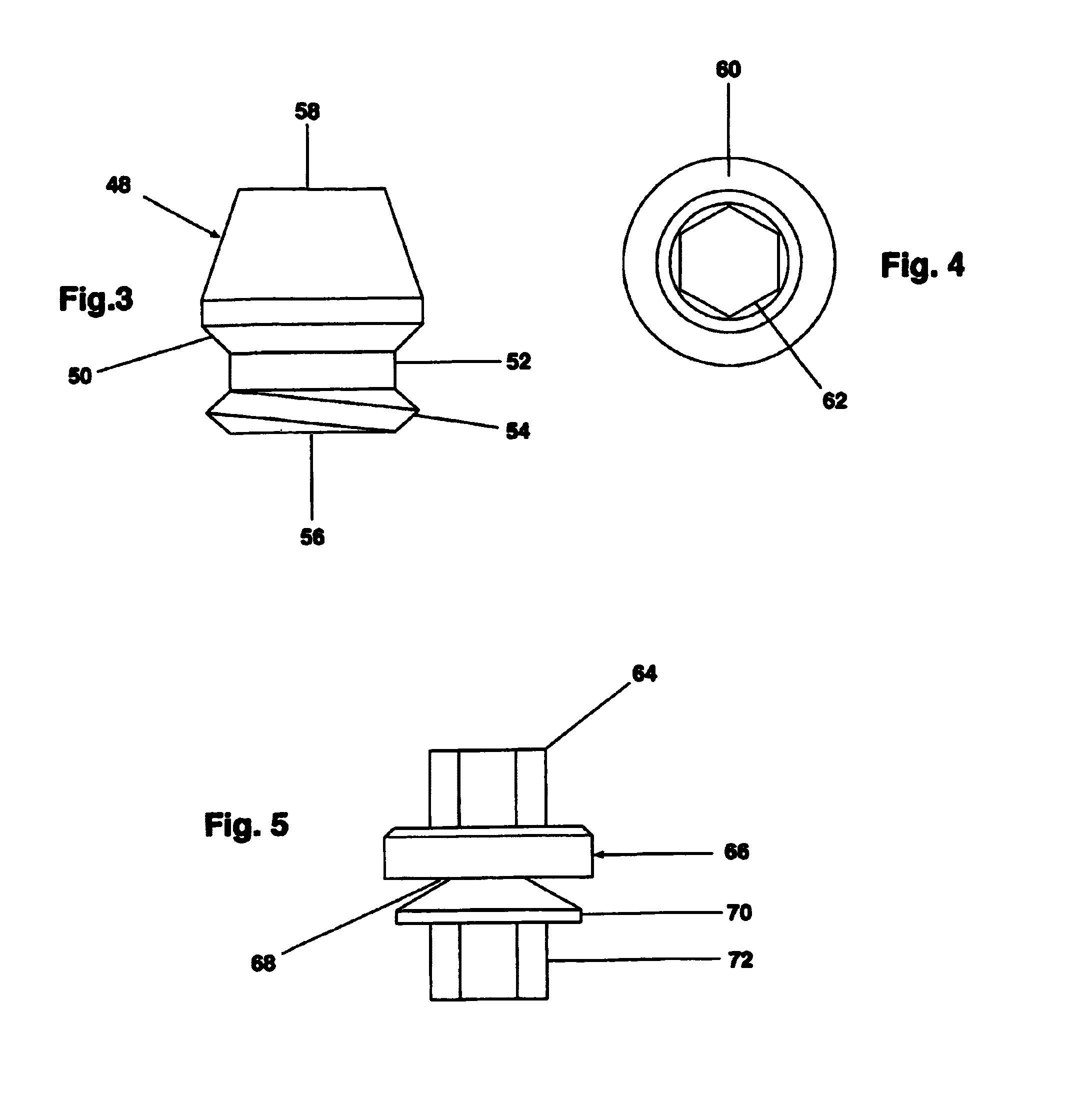
Dental tool with shear pin handle
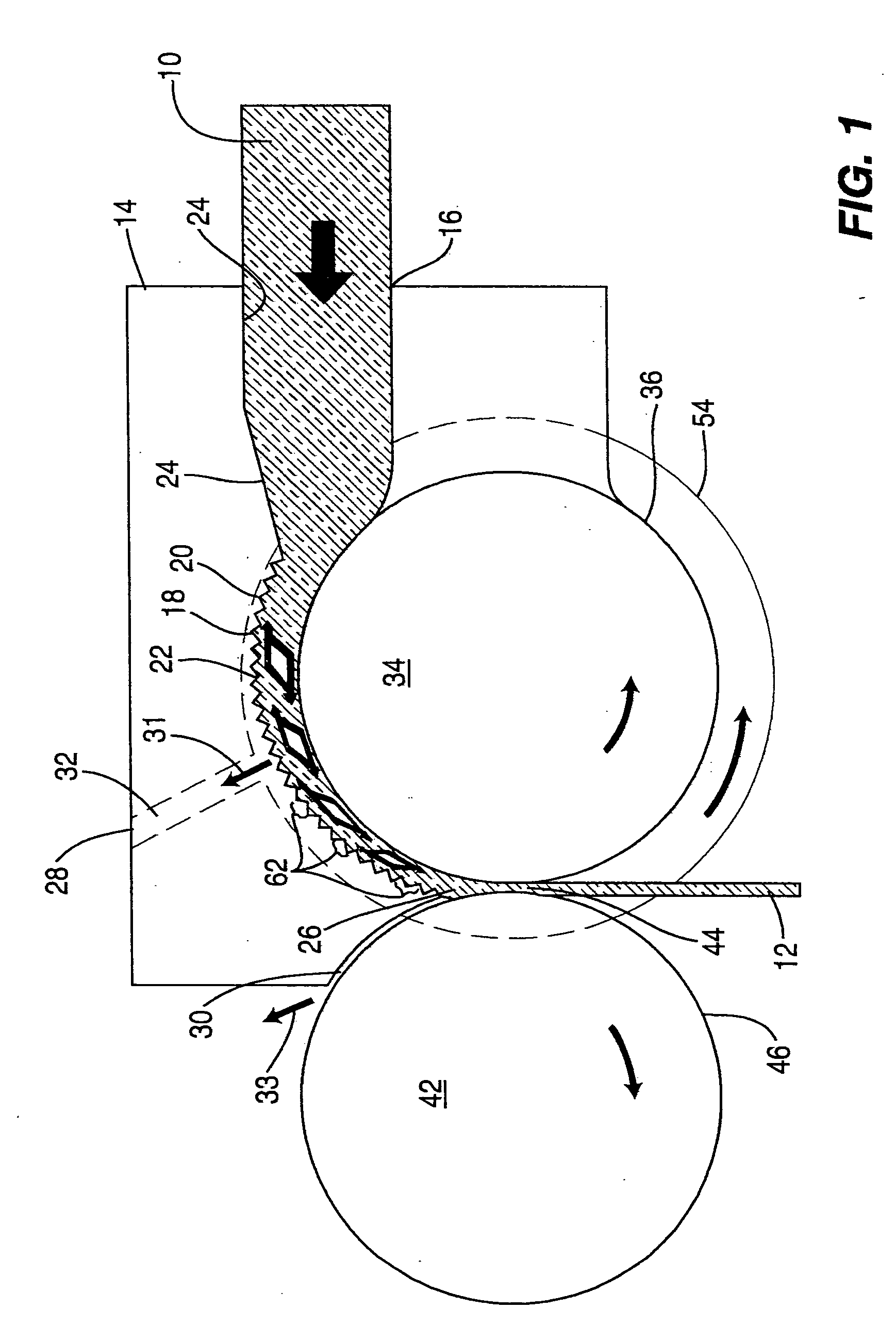
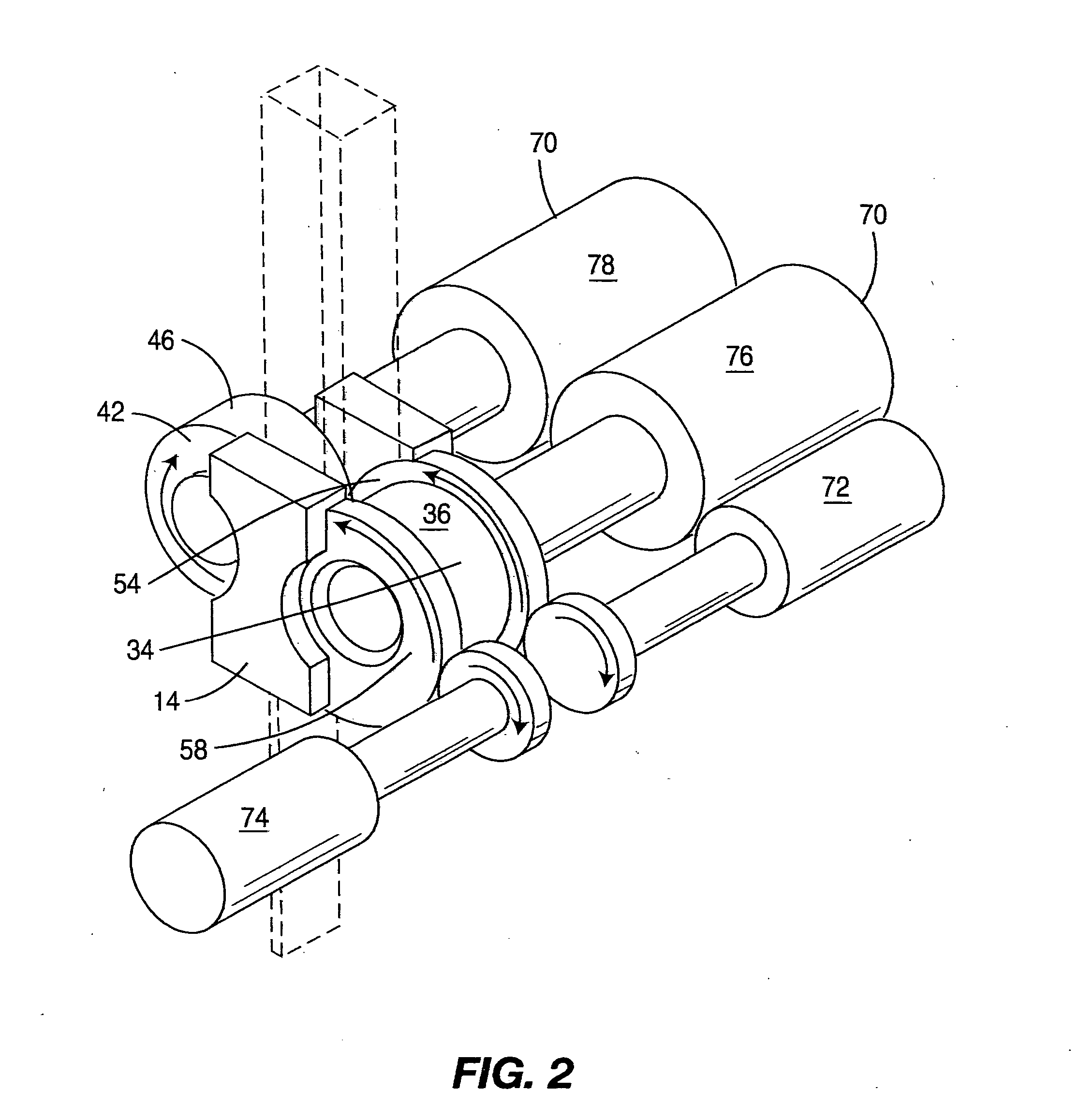
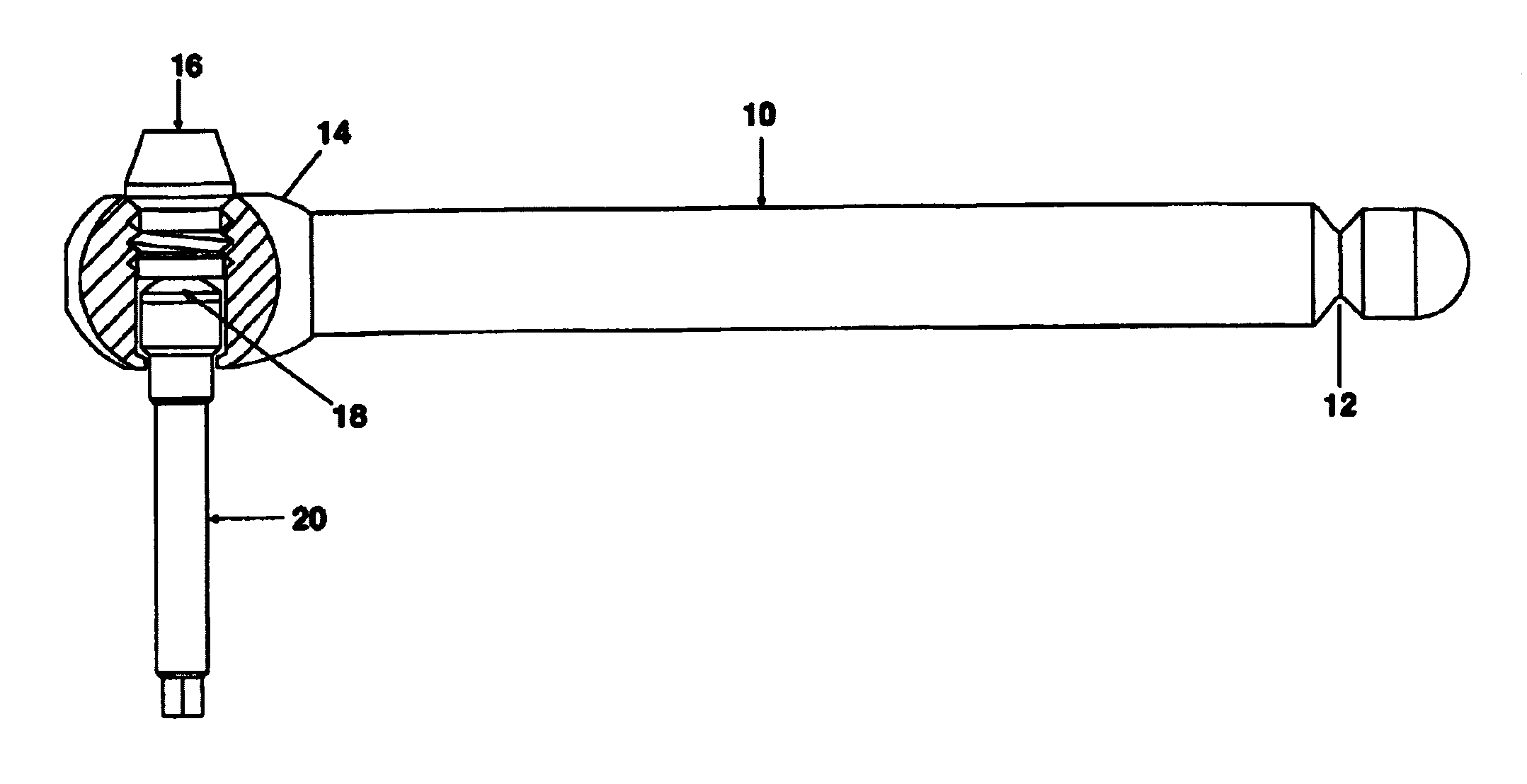
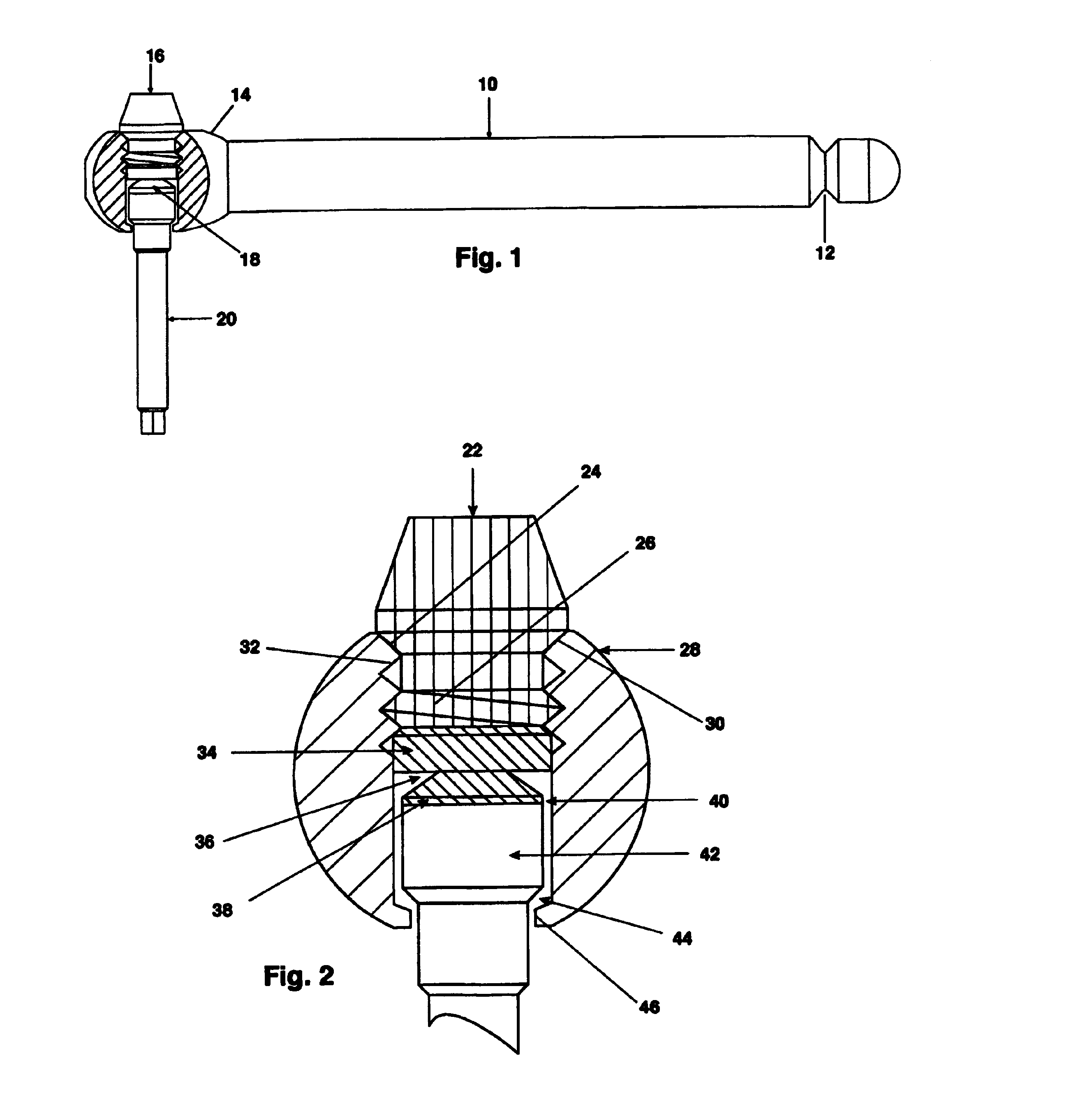
A tool is used to limit the torque applied to tighten the threaded connection of prosthesis components placed in skeletal bones, for example dental implants. The device had a handle, a retaining screw, a single use torque limiting shear pin and a drive shaft. The handle has a tapered counter sunk cross bore with left handed threads to allow installation of a drive shaft which engages a torque limiting shear pin which, in turn, engages a left hand threaded retaining screw. The drive shaft extends from the handle to engage any threaded fastener that has a head that corresponds to the drive shaft end. The drive shaft and the shear zone of the shear pin are completely isolated within the wrench handle so that all rotational force is utilized in the actual shearing of the shear pin to a torque accuracy of ±0.3 Ncm, approximately.
Owner:WALTON JAMES
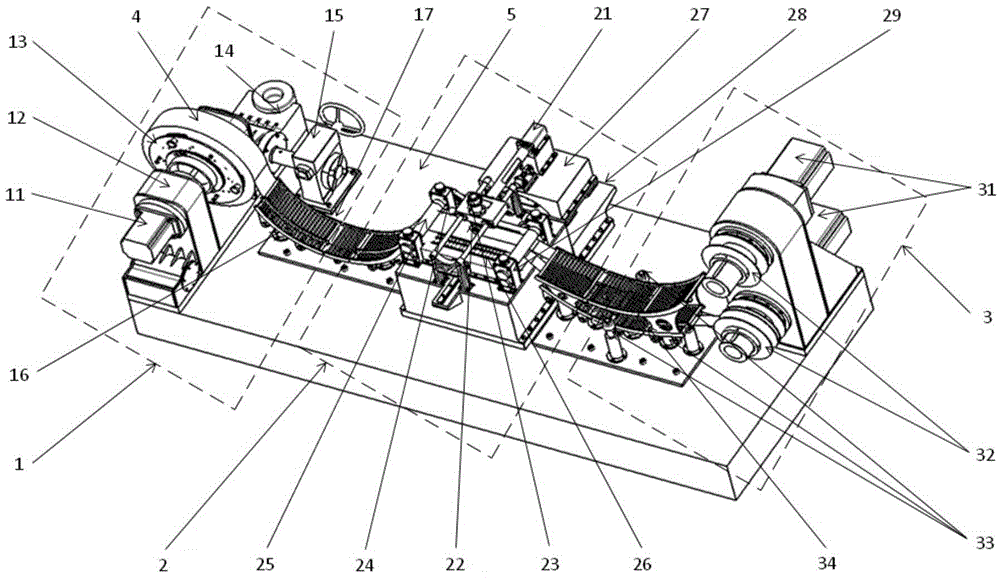
Horizontal geotechnical plane stress triaxial apparatus for pressure chamber structure
ActiveCN103454138AEasy to controlRealize measurementMaterial strength using steady shearing forcesMachine partsTest sample
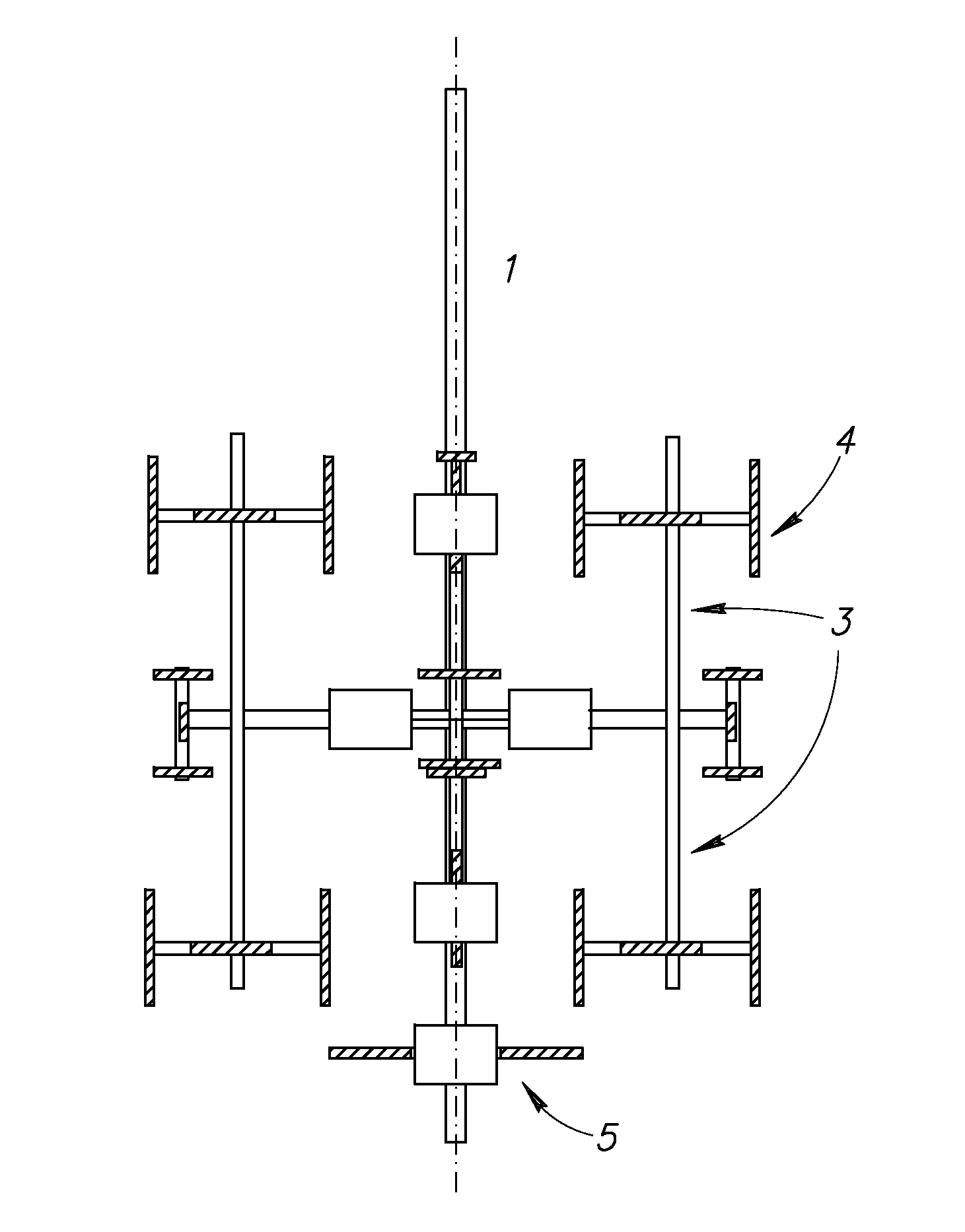
The invention discloses a horizontal geotechnical plane stress triaxial apparatus for a pressure chamber structure. The horizontal geotechnical plane stress triaxial apparatus comprises a main machine part, a three-dimensional stress loading and measuring mechanism and a collecting and controlling mechanism. The main machine part structurally comprises four columns fixedly installed on a base, wherein a bottom disc and a top cover are fixedly installed on the upper