Plant-fiber-loading-microbe self-repairing cement-based material
A technology of cement-based materials and plant fibers, which is applied in the field of building materials, can solve problems such as difficult to achieve lifelong self-repair of concrete, affect integrity and durability, and matrix defects, and achieve environmental protection and economy. The effect of simple preparation method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
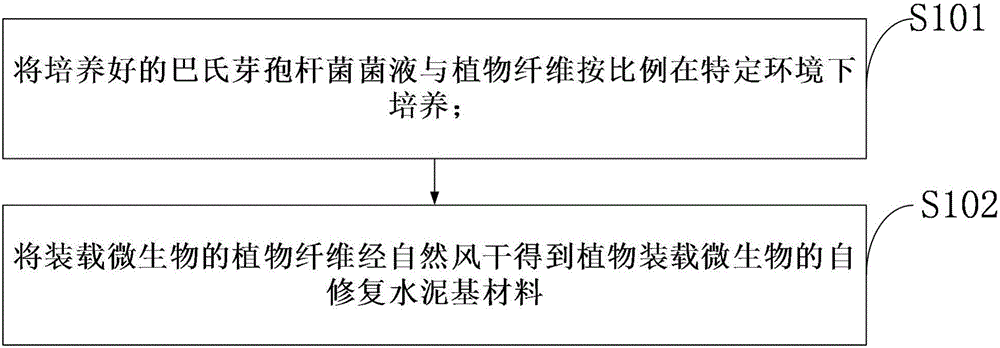
[0035] Such as figure 1 Shown: a preparation method of a self-repairing cement-based material loaded with plant fiber microorganisms, the preparation method of the self-repair cement-based material loaded with microorganisms in plant fibers comprises:
[0036] S101: Cultivate the cultured Bacillus Pasteurella bacteria liquid and the plant fiber in a specific environment in proportion;
[0037] S102: Naturally air-dry the plant fibers loaded with microorganisms to obtain a self-healing cement-based material loaded with microorganisms.
[0038] Further, the diameter of the plant fiber is less than 1mm, and the length is 10mm-20mm.
[0039] Further, the cultured Bacillus pasteurian bacteria liquid is: the facultative anaerobic bacillus bacterial liquid is obtained through anaerobic and aerobic environment cultivation, and the concentration of the bacterial liquid containing Bacillus pasteurianus is 1.0×10 9 cell / ml.
[0040] Furthermore, before using the plant fibers, soak the...
Embodiment
[0050] 1. The preparation process of the bamboo plant is: bamboo material→making bamboo slices→steaming bamboo slices→crushing and decomposing, then screen out the bamboo plants, and finally soak them in a solution with a pH value of 12.0 for 24 hours.
[0051] 2. The microorganism acquisition process is: take the beef extract peptone agar medium as the medium used for bacterial inoculation, adjust the pH value of the medium to 9.0 in the initial state, and sterilize the prepared medium using an autoclave, Then, in a sterile environment, insert 5ml of bacteria into every 100ml of culture medium. Further, the cultivation is carried out in an incubator, and the cultivation time is 20 hours. The environment of the incubator was set as aerobic and anaerobic respectively, and the temperature was set at 30°C.
[0052] 3. The process of loading microorganisms to the bamboo plants is as follows: soak the bamboo plants in the facultative anaerobic bacillus bacterium liquid, cultivate ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com