Distributed Bragg reflection laser-based chirp microwave generating device
A microwave generating device and distributed Bragg technology, applied in the microwave field, can solve problems such as low time-bandwidth product and compression, deterioration of radar performance, narrow center frequency tuning range, etc., and achieve high time-bandwidth product and compression ratio, flexible bandwidth and period , the effect of high power flatness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
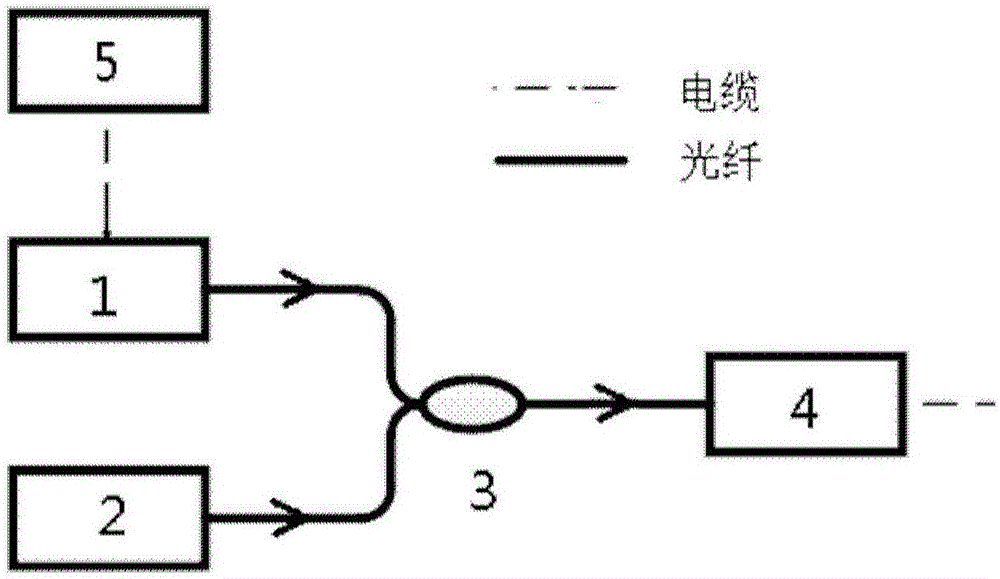
[0036] This embodiment provides a chirped microwave generation device based on a distributed Bragg reflection laser, such as figure 1 As shown, the chirped microwave generating device includes a distributed Bragg reflection laser 1 , a tunable single-mode laser 2 , an optical coupler 3 , a photodetector 4 and an arbitrary waveform generator 5 .
[0037] Arbitrary waveform generator 5 and distributed Bragg reflection laser 1 adopt cable connection, provide electrical signal for distributed Bragg reflection laser 1, can be voltage signal or current signal, preferably voltage signal, thereby change the lasing wavelength of distributed Bragg reflection laser 1 , so that the laser output from the distributed Bragg reflection laser 1 has a specific chirp.
[0038] Both the distributed Bragg reflection laser 1 and the tunable single-mode laser 2 are connected to the optical coupler 3 by optical fiber, and the laser with a specific chirp output by the distributed Bragg reflection lase...
Embodiment 2
[0046] This embodiment provides a chirped microwave generation device based on a distributed Bragg reflection laser, such as Figure 4 As shown, compared with Embodiment 1, the only difference is that an optical isolator 6 is added between the distributed Bragg reflection laser 1 and the optical coupler 3 to avoid adverse effects caused by the optical feedback at the optical coupler 3 back to the distributed Bragg reflection laser 1 .
[0047] In this embodiment, the chirped laser output by the distributed Bragg reflection laser 1 is transmitted to the optical isolator 6 through the optical fiber, and then transmitted to the optical coupler 3 and coupled with the single-mode laser output by the tunable single-mode laser 2 through the optical fiber, and the coupled laser It is transmitted to the photodetector 4 through the optical fiber, and the photodetector 4 converts the beat frequency signal of the coupled laser into an electrical signal, and outputs chirped microwaves to t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com