sections of the four columns, side walls are fixedly connected to four sides of the bottom disc and the top cover, and the bottom disc, the top cover and the four side walls jointly encircle a pressure chamber. A cuboid test sample is placed in the center of an inner cavity of the pressure chamber. The three-dimensional stress loading and measuring mechanism comprises large stress, small stress and intermediate stress loading and measuring mechanisms. According to the device disclosed by the invention, three-dimensional stress, two-dimensional stress and unsaturated three-dimensional stress can be obtained through a plane stress triaxial test, and the stresses do not interfere with each other. Study on shear zones and local deformation of the plane stress test is realized. The mechanical property and strength deformation mechanism of non-saturated soil can be searched under the condition of a plane stress path.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
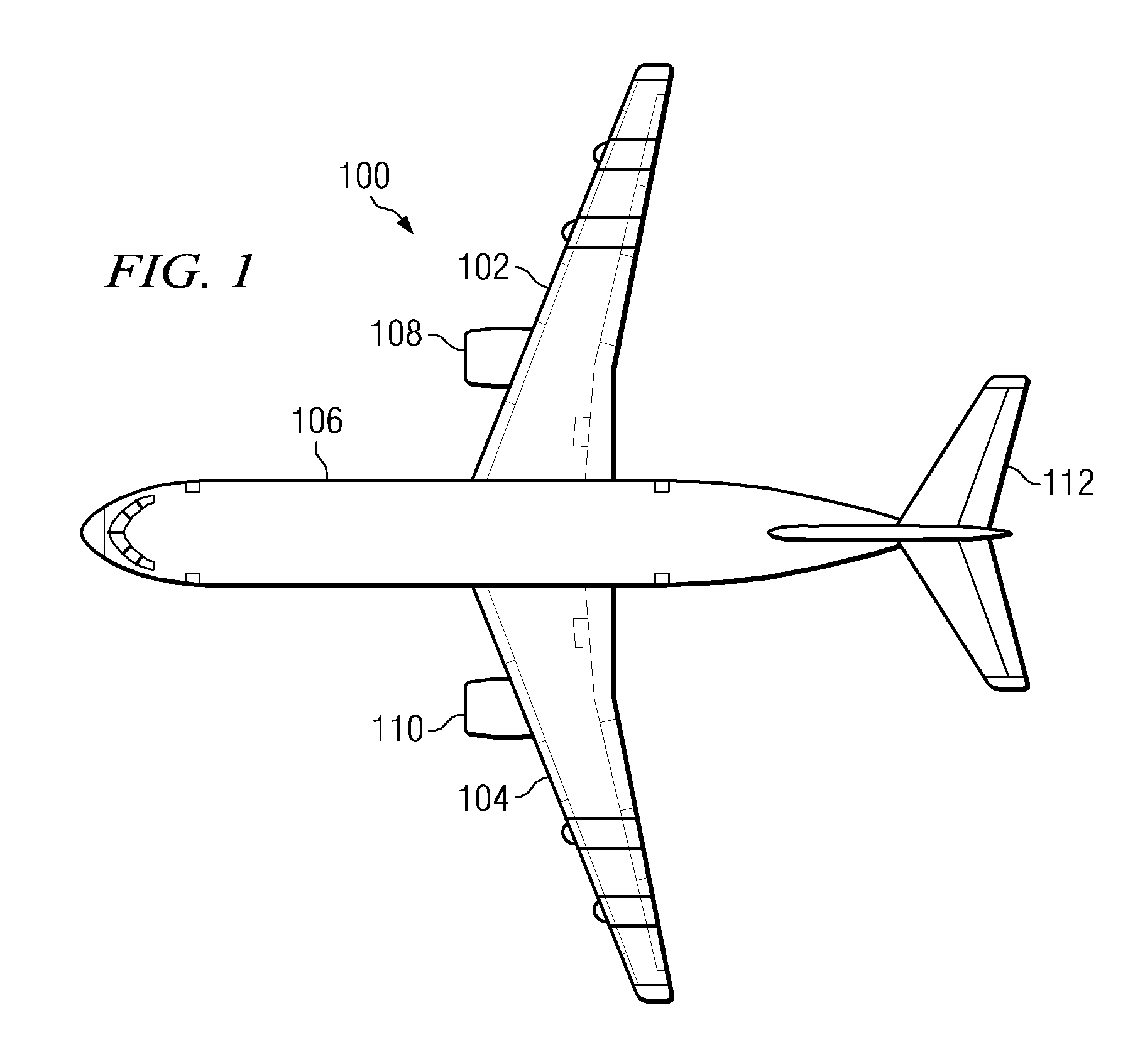
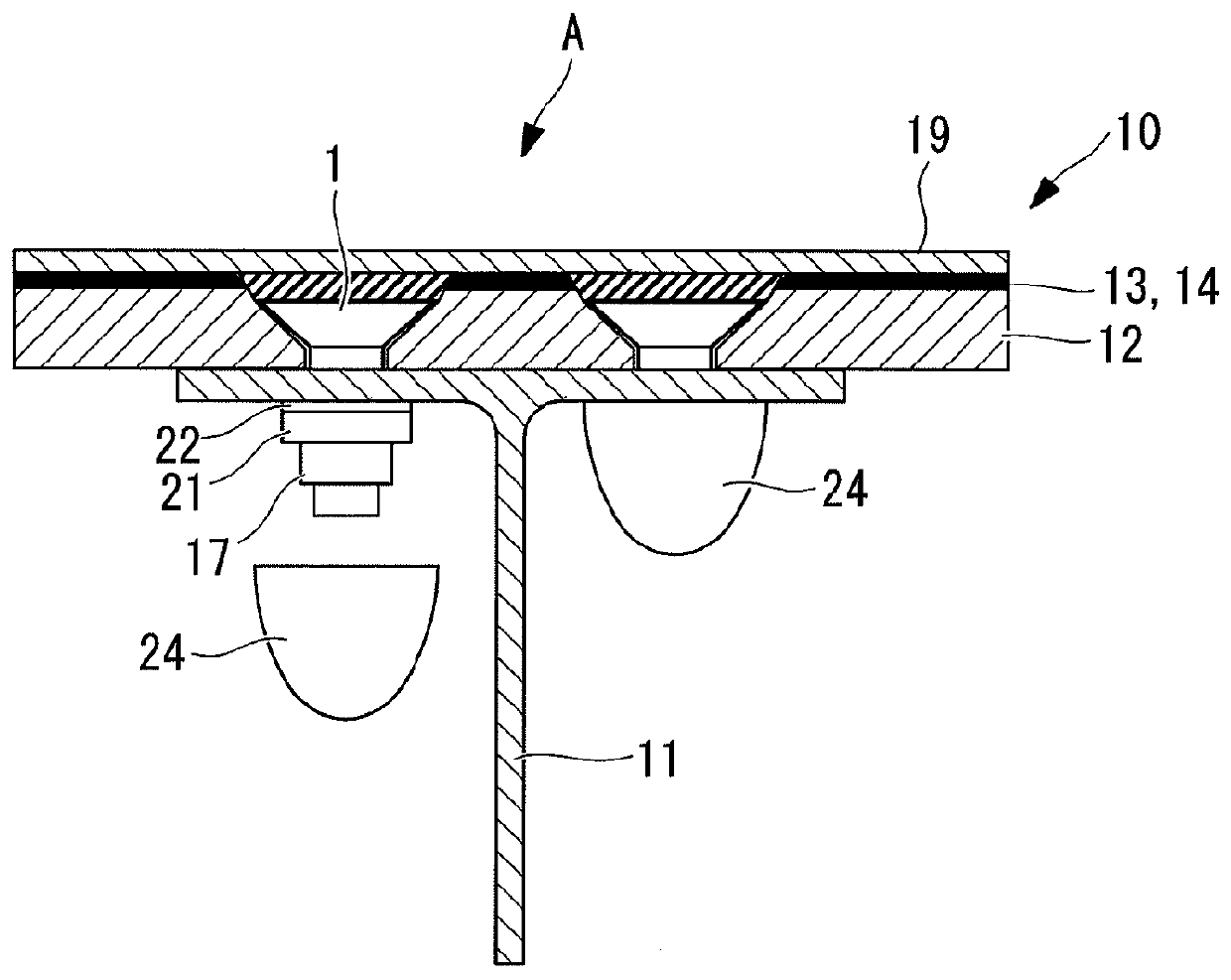
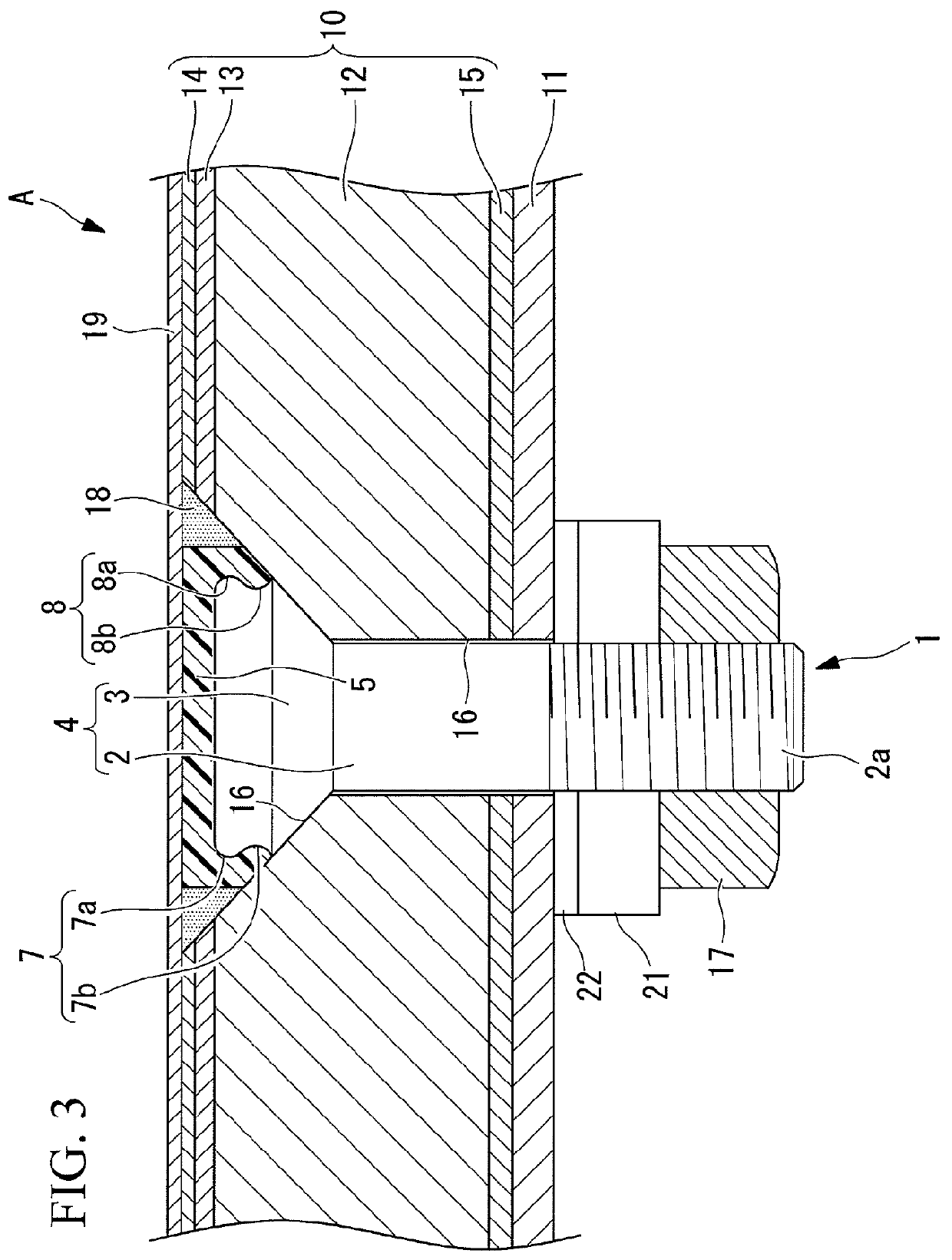
Aircraft assembly
ActiveUS8413929B2Not easily destroyedImprove reliabilityNutsAircraft lighting protectorsCopper foilEngineering
An aircraft assembly is equipped with a lightning protection structure that is not easily destroyed by lightning current and that is highly reliable. The aircraft assembly includes a skin in which a CFRP layer serves as a main structure, a shear-tie that supports the skin from the inside, and a fastener that couples the skin and the shear-tie. A copper foil and an outside GRFP layer are provided on an outer surface side of the skin, in this order towards the outside, and a copper paint layer, which contains copper powder, is provided on the outside GFRP layer.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
