Pyrazine compounds and their use in medicine
A compound and drug technology, applied in the field of new small molecule fluorescent compounds, to achieve the effect of good brain penetration and enhanced fluorescence intensity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Embodiment one: the synthesis of the compound shown in formula (I)
[0027] The synthetic route of the compound represented by the formula (I) of the present invention is as follows: figure 1 shown.
[0028] Synthetic PB-1
[0029]
[0030] Dissolve 2-methylpyrazine (282.3 mg, 3 mmol) and 4-N,N dimethylaminocinnamaldehyde (175.4 mg, 1 mmol) in 20 mL of dry tetrahydrofuran, add potassium tert-butoxide (448.8 mg, 4 mmol ), heated to reflux at 80°C for 2 hours, and the solvent was removed by rotary evaporation; 20 mL of water was added to precipitate a solid, and after suction filtration, the resulting solid was separated by column chromatography to obtain 105.8 mg of PB-1, with a yield of 42.1%. The structure is as follows: 1 H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl 3 ): δ 8.50 (s, 1H), 8.47 (s, 1H), 8.30(s, 1H), 7.51 (dt, J = 36.4, 18.2 Hz, 1H), 7.38 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 6.83 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, 1H),6.81 (d, J = 4.1 Hz, 1H), 6.70 (d, J = 7.7 Hz, 1H), 6.61 (s,1H), 6.58 (s, 1H), 3.00 (...
Embodiment 2
[0031] Embodiment two: the synthesis of the compound shown in formula (II)
[0032] The synthetic route of the compound represented by the formula (II) of the present invention is as follows: figure 1 shown.
[0033] Synthetic QB-1
[0034]
[0035] Dissolve 2-methylquinoxaline (288 mg, 2 mmol) and 4-N,N dimethylaminocinnamaldehyde (175.4 mg, 1 mmol) in 15 mL of sodium hydroxide solution (5mol / L), add Aliquat 336 (43 mg, 0.1 mmol), heated to reflux at 100°C for 10 hours, cooled, filtered, and the resulting solid was separated by column chromatography to obtain 91.0 mg of QB-1, with a yield of 30.2%. The structure is as follows: 1 H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl 3 ): δ 8.90 (s, 1H), 8.03-7.99 (m, 1H), 7.73-7.63 (m, 4H),7.40 (d, 2H, J = 8.8 Hz), 6.89 (d, 2H, J = 8.0 Hz ), 6.81 (d, 1H, J = 15.6Hz), 6.70 (d, 2H, J = 8.8 Hz), 3.02 (s, 6H).
Embodiment 3
[0036] Embodiment three: the mensuration of optical parameter
[0037] 1. Determination of maximum absorption wavelength and molar absorption coefficient
[0038] Using dichloromethane as solvent, prepare compounds with a certain concentration gradient, such as 1, 5, 10, 20, and 25 μM solutions, scan the ultraviolet absorption spectrum with a UV-visible spectrophotometer, and record the maximum absorption wavelength (λ abs ) and absorbance, and calculate the molar absorption coefficient ε (M -1 cm -1 ). The maximum absorption wavelengths and molar absorption coefficients of some compounds in the examples of the present invention are shown in Table 1.
[0039] 2. Determination of fluorescence excitation wavelength and fluorescence emission wavelength
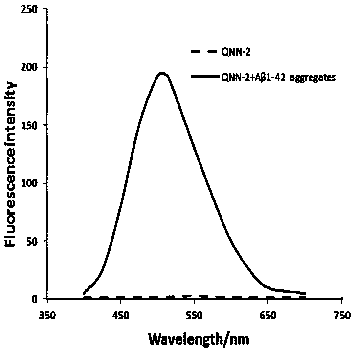
[0040] The compounds of the present invention have good fluorescence properties. In order to investigate the fluorescence properties of the compounds of the present invention, the specific implementation steps are: accurate...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com