Curve cutting machine for amorphous alloy strips
ActiveCN104551200AReduce tensionAvoid tearingStock shearing machinesShearing machine accessoriesAlloyEngineering
The invention relates to a curve cutting machine for amorphous alloy strips. The curve cutting machine comprises a strip discharging zone, a shearing zone and a strip collecting zone which are sequentially arranged. The strip discharging zone comprises a strip discharging servo motor, a hoisting device and a strip discharging zone pressure sensor, and the rolled amorphous strips are arranged on the hoisting device and can be driven by the strip discharging servo motor to rotate so as to be discharged; the shearing zone comprises a servo motor, a cutting blade group, a cutting sliding table, a speed sensor, a rubber wheel pressure group, an absorption worktable, a displacement worktable, a displacement table feeding system and a pressure regulating mechanism; the strip collecting zone comprises strip collecting servo motors, strip collecting wheels, strip collecting zone pressure sensors and a positioning clamp plate. The curve cutting machine has the advantages that the amorphous alloy strips can be conveyed under the linkage effects of the multiple groups of servo motors, can be shorn and machined in the shearing zone and can be wound and collected in the strip collecting zone after being shorn; requirements on transversely and longitudinally shearing the amorphous alloy strips can be met by the cutting machine which is applicable to the amorphous alloy strips.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
Stirring propeller for sucking and dispersing easy-to-self-polymerized gas
InactiveCN101745334AReduce delivery pressureGood dispersionMixing methodsRotary stirring mixersCircular discPropeller
The invention relates to a stirring propeller for sucking and dispersing easy-to-self-polymerized gas, which comprises a vertical cylindrical propeller shaft and an easy-to-self-polymerized gas inlet pipe. The stirring propeller is characterized in that the end of the cylindrical propeller shaft is connected with the upper circular disc of a curved disc turbine through a fixing ring, the center of the lower circular disc of the curved disc turbine is provided with a gas inlet; the periphery of the gas inlet is connected with a gas inlet diversion cylinder, the end of the easy-to-self-polymerized gas inlet pipe is arranged in the gas inlet diversion cylinder, the peripheries of the upper circular disc and the lower circular disc are connected through 4-12 arc-shaped blades which are distributed in a turbine shape. The invention has the advantages that: during the stirring, the strong negative pressure can be generated at the center of the turbine to pump the gas in, thereby reducing the gas conveying pressure and reducing the self-polymerization; the gas pumped in can be sprayed out along the radial directions of the circular discs along the swirling channel, thereby preventing the gas from passing through the low shear zone around the hub, and achieving high stirring efficiency and good dispersing effect; and blades can be additionally arranged on the stirring shaft to enhance the gas dispersing effect.
Owner:SHANGHAI WUJING CHEM +1
Process for Producing Exfoliated and/or Dispersed Polymer Composites and/or Nanocomposites via Solid-State/Melt Extrusion (SSME)
A method for solid-state / melt extrusion, as can be accomplished using a unitary extruder apparatus comprising a solid-state shearing zone and a melt-state extrusion zone.
Owner:BUCKNELL UNIVERSITY
Combined beam of FRP, wood and steel reinforced concrete
InactiveCN103603462AIncreased bending stiffnessImprove flexural strengthBuilding repairsGirdersEngineeringRebar
The invention discloses a combined beam of FRP, wood and steel reinforced concrete. The combined beam comprises steel reinforced concrete wing panels, shearing force connecting pieces, wood beams, FRP reinforcing members, FRP cloths, steel ribs and U-shaped stirrups, wherein the shearing force connecting pieces are disposed between the steel reinforced concrete wing panels and the wood beams; the FRP reinforcing members are disposed at the bottom of, in a cross section at the middle and lower part of and in the side surface of the wood beams; the bending zone of the combined beam is reinforced by transverse winding the FRP cloths; and the FRP reinforcing members in the bending shear zone of combined beam are anchored by using the U-shaped stirrups. The combined materials play the functions of their own and work cooperatively, so that cross sectional inertia of the wood-steel reinforced concrete combined beam is greatly increased; and strength and rigidity of original components are effectively increased. The combined beam has the advantages of light self-weight, good mechanical performances, low energy consumption and renewability, and can be widely applied in the fields of reinforcement of ancient architectures and modern wood structures.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
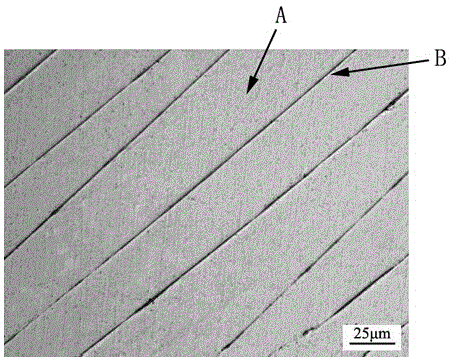
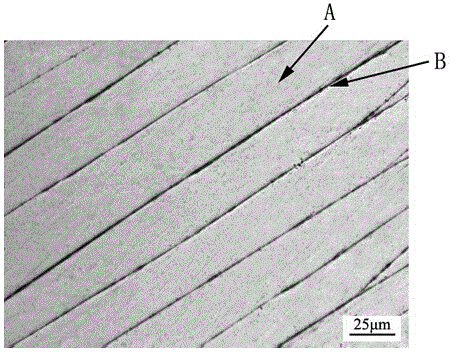
Method for observing inner shearing zone of zirconium base amorphous alloy
InactiveCN103983499AClear shear band morphologyClear shapePreparing sample for investigationMicro structureMetallic materials
The invention discloses a method for observing inner shearing zone of zirconium base amorphous alloy, and belongs to the technical field of metal material micro-structure observation. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: (1) carrying out plastic deformation on zirconium base amorphous alloy through rolling; (2) carrying out step-by-step grinding on the plastically-deformed zirconium base amorphous alloy test-piece to obtain at least one observation surface; (3) carrying out mechanical polishing on the observation surface of the test-piece; (4) etching the polished observation surface of the test-piece; (5) observing the morphology of the inner shearing zone of the test-piece through an optical microscope. The observation method overcomes the shortages of conventional methods that directly use a scanning electron microscope to observe a test-piece surface or use a transmission electron microscope to observe the test-piece interior, is capable of clearly observing the morphology and distributions of shearing zones in deformed zirconium base amorphous alloy, is easy and practicable, and does not need special equipment.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Viscous fan drive having modified land design and armature venting
ActiveUS7621386B2Travel can be limitedLarge torque generationFluid couplingsFluid clutchesCouplingEngineering
A viscous fan drive in which the output drive to the fan is controlled by the movement of viscous fluid from a fluid reservoir and into the operating and working chamber of the coupling during normal operation. The input-coupling assembly and cover member are formed with a unique combination of continuous and non-continuous radially extending lands and grooves designed to distribute the viscous fluid in a continuous film throughout the shear zone so as to maximize output fan speed at a given input speed. An armature-venting feature is designed to simplify the opening and closing of the valve disk in an electronic version of the viscous fan drive depending upon the desired operating condition.
Owner:BORGWARNER INC
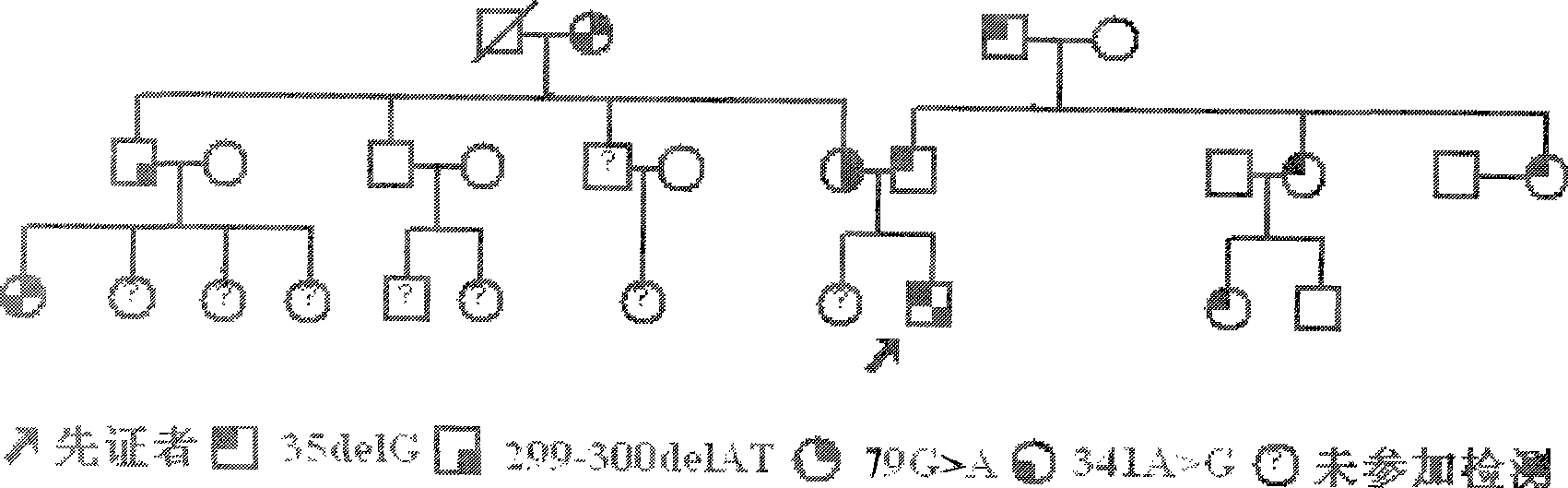
Method for detecting hereditary hearing loss relative connexin 26 gene GJB2 mutation and kit for detection
InactiveCN101363054AImprove diagnosis rateEasy diagnosisMicrobiological testing/measurementLink proteinExon
The invention relates to a method for testing gap linking protein 26 gene GJB2 mutation related to hereditary hearing impairment, which completely enlarges GJB2 gene base boot sector, exon 1, exon 2 and shear zone by polymerase chain reaction; and then, DNA sequence is measured to detect whether GJB2 genetic mutation exists; the method of the invention can completely cover all the genetic mutation of the GJB2 gene base boot sector, the exon 1, the exon 2 and the shear zone, so that detectable rate of the GJB2 genetic mutation and diagnosis rate of hereditary hearing impairment related to the GJB2 gene are improved; compared with that sequence measurement is separately carried out on a GJB2 code area, the method is more comprehensive and reliable, so as to be beneficial to the diagnosis of hereditary hearing impairment.
Owner:ドングァン アオマイヤ ジェネティック テクノロジー カンパニー リミテッド
Current loading method used during pulse current auxiliary precision blanking machining
ActiveCN110369600AImprove toughnessImprove featuresShaping toolsMetal working apparatusMetallic materialsElectrocaloric effect
Currents act on metal, and an electric heating effect and electrically induced plasticity are achieved, wherein a high-frequency pulse current effect has the capacity of healing metal plastic strain damage. Electrically induced plasticity and electric heating softening effects are introduced into the precision blanking technology, and the precision blanking difficulty of high-strength steel platesis reduced. Metal materials are heated to expand through the electric heating effect, the defect that in the blanking medium-terminal stage, hydrostatic pressure stress of shear zones of the metal materials is reduced rapidly is relieved, and the capacity of restraining production-extension of holes of the shear zones is improved. By means of a good-time and proper pulse current acting manner anda loading method, current energy is intensively injected in good time at high density aiming at local zones, where the holes and micro-cracks are easily generated in the blanking process, of the shear zones, strain damage is repaired, the situation that the micro-cracks are further developed into macro-cracks, and a rough tear zone on a precision blanking section is finally formed is avoided, anda higher possibility is provided for enabling precision blanking to be more widely applied to high-strength type materials.
Owner:AIR FORCE UNIV PLA +1
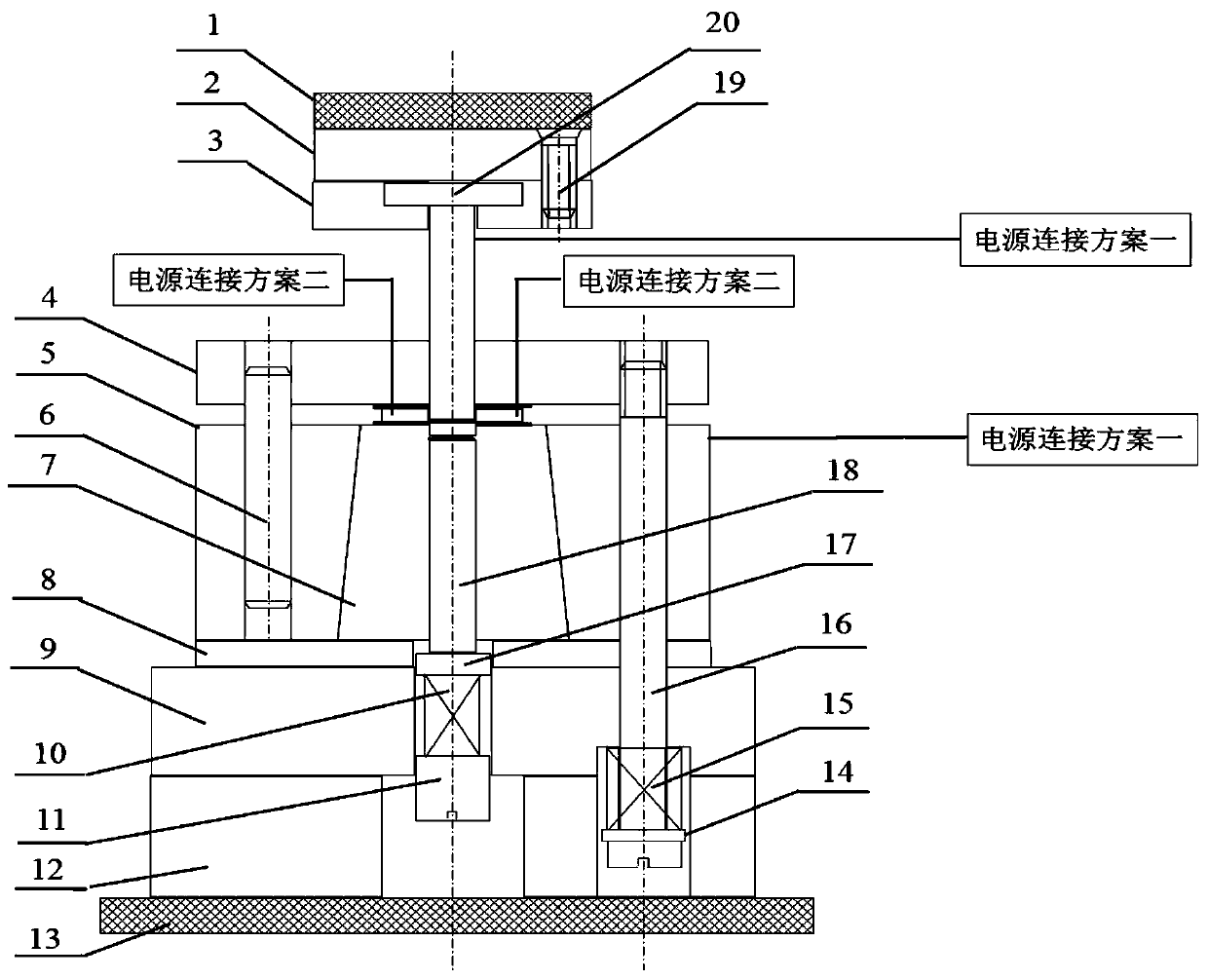
Visual shearing and sample loading box applicable to direct shear test of coarse-grained soil
ActiveCN103852371ADirect observation of forceUnderstanding Shear FailureMaterial strength using steady shearing forcesStress conditionsEngineering
The invention discloses a visual shearing and sample loading box applicable to direct shear test of coarse-grained soil. The visual shearing and sample loading box applicable to the direct shear test of the coarse-grained soil comprises an upper shearing box, a lower shearing box, a bearing plate, a rigid assembly A and a rigid assembly B, wherein the rigid assembly A and the rigid assembly B are used for transmitting pressure and shearing force; the upper shearing box and the lower shearing box are connected in series and fixed together through a fixing pin; the bearing plate is mounted above the upper shearing box; the rigid assembly A is arranged on the bearing plate; the rigid assembly B is arranged on the side surface of the upper shearing box; a foam gasket and limit steel balls are also arranged between the upper shearing box and the lower shearing box; the upper shearing box and the lower shearing box are made of completely-transparent tempered glass; mark strips are posted on the inner side walls of the upper shearing box and the lower shearing box. Due to the adoption of the visual shearing and sample loading box applicable to the direct shear test of the coarse-grained soil, the stress condition of the coarse-grained soil particles can be directly observed; by observing movement of the particles and deformation of the soil, the condition that the soil is sheared and damaged can be more deeply known and the principle of the direct shear test can be known, and thus the stress condition of the soil and a development process of a shear zone can be well known.
Owner:CHINA POWER CONSRTUCTION GRP GUIYANG SURVEY & DESIGN INST CO LTD
Processes for improving tool life and surface finish in high speed machining
InactiveUS20100086369A1Enhanced grain boundary diffusionReduce wearLathesAutomatic/semiautomatic turning machinesPerformance toolEngineering
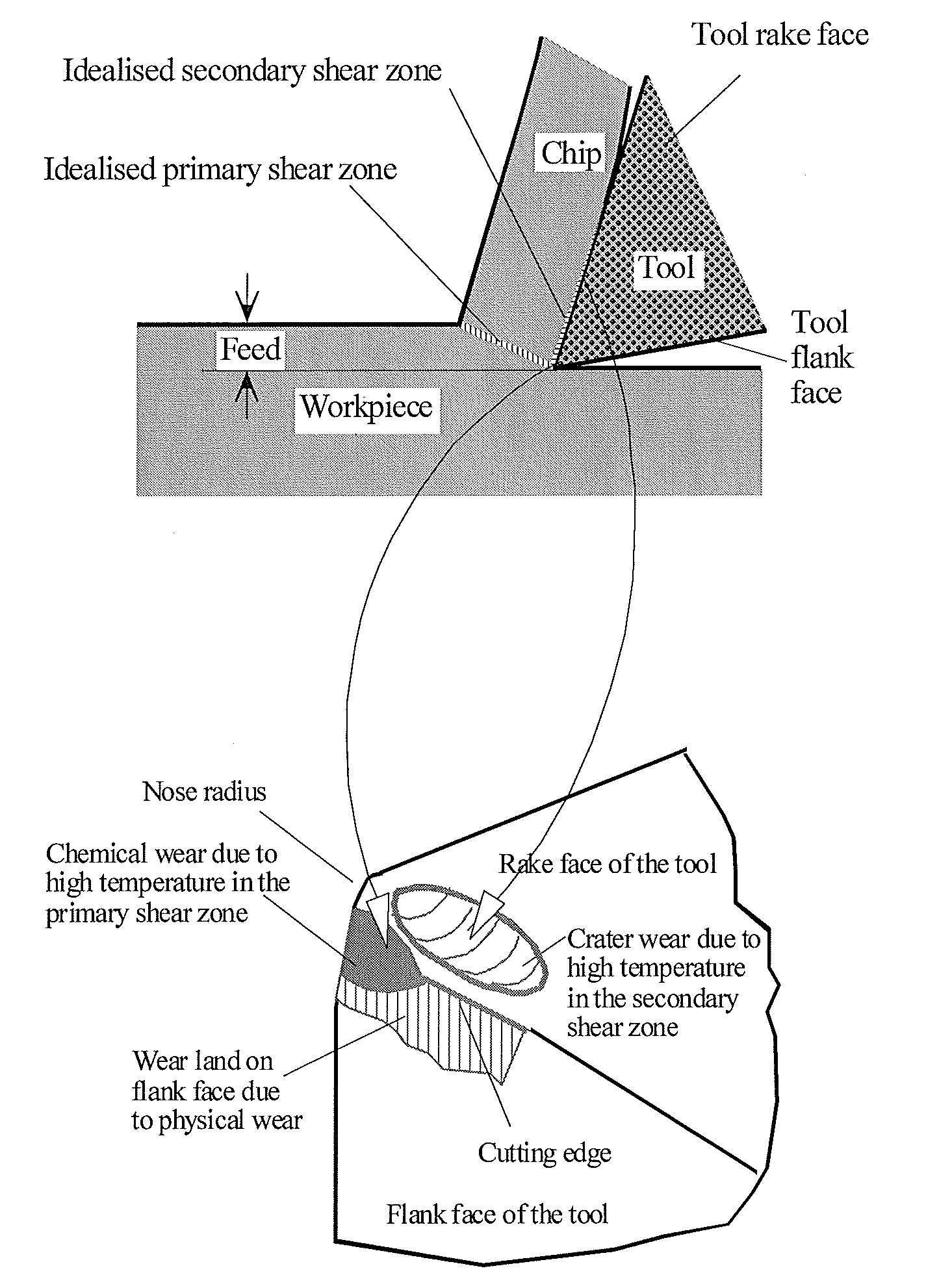
Processes for high speed machining of workpiece materials using high performance tools with prolonged tool life and improved surface finish are provided by vibrating the tool and / or the workpiece at a frequency greater than the frequency of shear localization in the primary shear zone or chip segmentation occurring in the absence of tool vibration, with an amplitude sufficient to break up the tool-chip atomic contact, thereby decreasing the tool-chip contact length through decreasing the tool-chip contact time, thereby suppressing accelerated chemical tool wear caused by dissolution of the tool into the workpiece by nanocrystalline grain boundary diffusion and grain boundary sliding mechanisms by preventing shear localization associated with nanocrystalline grain formation in the primary shear zone of the chip, and suppressing oxidation wear of the tool by preventing segmentation of the chip.
Owner:SUBRAMANIAN SUNDARESA V
Three-screw extruder
ActiveCN104494103AImprove the mixing effectIncrease the number of stirringIsoetes triquetraEngineering
The invention provides a three-screw extruder which has a simple structure, has more shearing zones for shearing, mixing, compounding, exhausting, reacting and self-cleaning compared with a single screw extruder and the double-screw extruder, and is particularly suitable for uniformly dispersing and compounding high-sensitivity and high-viscosity materials and materials which contain moisture and volatile components and are required to be degassed. The three-screw extruder comprises an outer barrel and is characterized in that the outer barrel is a semi-elliptical, a feeding hole is formed in the upper end of the front side of the outer barrel, a discharge hole is formed in the lower end of the rear side of the outer barrel, a driving end is connected at one end, which is provided with the feeding hole, of the outer barrel, an output end is connected at one end, provided with the discharge hole, of the outer barrel, three screws which rotate in the same direction and are distributed in an equilateral triangle manner are arranged in the outer barrel, and a first mixing zone, a second mixing zone and a third mixing zone are sequentially arranged on the screw rod in an axial direction of the screw rod respectively.
Owner:WUXI PROFESSIONAL COLLEGE OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com